Spark高级数据分析(1) ——纽约出租车轨迹的空间和时间数据分析
前言
本文在之前搭建的集群上,运行一个地理空间分析的示例,示例来自于《Spark高级数据分析》第八章。
Github项目地址:https://github.com/sryza/aas/tree/master/ch08-geotime ,
这个例子是通过分析纽约市2013年1月份的出租车数据,统计纽约市乘客下车点落在每个行政区的个数。
在开始正文之前,需要掌握以下基础知识:
- Scala基础语法
- Spark基础概念和原理(推荐《Spark快速大数据大分析》)
纽约出租车地理空间数据分析的主要流程:
- 数据获取
- 数据时间和和空间处理类库
- 数据预处理与地理空间分析
- 提交应用至集群,分布式计算
数据获取
本文的数据是纽约市2013年1月份乘客打车费用数据,数据大小是914.9M,解压后为2.5G。
数据下载地址
http://www.andresmh.com/nyctaxitrips/(trip_data_1.csv.zip)
数据下载方式
- 直接在window下载,上传至linux服务器,注意我的集群是docker容器,直接传到容器master节点。
- 在linux直接下载,命令如下
wget http://www.andresmh.com/nyctaxitrips/(trip_data_1.csv.zip)数据描述
#解压数据集
unzip trip_data_1.csv.zip
# 查看前10行数据
head -n 10 trip_data_1.csv结果如下图
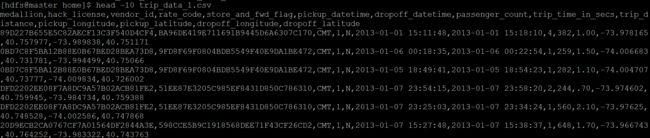
数据字段描述:
vendor_id:类型 rate_code:比率 store_and_fwd_flag:是否是四驱
pickup_datatime:客人上车时间 dropoff_datatime:客人下车时间
passenger_count:载客数量 trip_time_in_secs:载客时间 trip_distance:载客距离
pickup_longitude:客人上车经度 pickup_latitude:客人上车维度
dropoff_longitude:客人下车经度 dropoff_latitude:客人下车维度数据处理第三方类库
注意scala是可以直接调用java类库的。
时间处理类库:joda-time,nscala-time_2.11.jar(2.11对应scala版本)
本文空间关系处理库采用Esri的esri-geometry-api,当然也可以采用GeoTools等开源库。
自定义RichGeometry类封装Esri矢量空间处理接口;
package com.cloudera.datascience.geotime
import com.esri.core.geometry.{GeometryEngine, SpatialReference, Geometry}
import scala.language.implicitConversions
/**
* A wrapper that provides convenience methods for using the spatial relations in the ESRI
* GeometryEngine with a particular instance of the Geometry interface and an associated
* SpatialReference.
*
* @param geometry the geometry object
* @param spatialReference optional spatial reference; if not specified, uses WKID 4326 a.k.a.
* WGS84, the standard coordinate frame for Earth.
*/
class RichGeometry(val geometry: Geometry,
val spatialReference: SpatialReference = SpatialReference.create(4326)) extends Serializable {
def area2D(): Double = geometry.calculateArea2D()
def distance(other: Geometry): Double = {
GeometryEngine.distance(geometry, other, spatialReference)
}
def contains(other: Geometry): Boolean = {
GeometryEngine.contains(geometry, other, spatialReference)
}
def within(other: Geometry): Boolean = {
GeometryEngine.within(geometry, other, spatialReference)
}
def overlaps(other: Geometry): Boolean = {
GeometryEngine.overlaps(geometry, other, spatialReference)
}
def touches(other: Geometry): Boolean = {
GeometryEngine.touches(geometry, other, spatialReference)
}
def crosses(other: Geometry): Boolean = {
GeometryEngine.crosses(geometry, other, spatialReference)
}
def disjoint(other: Geometry): Boolean = {
GeometryEngine.disjoint(geometry, other, spatialReference)
}
}
/**
* Helper object for implicitly creating RichGeometry wrappers
* for a given Geometry instance.
*/
object RichGeometry extends Serializable {
implicit def createRichGeometry(g: Geometry): RichGeometry = new RichGeometry(g)
}数据预处理与地理空间分析
上传原始数据到HDFS集群
#在Hdfs集群下创建taxidata目录,注意必须带/
hadoop fs -mkdir /taxidata
#上传本地物理机数据至HDFS集群
hadoop fs -put trip_data_1.csv /taxidata/trip_data_1.csv自定义safe函数处理格式不正确的数据
详细请看代码注释第三部分
地理空间分析
获取纽约行政区划数据,利用esri gerometry类库判断各行政区下车点的记录数(详细请看代码注释第四部分)。
/**
* 打车信息类
* **/
case class Trip(
pickupTime: DateTime,
dropoffTime: DateTime,
pickupLoc: Point,
dropoffLoc: Point)
/**
* 出租车数据地理空间分析
*/
object RunGeoTime extends Serializable {
val formatter = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss", Locale.ENGLISH)
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
/*--------------1.初始化SparkContext-------------------*/
val sc = new SparkContext(new SparkConf().setAppName("SpaceGeo"))
/*--------------2.读取HDFS数据-------------------*/
val taxiRaw = sc.textFile("hdfs://master:9000/taxidata")
/*--------------3.出租车数据预处理------------------*/
//3.1 利用自定义的safe函数处理原始数据
val safeParse = safe(parse)
val taxiParsed = taxiRaw.map(safeParse)
//taxiParsed数据持久化
taxiParsed.cache()
//查看非法数据
/* val taxiBad = taxiParsed.collect({
case t if t.isRight => t.right.get
})*/
//collect返回到驱动器,为了单机开发和测试使用,不建议集群使用
//taxiBad.collect().foreach(println)
/*val taxiGood = taxiParsed.collect({
case t if t.isLeft => t.left.get
})
taxiGood.cache()*/
//3.2 剔除非法数据结果,获得正确格式的数据
val taxiGood=taxiParsed.filter(_.isLeft).map(_.left.get)
taxiGood.cache()
//自定义一次打车的乘坐时间函数
def hours(trip: Trip): Long = {
val d = new Duration(trip.pickupTime, trip.dropoffTime)
d.getStandardHours
}
//3.3 打印统计乘客上下车时间的记录,打印结果如执行分析结果图中的1
taxiGood.values.map(hours).countByValue().toList.sorted.foreach(println)
taxiParsed.unpersist()
//根据上面的输出结果,统计一次乘车时间大于0小于3小时的记录
val taxiClean = taxiGood.filter {
case (lic, trip) => {
val hrs = hours(trip)
0 <= hrs && hrs < 3
}
}
/*--------------4.出租车数据空间分析------------------*/
//4.1 获取纽约行政区划数据
val geojson = scala.io.Source.fromURL(getClass.getResource("/nyc-boroughs.geojson")).mkString
//转换为地理要素
val features = geojson.parseJson.convertTo[FeatureCollection]
val areaSortedFeatures = features.sortBy(f => {
val borough = f("boroughCode").convertTo[Int]
(borough, -f.geometry.area2D())
})
val bFeatures = sc.broadcast(areaSortedFeatures)
//4.2 判断乘客下车点落在那个行政区
def borough(trip: Trip): Option[String] = {
val feature: Option[Feature] = bFeatures.value.find(f => {
f.geometry.contains(trip.dropoffLoc)
})
feature.map(f => {
f("borough").convertTo[String]
})
}
//4.3 第一次统计打印各行政区下车点的记录,打印结果如执行分析结果图中的2
taxiClean.values.map(borough).countByValue().foreach(println)
//4.4 剔除起点和终点数据缺失的数据
def hasZero(trip: Trip): Boolean = {
val zero = new Point(0.0, 0.0)
(zero.equals(trip.pickupLoc) || zero.equals(trip.dropoffLoc))
}
val taxiDone = taxiClean.filter {
case (lic, trip) => !hasZero(trip)
}.cache()
//4.5 踢出零点数据后统计打印各行政区下车点的记录,打印结果如执行分析结果图中的3
taxiDone.values.map(borough).countByValue().foreach(println)
taxiGood.unpersist()
//输出地理空间分析结果到HDFS
//taxiDone.saveAsTextFile("hdfs://master:9000/GeoResult")
}
//字符串转double
def point(longitude: String, latitude: String): Point = {
new Point(longitude.toDouble, latitude.toDouble)
}
//获取taxiraw RDD记录中的出租车司机驾照和Trip对象
def parse(line: String): (String, Trip) = {
val fields = line.split(',')
val license = fields(1)
// Not thread-safe:
val formatterCopy = formatter.clone().asInstanceOf[SimpleDateFormat]
val pickupTime = new DateTime(formatterCopy.parse(fields(5)))
val dropoffTime = new DateTime(formatterCopy.parse(fields(6)))
val pickupLoc = point(fields(10), fields(11))
val dropoffLoc = point(fields(12), fields(13))
val trip = Trip(pickupTime, dropoffTime, pickupLoc, dropoffLoc)
(license, trip)
}
//非法记录数据处理函数
def safe[S, T](f: S => T): S => Either[T, (S, Exception)] = {
new Function[S, Either[T, (S, Exception)]] with Serializable {
def apply(s: S): Either[T, (S, Exception)] = {
try {
Left(f(s))
} catch {
case e: Exception => Right((s, e))
}
}
}
}
}分布式计算
打包应用
Windows下环境spark项目环境配置
在Windows上安装maven scala2.11.8(我的版本),intelij 及inteli的scala插件,导入ch08-geotime项目,如下图
配置pom文件
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<groupId>com.cloudera.datascience.geotimegroupId>
<artifactId>ch08-geotimeartifactId>
<packaging>jarpackaging>
<name>Temporal and Geospatial Analysisname>
<version>2.0.0version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.scala-langgroupId>
<artifactId>scala-libraryartifactId>
<version>2.11.8version>
<scope>providedscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hadoopgroupId>
<artifactId>hadoop-clientartifactId>
<version>2.7.3version>
<scope>providedscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.sparkgroupId>
<artifactId>spark-core_2.11artifactId>
<version>2.0.1version>
<scope>providedscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.nscala-timegroupId>
<artifactId>nscala-time_2.11artifactId>
<version>1.8.0version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.esri.geometrygroupId>
<artifactId>esri-geometry-apiartifactId>
<version>1.2.1version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.spraygroupId>
<artifactId>spray-json_2.11artifactId>
<version>1.3.2version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>joda-timegroupId>
<artifactId>joda-timeartifactId>
<version>2.9.4version>
dependency>
dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>net.alchim31.mavengroupId>
<artifactId>scala-maven-pluginartifactId>
<version>3.2.2version>
<configuration>
<scalaVersion>2.11.8scalaVersion>
<scalaCompatVersion>2.11.8scalaCompatVersion>
<args>
<arg>-uncheckedarg>
<arg>-deprecationarg>
<arg>-featurearg>
args>
<javacArgs>
<javacArg>-sourcejavacArg>
<javacArg>1.8.0javacArg>
<javacArg>-targetjavacArg>
<javacArg>1.8.0javacArg>
javacArgs>
configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<phase>compilephase>
<goals>
<goal>compilegoal>
goals>
execution>
executions>
plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.pluginsgroupId>
<artifactId>maven-assembly-pluginartifactId>
<version>2.6version>
<configuration>
<archive>
<manifest>
<mainClass>com.cloudera.datascience.geotime.RunGeoTimemainClass>
manifest>
archive>
<descriptorRefs>
<descriptorRef>jar-with-dependenciesdescriptorRef>
descriptorRefs>
<recompressZippedFiles>falserecompressZippedFiles>
configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>make-assemblyid>
<phase>packagephase>
<goals>
<goal>singlegoal>
goals>
execution>
executions>
plugin>
plugins>
build>
project>
Maven打包
在ch08-geotime项目下Terminal命令行
# maven打包,打包结果输入到target目录下
名称为ch08-geotime-2.0.0-jar-with-dependencies.jar(包含依赖包)
mvn clean
mvn package提交应用到集群
上传jar包至master节点,确保集群已启动,提交应用至集群,主要过程如下:
- 用户通过 spark-submit 脚本提交应用。
- spark-submit 脚本启动驱动器程序,调用用户定义的 main() 方法。
- 驱动器程序与集群管理器通信,申请资源以启动执行器节点。
- 集群管理器为驱动器程序启动执行器节点。
- 驱动器进程执行用户应用中的操作。 根据程序中所定义的对RDD的转化操作和行动操
作,驱动器节点把工作以任务的形式发送到执行器进程。- 任务在执行器程序中进行计算并保存结果。
- 如果驱动器程序的 main() 方法退出,或者调用了 SparkContext.stop()
驱动器程序会终止执行器进程,并且通过集群管理器释放资源。
————————《Spark快速大数据分析》
- 利用yarn集群提交应用
# --class 运行 Java 或 Scala 程序时应用的主类
# --master 表示要连接的集群管理器
# --deploy-mode 选择在本地(客户端“ client”)启动驱动器程序,还是在集群中的一台工作节点机
器(集群“ cluster”)上启动。在客户端模式下, spark-submit 会将驱动器程序运行
在 spark-submit 被调用的这台机器上。在集群模式下,驱动器程序会被传输并执行
于集群的一个工作节点上。默认是本地模式
# --name 应用的显示名,会显示在 Spark 的网页用户界面中
# 最后是应用入口的 JAR 包或 Python 脚本
spark-submit --class com.cloudera.datascience.geotime.RunGeoTime
--master yarn --deploy-mode cluster
--executor-memory 2g --executor-cores 2
--name "taxiGeoSpace"
/home/ch08-geotime/ch08-geotime-space-2.0.0.jar - 利用spark自带的管理器提交应用
# 注意集群模式地址是 spark://master:6066,客户端模式地址是spark://master:7077
spark-submit --class com.cloudera.datascience.geotime.RunGeoTime
--master spark://master:6066 --deploy-mode cluster
--executor-memory 2g --executor-cores 2 --name "taxiGeoSpace1"
/home/ch08-geotime/ch08-geotime-space--2.0.0.jar执行结果如下图

总结
执行时间是3min,后期要了解spark集群的运行参数配置
参考文献
- 《Spark快速大数据分析》
- 《Spark高级数据分析》
- http://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/running-on-yarn.html Running Spark on YARN