剑指offer题解------Python语言实现
面试题3:数组中重复的数字
哈希法:时间复杂度O(n),空间复杂度O(n)
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
# 这里要特别注意~找到任意重复的一个值并赋值到duplication[0]
# 函数返回True/False
def duplicate(self, numbers, duplication):
# write code here
dic = dict()
for item in numbers:
if item not in dic:
dic[item] = 1
else:
duplication[0] = item
return True
return False面试题4:二维数组中的查找
当从二维数组的左上角或者右下角进行遍历时,一次只能排除一个数据,当右上角或者左下角开始遍历时,一次可以排除一行或者一列数据。所以我们从(0,n-1)处开始,小了往下,大了往左。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
# array 二维列表
def Find(self, target, array):
if not array:
return False
raws = len(array)
columns = len(array[0])
i = 0
j = columns -1
while i < raws and j >= 0: # 在整个二维数组中进行寻找
if array[i][j] == target:
return True
elif array[i][j] > target:
j -= 1
else:
i += 1
return False # 没有找到面试题5:替换空格
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
# s 源字符串
def replaceSpace(self, s):
# write code here
return '%20'.join(s.split(' '))
# return s.replace(' ', '%20') #或者调用函数面试题6:从尾到头打印链表
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
# 返回从尾部到头部的列表值序列,例如[1,2,3]
def __init__(self):
self.result = []
def printListFromTailToHead(self, listNode):
if listNode: # 递归实现系统栈 只能使用if使用while会造成死循环
self.printListFromTailToHead(listNode.next)
self.result.append(listNode.val)
return self.result面试题7:重建二叉树
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
# 返回构造的TreeNode根节点
def reConstructBinaryTree(self, pre, tin):
if not pre:
return
t = pre[0]
root = TreeNode(t)
i = tin.index(t)
root.left = self.reConstructBinaryTree(pre[1:i+1],tin[:i])
root.right = self.reConstructBinaryTree(pre[i+1:],tin[i+1:])
return root面试题8:二叉树的下一个结点
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class TreeLinkNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def GetNext(self, pNode):
if not pNode:
return
if pNode.right: # 如果该结点有右孩子
z = pNode.right
while z.left: # 判断是否有左孩子,如果有找到最左边的
z = z.left
return z
# 以下代码特别容易出错,请注意
while pNode.next :
if pNode.next.left == pNode: # 如果当前结点是其父节点的左结点
return pNode.next # 直接将其父节点返回
pNode = pNode.next # 该结点为父节点的右结点,找到以该子树为左节点的父节点
return 面试题9:用两个栈实现队列
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.stack1 = []
self.stack2 = []
def push(self, node):
self.stack1.append(node)
def pop(self):
if not self.stack1 and not self.stack2:
return
elif self.stack2:
return self.stack2.pop()
else:
while self.stack1:
tmp = self.stack1.pop()
self.stack2.append(tmp)
return self.stack2.pop()面试题10:斐波那契数列
求斐波那契数列的第n项
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def Fibonacci(self, n):
# write code here
if n < 2:
return n
lst = [0,1]
for _ in range(n-1):
lst.append(lst[-1]+lst[-2])
return lst[-1]跳台阶
一只青蛙一次可以跳上1级台阶,也可以跳上2级。求该青蛙跳上一个n级的台阶总共有多少种跳法。
dp[n]=dp[n−1]+dp[n−2]dp[n]=dp[n−1]+dp[n−2]
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def jumpFloor(self, number):
# write code here
'''
n = 1 : 1
n = 2 : 1+1 = 2
n = 3 : f[n-2]+f[n-1]
'''
if number == 1 :
return 1
if number == 2:
return 2
tmp = [1,2]
for i in range(number - 2):
tmp.append(tmp[-1]+tmp[-2])
return tmp[-1]变态跳台阶
因为n级台阶,第一步有n种跳法:跳1级、跳2级、到跳n级
跳1级,剩下n-1级,则剩下跳法是f(n-1)
跳2级,剩下n-2级,则剩下跳法是f(n-2)
所以f(n)=f(n-1)+f(n-2)+...+f(1)
因为f(n-1)=f(n-2)+f(n-3)+...+f(1)
所以f(n)=2*f(n-1)
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def jumpFloorII(self, number):
# write code here
if number == 0:
return 0
if number ==1:
return 1
else:
return 2 * self.jumpFloorII(number - 1)或者直接套用数学归纳出来的公式 2 **(n-1)
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def jumpFloorII(self, number):
# write code here
if number == 0:
return 0
else:
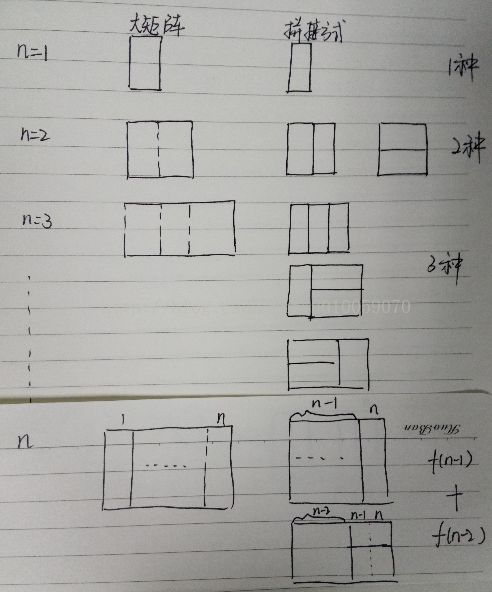
return 2 **(number - 1)矩形覆盖
可以用2*1的小矩形横着或者竖着去覆盖更大的矩形。用n个2*1的小矩形无重叠地覆盖一个2*n的大矩形,总共有多少种方法?
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def rectCover(self, number):
# write code here
if number<=2:
return number
dp = [1,2]
for i in range(number-2):
dp.append(dp[-1]+dp[-2])
return dp[-1]面试题11:旋转数组的最小数字
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def minNumberInRotateArray(self, array):
if not array:
return
n = len(array)
low = 0
high = n - 1
while low <= high:
mid = (low + high) // 2
if array[mid] > array[mid+1]: # 二分查找要查找的目标
return array[mid+1]
elif array[mid] > array[low]:
low = mid
else:
high = mid面试题15:二进制中1的个数
对于负数,最高位为1,而负数在计算机是以补码存在的,往右移,符号位不变,符号位1往右移,最终可能会出现全1的情况,导致死循环。与0xffffffff相与,就可以消除负数的影响
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def NumberOf1(self, n):
# write code here
if n < 0: # python没有无符号移动,负数需要处理下
n = n & 0xffffffff
return bin(n).count('1')面试题16:数值的整数次方
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def Power(self, base, exponent):
# write code here
flag = 0 # 判断是否为负数的标志
if base == 0 and exponent == 0:
return 'Input error'
elif base == 0:
return 0
elif exponent == 0:
return 1
elif exponent < 0:
flag = 1 # 如果幂为负数,则将标志置为1
exponent = -exponent
i = 1
result = 1
while i <= exponent:
result *= base
i += 1
if flag == 1:
return 1/result
else:
return result面试题18:
题目二:删除链表中重复的结点
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def deleteDuplication(self, pHead):
if not pHead:
return
head = ListNode(0)
head.next = pHead
pre = head
cur = head.next
while cur and cur.next:
if cur.val == cur.next.val:
while cur.next and cur.val == cur.next.val:
cur.next = cur.next.next
pre.next = cur.next
cur = pre.next
else:
pre = cur
cur = cur.next
return head.next面试题20:表示数值的字符串
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
# s字符串
def isNumeric(self, s):
if not s:
return
sign, point, hasE = False, False, False
for i in range(len(s)):
if s[i].lower() == 'e': # 判断e的存在及个数
if hasE: # 有两个e
return False
if i == len(s)-1: # e位于字符串最后
return False
hasE = True
elif s[i] == '+' or s[i] == '-':
if sign and s[i-1].lower() != 'e': # + -第二次出现 但并未位于e之后
return False
# 如果 + - 第一次出现且出现于字符串中间但并位于e之后
if not sign and i > 0 and s[i-1].lower() != 'e':
return False
sign = True
elif s[i] == '.': # 两个小数点或小数点与e不能同时出现
if hasE or point:
return False
point = True
elif ord(s[i]) < ord('0') or ord(s[i]) > ord('9'): # 如果当前字符不是一个数字
return False
return True面试题21:调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def reOrderArray(self, array):
arr1 = []
arr2 = []
for num in array:
if num % 2 == 1:
arr1.append(num)
else:
arr2.append(num)
arr1.extend(arr2)
return arr1面试题22:链表中倒数第k个结点
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def FindKthToTail(self, head, k):
if not head or not head.next:
return
slow = head
fast = head
for _ in range(k):
if fast:
fast = fast.next
else:
return
while fast:
fast = fast.next
slow = slow.next
return slow面试题24:链表中环的入口结点
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def EntryNodeOfLoop(self, pHead):
def isloop(pHead):
if not pHead:
return
slow = pHead
fast = pHead
while fast and fast.next: # 对于有环的链表来说 这个条件一直满足
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
if slow == fast:
return slow
return # 如果没环直接退出
end = isloop(pHead)
if not pHead or not end:
return
first = pHead
while end != first: # 2(a+b)=a+b+c+b
first = first.next
end = end.next
return first面试题24:反转链表
class Solution:
# 返回ListNode
def ReverseList(self, pHead):
pre = None
cur = pHead
while cur:
tmp = cur.next
cur.next = pre
pre = cur
cur = tmp
return pre# 通过设置虚拟头结点进行删除
class Solution:
# 返回ListNode
def ReverseList(self, pHead):
if not pHead or not pHead.next:
return pHead
head = ListNode(0)
head.next = pHead
pre = head.next
cur = head.next.next
while cur:
pre.next = cur.next
cur.next = head.next
head.next = cur
cur = pre.next
return head.next面试题25:合并两个排序的链表
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
# 返回合并后列表
def Merge(self, pHead1, pHead2):
head = ListNode(0)
cur = head
while pHead1 and pHead2:
if pHead1.val <= pHead2.val:
cur.next = pHead1
cur = cur.next
pHead1 = pHead1.next
else:
cur.next = pHead2
cur = cur.next
pHead2 = pHead2.next
if pHead1: # 如果还有剩余,将他们继续添加到cur后边
cur.next = pHead1
if pHead2:
cur.next = pHead2
return head.next面试题26:树的子结构
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def isSubtree(self,a,b): # 找到相等的根节点后 判断是否为子树
if not b: # ①判断B是否匹配完了,如果匹配完了说明为子结构
return True
if not a or a.val != b.val: # ②如果A匹配完了,或者A的值和B和值不等,直接返回False
return False # ③如果当前点相同,那同时看一下左子树和右子树的情况
return self.isSubtree(a.left, b.left) and self.isSubtree(a.right, b.right)
def HasSubtree(self, pRoot1, pRoot2):
if not pRoot1 or not pRoot2:
return False # 从根节点开始判断 判断左子树,判断右子树
return self.isSubtree(pRoot1,pRoot2)or self.HasSubtree(pRoot1.left,pRoot2) or self.HasSubtree(pRoot1.right,pRoot2)面试题27:二叉树的镜像
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
# 返回镜像树的根节点
# 二叉树的本质就是递归,将完整的二叉树先缩小规模看成只有两个叶结点的子二叉树
# 其顺序与后序遍历相同 先两个子节点 然后根结点
def Mirror(self, root):
if root == None:
return
self.Mirror(root.left)
self.Mirror(root.right)
tmp = root.left
root.left = root.right
root.right = tmp
return root面试题28:对称的二叉树
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def is_mirror(self, left, right):
if not left and not right:
return True
if not left or not right:
return False
if left.val == right.val:
return self.is_mirror(left.left, right.right) and self.is_mirror(left.right, right.left)
def isSymmetrical(self, pRoot):
if not pRoot:
return True
return self.is_mirror(pRoot.left, pRoot.right)面试题29:顺时针打印矩阵
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
# matrix类型为二维列表,需要返回列表
def printMatrix(self, matrix):
res = []
while matrix: # 只要矩阵不为空就一直循环
res += matrix.pop(0) # 方向:上
if matrix and matrix[0]: # 方向:右 第二个条件 确保是一个二维数组
for row in matrix:
res.append(row.pop())
if matrix: # 方向:下
res += matrix.pop()[::-1]
if matrix and matrix[0]: # 方向:左
for row in matrix[::-1]:
res.append(row.pop(0))
return res面试题30:包含min函数的栈
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.stack1 = []
self.stack2 = []
def push(self, node):
self.stack1.append(node)
if not self.stack2 or node <= self.stack2[-1]:
self.stack2.append(node)
def pop(self):
if self.stack2[-1] == self.stack1[-1]:
self.stack2.pop()
self.stack1.pop()
def top(self):
return self.stack1[-1]
def min(self):
if self.stack2:
return self.stack2[-1]
return面试题31:栈的压入、弹出序列
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def IsPopOrder(self, pushV, popV):
stack = []
pushLen = len(pushV)
popLen = len(popV)
if pushLen != popLen:
return False
pushIndex = 0
popIndex = 0
while pushIndex < pushLen:
stack.append(pushV[pushIndex])
pushIndex += 1
while len(stack) != 0 and stack[-1] == popV[popIndex]:
stack.pop()
popIndex += 1
return len(stack) == 0 and pushIndex == popIndex面试题32:
题目一:从上往下打印二叉树
class Solution:
# 返回从上到下每个节点值列表,例:[1,2,3]
def PrintFromTopToBottom(self, root):
res = []
if root is None:
return res
queue = [root]
while queue:
item = queue.pop(0)
res.append(item.val)
if item.left:
queue.append(item.left)
if item.right:
queue.append(item.right)
return res题目二:把二叉树打印成多行
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
# 返回二维列表[[1,2],[4,5]]
def Print(self, pRoot):
if pRoot is None:
return []
queue = [pRoot]
result = []
while queue:
tmp = []
n = len(queue)
for _ in range(n):
node = queue.pop(0)
tmp.append(node.val)
if node.left: # -_-|| 调试了好多次,原来是用成了汉字冒号!!!
queue.append(node.left) # 牛客也没有提示啊!!!!!
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
result.append(tmp)
return result题目三:按之字形顺序打印二叉树
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def Print(self, pRoot):
if pRoot is None:
return []
queue = [pRoot]
result = []
i = 1
while queue:
n = len(queue)
tmp = []
for _ in range(n):
m = queue.pop(0)
tmp.append(m.val)
if m.left:
queue.append(m.left)
if m.right:
queue.append(m.right)
if i%2 == 0:
tmp = tmp[::-1]
i += 1
result.append(tmp)
return result面试题33:二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def VerifySquenceOfBST(self, sequence):
if len(sequence) == 0:
return False
root = sequence[-1] # 最后一个为根节点
n = len(sequence)-1 # 最后一个元素的索引
i = 0
while i < n: # 找到第一个大于跟结点的位置
if sequence[i] > root:
break
i += 1
j = i
while j < n: # 判断右子树的元素是否都比根节点大
if sequence[j] < root:
return False
j += 1
left = True
right = True
if i != 0: # 避免 i = 0
left = self.VerifySquenceOfBST(sequence[:i])
right = self.VerifySquenceOfBST(sequence[i:])
return left and right面试题34:二叉树中和为某一值的路径
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
# 返回二维列表,内部每个列表表示找到的路径
def __init__(self):
self.sums = 0 # 存放当前和
self.rode = [] # 当前路径
self.res = [] # 二维结果列表
def FindPath(self, root, expectNumber):
if not root or not expectNumber:
return []
self.sums += root.val
self.rode.append(root.val)
if not root.left and not root.right and self.sums == expectNumber:
# 注意此处是self.rode[:] 不加[:] 直接使用变量名会返回空的二维列表
# 可变对象与不可变对象的复制 隐藏很深的bug!!
self.res.append(self.rode[:]) # 这里也不能直接return 因为后边还要逐个弹出
self.FindPath(root.left, expectNumber)
self.FindPath(root.right, expectNumber)
self.sums -= root.val
self.rode.pop()
return self.res面试题35:复杂链表的复制
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class RandomListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.label = x
# self.next = None
# self.random = None
class Solution:
# 返回 RandomListNode
def Clone(self, pHead):
if not pHead:
return None
# 第一步:复制节点在原节点之后
pCur = pHead
while pCur:
node = RandomListNode(pCur.label)
node.next = pCur.next
pCur.next = node
pCur = node.next
# 第二步:复制random节点
pCur = pHead
while pCur:
if pCur.random:
pCur.next.random = pCur.random.next
pCur = pCur.next.next
# 第三步:将新旧链表分离
pCur = pHead
head = pHead.next
cur = head
while pCur:
pCur.next = pCur.next.next
if cur.next:
cur.next = cur.next.next
cur = cur.next
pCur = pCur.next
return head
面试题36:二叉搜索树与双向链表
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.end = None
def Convert(self, root):
if not root:
return
self.Convert(root.left)
root.left = self.end
if self.end:
self.end.right = root
else:
self.head = root
self.end = root
self.Convert(root.right)
return self.head面试题37:序列化二叉树
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def Serialize(self, root):
def pre_order(root):
if not root:
result.append('#')
return
result.append(str(root.val))
pre_order(root.left)
pre_order(root.right)
result = []
pre_order(root)
return ' '.join(result)
def Deserialize(self, s):
vals = iter(s.split())
def pre_order():
val = next(vals)
if val == '#':
return None
root = TreeNode(int(val))
root.left = pre_order()
root.right = pre_order()
return root
return pre_order()
面试题38:字符串的排列
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def Permutation(self, ss):
if not ss: # 递归出口
return []
n = len(ss)
if n == 1:
return [ss]
res = []
for i in range(n): # 逐渐缩小问题的规模
tmp = self.Permutation(ss[:i]+ss[i+1:]) # 对除当前字符外的其他字符进行全排列
for j in tmp:
res.append(ss[i]+j) # 将该字符与全排列的其余字符做拼接
return sorted(list(set(res))) # 对拼接后的字符 去重 排序
面试题39:数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
哈希法:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def MoreThanHalfNum_Solution(self, numbers):
if not numbers:
return
n = len(numbers)
dic = dict()
for num in numbers:
if num not in dic:
dic[num] = 1
else:
dic[num] += 1
if dic[num] > n/2:
return num
return 0 # 如果没有则返回0
面试题40:最小的k个数
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
################## 八大排序算法实现最小的K个数 #######################
class Solution:
# 选择排序
def select_sort(self, tinput):
n = len(tinput)
for i in range(n):
min_i = i
for j in range(i+1, n):
if tinput[min_i] > tinput[j]:
min_i = j
tinput[i], tinput[min_i] = tinput[min_i], tinput[i]
return tinput
# 冒泡排序(优化版)
def bubble_sort(self, tinput):
n = len(tinput)
for i in range(n)[::-1]:
count = 0
for j in range(i):
if tinput[j] > tinput[j+1]:
tinput[j], tinput[j+1] = tinput[j+1], tinput[j]
count += 1
if count == 0:
return tinput
return tinput
# 插入排序
def insert_sort(self, tinput):
n = len(tinput)
for i in range(1, n):
j = i
while j >0:
if tinput[j] < tinput[j-1]:
tinput[j], tinput[j-1] = tinput[j-1], tinput[j]
j -= 1
else:
break
return tinput
# 希尔排序
def shell(self,tinput):
n = len(tinput)
gap = n // 2 # 使用不同的gap对数组进行预排序
while gap >0:
for i in range(gap, n): # 对每一个gap都需要对gap后的每一个关键字进行插入排序
j = i # 初始化一个指针
while j >= gap:
if tinput[j] < tinput[j - gap]: # 对一个gap进行插入排序
tinput[j], tinput[j - gap] = tinput[j - gap], tinput[j]
j -= gap # 一个gap的前一个关键字
else:
break
gap = gap // 2
return tinput
# 快速排序
def quick_sort(self, tinput,left, right):
if left >= right: # 递归出口
return tinput
i = left
j = right
tmp = tinput[i] # 选当前序列的第一个关键字为枢纽
while i < j: # 完成一次排序 将小于tmp的值放到tmp的左边,大于tmp的值放到tmp的右边
while i < j and tinput[j] >= tmp: # 从右往左扫描,找到一个小于tmp的关键字
j -= 1
tinput[i] = tinput[j]
while i < j and tinput[i] <= tmp: # 从左往右扫描,找到一个大于tmp的关键字
i += 1
tinput[j] = tinput[i]
tinput[i] = tmp # 一次循环结束后,i = j
self.quick_sort(tinput,left, i-1)
self.quick_sort(tinput,i+1, right)
return tinput
# 归并排序
def merge_sort(self,tinput):
def merge(list1, list2):
i, j = 0, 0
n1 = len(list1)
n2 = len(list2)
result = []
while i < n1 and j < n2:
if list1[i] <= list2[j]:
result.append(list1[i])
i += 1
else:
result.append(list2[j])
j += 1
if list1:
result.extend(list1[i:]) # 注意这里是extend而不是append
#result += list1[i:] # 这样写也可以 [] + [] ==> [].entend([])
if list2:
result.extend(list2[j:])
return result
n = len(tinput)
if n <=1:
return tinput
tmp = n/2
left = self.merge_sort(tinput[:tmp])
right = self.merge_sort(tinput[tmp:])
return merge(left, right)
# 堆排序
def heap_sort(self,lists):
def adjust_heap(lists, i, size): # 输入参数:数组,调整节点位置,数组长度
lchild = 2 * i + 1 # 当前结点左孩子的索引
rchild = 2 * i + 2 # 当前结点右孩子的索引
maxs = i
if i < size // 2: # 如果当前结点为非叶子节点
if lchild < size and lists[lchild] > lists[maxs]:
maxs = lchild
if rchild < size and lists[rchild] > lists[maxs]:
maxs = rchild
if maxs != i: # 如果当前结点满足大顶堆要求不交换,不满足进行交换并对其孩子结点进行调整
lists[maxs], lists[i] = lists[i], lists[maxs]
adjust_heap(lists, maxs, size) # 对交换后的孩子结点进行调整
def build_heap(lists, size): # 输入参数为:数组,数组长度
for i in range(size//2)[::-1]: # 对每一个非叶子节点进行调整
adjust_heap(lists, i, size)
size = len(lists)
build_heap(lists, size) # 对当前数组,建一个大顶堆
for i in range(size)[::-1]: # 依次将第i大的元素放到第i个位置
lists[0], lists[i] = lists[i], lists[0]
adjust_heap(lists, 0, i) # 对堆顶位置进行调整
return lists
# 基数排序
def radix(self, tinput):
if not tinput:
return []
k = len(str(max(tinput)))
bucket = [[] for i in range(10)]
for i in range(k):
for num in tinput:
bucket[num/(10**i)%10].append(num)
del tinput[:]
for z in bucket:
tinput += z
del z[:]
return tinput
def GetLeastNumbers_Solution(self, tinput, k):
left = 0
right = len(tinput)-1
#tinput = self.select_sort(tinput)
#tinput = self.insert_sort(tinput)
#tinput = self.bubble_sort(tinput)
#tinput = self.shell(tinput)
#tinput = self.quick_sort(tinput,left,right)
#tinput = self.radix(tinput)
#tinput = self.heap_sort(tinput)
tinput = self.merge_sort(tinput)
n = len(tinput)
if k<=n:
return tinput[:k]
else:
return []
面试题41:数据流中的中位数
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.arr = []
def Insert(self, num):
self.arr.append(num)
def GetMedian(self,x):
self.arr.sort()
n = len(self.arr)
m = n // 2
if n % 2 == 0:
return (self.arr[m] + self.arr[m-1])/2.0
return self.arr[m]
面试题42:连续子数组的最大和
从前往后加,加入新元素后如果和大于零则有用,小于零将 sub_sum置为零则重新开始记录
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def FindGreatestSumOfSubArray(self, array):
max_sum = 0
sub_sum = 0
for num in array:
sub_sum += num
if sub_sum < 0:
sub_sum = 0
if sub_sum > max_sum:
max_sum = sub_sum
if max_sum == 0:
return max(array)
return max_sum
面试题43:1-n整数中1出现的次数
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def NumberOf1Between1AndN_Solution(self, n):
# write code here
a = ''
for i in range(1, n+1):
a += str(i)
return a.count("1")面试题45:把数组排成最小的数
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# python3的sort方法没有了cmp参数,需要对其key参数进行以下处理
# import functools.cmp_to_key
# key = cmp_to_key(self.cmp)
class Solution:
def cmp(self, a, b):
return 1 if a+b > b+a else -1
def PrintMinNumber(self, numbers):
string = map(str, numbers) # string = [str(num) for num in numbers]
string.sort(self.cmp)
return ''.join(string)面试题:字符流中第一个不重复的元素
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
# 返回对应char
def __init__(self):
self.s = '' # 用于记录加入的总字符串
self.dic = dict() # 用于统计单个字符串出现的次数
def FirstAppearingOnce(self):
for i in self.s:
if self.dic[i] == 0:
return i
return '#'
def Insert(self, char): # 用于添加单个字符
self.s += char
if char not in self.dic:
self.dic[char] = 0
else:
self.dic[char] += 1面试题49:丑数
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def GetUglyNumber_Solution(self, index):
if index <= 1:
return index
res = [1] * index
i2, i3, i5 = 0, 0, 0 # 声明三个索引,可看做是存放排序丑数分别乘以2 3 5的三个队列
for i in range(1, index):# 循环一次产生一个大于已有序丑数的最小丑数
num2 = res[i2]*2 # 产生最有可能的三个丑数
num3 = res[i3]*3
num5 = res[i5]*5
res[i] = min(num2, min(num3, num5)) # 在产生的三个丑数当中选取最小的一个
if res[i] == num2:
i2 += 1
if res[i] == num3:
i3 += 1
if res[i] == num5:
i5 += 1
return res[-1]面试题50:第一个只出现一次的字符
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def FirstNotRepeatingChar(self, s):
dic = dict()
for tmp in s:
if tmp not in dic:
dic[tmp] = 0
else:
dic[tmp] += 1
for i in range(len(s)):
if dic[s[i]] == 0:
return i
return -1
面试题52:两个链表的第一个公共结点
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def FindFirstCommonNode(self, pHead1, pHead2):
if not pHead1 or not pHead2:
return
p, q = pHead1, pHead2
len1, len2 = 0, 0
while p:
len1 += 1
p = p.next
while q:
len2 += 1
q = q.next
if len1 > len2:
p, q = pHead1, pHead2
else:
p, q = pHead2, pHead1
for i in range(abs(len1-len2)):
p = p.next
while p != q:
p = p.next
q = q.next
return p # -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def FindFirstCommonNode(self, pHead1, pHead2):
if not pHead1 or not pHead2:
return
dic = dict()
while pHead1: # 将该链表放入字典中(哈希表)查找时间复杂度为O(1)
dic[pHead1] = 0
pHead1 = pHead1.next
while pHead2:
if pHead2 in dic:
return pHead2
pHead2 = pHead2.next
return面试题53:数字在排序数组中出现的次数
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def binary_search(self, data, k):
if not data:
return
n = len(data)
left = 0
right = n - 1
while left <= right:
mid = (left + right) // 2
if data[mid] == k:
return mid
elif data[mid] > k:
right = mid - 1
else:
left = mid + 1
return left
def GetNumberOfK(self, data, k):
if not data:
return 0
return self.binary_search(data, k+0.5) - self.binary_search(data, k-0.5)
面试题55:
题目一 二叉树的深度:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def TreeDepth(self, pRoot):
if pRoot == None: # 递归出口
return 0
return max(self.TreeDepth(pRoot.left),self.TreeDepth(pRoot.right))+1
题目二 平衡二叉树:
如果直接从上向下计算树的深度,判断是否满足平衡二叉树的定义,会多次重复遍历下层结点,增加了不必要的开销。
如果改为从下往上遍历,如果子树是平衡二叉树,则返回子树的高度;如果发现子树不是平衡二叉树,则直接停止遍历,这样至多只对每个结点访问一次。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def get_depth(self, p):
if not p:
return 0
left = self.get_depth(p.left) # 当前结点左子树的深度
if left == -1: # 左子树不是平衡二叉树
return -1
right = self.get_depth(p.right) # 当前结点右子树的深度
if right == -1: # 右子树不是平衡二叉树
return -1
if abs(left - right) > 1: # 如果以当前结点为根节点的树不是平衡二叉树
return -1
else:
return max(left, right) + 1 # 当前子树为平衡二叉树,返回当前子树的深度
def IsBalanced_Solution(self, p):
return self.get_depth(p) != -1另一种解法:复杂度较高
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def treeDepth(self, root):
if root == None:
return 0
return max(self.treeDepth(root.left),self.treeDepth(root.right)) + 1
def IsBalanced_Solution(self, pRoot):
if pRoot == None:
return True
return abs(self.treeDepth(pRoot.left) - self.treeDepth(pRoot.right))<= 1
面试题54:二叉搜索树的第k个结点
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
# 返回对应节点TreeNode
def KthNode(self, pRoot, k):
result = []
# 二叉排序树的顺序与该二叉树的中序遍历顺序相同
def in_order(pRoot): # 注意类方法内部的函数不需要 self
if pRoot == None:
return
in_order(pRoot.left)
result.append(pRoot) # 将中序遍历的结果放入一个数组中
in_order(pRoot.right)
in_order(pRoot)
if k == 0 or k > len(result):
return
return result[k-1] # 取出第k个结点空间复杂度较小的另一种方案:
class Solution:
# 返回对应节点TreeNode
def __init__(self):
self.num = 0
self.res = [] # 因为递归嵌套了很多函数 不能直接将结果return
def KthNode(self, pRoot, k):
if not pRoot or k < 1:
return
self.KthNode(pRoot.left, k)
self.num += 1
if self.num == k:
self.res.append(pRoot) # 将结果暂存在一个列表中
self.KthNode(pRoot.right, k)
if self.res:
return self.res[0] 面试题57:和为S的两个数字
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def FindNumbersWithSum(self, array, tsum):
# write code here
min_mul = float('inf') # 将初始最小值设置为无穷大,负无穷:-float('inf') 或 float('-inf'),其中,inf 均可以写成 Inf
min_i = 0
for i in array:
if tsum - i in array and i * (tsum - i) < min_mul:
min_i = i
min_mul = i * (tsum - i)
if min_mul == float('inf'):
return []
a = [min_i, tsum - min_i]
sorted(a)
return a[0], a[1]
# 方法二
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def FindNumbersWithSum(self, array, tsum):
dic = dict()
result = []
min_res = 999999999
min_lst = []
for num in array:
dic[num] = num
for i in array:
if tsum - i in dic:
result.append([i, tsum - i])
for lst in result:
if lst[0]*lst[1] < min_res:
min_res = lst[0]*lst[1]
min_lst = lst
return sorted(min_lst)题目二:和为S的连续正数序列
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def FindContinuousSequence(self, s):
i, j = 1, 2
res = []
while i < (s+1)//2: # 较小的值增加到该值结束
tmp = sum(range(i,j+1)) # 对i-j之间的序列求和
if tmp < s: # 当前序列和较小 对j加一
j += 1
elif tmp > s: # 当前序列和较大对i加一
i += 1
else: # tmp = s时
res.append(range(i, j+1))
j += 1 # 或者i += 1 制造新的不相等 避免死循环
return res面试题58:翻转字符串
题目一:
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def ReverseSentence(self, s):
# write code here
lst = s.split(' ')[::-1]
return ' '.join(lst) # 传入可迭代对象,以‘ ’进行拼接
题目二:左旋转字符串
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def LeftRotateString(self, s, n):
# write code here
return s[n:] + s[:n]
面试题:数组中只出现一次的数字
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
# 返回[a,b] 其中ab是出现一次的两个数字
def FindNumsAppearOnce(self, array):
# write code here
sum = 0
for i in array:
sum ^= i
for i in array:
if i^sum in array:
return [i, i^sum]面试题61:扑克牌中的顺子
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def IsContinuous(self, numbers):
if not numbers:
return False
numbers.sort() # 第一步:先对数组排序
zero_num = numbers.count(0) # 第二步:计算数组中大小王的个数
for i in range(len(numbers)-1):
if numbers[i] != 0:
if numbers[i] == numbers[i+1]: # 出现对子直接返回
return False
zero_num = zero_num - (numbers[i+1] - numbers[i])+1 #第三步:弥补空缺数
if zero_num < 0:
return False
return True面试题66:构建乘积数组
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def multiply(self, A):
if not A:
return []
n = len(A)
B = [1]*n
for i in range(1, n): # 计算A正三角并将值赋给B的相应位置
B[i] = B[i-1] * A[i-1]
temp = 1 # 倒三角第一个元素初始化为1
for i in range(n-2, -1, -1):
temp *= A[i+1] # 计算倒三角
B[i] *= temp # 得到最终结果
return B
面试题67:把字符串转换成整数
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
class Solution:
def StrToInt(self, s):
if not s:
return 0
res = 0
flag = 1
for i in range(len(s)):
if i == 0 and s[i] == '+':
continue
elif i == 0 and s[i] == '-':
flag = -1
continue
n = ord(s[i]) - ord('0') # 计算当前字符所对应数字的ASC码
if n>=0 and n<=9:
res = 10*res + n
else:
return 0
return res * flag