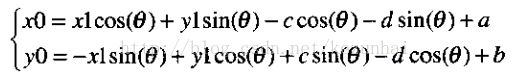PhotoShop算法实现--图像旋转(十九)
PhotoShop算法实现--图像旋转(十九)
http://blog.csdn.net/kezunhai
图像旋转是图像处理中的一种基本技术,在图像校正或定位中有广泛的应用。图像旋转就是将图像绕一个顶点旋转一定的角度。如图所示:
点(x0,y0)经过旋转theta角度后坐标编程(x1,y),则有:
上述的推导的旋转公司是以坐标轴原点进行的,如果是绕某一指定的点(a,b)旋转,则先要将坐标系平移到该点,然后再进行旋转,然后平移新的坐标到原点。
坐标系的转换过程的推导较为复杂,有兴趣的读者可以参考(Viusal C++数字图像处理-何斌),下面给出结论(其中(a,b)是未旋转的中心坐标, (c,d)是旋转后的中心坐标):
则新图像的宽度和高度为:
实现代码:
unsigned char getPixel(Mat& img, int row, int col, int ch)
{
return ((unsigned char*)img.data + img.step*row)[col*img.channels()+ch];
}
void setPixel(Mat& img, int row, int col, int ch,uchar val)
{
((unsigned char*)img.data + img.step*row)[col*img.channels()+ch] = val;
}void PhotoShop::Rotate(Mat& img, Mat& dst, float angle)
{
int width = img.cols;
int height = img.rows;
int chns = img.channels();
// 计算余弦和正弦
float fcos = cos(angle/180.0*PI);
float fsin = sin(angle/180.0*PI);
// 求新图的四个顶点
int x1 = -(width-1)/2*fcos + (height-1)/2*fsin ;
int y1 = (width-1)/2*fsin + (height-1)/2*fcos;
int x2 = (width-1)/2*fcos + (height-1)/2*fsin;
int y2 = -(width-1)/2*fsin + (height-1)/2*fcos;
int x3 = (width-1)/2*fcos - (height-1)/2*fsin;
int y3 = -(width-1)/2*fsin - (height-1)/2*fcos;
int x4 = -(width-1)/2*fcos - (height-1)/2*fsin;
int y4 = (width-1)/2*fsin - (height-1)/2*fcos;
// 新图的宽和高
int newWidth = max(abs(x3-x1), abs(x4-x2)); // 这里对于转出去的区域用白色填充
int newHeight = max(abs(y3-y1),abs(y4-y2));
// f1 = -c*cos(theta) - d*sin(theta)+a
// f2 = c*sin(theta) - d*cos(theta)+b
float f1 = -(newWidth-1)/2*fcos-(newHeight-1)/2*fsin + (width-1)/2;
float f2 = (newWidth-1)/2*fsin - (newHeight-1)/2*fcos + (height-1)/2;
// x0 = x1*cos(theta) + y1*sin(theta)+f1
// y0 = -x1*sin(theta)+ y1*cos(theta)+f2
dst.create(newHeight, newWidth, img.type());
int i, j, i0, j0, k;
for ( i=0; i=0 && i0=0 && j0 实现效果:
作者:kezunhai 出处:http://blog.csdn.net/kezunhai 欢迎转载或分享,但请务必声明文章出处。