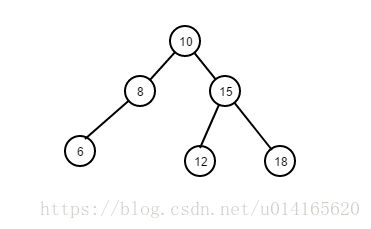
数据机构与算法:二叉查找树(Binary Search Tree)Java实现
个人总结,如有错误,感谢指正
二叉查找树(Binary Search Tree)
一、简介
二叉树(Binary Tree):每个节点最多有两个子节点的树。
二叉查找树(binary srarch tree):具有如下性质的二叉树称为二叉查找树:
对于动态数组(ArrayList)与链表(LinkedList)结构,动态数组在查询方面效率较高,链表结构在插入方面效率较高,而二叉查找树融合了上面两者的优势。
二、实现
下面用Java实现二叉查找树,包含二叉查找树定义、前序/中序/后序遍历、查找、最大值、最小值、插入、删除。
定义
用一个内部类定义二叉树节点BinaryNode,它包含指向左右两个子节点的left、right,以及表示节点值的key,key需要支持排序。
public class BinarySearchTree<T extends Comparable<T>> {
//二叉查找树根节点
private BinaryNode root;
//二叉树节点定义
private static class BinaryNode<T extends Comparable<T>> {
T key; //节点值
BinaryNode left; //左节点
BinaryNode right; //右节点
public BinaryNode(T key){
this(key, null, null);
}
public BinaryNode(T key, BinaryNode left, BinaryNode right) {
this.key = key;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
...
} 遍历
二叉查找树遍历包含前序、中序、后序遍历。这里的“前、中、后”都是针对“当前节点”而言,遍历顺序分别如下:
前序遍历:当前节点、左节点、右节点;
中序遍历:左节点、当前节点、右节点;
后序遍历:左节点、右节点、当前节点。
遍历每个节点都按上述顺序进行。
/**
* 前序遍历
* @param node 待遍历二叉查找树BST根节点
*/
private void preOrder(BinaryNode node) {
if (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.key + " ");
preOrder(node.left);
preOrder(node.right);
}
}
/**
* 前序遍历
*/
public void preOrder() {
preOrder(this.root);
}
/**
* 中序遍历
* @param node 待遍历BST根节点
*/
private void midOrder(BinaryNode node) {
if (node != null) {
midOrder(node.left);
System.out.print(node.key + " ");
midOrder(node.right);
}
}
/**
* 中序遍历
*/
public void midOrder() {
midOrder(this.root);
}
/**
* 后序遍历
* @param node 待遍历BST根节点
*/
private void postOrder(BinaryNode node) {
if (node != null) {
postOrder(node.left);
postOrder(node.right);
System.out.print(node.key + " ");
}
}
/**
* 后序遍历
*/
public void postOrder() {
postOrder(this.root);
} 查找
在二叉查找树BST中查找值为key的节点,将key和节点的key进行比较,如果小于,则在左子树中查找,如果大于,则在右子树中查找,如果等于,则查找成功。下面是递归和非递归两种实现方式:
/**
* (递归实现)在root为根节点的二叉树中查找节点值为key的节点
* @param root
* @param key
* @return
*/
private BinaryNode search(BinaryNode root, T key) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
//如果key小于当前节点值,则在左树中查找
if (key.compareTo(root.key) < 0) {
return search(root.left, key);
//如果key小于当前节点值,则在左树中查找
} else if (key.compareTo(root.key) > 0) {
return search(root.right, key);
//如果key等于当前节点值,直接返回
} else {
return root;
}
}
/**
* (非递归实现)在root为根节点的二叉树中查找节点值为key的节点
* @param root
* @param key
* @return
*/
private BinaryNode cycleSearch(BinaryNode root, T key) {
while (root != null) {
//如果key小于当前节点值,则在左树中查找
if (key.compareTo(root.key) < 0) {
root = root.left;
//如果key小于当前节点值,则在左树中查找
} else if (key.compareTo(root.key) > 0) {
root = root.right;
//如果key等于当前节点值,直接返回
} else {
return root;
}
}
return root;
}
/**
* 查找
*/
public BinaryNode search(T key) {
return search(this.root, key);
//return cycleSearch(this.root, key);
} 最小值、最大值
因为二叉查找树左子树的值都比根节点小,右子树的值都比根节点大,所以最小值即为最左边节点的值,最大值即为最右边节点的值。
/**
* 查找最小值,即最左边节点值
*/
private T findMin(BinaryNode root){
if(root == null){
return null;
}
while(root.left != null){
root = root.left;
}
return root.key;
}
/**
* 最小值
*/
public T findMin(){
return findMin(this.root);
}
/**
* 查找最大值,即查找最右节点值
*/
private T findMax(BinaryNode root){
if(root == null){
return null;
}
while(root.right != null){
root = root.right;
}
return root.key;
}
/**
* 最大值
*/
public T findMax(){
return findMax(this.root);
} 插入
在二叉查找树中插入新节点newNode,将新节点的值和当前节点值进行比较,如果小于,在左边插入,如果大于,在右边插入。
/**
* 在二叉查找树bst中插入新节点newNode
* @param bst
* @param newNode
* @return
*/
private boolean insert(BinarySearchTree bst, BinaryNode newNode){
//如果root为空,则新节点作为根节点
BinaryNode root = bst.root;
if(root == null){
bst.root = newNode;
return true;
}
while(root != null){
int cmp = newNode.key.compareTo(root.key);
//小于,在左边插入
if(cmp < 0){
if(root.left == null){
root.left = newNode;
return true;
}else{
root = root.left;
}
//大于,在右边插入
}else if(cmp > 0){
if(root.right == null){
root.right = newNode;
return true;
}else{
root = root.right;
}
//等于,则插入失败,返回false
}else{
return false;
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* 插入
*/
public boolean insert(BinaryNode newNode){
return insert(this, newNode);
} 删除
从二叉查找树中删除节点时,分三种情况:
- 待删除节点为叶节点,则直接删除
- 待删除节点只有一个子节点,则用子节点的值代替该节点的值,然后删除该子节点
- 待删除节点有两个子节点,这种情况相对比较负责,一般用其右子树中最小节点的值替代该节点值,然后删除该最小节点。
懒惰删除:当需要从树中删除某个节点时,并不会真的将该节点从树中移除,而是仍留在树中,只是被标记为已删除,这样在对树进行操作时,遇到被标记为已删除的节点时,直接跳过。这样,可以提高删除操作效率。
/**
* 从二叉查找树bst中删除值为key的节点
* @param bst
* @param key
* @return
*/
private boolean remove(BinarySearchTree bst, T key){
BinaryNode tRoot = bst.root;
if(tRoot == null){
return false;
}
BinaryNode pNode = tRoot;
BinaryNode rmNode = tRoot;
//是否左节点
boolean isLeft = false;
while(rmNode != null){
int cmp = key.compareTo(rmNode.key);
if(cmp < 0){
isLeft = true;
pNode = rmNode;
rmNode = rmNode.left;
} else if(cmp > 0){
isLeft = false;
pNode = rmNode;
rmNode = rmNode.right;
} else{
//叶节点,直接删除
if(rmNode.left == null && rmNode.right == null){
if(rmNode == tRoot){
tRoot = null;
}else if(isLeft){
pNode.left = null;
}else{
pNode.right = null;
}
}
//只有左节点
else if(rmNode.left != null && rmNode.right == null){
if(rmNode == tRoot){
tRoot = null;
}else if(isLeft){
pNode.left = rmNode.left;
}else{
pNode.right = rmNode.left;
}
}
//只有右节点
else if(rmNode.left == null && rmNode.right != null){
if(rmNode == tRoot){
tRoot = null;
}else if(isLeft){
pNode.left = rmNode.right;
}else{
pNode.right = rmNode.right;
}
}
//两个节点
else if(rmNode.left != null && rmNode.right != null){
//被删除节点右子树没有左节点,直接用右节点替换
if(rmNode.right.left == null){
rmNode.key = rmNode.right.key;
rmNode.right = rmNode.right.right;
return true;
}
//右子树最小节点
BinaryNode currNode = rmNode.right;
//替代节点
BinaryNode replaceNode = rmNode.right;
//替代节点父节点
BinaryNode repParent = rmNode.right;
while(currNode != null){
repParent = replaceNode;
replaceNode = currNode;
currNode = currNode.left;
}
repParent.left = replaceNode.right;
rmNode.key = replaceNode.key;
if(rmNode == tRoot){
tRoot = null;
}
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* 删除
*/
public boolean remove(T key){
return this.remove(this, key);
} 测试
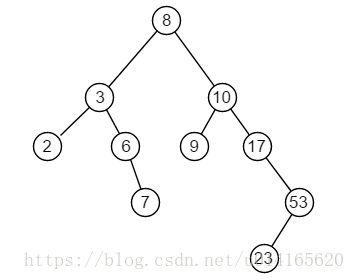
调用上面的实现方法进行测试,使用数组 [8,3,10,6,7,9,17,2,53,23] 作为二叉查找树数据:
public static void main(String[] args){
Integer[] intArr = new Integer[]{8,3,10,6,7,9,17,2,53,23};
BinarySearchTree bst = new BinarySearchTree();
//构造二叉树,循环插入数据
for(int num : intArr){
bst.insert(new BinaryNode(num));
}
System.out.println("前序遍历:");
bst.preOrder();
System.out.println("\n中序遍历:");
bst.midOrder();
System.out.println("\n后序遍历:");
bst.postOrder();
System.out.println("\n最大值:" + bst.findMax());
System.out.println("最小值:" + bst.findMin());
System.out.println("查找6:" );
BinaryNode node6 = bst.search(6);
System.out.println(node6 == null ? "" : node6.key);
System.out.println("查找33:" );
BinaryNode node33 = bst.search(33);
System.out.println(node33 == null ? "" : node33.key);
System.out.println("删除2:" );
bst.remove(2);
//System.out.println("删除6:" );
//bst.remove(6);
//System.out.println("删除10:" );
//bst.remove(10);
bst.midOrder();
} 使用数组[8,3,10,6,7,9,17,2,53,23] 构造二叉查找树如下:
测试结果
前序遍历:
8 3 2 6 7 10 9 17 53 23
中序遍历:
2 3 6 7 8 9 10 17 23 53
后序遍历:
2 7 6 3 9 23 53 17 10 8
最大值:53
最小值:2
查找6:
6
查找33:
没有找到值为33的节点
删除2:
3 6 7 8 9 10 17 23 53
删除6:
2 3 7 8 9 10 17 23 53
删除10:
2 3 6 7 8 9 17 23 53 以上就是二叉查找树及其Java实现,如有错误,感谢指正。