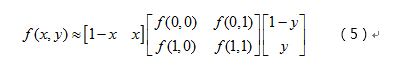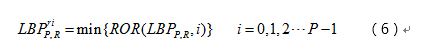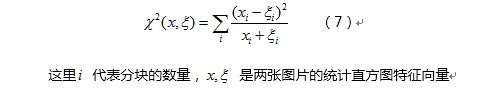图像特征LBP原理及C++实现
本文主要介绍了原始LBP以及各种改进LBP的原理,最后通过C++实现各种LBP得到LBP图谱。
LBP(Local Binary Patterns,局部二值模式)是一种能够有效地度量和提取图像局部纹理信息的算子,具有旋转不变性和灰度不变性等显著的优点。它是人脸识别中一种提取特征的重要方法,具有对光照不敏感的特性,但是对姿态和表情的鲁棒性不强。
一、原始LBP
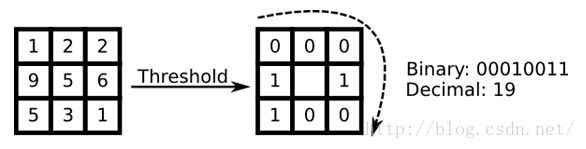
1996年,Ojala大牛搞出了LBP特征。原始的LBP算法的基本思想是在3*3的窗口内,以窗口中心像素为阈值,将相邻的8个像素的灰度值与其进行比较,若周围像素值大于中心像素值,则该像素点的位置被标记为1,否则为0。
这样,3*3邻域内的8个点经过比较可产生8位二进制数,如图1中00010011(通常转换为十进制数即LBP码,共256种),即得到该窗口中心像素点的LBP值,并用这个值来反映该区域的纹理信息。如下图所示:
LBP的操作可以被定义为:
这里,S是一个函数符号:
二、LBP扩展
基本的LBP算子只局限在3*3的邻域内,对于较大图像大尺寸的结构不能很好的提取需要的纹理特征,因此研究人员不断对其提出了各种改进和优化。
1、圆形LBP算子
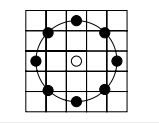
基本的 LBP算子的最大缺陷在于它只覆盖了一个固定半径范围内的小区域,这显然不能满足不同尺寸和频率纹理的需要。为了适应不同尺度的纹理特征,并达到灰度和旋转不变性的要求,Ojala等对 LBP 算子进行了改进,将 3×3邻域扩展到任意邻域,并用圆形邻域代替了正方形邻域,改进后的 LBP 算子允许在半径为 R 的圆形邻域内有任意多个像素点。从而得到了诸如半径为R的圆形区域内含有P个采样点的LBP算子。
比如下图定义了一个5X5的领域:
上图中的8个黑色的采样点,每个采样点的值可以通过下式计算
通过上式可以计算任意个采样点的坐标,但是计算得到的坐标未必完全是整数,所以可以通过双线性插值来得到该采样点的像素值:
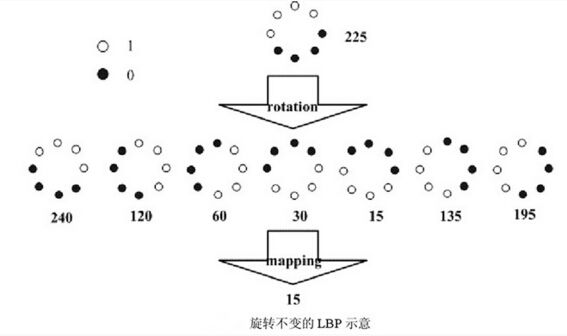
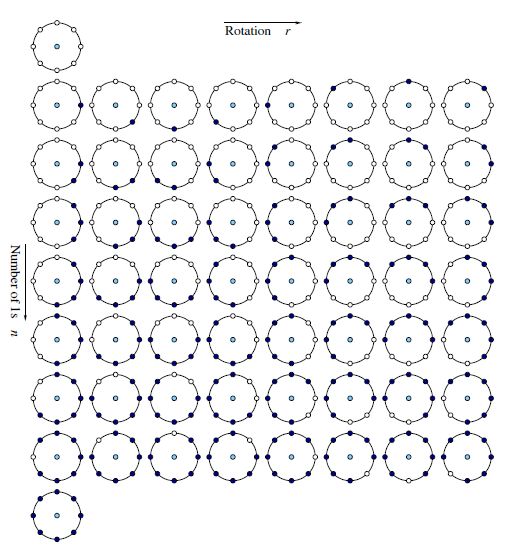
2、LBP旋转不变模式
由于编码的起始点是一定的,每一种二值编码模式经旋转(循环位移)后会产生不同的编码结果。为了形成旋转不变的编码模式,对同一编码模式经旋转后产生的编码结果编码为同一值,即这些旋转结果中的最小值。
一共36个旋转不变的LBP编码模式,如下图所示:
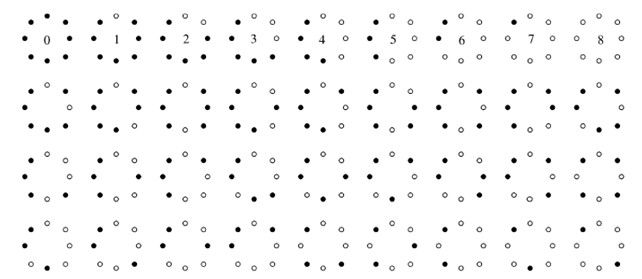
3、LBP等价模式
原始的LBP算子,随着邻域内采样点数的增加,二进制模式的种类是急剧增加的。
对于半径为R的圆形区域内含有P个采样点的LBP算子将会产P^2中模式,如5X5领域内20个采样点,有2^20=104857种二进制模式。过多的二值模式对于特征的提取以及信息的存取都是不利的。例如,将LBP算子用于人脸识别时,常采用的LBP模式的统计直方图来表达人脸信息,而较多的模式种类将使得数据量过大,且直方图过于稀疏。因此,需要对原始LBP模式进行降维,使得数据量减少的情况下能最好的代表图像的信息。
旋转LBP模式同样存在缺陷,大量的实验证明LBP模式的36种情况在一幅图像中分布出现的频率差异较大,得到的效果不是很好。因此人们提出了uniform LBP。“等价模式”被定义为:当某个LBP所对应的循环二进制数从0到1或者从1到0最多有两次跳变时,该LBP所对应的二进制就称为一个等价模式。在实际图像中,计算出来的大部分值都在等价模式之中,可达百分之90%以上。uniformLBP模式的个数为P(P-1)+2,P为领域像素点个数。对于8个采样点,uniform形式有58种输出, 其他的所有值为第59类,这样直方图从原来的256维降到了59维,并且可以减少高频噪声带来的影响。
uniform形式的58种LBP模式如下图所示:
三、LBP人脸识别
将LBP用于人脸识别时,一般不将LBP图作为特征用于识别,而是统计LBP特征图的直方图作为特征向量用于分类识别。
但是如果直接统计两张完整图片的LBP直方图进行分类识别的话,一但人脸位置没有对准,识别效果会很差。所以,LBP人脸识别的一般做法是将人脸图像进行分块,对每块子图像进行LBP直方图统计,并将所以块的直方图首尾相连组成一个向量,这个向量即是人脸的特征描述。通过比较两张人脸图像的统计直方图特征向量的相似度,即可实现人脸识别。人脸分块示意图:
统计直方图特征向量相似度的计算公式:
对LBP特征向量进行提取的一般步骤:
- 首先将一张图片分成若干个子块图片区域(cell)
- 对于每个cell中的一个像素,将相邻的8个像素的灰度值与其进行比较,若周围像素值大于中心像素值,则该像素点的位置被标记为1,否则为0。这样,3*3邻域内的8个点经比较可产生8位二进制数,即得到该窗口中心像素点的LBP值
- 然后计算每个cell的直方图,即每个数字(假定是十进制数LBP值)出现的频率;然后对该直方图进行归一化处理
- 最后将得到的每个cell的统计直方图进行连接成为一个特征向量,也就是整幅图的LBP纹理特征向量
- 通过一定的方法比较两张图片的LBP特征向量的相似度来实现人脸识别
四、各版本LBP的C++实现
#include
using namespace cv;
//原始LBP
Mat LBP(Mat img)
{
Mat result;
result.create(img.rows - 2, img.cols -2 , img.type());
result.setTo(0);
for(int i = 1; i(i, j);
uchar code = 0;
code |= (img.at(i-1, j-1) >= center)<<7;
code |= (img.at(i-1, j) >= center)<<6;
code |= (img.at(i-1, j+1) >= center)<<5;
code |= (img.at(i, j+1) >= center)<<4;
code |= (img.at(i+1, j+1) >= center)<<3;
code |= (img.at(i+1, j) >= center)<<2;
code |= (img.at(i+1, j-1) >= center)<<1;
code |= (img.at(i, j-1) >= center)<<0;
result.at(i -1, j -1) = code;
}
}
return result;
}
//圆形LBP
Mat ELBP(Mat img, int radius, int neighbors)
{
Mat result;
result.create(img.rows-radius*2, img.cols-radius*2, img.type());
result.setTo(0);
for(int n=0; n(radius * cos(2.0*CV_PI*n/static_cast(neighbors)));
float y = static_cast(-radius * sin(2.0*CV_PI*n/static_cast(neighbors)));
// relative indices
int fx = static_cast(floor(x));
int fy = static_cast(floor(y));
int cx = static_cast(ceil(x));
int cy = static_cast(ceil(y));
// fractional part
float ty = y - fy;
float tx = x - fx;
// set interpolation weights
float w1 = (1 - tx) * (1 - ty);
float w2 = tx * (1 - ty);
float w3 = (1 - tx) * ty;
float w4 = tx * ty;
// iterate through your data
for(int i=radius; i < img.rows-radius;i++)
{
for(int j=radius;j < img.cols-radius;j++)
{
// calculate interpolated value
float t = static_cast(w1*img.at(i+fy,j+fx) + w2*img.at(i+fy,j+cx) + w3*img.at(i+cy,j+fx) + w4*img.at(i+cy,j+cx));
// floating point precision, so check some machine-dependent epsilon
result.at(i-radius,j-radius) += ((t > img.at(i,j)) || (std::abs(t-img.at(i,j)) < std::numeric_limits::epsilon())) << n;
}
}
}
return result;
}
//八位二进制跳变次数
int getHopCount(uchar i)
{
uchar a[8] ={0};
int cnt =0;
int k = 7;
while(k)
{
a[k] = i&1;
i = i>>1;
--k;
}
for(int k =0; k<7;k++)
{
if(a[k] !=a[k+1])
++cnt;
}
if(a[0] != a[7])
++cnt;
return cnt;
}
//旋转不变LBP
Mat RILBP(Mat img)
{
uchar RITable[256];
int temp;
int val;
Mat result;
result.create(img.rows - 2, img.cols -2 , img.type());
result.setTo(0);
for(int i = 0; i<256; i++)
{
val =i;
for(int j =0; j<7; j++)
{
temp = i>>1;
if(val>temp)
{
val = temp;
}
}
RITable[i] = val;
}
for(int i = 1; i(i, j);
uchar code = 0;
code |= (img.at(i-1, j-1) >= center)<<7;
code |= (img.at(i-1, j) >= center)<<6;
code |= (img.at(i-1, j+1) >= center)<<5;
code |= (img.at(i, j+1) >= center)<<4;
code |= (img.at(i+1, j+1) >= center)<<3;
code |= (img.at(i+1, j) >= center)<<2;
code |= (img.at(i+1, j-1) >= center)<<1;
code |= (img.at(i, j-1) >= center)<<0;
result.at(i -1, j -1) = RITable[code];
}
}
return result;
}
//UniformLBP
Mat UniformLBP(Mat img)
{
uchar UTable[256];
memset(UTable, 0, 256*sizeof(uchar));
uchar temp =1;
for(int i =0; i<256; i++)
{
if(getHopCount(i)<=2)
{
UTable[i] = temp;
++temp;
}
}
Mat result;
result.create(img.rows - 2, img.cols -2 , img.type());
result.setTo(0);
for(int i = 1; i(i, j);
uchar code = 0;
code |= (img.at(i-1, j-1) >= center)<<7;
code |= (img.at(i-1, j) >= center)<<6;
code |= (img.at(i-1, j+1) >= center)<<5;
code |= (img.at(i, j+1) >= center)<<4;
code |= (img.at(i+1, j+1) >= center)<<3;
code |= (img.at(i+1, j) >= center)<<2;
code |= (img.at(i+1, j-1) >= center)<<1;
code |= (img.at(i, j-1) >= center)<<0;
result.at(i -1, j -1) = UTable[code];
}
}
return result;
}
int main()
{
Mat src = imread("../data/lena.bmp", 0);
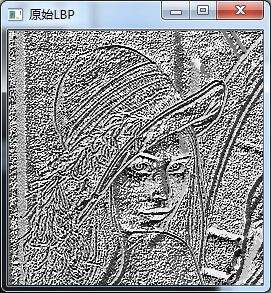
Mat dst = LBP(src);
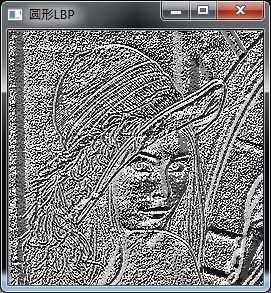
Mat edst = ELBP(src, 1, 8);
Mat pic = RILBP(src);
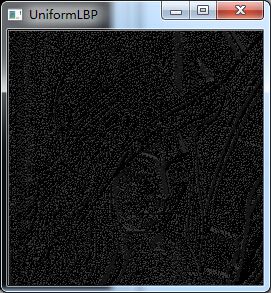
Mat img = UniformLBP(src);
imshow("原始图片", src);
imshow("原始LBP", dst);
imshow("圆形LBP", edst);
imshow("旋转不变LBP", pic);
imshow("UniformLBP", img);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
} 代码运行结果,如下图所示: