通过zookeeper实现分布式锁的原理浅谈
基于 Curator 实现分布式锁,curator是zk的一个客户端,像zkClient一样。
1.先说下工作原理:
我们可以利用 zookeeper 节点的特性来实现独占锁,就是同级节点的唯一性,多进程往 zookeeper 的指定节点下创建一个相同名称的节点,只有一个能成功,另外一个是创建失败;创建失败的节点全部通过 zookeeper 的 watcher 机制来监听zookeeper 这个子节点的变化,一旦监听到子节点的删除事件,则再次触发所有进程去写锁;到这里可能有人会说这样有问题哈,如果锁释放了之后其他的节点都会去争抢锁,产生了所谓的惊群效应。别急我们都能想到的问题,zk设计者铁定也会想到的哈。zk的数据结构还有watch机制,就是后一个节点监听前一个节点,这样的话第一个释放了只有第二个知道,他就顶上了,不就解决了么。
2.好下面上代码吧简单demo。分布式锁的简单实现
package com.gupaoedu.curator;
import org.apache.curator.framework.CuratorFramework;
import org.apache.curator.framework.CuratorFrameworkFactory;
import org.apache.curator.framework.recipes.locks.InterProcessLock;
import org.apache.curator.framework.recipes.locks.InterProcessMutex;
import org.apache.curator.retry.ExponentialBackoffRetry;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
- 分布式锁
- @author 张
*/
public class LockDemo {
private static String CONNECTION_STR="192.168.88.129:2181,192.168.88.130:2181,192.168.88.131:2181";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
CuratorFramework curatorFramework = CuratorFrameworkFactory.builder().
connectString(CONNECTION_STR).sessionTimeoutMs(40000).
retryPolicy(new ExponentialBackoffRetry(1000, 3)).build();
curatorFramework.start();
final InterProcessMutex lock=new InterProcessMutex(curatorFramework,"/locks");
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
new Thread(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"->尝试竞争锁");
try {
lock.acquire(); //阻塞竞争锁
//TimeUnit unit;
//lock.acquire(3,unit)
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"->成功获得了锁");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
Thread.sleep(1000*60);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
lock.release(); //释放锁
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"Thread-"+i).start();
}
}
}
上面的代码
lock.acquire(); //阻塞竞争锁
//TimeUnit unit;
//lock.acquire(3,unit)
带有参数的是指定时间内去等待争抢锁。不带的是一直等待。
好了看下效果图哈。

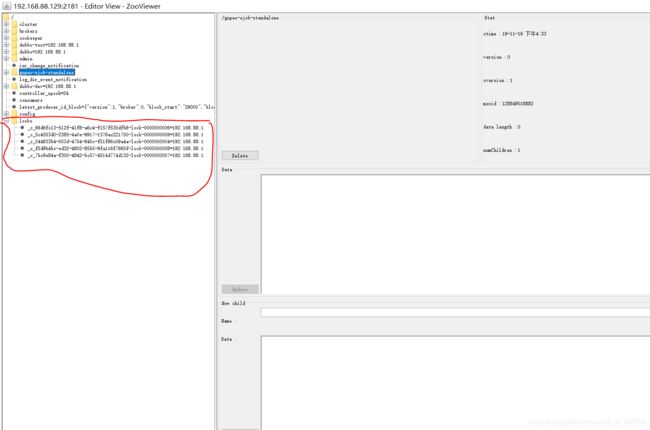
3.好了开始分析源码。
源码大致分为两部
1.创建当前线程所对应的锁文件路径
2.争抢锁
先看下上面节点的名称是怎么来的:
final InterProcessMutex lock=new InterProcessMutex(curatorFramework,"/locks");
上面这句话是把zk的客户端curator,和锁的命名空间传入到源码中。
/**
* @param client client
* @param path the path to lock
*/
源码1. public InterProcessMutex(CuratorFramework client, String path)
{
// 源码
this(client, path, new StandardLockInternalsDriver());
}
/**
* @param client client
* @param path the path to lock
* @param driver lock driver
*/
源码2. public InterProcessMutex(CuratorFramework client, String path, LockInternalsDriver driver)
{
// LOCK_NAME = private static final String LOCK_NAME = “lock-”;
this(client, path, LOCK_NAME, 1, driver);
}
源码3,
InterProcessMutex(CuratorFramework client, String path, String lockName, int maxLeases, LockInternalsDriver driver)
{
basePath = PathUtils.validatePath(path);
internals = new LockInternals(client, driver, path, lockName, maxLeases);
}
源码4
LockInternals(CuratorFramework client, LockInternalsDriver driver, String path, String lockName, int maxLeases)
{
this.driver = driver;
this.lockName = lockName; //“lock-”;
this.maxLeases = maxLeases; // 1
this.client = client.newWatcherRemoveCuratorFramework(); // 新建wantch客户吨
this.basePath = PathUtils.validatePath(path); // 返回的还是我们自己定义的那个 /locks 这里是检查而已。
this.path = ZKPaths.makePath(path, lockName);
}
源码5:
LockInternals(CuratorFramework client, LockInternalsDriver driver, String path, String lockName, int maxLeases)
{
this.driver = driver;
this.lockName = lockName;
this.maxLeases = maxLeases;
this.client = client.newWatcherRemoveCuratorFramework();
this.basePath = PathUtils.validatePath(path);
this.path = ZKPaths.makePath(path, lockName); // 自定义的namespace和源码默认的lock相结合 “/locks/lock-lock-”
}
源码6
public static String makePath(String parent, String child)
{
StringBuilder path = new StringBuilder();
joinPath(path, parent, child);
return path.toString(); // 返回的是我们最上面见到的所得名称啊。/locks/_c_5e722dc4-0e62-418d-87ae-9203e0add6aa-lock-xxxxxx
}
下面分析 锁是怎么争抢的
lock.acquire(); //阻塞竞争锁
源码1
@Override
public void acquire() throws Exception
{
if ( !internalLock(-1, null) ) // 如果返回的是false直接异常了
{
throw new IOException("Lost connection while trying to acquire lock: " + basePath);
}
}
源码2
private boolean internalLock(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws Exception
{
/*
Note on concurrency: a given lockData instance
can be only acted on by a single thread so locking isn’t necessary
*/
//获取当前线程
Thread currentThread = Thread.currentThread();
// 拿到当前线程对应的LockData ,threadData这是个concurretHashMap
// LockData包含final Thread owningThread(当前线程);final String lockPath;(锁的全路径)final AtomicInteger lockCount = new AtomicInteger(1);(记录冲入次数的)
LockData lockData = threadData.get(currentThread);
if ( lockData != null )
{// 如果当前线程获得了锁,记录重入次数
// re-entering
lockData.lockCount.incrementAndGet();
return true;
}
// 获得锁的全路径
String lockPath = internals.attemptLock(time, unit, getLockNodeBytes());
if ( lockPath != null )
{// 获得锁后把锁信息保存起来,这不就和上面的对应起来么
LockData newLockData = new LockData(currentThread, lockPath);
threadData.put(currentThread, newLockData);
return true;
}
return false;
}
重点在这里啊怎么获得锁的全路径
// 获得锁的全路径
String lockPath = internals.attemptLock(time, unit, getLockNodeBytes());
String attemptLock(long time, TimeUnit unit, byte[] lockNodeBytes) throws Exception
{
final long startMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
final Long millisToWait = (unit != null) ? unit.toMillis(time) : null; //竞争锁时候带有等待时间时候用的
final byte[] localLockNodeBytes = (revocable.get() != null) ? new byte[0] : lockNodeBytes; // 就是我们最开始看到所文件的实际效果图的最后几位的ID
int retryCount = 0;
String ourPath = null;
boolean hasTheLock = false;
boolean isDone = false;
while ( !isDone )
{
isDone = true;
try
{
ourPath = driver.createsTheLock(client, path, localLockNodeBytes); // 当前线程所对应的锁文件的全路径
hasTheLock = internalLockLoop(startMillis, millisToWait, ourPath); //是否获得了锁的标记
}
catch ( KeeperException.NoNodeException e )
{
// gets thrown by StandardLockInternalsDriver when it can't find the lock node
// this can happen when the session expires, etc. So, if the retry allows, just try it all again
if ( client.getZookeeperClient().getRetryPolicy().allowRetry(retryCount++, System.currentTimeMillis() - startMillis, RetryLoop.getDefaultRetrySleeper()) )
{
isDone = false;
}
else
{
throw e;
}
}
}
if ( hasTheLock )
{
return ourPath; // 返回锁文件路径
}
return null;
}
获取锁文件最终存放的路径:
@Override
public String createsTheLock(CuratorFramework client, String path, byte[] lockNodeBytes) throws Exception
{
String ourPath;
// 下面是在创建临时节点EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL 也就是锁文件的类型啊,把最终锁文件的路径返回去
if ( lockNodeBytes != null )
{
ourPath = client.create().creatingParentContainersIfNeeded().withProtection().withMode(CreateMode.EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL).forPath(path, lockNodeBytes);
}
else
{
ourPath = client.create().creatingParentContainersIfNeeded().withProtection().withMode(CreateMode.EPHEMERAL_SEQUENTIAL).forPath(path);
}
return ourPath;
}
// 获取锁的核心代码
private boolean internalLockLoop(long startMillis, Long millisToWait, String ourPath) throws Exception
{
boolean haveTheLock = false;
boolean doDelete = false;
try
{
if ( revocable.get() != null )
{
client.getData().usingWatcher(revocableWatcher).forPath(ourPath);
}
while ( (client.getState() == CuratorFrameworkState.STARTED) && !haveTheLock )
{
List children = getSortedChildren(); // 这句是在把该namespace下的锁文件排序,从小到大的顺序。
String sequenceNodeName = ourPath.substring(basePath.length() + 1); // +1 to include the slash // 当前线程所对应的锁的序号下标索引位置
PredicateResults predicateResults = driver.getsTheLock(client, children, sequenceNodeName, maxLeases);
if ( predicateResults.getsTheLock() )
{
haveTheLock = true;
}
else
{
String previousSequencePath = basePath + "/" + predicateResults.getPathToWatch();
synchronized(this)
{
try
{
// use getData() instead of exists() to avoid leaving unneeded watchers which is a type of resource leak
client.getData().usingWatcher(watcher).forPath(previousSequencePath);
// 上面是在监听前一个节点
if ( millisToWait != null )
{
millisToWait -= (System.currentTimeMillis() - startMillis);
startMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
if ( millisToWait <= 0 )
{
doDelete = true; // timed out - delete our node
break;
}
wait(millisToWait);
}
else
{
wait();
}
}
catch ( KeeperException.NoNodeException e )
{
// it has been deleted (i.e. lock released). Try to acquire again
}
}
}
}
}
catch ( Exception e )
{
ThreadUtils.checkInterrupted(e);
doDelete = true;
throw e;
}
finally
{
if ( doDelete )
{ // 删除当前节点的锁文件
deleteOurPath(ourPath);
}
}
return haveTheLock;
}
@Override
public PredicateResults getsTheLock(CuratorFramework client, List children, String sequenceNodeName, int maxLeases) throws Exception
{
int ourIndex = children.indexOf(sequenceNodeName);
validateOurIndex(sequenceNodeName, ourIndex); //当前名称文件夹所对应的下标索引
boolean getsTheLock = ourIndex < maxLeases; //maxLeases =1 ,也就是说当前索引是0时候就获得锁成功了
String pathToWatch = getsTheLock ? null : children.get(ourIndex - maxLeases);
//把该线程是否获得了锁,和锁文件路径的结果往上成返回。
return new PredicateResults(pathToWatch, getsTheLock);
}