Unity Shaders and Effects Cookbook (3-6) 创建各向异性高光类型(Anisotropic) 模拟金属拉丝效果
这一次学习各向异性高光类型,名字真拗口,Anisotropic 这个英文单词也很拗口。
各向异性是模拟物体表面 沟槽方向性的高光反射类型,他会修改或延伸垂直方向上的高光。
比如模拟金属拉丝的效果,就可以使用各向异性来模拟。
转自http://blog.csdn.net/huutu http://www.thisisgame.com.cn
首先需要准备一张各向异性 的法线贴图,代表各向异性镜面高光的方向性。
注意法线贴图导入到Unity之后要在属性面板中勾选类型为 Normal Map。
首先在 Properties 块中添加相应的属性
Properties
{
_MainTex ("Base (RGB)", 2D) = "white" {}
_MainTint("Diffuse Tint",Color)=(1,1,1,1)
_SpecularColor("Specular Color",Color)=(1,1,1,1)
_Specular("Specular Amount",Range(0,1))=0.5
_SpecularPower("Specular Power",Range(0,1))=0.5
_AnisoDir("Anisotropic Direction",2D)=""{}
_AnisoOffset("Anisotropic Offset",Range(-1,1))=-0.2
}然后声明对应的变量供Subshader 使用
sampler2D _MainTex;
float4 _MainTint;
float4 _SpecularColor;
float _Specular;
float _SpecularPower;
sampler2D _AnisoDir;
float _AnisoOffset;其中的 _AnisoDir 是留给法线贴图的。
因为需要读取法线贴图的数据,所以修改 Input 结构体,把法线贴图的 UV 变量加入。
struct Input {
float2 uv_MainTex;
float2 uv_AnisoDir;
};Unity 中默认的 SurfaceOutput 不符合我们这个Shader 的需求了,所以需要自定义一个
struct SurfaceAnisoOutput
{
fixed3 Albedo;
fixed3 Normal;
fixed3 Emission;
fixed3 AnisoDirection;
half Specular;
fixed Gloss;
fixed Alpha;
};然后在 Surf 函数中,使用 UnpackNormal 读取 法线贴图中的数据。通过 SurfaceAnisoOutput 传递到 光照模型函数中
void surf (Input IN, inout SurfaceAnisoOutput o) {
half4 c = tex2D (_MainTex, IN.uv_MainTex) * _MainTint;
float3 anisoTex=UnpackNormal(tex2D(_AnisoDir,IN.uv_AnisoDir));
o.AnisoDirection=anisoTex;
o.Specular=_Specular;
o.Gloss=_SpecularPower;
o.Albedo = c.rgb;
o.Alpha = c.a;
}添加光照模型函数
inline fixed4 LightingAnisotropic(SurfaceAnisoOutput s,fixed3 lightDir,half3 viewDir,fixed atten)
{
//计算半角向量
fixed3 halfVector=normalize(normalize(lightDir)+normalize(viewDir));
//计算法线和光照方向的cos值
float NdotL=saturate(dot(s.Normal,lightDir));
//
fixed HdotA=dot(normalize(s.Normal + s.AnisoDirection) , halfVector);
float aniso=max(0,sin(radians((HdotA + _AnisoOffset)*180)));
float spec=saturate(pow(aniso,s.Gloss*128) * s.Specular);
fixed4 c;
c.rgb=( (s.Albedo * _LightColor0.rgb * NdotL) + (_LightColor0.rgb * _SpecularColor.rgb * spec)) * (atten * 2);
c.a=1.0;
return c;
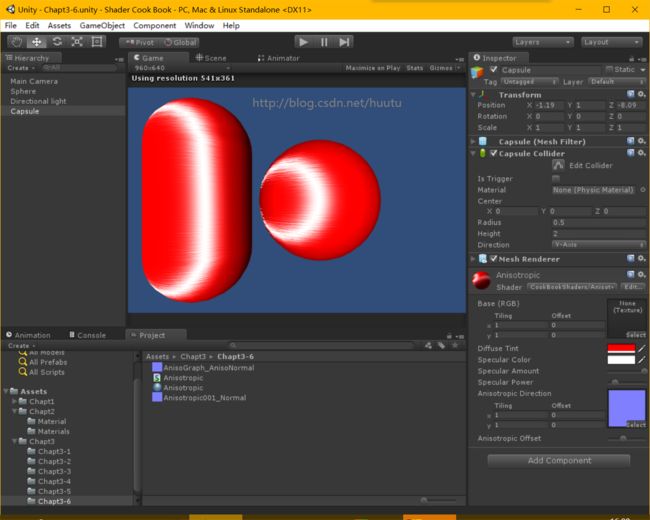
}Shader 编写好之后,创建 Material,在场景中创建3D GameObject,设置 Material,然后把法线贴图 赋值到 Material 中,最终效果如下 转自http://blog.csdn.net/huutu http://www.thisisgame.com.cn
实现原理:
在光照模型函数中,首先计算半角向量
//计算半角向量
fixed3 halfVector=normalize(normalize(lightDir)+normalize(viewDir));然后将 顶点法线 与 各向异性法线贴图的每个像素求和,然后进行normalize,再与 半角向量 进行点积运算。
fixed HdotA=dot(normalize(s.Normal + s.AnisoDirection) , halfVector);这样得到的浮点值 HdotA。
当HdotA ==1,表示物体表面法线 与 halfVector 平行。
当 HdotA==0,表示物体表面法线 与 halfVector 垂直。
然后,使用 sin() 函数对这个值进行修改。
loat aniso=max(0,sin(radians((HdotA + _AnisoOffset)*180)));最后,对 aniso 值产生的效果进行放大,对它进行 s.Gloss 方求幂,再乘上 s.Specular 值,在全局范围内降低它的强度。
float spec=saturate(pow(aniso,s.Gloss*128) * s.Specular);书上提到,需要指定着色器使用 Shader model 3.0 模式。
#pragma target 3.0我测试后法线不指定也是可以的。
到wiki上找到关于 target 的一些比较
2.0 or default
Compiles the shader under shader model 2. Model 2 has more limitations than 3 but is more compatible. Uses shader model 1.1 for vertex shaders.
Vertex: 128 instruction limit. Fragment: 96 instruction limit (32 texture + 64 arithmetic), 16 temporary registers and 4 texture indirections.
3.0
Compiles the shader under shader model 3. Model 3 is more powerful and flexible than 2 but is less compatible.
Vertex: no instruction limit.
Fragment: 1024 instruction limit (512 texture + 512 arithmetic), 32 temporary registers and 4 texture indirections.
It is possible to override these limits using #pragma profileoption directive.
For example, #pragma profileoption MaxTexIndirections=256 raises texture indirections limit to 256.
See #pragma profileoption for more information. Note that some shader model 3.0 features, like derivative instructions, aren't supported by vertex or fragment shaders.
You can use #pragma glsl to translate to GLSL instead which has fewer restrictions. See #pragma glsl for more information.
查看相关网页
http://www.ceeger.com/Components/SL-ShaderPrograms.html
http://wiki.unity3d.com/index.php?title=Shader_Code
示例项目打包下载:
http://pan.baidu.com/s/1eSK1rl4