验证码识别
验证码识别是3年前的一个小愿望了(当时是做一个自动回帖器,抽奖iphone),但自己这两年主要在做分布式架构,今年终于抽出了空,又战胜了对数学的恐惧,在coursera上学习了吴恩达的机器学习和深度学习,验证码识别也算是对部分课程的实践,下面就来整理一下这次识别的过程。
- 验证码识别主流程
- 识别细节
- 1 目标检测检测出验证码图片中的字符边距
- 11 labelImg使用
- 12 darknet使用教程
- 2 图片黑白处理
- 3 cnn识别算法
- 1 目标检测检测出验证码图片中的字符边距
- 训练结束识别验证码
1. 验证码识别主流程
- 目标检测,检测出字符边距,主要是获得weight,并输出坐标
- 图片黑白处理
- cnn识别算法
2. 识别细节
2.1 目标检测,检测出验证码图片中的字符边距
这个部分使用了yolov2算法,下面介绍一下yolov2算法:
A. 理论:yolov2算法整体来说其实是把图片分成一个一个小格子,然后每个格子会有一个输出
2.1.1 labelImg使用
http://blog.csdn.net/dcrmg/article/details/78496002
首先,采用上述博客的方法对验证码进行手工的打标签,把验证码的目标边框转换为darknet使用的格式, 接下来,如果需要使用gpu,那么按照
2.1.2 darknet使用教程
darknet的使用主要有2个部分要注意,
第一块是:gpu训练darknet
如果使用gpu来训练darknet(比如我就是去百度租了5块1个小时的gpu进行训练,效率真的提高了很多),那么需要注意一些安装和配置:
1. 百度的gpu机器需要安装cudnn
a. 首先下载 https://developer.nvidia.com/rdp/cudnn-download , 请注意一定要下载cudnn-8.0-linux-x64-v5.1.tgz,别的版本可能会有问题
b. 安装cudnn
$ cd ~
$ sudo tar xvf cudnn-8.0-linux-x64-v5.1.tgz
$ cd cuda/include
$ sudo cp *.h /usr/local/include/
$ cd ../lib64
$ sudo cp lib* /usr/local/lib/
$ cd /usr/local/lib# sudo chmod +r libcudnn.so.5.1.5
$ sudo ln -sf libcudnn.so.5.1.5 libcudnn.so.5
$ sudo ln -sf libcudnn.so.5 libcudnn.so
$ sudo ldconfig- 编译darknet:
由于要使用gpu的方式,所以我们需要修改一些配置文件后进行编译:
a. 修改makefile
GPU=1
CUDNN=1b. 修改cuda的路径
ifeq ($(GPU), 1)
COMMON+= -DGPU -I/usr/local/cuda-8.0/include/
CFLAGS+= -DGPU
LDFLAGS+= -L/usr/local/cuda-8.0/lib64 -lcuda -lcudart -lcublas -lcurand
#########################
NVCC=/usr/local/cuda-8.0/bin/nvccc. make即可, 这就会产生gpu训练版本的darknet源码了,现在只需要参考:http://blog.csdn.net/dcrmg/article/details/78496002 进行运行即可。
d. 接下来就训练吧,训练产生的参数都会保存到一个文件backup下面的yolo-voc.backup, 这个文件可要好好的保存哦,可以说weight在手,一切都飞不走,我在百度的机器上跑一天,基本测试集最后能达到100%的iou,和90%的覆盖比,基本够用啦。
./darknet detector train cfg/voc.data cfg/yolo-voc.2.0.cfg cfg/yolo-voc.weightf. 上面的训练结束之后(以测试集能达到100%的iou,90%的覆盖比为准),我们又需要改造一下代码,让darknet能够输出中心位置的坐标,而不仅仅是在图片上显示出来。打开darknet的代码: src/image.c, 在如下函数新增一句话:
void draw_detections(image im, int num, float thresh, box *boxes, float **probs, float **masks, char **names, image **alphabet, int classes)
{
int i,j;
for(i = 0; i < num; ++i){
char labelstr[4096] = {0};
int class = -1;
for(j = 0; j < classes; ++j){
if (probs[i][j] > thresh){
if (class < 0) {
strcat(labelstr, names[j]);
class = j;
} else {
strcat(labelstr, ", ");
strcat(labelstr, names[j]);
}
}
}
if(class >= 0){
int width = im.h * .006;
/*
if(0){
width = pow(prob, 1./2.)*10+1;
alphabet = 0;
}
*/
//printf("%d %s: %.0f%%\n", i, names[class], prob*100);
int offset = class*123457 % classes;
float red = get_color(2,offset,classes);
float green = get_color(1,offset,classes);
float blue = get_color(0,offset,classes);
float rgb[3];
//width = prob*20+2;
rgb[0] = red;
rgb[1] = green;
rgb[2] = blue;
box b = boxes[i];
int left = (b.x-b.w/2.)*im.w;
int right = (b.x+b.w/2.)*im.w;
int top = (b.y-b.h/2.)*im.h;
int bot = (b.y+b.h/2.)*im.h;
if(left < 0) left = 0;
if(right > im.w-1) right = im.w-1;
if(top < 0) top = 0;
if(bot > im.h-1) bot = im.h-1;
draw_box_width(im, left, top, right, bot, width, red, green, blue);
//------------------新增这句话--------------------------------
printf("rect:%d, %d, %d, %d\n", left, top, right, bot);
//----------------------------------------------------------
if (alphabet) {
image label = get_label(alphabet, labelstr, (im.h*.03)/10);
draw_label(im, top + width, left, label, rgb);
free_image(label);
}
if (masks){
image mask = float_to_image(14, 14, 1, masks[i]);
image resized_mask = resize_image(mask, b.w*im.w, b.h*im.h);
image tmask = threshold_image(resized_mask, .5);
embed_image(tmask, im, left, top);
free_image(mask);
free_image(resized_mask);
free_image(tmask);
}
}
}
}g. 重新make,得到darknet
h. 进行预测:
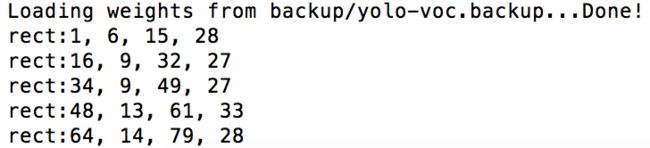
./darknet detector test cfg/voc.data cfg/yolo-voc.2.0.cfg backup/yolo-voc.backup a.png|grep "rect"
# 注意rect打印出来的结果不一定是从左到右,所以我们需要进行排序,让识别的部分能从左到右识别
echo "${result//rect:/}"|sort -n -t "," -k 1 >"${destPath}"/tmp好的,已经打印出我们的字符的坐标了。第一步顺利完成。
2.2 图片黑白处理
当图片的边框已经识别出来了,我们就需要根据给出的坐标将其切割,并二值化为黑白图片。
可以使用如下的python代码进行切割:
# -*-coding:utf-8-*-
from PIL import Image
import sys
# x1(左上角坐标x), y1(左上角坐标y), x2(右下角坐标x), y2(右下角坐标y), picName(文件名), picPath(文件路径), codeName(单字符名字), destPath(目标路径)
x1 = sys.argv[1]
y1 = sys.argv[2]
x2 = sys.argv[3]
y2 = sys.argv[4]
picName = sys.argv[5]
picPath = sys.argv[6]
codeName = sys.argv[7]
destPath = sys.argv[8]
im = Image.open(picPath)
region = im.crop((float(x1), float(y1), float(x2), float(y2)))
cropPath= destPath + "/" + codeName + "_" + picName +"_ori.png"
bwPath= destPath+ "/" + codeName + "_" + picName +".png"
region.save(destPath + "/" + codeName + "_" + picName +"_ori.png")可以用如下代码进行二值化为黑白图片:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""Binarize (make it black and white) an image with Python."""
from PIL import Image
from scipy.misc import imsave
import numpy
def binarize_image(img_path, target_path, threshold):
"""Binarize an image."""
image_file = Image.open(img_path)
image = image_file.convert('L') # convert image to monochrome
image = numpy.array(image)
image = binarize_array(image, threshold)
imsave(target_path, image)
def binarize_array(numpy_array, threshold=254):
"""Binarize a numpy array."""
for i in range(len(numpy_array)):
for j in range(len(numpy_array[0])):
# print(numpy_array[i][j])
if numpy_array[i][j] > threshold:
numpy_array[i][j] = 255
else:
numpy_array[i][j] = 0
return numpy_array
def get_parser():
"""Get parser object for script xy.py."""
from argparse import ArgumentParser, ArgumentDefaultsHelpFormatter
parser = ArgumentParser(description=__doc__,
formatter_class=ArgumentDefaultsHelpFormatter)
parser.add_argument("-i", "--input",
dest="input",
help="read this file",
metavar="FILE",
required=True)
parser.add_argument("-o", "--output",
dest="output",
help="write binarized file hre",
metavar="FILE",
required=True)
parser.add_argument("--threshold",
dest="threshold",
default=200,
type=int,
help="Threshold when to show white")
return parser
if __name__ == "__main__":
args = get_parser().parse_args()
binarize_image(args.input, args.output, args.threshold)调用方式:
# cropPath:源文件
# bwPath: 目标文件
python ./convertblack.py -i "$cropPath" -o "$bwPath" --threshold 254至此,我们的切割与黑白化就完成了。
2.3 cnn识别算法
这个部分我主要参考了tensorflow识别mnist的代码,对其进行了改造,我的识别图片resize到24*24,一共有62个类别(0-9, a-z, A-Z), 主要有如下2个文件:一个是huobi.py,主要是识别的主体部分:
# Copyright 2015 The TensorFlow Authors. All Rights Reserved.
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
# ==============================================================================
"""Functions for downloading and reading MNIST data."""
from __future__ import absolute_import
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_function
import gzip
import os
import tempfile
import numpy
from six.moves import urllib
from six.moves import xrange # pylint: disable=redefined-builtin
import tensorflow as tf
#from tensorflow.contrib.learn.python.learn.datasets.mnist import read_data_sets
import tensorflow as tf
import read_huobi
reSizePic=24
#0-9,a-z,A-Z, 62
classNum=62
originalPicSize=reSizePic*reSizePic
# read to mnist
#mnist = read_data_sets('/Users/zxx/PycharmProjects/neural/mnist/date/', one_hot=True)
mnist = read_huobi.load_huobi("/Users/zxx/PycharmProjects/neural/VerifyCodeDetection/darknet/darknet/results/")
x = tf.placeholder("float", shape=[None, originalPicSize], name='input_x')
y_ = tf.placeholder("float", shape=[None, classNum], name='input_y')
def weight_variable(shape):
initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=0.1)
return tf.Variable(initial)
def bias_variable(shape):
initial = tf.constant(0.1, shape=shape)
return tf.Variable(initial)
def conv2d(x, W):
return tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
def max_pool_2x2(x):
return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1],
strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
# 1 layer: 5*5*1(input 1), 32 filters
W_conv1 = weight_variable([5, 5, 1, 32])
b_conv1 = bias_variable([32])
x_image = tf.reshape(x, [-1,reSizePic,reSizePic,1])
h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x_image, W_conv1) + b_conv1)
h_pool1 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv1)
# pool1 output 12
#2 layer: 5*5*32(layer 1 output 32), 64 filters
W_conv2 = weight_variable([5, 5, 32, 64])
b_conv2 = bias_variable([64])
h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1, W_conv2) + b_conv2)
h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2)
# pool2 output 6,
# conection 1, the 6 is related to input size
W_fc1 = weight_variable([(reSizePic/4) * (reSizePic/4) * 64, 1024])
b_fc1 = bias_variable([1024])
h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2, [-1, (reSizePic/4)*(reSizePic/4)*64])
h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat, W_fc1) + b_fc1)
# drop out
keep_prob = tf.placeholder("float", name='keep_prob')
h_fc1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1, keep_prob)
# output layer
W_fc2 = weight_variable([1024, classNum])
# 0-9, a-z, a-Z=10+26+26=62
b_fc2 = bias_variable([classNum])
y_conv=tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(h_fc1_drop, W_fc2) + b_fc2)
# loss
cross_entropy = -tf.reduce_sum(y_*tf.log(y_conv))
# backproporation
train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1e-4).minimize(cross_entropy)
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_conv,1), tf.argmax(y_,1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, "float"))
graph_location = tempfile.mkdtemp() # temp file
print('Saving graph to: %s' % graph_location)
train_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(graph_location)
train_writer.add_graph(tf.get_default_graph())
saver=tf.train.Saver(tf.global_variables())
tf.add_to_collection('pred_network', y_conv)
tf.add_to_collection('accuracy_network', accuracy)
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.initialize_all_variables())
for i in range(1000):
batch = mnist.train.next_batch(1448)
if i%100 == 0:
save_path ='./tf_model/model_'+'%d'%i
print('%s' % save_path)
saver.save(sess, save_path)
train_accuracy = accuracy.eval(feed_dict={
x:batch[0], y_: batch[1], keep_prob: 1.0})
print("step %d, training accuracy %g"%(i, train_accuracy))
train_step.run(feed_dict={x: batch[0], y_: batch[1], keep_prob: 0.5})
print("test accuracy %g"%accuracy.eval(feed_dict={
x: mnist.test.images, y_: mnist.test.labels, keep_prob: 1.0}))另一个是read_huobi.py,主要用于图片的处理和读取:
from __future__ import absolute_import
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_function
import gzip
import numpy as np
from six.moves import xrange # pylint: disable=redefined-builtin
import numpy
from tensorflow.contrib.learn.python.learn.datasets import base
from tensorflow.python.framework import dtypes
from tensorflow.python.framework import random_seed
import shutil
import os
import random
from PIL import Image
class DataSet(object):
def __init__(self,
images,
labels,
fake_data=False,
one_hot=False,
dtype=dtypes.float32,
reshape=True,
seed=None):
"""Construct a DataSet.
one_hot arg is used only if fake_data is true. `dtype` can be either
`uint8` to leave the input as `[0, 255]`, or `float32` to rescale into
`[0, 1]`. Seed arg provides for convenient deterministic testing.
"""
seed1, seed2 = random_seed.get_seed(seed)
# If op level seed is not set, use whatever graph level seed is returned
numpy.random.seed(seed1 if seed is None else seed2)
dtype = dtypes.as_dtype(dtype).base_dtype
if dtype not in (dtypes.uint8, dtypes.float32):
raise TypeError('Invalid image dtype %r, expected uint8 or float32' %
dtype)
if fake_data:
self._num_examples = 10000
self.one_hot = one_hot
else:
assert images.shape[0] == labels.shape[0], (
'images.shape: %s labels.shape: %s' % (images.shape, labels.shape))
self._num_examples = images.shape[0]
# Convert shape from [num examples, rows, columns, depth]
# to [num examples, rows*columns] (assuming depth == 1)
if reshape:
assert images.shape[3] == 1
images = images.reshape(images.shape[0],
images.shape[1] * images.shape[2])
if dtype == dtypes.float32:
# Convert from [0, 255] -> [0.0, 1.0].
images = images.astype(numpy.float32)
images = numpy.multiply(images, 1.0 / 255.0)
self._images = images
self._labels = labels
self._epochs_completed = 0
self._index_in_epoch = 0
@property
def images(self):
return self._images
@property
def labels(self):
return self._labels
@property
def num_examples(self):
return self._num_examples
@property
def epochs_completed(self):
return self._epochs_completed
def next_batch(self, batch_size, fake_data=False, shuffle=True):
"""Return the next `batch_size` examples from this data set."""
if fake_data:
fake_image = [1] * 529
if self.one_hot:
fake_label = [1] + [0] * 62
else:
fake_label = 0
return [fake_image for _ in xrange(batch_size)], [
fake_label for _ in xrange(batch_size)
]
start = self._index_in_epoch
# Shuffle for the first epoch
if self._epochs_completed == 0 and start == 0 and shuffle:
perm0 = numpy.arange(self._num_examples)
numpy.random.shuffle(perm0)
self._images = self.images[perm0]
self._labels = self.labels[perm0]
# Go to the next epoch
if start + batch_size > self._num_examples:
# Finished epoch
self._epochs_completed += 1
# Get the rest examples in this epoch
rest_num_examples = self._num_examples - start
images_rest_part = self._images[start:self._num_examples]
labels_rest_part = self._labels[start:self._num_examples]
# Shuffle the data
if shuffle:
perm = numpy.arange(self._num_examples)
numpy.random.shuffle(perm)
self._images = self.images[perm]
self._labels = self.labels[perm]
# Start next epoch
start = 0
self._index_in_epoch = batch_size - rest_num_examples
end = self._index_in_epoch
images_new_part = self._images[start:end]
labels_new_part = self._labels[start:end]
return numpy.concatenate((images_rest_part, images_new_part), axis=0) , numpy.concatenate((labels_rest_part, labels_new_part), axis=0)
else:
self._index_in_epoch += batch_size
end = self._index_in_epoch
return self._images[start:end], self._labels[start:end]
def dense_to_one_hot(labels_dense, num_classes):
"""Convert class labels from scalars to one-hot vectors."""
num_labels = labels_dense.shape[0]
# arange dengchashulie
index_offset = numpy.arange(num_labels) * num_classes
labels_one_hot = numpy.zeros((num_labels, num_classes))
labels_one_hot.flat[index_offset + labels_dense.ravel()] = 1
return labels_one_hot
def load_predict_huobi(imgDir,dtype=dtypes.float32,
reshape=True,
seed=None,reSize=24):
train_images, train_labels = load_img(imgDir, reSize=reSize)
validation_images, validation_labels = load_img(imgDir, reSize=reSize)
test_images, test_labels = load_img(imgDir,reSize=reSize)
train = DataSet(train_images, train_labels, dtype=dtype, reshape=reshape, seed=seed)
validation = DataSet(validation_images, validation_labels, dtype=dtype, reshape=reshape,seed=seed)
test = DataSet(test_images, test_labels, dtype=dtype, reshape=reshape, seed=seed)
return base.Datasets(train=train, validation=validation, test=test)
def load_huobi(imgDir,dtype=dtypes.float32,
reshape=True,
seed=None, reSize=24):
train_images, train_labels = load_img(imgDir + "/trainImg/", reSize=reSize)
validation_images, validation_labels = load_img(imgDir + "/validationImg/", reSize=reSize)
test_images, test_labels = load_img(imgDir + "/testImg/", reSize=reSize)
train = DataSet(train_images, train_labels, dtype=dtype, reshape=reshape, seed=seed)
validation = DataSet(validation_images, validation_labels, dtype=dtype, reshape=reshape,seed=seed)
test = DataSet(test_images, test_labels, dtype=dtype, reshape=reshape, seed=seed)
return base.Datasets(train=train, validation=validation, test=test)
def convert_label_to_int_index(label):
# 0-9 1-10
# a-z 11-36
# A-Z 37-62
inta = ord('a')
intz = ord('z')
intA = ord('A')
intZ = ord('Z')
int0 = ord('0')
intLabel = ord(label)
if intLabel>=inta and intLabel<=intz:
return intLabel - inta + 10
elif intLabel>=intA and intLabel<=intZ:
return intLabel - intA + 36
else:
return intLabel - int0
def convert_int_index_to_label(int_index):
# 0-9 0-9
# a-z 10-35
# A-Z 36-61
inta = ord('a')
intz = ord('z')
intA = ord('A')
intZ = ord('Z')
int0 = ord('0')
intLabel = int_index
if int_index>=0 and int_index<=9:
label = chr(int_index + int0)
elif int_index>=10 and int_index<=35:
label = chr(int_index - 10 + inta)
else:
label = chr(int_index - 36 + intA)
return label
def load_img(imgDir, reSize=24):
imgs = os.listdir(imgDir)
imgNum = len(imgs)
data = np.empty((imgNum,reSize,reSize,1),dtype="float32")
label = np.empty((imgNum,),dtype="uint8")
for i in range (imgNum):
im = Image.open(imgDir+"/"+imgs[i]).convert('L')
img = im.resize((reSize, reSize),Image.ANTIALIAS)
arr = np.asarray(img,dtype="float32")
data[i,:,:,:] = arr.reshape(reSize,reSize,1)
label[i] = convert_label_to_int_index(imgs[i].split('_')[0])
print(label[i])
labels_one_hot = dense_to_one_hot(label, 62)
print("data.shape=" + str(data.shape))
print("label.shape=" + str(labels_one_hot.shape))
return data,labels_one_hot
def random_split_img(srcDir, validation_size=100, test_size=10):
imgs = os.listdir(srcDir)
random.shuffle(imgs)
imgNum = len(imgs)
test_images = imgs[:validation_size]
validation_images = imgs[validation_size:validation_size+test_size]
train_images = imgs[validation_size+test_size:]
if os.path.exists(srcDir + "/trainImg/"):
shutil.rmtree(srcDir + "/trainImg/")
if os.path.exists(srcDir + "/testImg/"):
shutil.rmtree(srcDir + "/testImg/")
if os.path.exists(srcDir + "/validationImg/"):
shutil.rmtree(srcDir + "/validationImg/")
os.mkdir(srcDir + "/trainImg/")
os.mkdir(srcDir + "/testImg/")
os.mkdir(srcDir + "/validationImg/")
for i in range (imgNum):
if not os.path.isdir(srcDir + imgs[i]):
if i < validation_size :
moveFileto(srcDir + imgs[i], srcDir + "/validationImg/" + imgs[i])
elif i < (validation_size + test_size) :
moveFileto(srcDir + imgs[i], srcDir + "/testImg/" + imgs[i])
else :
moveFileto(srcDir + imgs[i], srcDir + "/trainImg/" + imgs[i])
def moveFileto(sourceDir, targetDir):
shutil.copy(sourceDir, targetDir)验证cnn识别算法识别率的load_huobi.py
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import read_huobi
import sys
filePath=sys.argv[1]
destFileName=sys.argv[2]
reSize=sys.argv[3]
with tf.Session() as sess:
new_saver = tf.train.import_meta_graph("tf_model/model_900.meta")
new_saver.restore(sess, "tf_model/model_900")
y = tf.get_collection('pred_network')[0]
accurancy = tf.get_collection('accurancy_network')
graph = tf.get_default_graph()
x = graph.get_operation_by_name('input_x').outputs[0]
y_ = graph.get_operation_by_name('input_y').outputs[0]
keep_prob = graph.get_operation_by_name('keep_prob').outputs[0]
mnist = read_huobi.load_predict_huobi(filePath, reSize)
batch = mnist.train.next_batch(mnist.train.num_examples)
y_pre = sess.run(y, feed_dict={x:batch[0], keep_prob:1.0})
right=0
error=0
resultLabel = np.ones((1,mnist.train.num_examples))
resultLabel = resultLabel.astype(np.str)
for i in range(mnist.train.num_examples):
y_pre_list = y_pre[i].tolist()
y_batch_list = batch[1][i].tolist()
predict_y=str(read_huobi.convert_int_index_to_label(y_pre_list.index(max(y_pre_list))))
real_y=str(read_huobi.convert_int_index_to_label(y_batch_list.index(max(y_batch_list))))
resultLabel[0][int(real_y)] = predict_y
resultStr=""
for i in range(mnist.train.num_examples):
resultStr+=resultLabel[0][i]
fo = open(filePath+"/"+destFileName+".txt", "wb")
fo.write(resultStr);
fo.close()
4. 训练结束,识别验证码
这里主要涉及到3个文件,一个是总调用流程predict.sh :
picSrc="/Users/baidu/PycharmProjects/neural/mnist/srcImg/"
splitDest="/Users/baidu/PycharmProjects/neural/mnist/results/"
rm -rf "${splitDest}"
# splitpic
cd "/Users/baidu/PycharmProjects/neural/VerifyCodeDetection/darknet/darknet"
sh splitImg.sh "${picSrc}" "${splitDest}"
#predict
cd /Users/baidu/PycharmProjects/neural/mnist/
allPicDirName=`ls "${splitDest}"`
for picDirName in $allPicDirName
do
result=`python predict_huobi.py "${splitDest}/$picDirName" "$picDirName"`
echo "result:$result"
done从上面的代码可以看到,还涉及到2个脚本,一个是splitImg.sh,用于调用darknet分割图片中的每一个字符:
function splitPic()
{
picName=$1
filePath=$2
destPath=$3
result=`./darknet detector test cfg/voc.data cfg/yolo-voc.2.0.cfg backup/yolo-voc.backup "${filePath}"|grep "rect"`
echo "${result//rect:/}"|sort -n -t "," -k 1 >"${destPath}"/tmp
cat ${destPath}/tmp
pic=0
while read line
do
x1=`echo $line|awk -F ', ' '{print $1}'`
y1=`echo $line|awk -F ', ' '{print $2}'`
x2=`echo $line|awk -F ', ' '{print $3}'`
y2=`echo $line|awk -F ', ' '{print $4}'`
#train
#codeName="${picName:$pic:1}"
#predict
codeName="${pic}"
python ./screen.py "$x1" "$y1" "$x2" "$y2" "$picName" "$filePath" "$codeName" "$destPath"
cropPath="${destPath}/${codeName}_${picName}_ori.png"
bwPath="${destPath}/${codeName}_${picName}.png"
python ./convertblack.py -i "$cropPath" -o "$bwPath" --threshold 254
rm "$cropPath"
pic=$((pic+1))
done < "${destPath}/tmp"
rm "${destPath}/tmp"
echo "Done"
}
destPath="./results/"
srcPath="/Users/baidu/PycharmProjects/neural/VerifyCodeDetection/darknet/darknet/validateImage/"
if [ "$1" != "" ];then
srcPath="$1"
fi
if [ "$2" != "" ];then
destPath="$2"
fi
allPicName=`ls "${srcPath}"`
for picName in $allPicName
do
picName=`echo $picName |awk -F '.png' '{print $1}'`
destPath="${destPath}/${picName}/"
mkdir -p "$destPath"
#filePath="/Users/baidu/PycharmProjects/neural/VerifyCodeDetection/darknet/darknet/validateImage/${picName}.png"
filePath="${srcPath}/${picName}.png"
splitPic "$picName" "$filePath" "$destPath";
echo $picName
done
#usage:
#sh splitImg.sh "/Users/zxx/PycharmProjects/neural/mnist/srcImg/" "/Users/zxx/PycharmProjects/neural/mnist/results/"第三个脚本是真正的识别脚本: predict_huobi.py
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import read_huobi
import sys
filePath=sys.argv[1]
destFileName=sys.argv[2]
reSize=sys.argv[3]
with tf.Session() as sess:
new_saver = tf.train.import_meta_graph("tf_model/model_900.meta")
new_saver.restore(sess, "tf_model/model_900")
y = tf.get_collection('pred_network')[0]
accurancy = tf.get_collection('accurancy_network')
graph = tf.get_default_graph()
x = graph.get_operation_by_name('input_x').outputs[0]
y_ = graph.get_operation_by_name('input_y').outputs[0]
keep_prob = graph.get_operation_by_name('keep_prob').outputs[0]
mnist = read_huobi.load_predict_huobi(filePath, reSize)
batch = mnist.train.next_batch(mnist.train.num_examples)
y_pre = sess.run(y, feed_dict={x:batch[0], keep_prob:1.0})
right=0
error=0
resultLabel = np.ones((1,mnist.train.num_examples))
resultLabel = resultLabel.astype(np.str)
for i in range(mnist.train.num_examples):
y_pre_list = y_pre[i].tolist()
y_batch_list = batch[1][i].tolist()
predict_y=str(read_huobi.convert_int_index_to_label(y_pre_list.index(max(y_pre_list))))
real_y=str(read_huobi.convert_int_index_to_label(y_batch_list.index(max(y_batch_list))))
resultLabel[0][int(real_y)] = predict_y
resultStr=""
for i in range(mnist.train.num_examples):
resultStr+=resultLabel[0][i]
fo = open(filePath+"/"+destFileName+".txt", "wb")
fo.write(resultStr);
fo.close()