第十章 Caché 算法与数据结构 二叉堆
文章目录
-
第十章 Caché 算法与数据结构 二叉堆 - 最大堆
- 最小堆
- 插入节点
- 构建二叉堆
- 完整代码
- 二叉堆类
- 调用
第十章 Caché 算法与数据结构 二叉堆
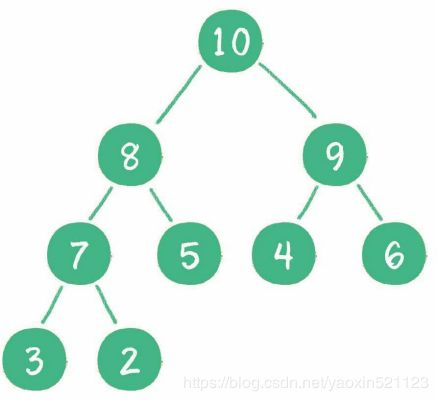
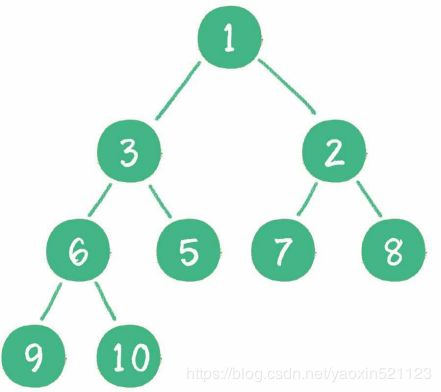
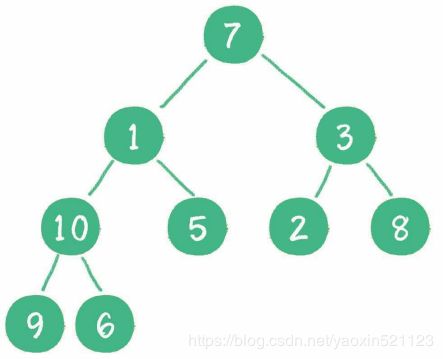
二叉堆本质上是一种完全二叉树:
- 最大堆:任何一个父节点的值,都大于或等于它左,右孩子节点的值。
- 最小堆:任何一个父节点的值,都小雨或等于它左,右孩子节点的值。
- 二叉堆的根节点叫做堆顶。
- 二叉堆的特性绝对了堆顶是整个堆中最大元素或最小元素。
最大堆
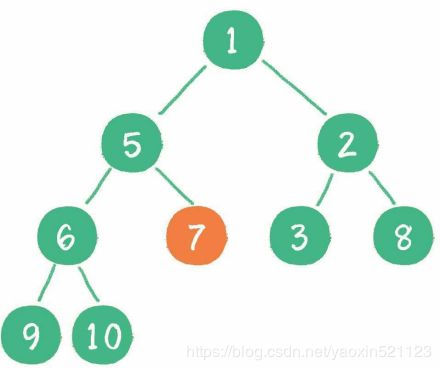
最小堆
插入节点
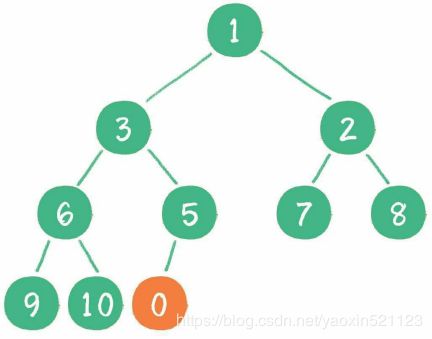
当二叉堆插入节点时,插入位置是完全二叉树的最后一个位置。例如插入一个新节点,值是 0。
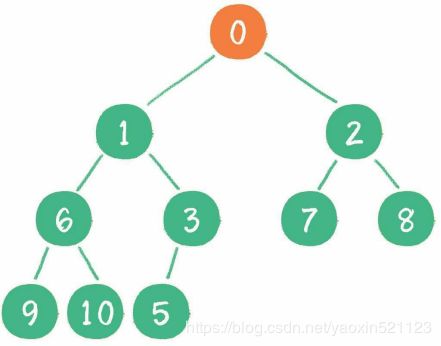
这时,新节点的父节点5比0大,显然不符合最小堆的性质。于是让新节点“上 浮”,和父节点交换位置。直到最后。
构建二叉堆
下面举一个无序完全二叉树的例子:
- 首先,从最后一个非叶子节点开始,也就是从节点10开始。如果节点10大于它 左、右孩子节点中最小的一个,则节点10“下沉”。
- 接下来轮到节点3,如果节点3大于它左、右孩子节点中最小的一个,则节点 3“下沉”。
- 然后轮到节点1,如果节点1大于它左、右孩子节点中最小的一个,则节点1“下 沉”。事实上节点1小于它的左、右孩子,所以不用改变。
- 接下来轮到节点7,如果节点7大于它左、右孩子节点中最小的一个,则节点 7“下沉”。
- 经过几轮
完整代码
二叉堆类
Class PHA.YX.Arithmetic.Heap Extends %RegisteredObject
{
/* 自定义数据有问题,不知道为啥不行,提示非法值 */
Method upAdjust(array)
{
#dim childIndex as %Integer = array.length() - 1
s resutlt = (childIndex - 1 ) / 2
#dim parentIndex as %Integer = +resutlt
#dim temp as %Integer = array.get(childIndex)
while((childIndex > 0)&&(temp < array.get(parentIndex))){
w temp,!
s array.get(childIndex) = array.get(parentIndex)
s childIndex = parentIndex
s parentIndex = (parentIndex - 1) / 2
}
s array.get(childIndex) = temp
}
/// 上浮调整
Method upAdjustArray(array As %ArrayOfDataTypes)
{
#dim childIndex as %Integer = array.Count() - 1
#dim parentIndex as %Integer = (childIndex - 1 ) \ 2 /* 这一定要取整数 */
/* temp保存插入的叶子节点值,用于最后的赋值 */
#dim temp as %Integer = array.GetAt(childIndex)
while((childIndex > 0)&&(temp < array.GetAt(parentIndex))){
/* 无需真正交换,单向赋值即可 */
d array.SetAt(array.GetAt(parentIndex),childIndex)
s childIndex = parentIndex
s parentIndex = (parentIndex - 1) \ 2
}
d array.SetAt(temp,childIndex)
q array
}
/// 下沉调整
Method downAjustArray(array As %ArrayOfDataTypes, parentIndex As %Integer, length As %Integer)
{
#dim temp as %Integer = array.GetAt(parentIndex)
#dim childIndex as %Integer = 2 * parentIndex + 1
while(childIndex < length){
;w "childIndex i:"_childIndex _ " array.GetAt(childIndex + 1):" _array.GetAt(childIndex + 1)_ " array.GetAt(childIndex):" _array.GetAt(childIndex),!
/* 如果有右孩子,且右孩子小于左孩子的值,则定位到右孩子 */
if (((childIndex + 1) < length)&&(array.GetAt(childIndex + 1) < array.GetAt(childIndex))){
s childIndex = childIndex + 1
}
;b:temp=1
;w "temp:"_temp _ " array.GetAt(childIndex):"_array.GetAt(childIndex),!
;w "childIndex:"_childIndex,!
;w array.GetAt(childIndex),!
/* 如果父节点小于任何一个孩子的值,直接跳出 */
if (temp <= array.GetAt(childIndex)){
quit /* 这一定是quit 而不是continue */
}
/* 无需真正交换,单向赋值即可 */
d array.SetAt(array.GetAt(childIndex), parentIndex)
s parentIndex = childIndex
s childIndex = 2 * childIndex + 1
}
d array.SetAt(temp, parentIndex)
}
/// 构建堆
Method buildHeap(array As %ArrayOfDataTypes)
{
/* 从最后一个非叶子节点开始,依次下沉调整 */
f i = (array.Count() - 2) \ 2 : -1 : 0 d
.;w "i:"_ i,!
.d ..downAjustArray(array,i,array.Count())
q array
}
}
调用
/// w ##class(PHA.YX.Arithmetic).HeapArray()
ClassMethod HeapArray()
{
s array = ##class(%ArrayOfDataTypes).%New()
d array.SetAt(1,0)
d array.SetAt(3,1)
d array.SetAt(2,2)
d array.SetAt(6,3)
d array.SetAt(5,4)
d array.SetAt(7,5)
d array.SetAt(8,6)
d array.SetAt(9,7)
d array.SetAt(10,8)
d array.SetAt(0,9)
#dim mHeap as PHA.YX.Arithmetic.Heap = ##class(PHA.YX.Arithmetic.Heap).%New()
s array = mHeap.upAdjustArray(array)
zw array
d array.Clear()
zw array
d array.SetAt(7,0)
d array.SetAt(1,1)
d array.SetAt(3,2)
d array.SetAt(10,3)
d array.SetAt(5,4)
d array.SetAt(2,5)
d array.SetAt(8,6)
d array.SetAt(9,7)
d array.SetAt(6,8)
zw array
s array = mHeap.buildHeap(array)
zw array
q ""
}
DHC-APP> w ##class(PHA.YX.Arithmetic).HeapArray()
array=