前言
用过猎豹清理大师或者相类似的安全软件,大家都知道它们都会有一个功能,那就是内存清理,而展现的形式是通过一个圆形的小球来显示内存大小,通过百分比数字以及进度条的形式来显示清理的进度。本文将对该效果的实现过程进行详细讲述,但不涉及内存清理的实现。
预览
我们先来看看最终实现的效果是怎样的(gif效果有点差):
从上面的图片,我们可以看出:
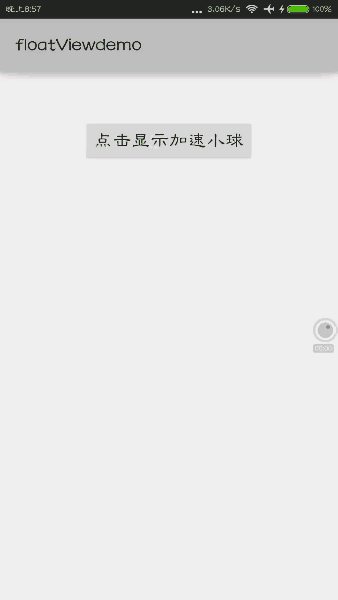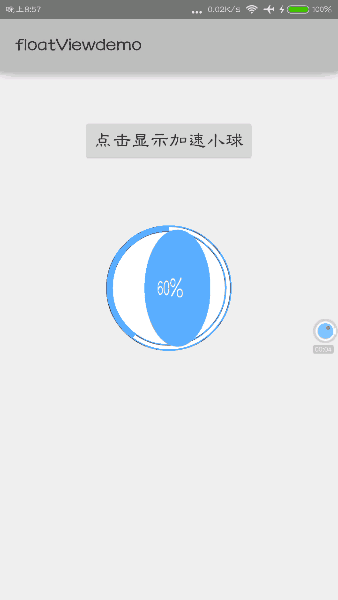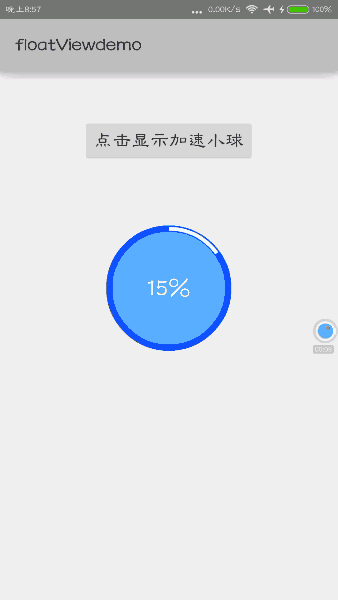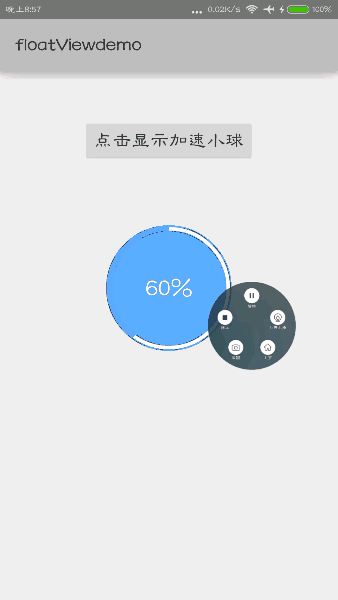
①当加速球View显示的时候,进度条以及百分比数字会从0%开始增加到某一数值(60%)。
②进度条停止增加后,中间的圆沿着Y轴开始翻转,会翻转180度,上面的百分比数字并不会出现镜像效果(下面会提到)。
③用户点击该小球后,开始清理内存,进度条和百分比数字会经历减小至0,再由0增加到某一数值的过程。
实现过程详解
其实上面的效果,笔者是仿照猎豹清理大师的加速球所实现的,略有不同,但大致形式相同。如果读者对上面的效果感兴趣,那么请继续读下去吧,接下来是正文部分。
Step 1.初始化
我们首先要新建一个LieBaoView.java,继承自View,我们重写它的构造函数如下:
public LieBaoView(Context context) {
super(context);
init();
}
public LieBaoView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
public LieBaoView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
init();
}
无论通过哪种方式实例化该View,都会调用init()方法,该方法主要用于处理初始化各种成员变量,那么我们又需要哪些成员变量或者哪些实例来帮助我们呢?
笔者的思路是这样的:通过一个空白的bitmap,我们在上面绘制圆形、文字等,这样最后再将这个bitmap绘制到我们的view上面。
因此,我们在初始化的时候,需要获取到各种Paint(画笔)、Bitmap(空白图片)、Canvas(画布)等的实例。我们再想一下:中间的圆是可以旋转的,那么中间的旋转圆就不能和别的圆放到同一个bitmap上,否则会给后面旋转的实现带来麻烦,因此我们可以准备两张空白的bitmap。那么,我们可以先这样:
public void init(){
//绘制背景圆的画笔
mBackgroundCirclePaint = new Paint();
mBackgroundCirclePaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mBackgroundCirclePaint.setColor(Color.argb(0xff, 0x10, 0x53, 0xff));
//绘制旋转圆的画笔
mFrontCirclePaint = new Paint();
mFrontCirclePaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mFrontCirclePaint.setColor(Color.argb(0xff, 0x5e, 0xae, 0xff));
//绘制文字的画笔
mTextPaint = new Paint();
mTextPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mTextPaint.setTextSize(80);
mTextPaint.setColor(Color.WHITE);
//绘制进度条的画笔
mArcPaint = new Paint();
mArcPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mArcPaint.setColor(Color.WHITE);
mArcPaint.setStrokeWidth(12);
mArcPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
mBitmap = Bitmap.createBitmap(mWidth,mHeight, Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888);
mBitmapCanvas = new Canvas(mBitmap); //将画布和Bitmap关联
//旋转bitmap与画布
mOverturnBitmap = Bitmap.createBitmap(mWidth,mHeight, Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888);
mOverturnBitmapCanvas = new Canvas(mOverturnBitmap);
//省略了一部分...
//Camera、Matrix、Runnable等下面会讲述
mMatrix = new Matrix();
mCamera = new Camera();
}
上面主要是初始化了各种不同的画笔类型,以及准备了两个Bitmap及其相关联的画布,我们在其关联的画布上进行绘制即可,这样就能得到有着内容的两个Bitmap了。
我们接着往下思考:如果要实现翻转效果,我们还需要些什么?Android SDK为我们准备好了一套工具:Camera和Matrix,利用这两个工具,我们可以很方便地实现对Bitmap的各种变换,比如缩放、平移、翻转等。关于Camera和Matrix,读者可以去搜索更详细的相关知识,这里就不展开来详谈了。最后,我们还需要Runnable,因为需要实现自动翻转以及进度条的自动增加与减少的,Runnable下面会详细讲述,先不用着急,当然了,还需要设置一个点击监听器。
Step 2.绘制图像
上面已经为我们准备好了画笔、画布等,我们接下来就来绘制所需的图像。通过重写View的onDraw()方法即可。
①绘制背景圆,也即上图中最外层深蓝色的圆:
mBitmapCanvas.drawCircle(mWidth / 2, mHeight / 2, mWidth / 2, mBackgroundCirclePaint);
②绘制中间的白色背景圆,也即旋转圆进行翻转的过程中,背景的白色部分:
mBitmapCanvas.drawCircle(mWidth / 2, mHeight / 2, mWidth / 2 - mPadding, mTextPaint);
③绘制进度条,弧形进度条该怎么实现呢?这里给出笔者的一个思路:通过canvas的drawArc()方法来实现,该方法能在一个矩形内绘制一个最大的圆(或者椭圆),设置画笔为空心以及画笔线条宽度为12左右即可,这样就能实现一个粗弧线了,然后通过不断地调用onDraw()方法,修改drawArc()的角度来实现进度条效果。如果大家还有什么别的实现方法,欢迎交流。
mBitmapCanvas.save();
//实例化一个矩形,该矩形的左上角和右下角坐标与原Bitmap并不重合,这是因为要使
//进度条与最外面的圆有一定的间隙
RectF rectF = new RectF(10,10,mWidth-10,mHeight-10);
//先将画布逆时针旋转90度,这样drawArc的起始角度就能从0度开始,省去不必要的麻烦
mBitmapCanvas.rotate(-90, mWidth / 2, mHeight / 2);
mBitmapCanvas.drawArc(rectF, 0, ((float)mProgress/mMaxProgress)*360, false, mArcPaint);
mBitmapCanvas.restore();
canvas.drawBitmap(mBitmap, 0, 0, null);
④绘制中间的旋转圆。上面说到,由于要实现翻转效果,那么不能再同一张Bitmap上绘制了,所以我们用另一张空白的Bitmap。旋转圆的绘制很简单,只要它的半径比外圆半径以及进度条宽度相加之和还要小即可:
mOverturnBitmapCanvas.drawCircle(mWidth / 2, mHeight / 2, mWidth / 2 - mPadding, mFrontCirclePaint);
⑤最后一步,在旋转圆上绘制百分比数字。绘制文字,要用到Canvas的drawText方法,我们重点来看看这个方法:
/**
* Draw the text, with origin at (x,y), using the specified paint. The
* origin is interpreted based on the Align setting in the paint.
*
* @param text The text to be drawn
* @param x The x-coordinate of the origin of the text being drawn
* @param y The y-coordinate of the baseline of the text being drawn
* @param paint The paint used for the text (e.g. color, size, style)
*/
public void drawText(@NonNull String text, float x, float y, @NonNull Paint paint) {
//...
}
第一个和第四个参数没什么好说的,第二个参数表示文字开始的x坐标,第三个参数表示文字的baseline的y坐标。要使文字居中显示,我们只需要设置适当的x、y坐标即可,那么baseline又是什么呢?它其实代表着文本的基准点,我们来看一幅图:
从图中可以看出,baseline以上至文本最高点为Ascent,为负值;baseline以下至文本最低点为Descent,为正值。因此,如果我们要使文本在控件内居中显示,那么我们可以利用-(ascent-descent)/2计算出文本的高度的一半,此时再利用mHeight/2(控件高度的一半)加上该值,即可得出在控件中的baseline值,此时也就实现了居中显示,代码如下:
String text = (int) (((float)mProgress / mMaxProgress) *100) + "%";
//获取文本的宽度
float textWidth = mTextPaint.measureText(text);
//获取文本规格
Paint.FontMetrics metrics = mTextPaint.getFontMetrics();
float baseLine = mHeight / 2 - (metrics.ascent + metrics.descent) /2;
mOverturnBitmapCanvas.drawText(text, mWidth / 2 - textWidth / 2, baseLine, mTextPaint);
最后,再将bitmap绘制到view上:
canvas.drawBitmap(mOverturnBitmap, mMatrix, null);
经过以上的绘制,我们先看看效果如何:
那么基本效果都已经实现了。接下来,我们将会实现动态效果。
Step 3.实现自动翻转的效果
从上面的动画效果来看,我们首先让进度条从0增加到某个数值,接着再自动翻转。增加数值的实现很简单,只需要启用一个Runnable,在Runnable内把mProgress值不断增加,再调用invalidate()方法刷新View即可。等进度条增加完毕,那么就开始翻转,翻转的话利用Camera和Matrix对中间的bitmap进行操作,不断改变角度就能实现,我们来看看代码:
在onDraw()方法内:
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
//....
//如果当前正在旋转
if(isRotating) {
mCamera.save();
//旋转角度
mCamera.rotateY(mRotateAngle);
//如果旋转角度大于或等于180度的时候,减去180度
if (mRotateAngle >= 180) {
mRotateAngle -= 180;
}
//根据Camera的操作来获得相应的矩阵
mCamera.getMatrix(mMatrix);
mCamera.restore();
mMatrix.preTranslate(-mWidth / 2, -mHeight / 2);
mMatrix.postTranslate(mWidth / 2, mHeight / 2);
}
canvas.drawBitmap(mOverturnBitmap, mMatrix, null);
//如果当前控件尚未进行翻转过程
if(!isRotating && !isInital){
//设置isIncreasing,表示先开始进度条的增加过程
isIncreasing = true;
isRotating = true;
postDelayed(mRotateRunnable,10);
}
接着,我们来写mRotateRunnable,Runnable的初始化在init()方法内:
mRotateRunnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//如果当前是正在增加过程
if(isIncreasing){
Log.d("cylog","mProgress:"+mProgress);
//当进度增加到某一个数值的时候,停止增加
if(mProgress >= 59){
isIncreasing = false;
}
mProgress++;
}else {
//如果增加过程结束,那么开始翻转
//如果mRotateAngle是大于90度的,表示bitmap已经翻转了90度,
//此时bitmap的内容变成镜像内容,为了不出现镜像效果,我们需要再转过180度,
//此时就变为正常的显示了,而这多转的180度在onDraw内会减去。
if (mRotateAngle > 90 && mRotateAngle < 180)
mRotateAngle = mRotateAngle + 3 + 180;
//如果mRotateAngle超过了180度,翻转过程完成
else if (mRotateAngle >= 180) {
isRotating = false;
isInital = true;
mRotateAngle = 0;
return;
} else
//每次角度增加3,这个可以微调,适当即可
mRotateAngle += 3;
}
invalidate();
//25ms后再次调用该方法
postDelayed(this,25);
}
};
经过以上的Runnable以及在onDraw()方法的配合,已经可以实现自动翻转的效果了。
Step 4.实现点击清理的效果
好了,我们来实现最后的效果,同样,我们利用一个Runnable来实现,由于该清理效果是需要用户点击小球后才开始清理的,所以我们需要一个事件监听器,每当用户点击后,在onClick方法内post一个Runnable即可。
先实现mCleaningRunnable,在init()方法内:
mCleaningRunnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//如果当前进度超过某一数值,那么停止清理
if (mProgress >= 60) {
isCleaning = false;
return;
}
//如果当前处于下降过程,mProgress不断减少,直到为0
if (isDescending) {
mProgress--;
if (mProgress <= 0)
isDescending = false;
} else {
mProgress++;
}
invalidate();
postDelayed(this,40);
}
};
setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
if(isCleaning) return;
//如果当前正在清理过程,那么直接return,防止post过多
//设置flag,来进行清理
isDescending = true;
isCleaning = true;
mProgress--;
postDelayed(mCleaningRunnable, 40);
}
});
上面的逻辑实现了,每当点击后,先把进度值不断减少直到0,接着又不断增加直到某个固定的值,通过每一个调用invalidate()方法来通知组件刷新,这样就实现了动态效果。
好了,到目前为止,所有的效果已经实现了,全部代码在下面贴上。谢谢大家的阅读~
public class LieBaoView extends View {
private Paint mBackgroundCirclePaint;
private Paint mFrontCirclePaint;
private Paint mTextPaint;
private Paint mArcPaint;
private Bitmap mBitmap;
private Bitmap mOverturnBitmap;
private Canvas mBitmapCanvas;
private Canvas mOverturnBitmapCanvas;
private Matrix mMatrix;
private Camera mCamera;
private int mWidth = 400;
private int mHeight = 400;
private int mPadding = 20;
private int mProgress = 0;
private int mMaxProgress = 100;
private int mRotateAngle = 0;
private Runnable mRotateRunnable;
private Runnable mCleaningRunnable;
private boolean isRotating;
private boolean isInital = false;
private boolean isDescending;
private boolean isIncreasing;
private boolean isCleaning;
public LieBaoView(Context context) {
super(context);
init();
}
public LieBaoView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
public LieBaoView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
init();
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(mWidth,mHeight);
}
public void init(){
//绘制背景圆的画笔
mBackgroundCirclePaint = new Paint();
mBackgroundCirclePaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mBackgroundCirclePaint.setColor(Color.argb(0xff, 0x10, 0x53, 0xff));
//绘制旋转圆的画笔
mFrontCirclePaint = new Paint();
mFrontCirclePaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mFrontCirclePaint.setColor(Color.argb(0xff, 0x5e, 0xae, 0xff));
//绘制文字的画笔
mTextPaint = new Paint();
mTextPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mTextPaint.setTextSize(80);
mTextPaint.setColor(Color.WHITE);
//绘制进度条的画笔
mArcPaint = new Paint();
mArcPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mArcPaint.setColor(Color.WHITE);
mArcPaint.setStrokeWidth(12);
mArcPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
mBitmap = Bitmap.createBitmap(mWidth,mHeight, Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888);
mBitmapCanvas = new Canvas(mBitmap); //将画布和Bitmap关联
//旋转bitmap与画布
mOverturnBitmap = Bitmap.createBitmap(mWidth,mHeight, Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888);
mOverturnBitmapCanvas = new Canvas(mOverturnBitmap);
mMatrix = new Matrix();
mCamera = new Camera();
mRotateRunnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//如果当前是正在增加过程
if(isIncreasing){
Log.d("cylog","mProgress:"+mProgress);
//当进度增加到某一个数值的时候,停止增加
if(mProgress >= 59){
isIncreasing = false;
}
mProgress++;
}else {
//如果增加过程结束,那么开始翻转
//如果mRotateAngle是大于90度的,表示bitmap已经翻转了90度,
//此时bitmap的内容变成镜像内容,为了不出现镜像效果,我们需要再转过180度,
//此时就变为正常的显示了,而这多转的180度在onDraw内会减去。
if (mRotateAngle > 90 && mRotateAngle < 180)
mRotateAngle = mRotateAngle + 3 + 180;
//如果mRotateAngle超过了180度,翻转过程完成
else if (mRotateAngle >= 180) {
isRotating = false;
isInital = true;
mRotateAngle = 0;
return;
} else
//每次角度增加3,这个可以微调,适当即可
mRotateAngle += 3;
}
invalidate();
//25ms后再次调用该方法
postDelayed(this,25);
}
};
mCleaningRunnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//如果当前进度超过某一数值,那么停止清理
if (mProgress >= 60) {
isCleaning = false;
return;
}
//如果当前处于下降过程,mProgress不断减少,直到为0
if (isDescending) {
mProgress--;
if (mProgress <= 0)
isDescending = false;
} else {
mProgress++;
}
invalidate();
postDelayed(this,40);
}
};
setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
if(isCleaning) return;
isDescending = true;
isCleaning = true;
mProgress--;
postDelayed(mCleaningRunnable, 40);
}
});
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
mBitmapCanvas.drawCircle(mWidth / 2, mHeight / 2, mWidth / 2, mBackgroundCirclePaint);
mBitmapCanvas.drawCircle(mWidth / 2, mHeight / 2, mWidth / 2 - mPadding, mTextPaint);
mBitmapCanvas.save();
//实例化一个矩形,该矩形的左上角和右下角坐标与原Bitmap并不重合,这是因为要使
//进度条与最外面的圆有一定的间隙
RectF rectF = new RectF(10,10,mWidth-10,mHeight-10);
//先将画布逆时针旋转90度,这样drawArc的起始角度就能从0度开始,省去不必要的麻烦
mBitmapCanvas.rotate(-90, mWidth / 2, mHeight / 2);
mBitmapCanvas.drawArc(rectF, 0, ((float)mProgress/mMaxProgress)*360, false, mArcPaint);
mBitmapCanvas.restore();
canvas.drawBitmap(mBitmap, 0, 0, null);
mOverturnBitmapCanvas.drawCircle(mWidth / 2, mHeight / 2, mWidth / 2 - mPadding, mFrontCirclePaint);
String text = (int) (((float)mProgress / mMaxProgress) *100) + "%";
//获取文本的宽度
float textWidth = mTextPaint.measureText(text);
//获取文本规格
Paint.FontMetrics metrics = mTextPaint.getFontMetrics();
float baseLine = mHeight / 2 - (metrics.ascent + metrics.descent) /2;
mOverturnBitmapCanvas.drawText(text, mWidth / 2 - textWidth / 2, baseLine, mTextPaint);
//如果当前正在旋转
if(isRotating) {
mCamera.save();
//旋转角度
mCamera.rotateY(mRotateAngle);
//如果旋转角度大于或等于180度的时候,减去180度
if (mRotateAngle >= 180) {
mRotateAngle -= 180;
}
//根据Camera的操作来获得相应的矩阵
mCamera.getMatrix(mMatrix);
mCamera.restore();
mMatrix.preTranslate(-mWidth / 2, -mHeight / 2);
mMatrix.postTranslate(mWidth / 2, mHeight / 2);
}
canvas.drawBitmap(mOverturnBitmap, mMatrix, null);
//如果当前控件尚未进行翻转过程
if(!isRotating && !isInital){
//设置isIncreasing,表示先开始进度条的增加过程
isIncreasing = true;
isRotating = true;
postDelayed(mRotateRunnable,10);
}
}
}