无权重
在查找最小路径上,图的题目特别多,无权重的情况,找最小路径就是图的广度优先遍历。广度优先遍历就是依靠队列来实现。由于比较简单,这里不贴代码了。
为什么是广度优先
图的遍历有深度和广度两种,那么为什么使用广度去找出最小路径呢。其实他成立的条件是无权重,就是每条路径的消费都是一样的。广度优先遍历对应的树的层次遍历,这样就更好理解了,树的层次遍历,由于是一层一层的看,那么层数最小的情况就是最短的情况。
无负权重
无负权重的情况下,迪杰斯特拉是个不错的选择。 迪杰斯特拉是大学算法课上基本都讲的内容。其实算法思想还好,写起来稍微繁琐一些。
算法讲解
迪杰斯特拉的重点就是对一个图标的填充。
迪杰斯特拉
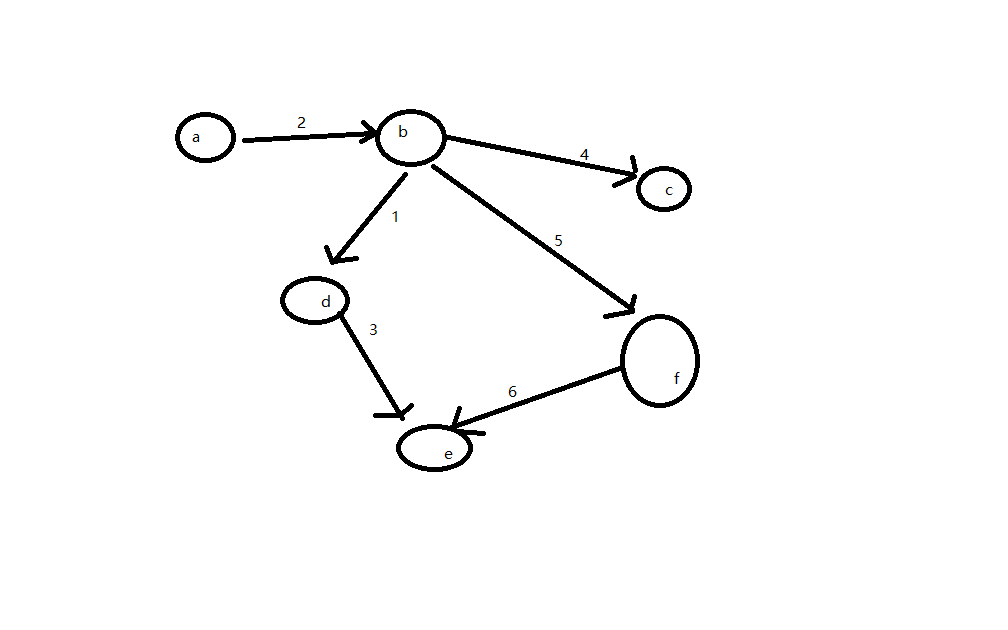
如上图,起点为a,终点是f。
初始化表格
我们先初始化表格,因为a是起点,所以没有包含在内计算。这个计算其实就是把起点相关的初始化到表格里。b是可达的,其余节点都是不可达的,所以花费默认都是没有。
| 节点 | 花费 | 是否访问 |
|---|---|---|
| b | 2 | - |
| c | - | - |
| d | - | - |
| e | - | - |
| f | - | - |
查找最小消耗的节点
根据上图,最小消耗的就是b
继续访问节点
b就当做被访问过了,b到c是4,所以c的花费就是6,然后类推其他f,d,e
| 节点 | 花费 | 是否访问 |
|---|---|---|
| b | 2 | 是 |
| c | 6 | - |
| d | 3 | - |
| e | - | - |
| f | 7 | - |
重复的步骤
- 找出最小没有访问的节点
- 访问节点的邻居节点
- 更新图表,保存消耗最小的值
结果
| 节点 | 花费 | 是否访问 |
|---|---|---|
| b | 2 | 是 |
| c | 6 | 是 |
| d | 3 | 是 |
| e | 6 | 是 |
| f | 7 | 是 |
终点是f,结果就是7
画出路径
上面的情况只是找出了最小消耗,想找出路径,修改表格就好,保存对应的父节点
代码实现
public class Dijkstra {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String[] startEnd = new String[2];
Map initData = initData(startEnd);
Set process = new HashSet<>();
Map costList = new HashMap<>();
init(initData, costList, startEnd[0]);
find(initData, process, costList);
NodeCost nodeCost = costList.get(startEnd[1]);
LinkedList list = new LinkedList<>();
System.out.println(nodeCost.cost);
list.addFirst(nodeCost.current);
while (nodeCost != null) {
list.addFirst(nodeCost.parent);
nodeCost = costList.get(nodeCost.parent);
}
System.out.println(list);
}
public static void find(Map initData, Set process, Map costList) {
NodeCost minNode = getMinNode(process, costList);
while (minNode != null) {
Node node = initData.get(minNode.current);
Map nextNode = node.nextNode;
Iterator> iterator = nextNode.entrySet().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Entry next = iterator.next();
int cost = minNode.cost + next.getValue();
NodeCost nodeCost = costList.get(next.getKey());
int oldCost = nodeCost.cost;
if (oldCost > cost) {
nodeCost.parent = node.name;
nodeCost.cost = cost;
}
}
process.add(node.name);
minNode = getMinNode(process, costList);
}
}
//找出最小消耗没有访问过的节点
public static NodeCost getMinNode(Set process, Map costList) {
Collection values = costList.values();
NodeCost preCost = null;
for (NodeCost cost : values) {
if (!process.contains(cost.current)) {
if (preCost == null) {
preCost = cost;
} else if (preCost.cost >= cost.cost) {
preCost = cost;
}
}
}
return preCost;
}
//初始化图表耗费
public static void init(Map initData, Map costList, String start) {
Collection values = initData.values();
Iterator iteratorValues = values.iterator();
while (iteratorValues.hasNext()) {
Node node = iteratorValues.next();
Map nextNode = node.nextNode;
Iterator> iterator = nextNode.entrySet().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Entry next = iterator.next();
NodeCost cost = new NodeCost();
cost.parent = node.name;
cost.current = next.getKey();
if (node.name.equals(start)) {
cost.cost = next.getValue();
} else {
cost.cost = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
NodeCost oldCost = costList.get(next.getKey());
if (oldCost == null || oldCost.cost == Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
costList.put(next.getKey(), cost);
}
}
}
}
//初始化图结构
public static Map initData(String[] startEnd) {
Map node = new HashMap<>();
Node a = new Node();
a.name = "a";
a.nextNode = new HashMap() {
{
put("b", 5);
put("f", 2);
}
};
node.put("a", a);
Node b = new Node();
b.name = "b";
b.nextNode = new HashMap() {
{
put("c", 4);
put("e", 2);
}
};
node.put("b", b);
Node c = new Node();
c.name = "c";
c.nextNode = new HashMap() {
{
put("d", 3);
put("e", 6);
}
};
node.put("c", c);
Node d = new Node();
d.name = "d";
node.put("d", d);
Node e = new Node();
e.name = "e";
e.nextNode = new HashMap() {
{
put("d", 1);
}
};
node.put("e", e);
Node f = new Node();
f.name = "f";
f.nextNode = new HashMap() {
{
put("b", 8);
put("e", 7);
}
};
node.put("f", f);
startEnd[0] = "a";
startEnd[1] = "d";
return node;
}
}
//图表的结构
class NodeCost {
String current;
String parent;
Integer cost;
public String getCurrent() {
return current;
}
public void setCurrent(String current) {
this.current = current;
}
public String getParent() {
return parent;
}
public void setParent(String parent) {
this.parent = parent;
}
public int getCost() {
return cost;
}
public void setCost(int cost) {
this.cost = cost;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "NodeCost [current=" + current + ", parent=" + parent + ", cost=" + cost + "]";
}
}
//原始数据结构
class Node {
String name;
Map nextNode = new HashMap<>();
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Map getNextNode() {
return nextNode;
}
public void setNextNode(Map nextNode) {
this.nextNode = nextNode;
}
}
这里代码挺多,但是大部分都是去初始化图的结构了,真正的操作胆码数量还是可以查看的。