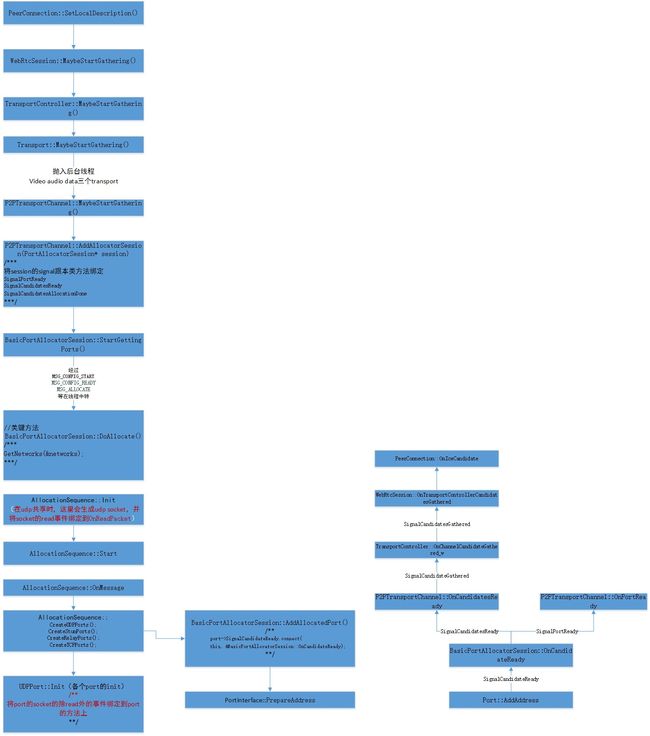
1、candidate的收集整体调用逻辑
先看整体的调用逻辑,再看各个类型candidate的收集过程
看关键的方法AllocationSequence::Init,这里会分配本地的udp端口
bool AllocationSequence::Init() {
if (IsFlagSet(PORTALLOCATOR_ENABLE_SHARED_SOCKET)) {
udp_socket_.reset(session_->socket_factory()->CreateUdpSocket(
rtc::SocketAddress(ip_, 0), session_->allocator()->min_port(),
session_->allocator()->max_port()));
if (udp_socket_) {
udp_socket_->SignalReadPacket.connect(
this, &AllocationSequence::OnReadPacket);
}
// Continuing if |udp_socket_| is NULL, as local TCP and RelayPort using TCP
// are next available options to setup a communication channel.
}
return true;
}
这个方法一直跟下去会发现bind时的方法是
int Win32Socket::Bind(const SocketAddress& addr) {
ASSERT(socket_ != INVALID_SOCKET);
if (socket_ == INVALID_SOCKET)
return SOCKET_ERROR;
sockaddr_storage saddr;
size_t len = addr.ToSockAddrStorage(&saddr);
int err = ::bind(socket_,
reinterpret_cast(&saddr),
static_cast(len));
UpdateLastError();
return err;
}
其中的端口为0,也就是说要绑定的端口由操作系统随机选择
下面来看其中关键的方法2 BasicPortAllocatorSession::DoAllocate
//basicportallocator.cc 341L
void BasicPortAllocatorSession::DoAllocate() {
bool done_signal_needed = false;
std::vector networks;
GetNetworks(&networks);
if (networks.empty()) {
LOG(LS_WARNING) << "Machine has no networks; no ports will be allocated";
done_signal_needed = true;
} else {
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < networks.size(); ++i) {
PortConfiguration* config = NULL;
if (configs_.size() > 0)
config = configs_.back();
uint32_t sequence_flags = flags();
if ((sequence_flags & DISABLE_ALL_PHASES) == DISABLE_ALL_PHASES) {
// If all the ports are disabled we should just fire the allocation
// done event and return.
done_signal_needed = true;
break;
}
if (!config || config->relays.empty()) {
// No relay ports specified in this config.
sequence_flags |= PORTALLOCATOR_DISABLE_RELAY;
}
if (!(sequence_flags & PORTALLOCATOR_ENABLE_IPV6) &&
networks[i]->GetBestIP().family() == AF_INET6) {
// Skip IPv6 networks unless the flag's been set.
continue;
}
// Disable phases that would only create ports equivalent to
// ones that we have already made.
DisableEquivalentPhases(networks[i], config, &sequence_flags);
if ((sequence_flags & DISABLE_ALL_PHASES) == DISABLE_ALL_PHASES) {
// New AllocationSequence would have nothing to do, so don't make it.
continue;
}
AllocationSequence* sequence =
new AllocationSequence(this, networks[i], config, sequence_flags);
if (!sequence->Init()) {
delete sequence;
continue;
}
done_signal_needed = true;
sequence->SignalPortAllocationComplete.connect(
this, &BasicPortAllocatorSession::OnPortAllocationComplete);
if (running_)
sequence->Start(); //开始建立port,然后开始搜集candidate
sequences_.push_back(sequence);
}
}
if (done_signal_needed) {
network_thread_->Post(this, MSG_SEQUENCEOBJECTS_CREATED);
}
}
AllocationSequence::AllocationSequence(BasicPortAllocatorSession* session,
rtc::Network* network,
PortConfiguration* config,
uint32_t flags)
: session_(session),
network_(network),
ip_(network->GetBestIP()),
config_(config),
state_(kInit),
flags_(flags),
udp_socket_(),
udp_port_(NULL),
phase_(0) {
}
bool AllocationSequence::Init() {
if (IsFlagSet(PORTALLOCATOR_ENABLE_SHARED_SOCKET)) {
udp_socket_.reset(session_->socket_factory()->CreateUdpSocket(
rtc::SocketAddress(ip_, 0), session_->allocator()->min_port(),
session_->allocator()->max_port()));
if (udp_socket_) {
udp_socket_->SignalReadPacket.connect(
this, &AllocationSequence::OnReadPacket);
}
// Continuing if |udp_socket_| is NULL, as local TCP and RelayPort using TCP
// are next available options to setup a communication channel.
}
return true;
}
可以看出:
(1)一个网络(比如)会建立一个AllocationSequence
(2)AllocationSequence对应这个网络的best ip
(3)一个AllocationSequence建立一套port(sequence->Start() 开始建立port,然后开始搜集candidate)
(4)经过测试IsFlagSet(PORTALLOCATOR_ENABLE_SHARED_SOCKET)为true,所以udp port是复用的
2、candidate的最终合成方法
首先看一下最终生成candidate的方法
//port.cc 230L
void Port::AddAddress(const rtc::SocketAddress& address,
const rtc::SocketAddress& base_address,
const rtc::SocketAddress& related_address,
const std::string& protocol,
const std::string& relay_protocol,
const std::string& tcptype,
const std::string& type,
uint32_t type_preference,
uint32_t relay_preference,
bool final) {
if (protocol == TCP_PROTOCOL_NAME && type == LOCAL_PORT_TYPE) {
ASSERT(!tcptype.empty());
}
std::string foundation =
ComputeFoundation(type, protocol, relay_protocol, base_address);
Candidate c(component_, protocol, address, 0U, username_fragment(), password_,
type, generation_, foundation, network_->id(), network_cost_);
c.set_priority(
c.GetPriority(type_preference, network_->preference(), relay_preference));
c.set_relay_protocol(relay_protocol);
c.set_tcptype(tcptype);
c.set_network_name(network_->name());
c.set_network_type(network_->type());
c.set_related_address(related_address);
candidates_.push_back(c);
SignalCandidateReady(this, c);
if (final) {
SignalPortComplete(this);
}
}
candidate的结构
candidate:499412426 1 udp 2122260223 192.168.0.136 54135 typ host generation 0 ufrag KQbng0ClMLl6gk2B network-id 3
//candidate:
// typ
// [raddr ] [rport ]
// *(SP extension-att-name SP extension-att-value)
对应AddAddress方法跟candidate的结构,来看candidate中各个元素的计算
foundation的计算
// Foundation: An arbitrary string that is the same for two candidates
// that have the same type, base IP address, protocol (UDP, TCP,
// etc.), and STUN or TURN server. If any of these are different,
// then the foundation will be different. Two candidate pairs with
// the same foundation pairs are likely to have similar network
// characteristics. Foundations are used in the frozen algorithm.
static std::string ComputeFoundation(const std::string& type,
const std::string& protocol,
const std::string& relay_protocol,
const rtc::SocketAddress& base_address) {
std::ostringstream ost;
ost << type << base_address.ipaddr().ToString() << protocol << relay_protocol;
return rtc::ToString(rtc::ComputeCrc32(ost.str()));
}
就是将type,protocol,relay_protocol,base_address等合并在一起,计算一个Crc32校验值
component_
component_(ICE_CANDIDATE_COMPONENT_DEFAULT) //port的构造函数中,port.cc 145L ICE_CANDIDATE_COMPONENT_DEFAULT = 1
//component_ 最初被传入的位置位于BaseChannel::SetTransport_w(channel.cc 249L 跟 258行中)
cricket::ICE_CANDIDATE_COMPONENT_RTP 1
cricket::ICE_CANDIDATE_COMPONENT_RTCP 2
generation_
最初设置于 P2PTransportChannel::AddAllocatorSession(P2PTransportChannel 275L)
session->set_generation(static_cast(allocator_sessions_.size()));
大部分情况下为0
network_cost_
跟当前网络类型有关
network_cost_ = (network_->type() == rtc::ADAPTER_TYPE_CELLULAR) ? kMaxNetworkCost : 0;
//网络类型
enum AdapterType {
// This enum resembles the one in Chromium net::ConnectionType.
ADAPTER_TYPE_UNKNOWN = 0,
ADAPTER_TYPE_ETHERNET = 1 << 0,
ADAPTER_TYPE_WIFI = 1 << 1,
ADAPTER_TYPE_CELLULAR = 1 << 2,
ADAPTER_TYPE_VPN = 1 << 3,
ADAPTER_TYPE_LOOPBACK = 1 << 4
};
priority的计算
//candidate.h 239
uint32_t GetPriority(uint32_t type_preference,
int network_adapter_preference,
int relay_preference) const {
// RFC 5245 - 4.1.2.1.
// priority = (2^24)*(type preference) +
// (2^8)*(local preference) +
// (2^0)*(256 - component ID)
// |local_preference| length is 2 bytes, 0-65535 inclusive.
// In our implemenation we will partion local_preference into
// 0 1
// 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5
// +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
// | NIC Pref | Addr Pref |
// +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+
// NIC Type - Type of the network adapter e.g. 3G/Wifi/Wired.
// Addr Pref - Address preference value as per RFC 3484.
// local preference = (NIC Type << 8 | Addr_Pref) - relay preference.
int addr_pref = IPAddressPrecedence(address_.ipaddr());
int local_preference = ((network_adapter_preference << 8) | addr_pref) +
relay_preference;
return (type_preference << 24) |
(local_preference << 8) |
(256 - component_);
}
先看各个变量的具体含义
type_preference 各个地址类型的偏好
具体赋值是
//port.h 83L,在各个port调用AddAddress时传参
enum IcePriorityValue {
// The reason we are choosing Relay preference 2 is because, we can run
// Relay from client to server on UDP/TCP/TLS. To distinguish the transport
// protocol, we prefer UDP over TCP over TLS.
// For UDP ICE_TYPE_PREFERENCE_RELAY will be 2.
// For TCP ICE_TYPE_PREFERENCE_RELAY will be 1.
// For TLS ICE_TYPE_PREFERENCE_RELAY will be 0.
// Check turnport.cc for setting these values.
ICE_TYPE_PREFERENCE_RELAY = 2,
ICE_TYPE_PREFERENCE_HOST_TCP = 90,
ICE_TYPE_PREFERENCE_SRFLX = 100,
ICE_TYPE_PREFERENCE_PRFLX = 110,
ICE_TYPE_PREFERENCE_HOST = 126
};
NIC Type 网卡类型的偏好,在network.cc 335L设置,代码如下
std::sort(networks_.begin(), networks_.end(), SortNetworks);
// Now network interfaces are sorted, we should set the preference value
// for each of the interfaces we are planning to use.
// Preference order of network interfaces might have changed from previous
// sorting due to addition of higher preference network interface.
// Since we have already sorted the network interfaces based on our
// requirements, we will just assign a preference value starting with 127,
// in decreasing order.
int pref = kHighestNetworkPreference;
for (Network* network : networks_) {
network->set_preference(pref);
addr_pref ip类型的Preference
//ipaddress.cc 482L
int IPAddressPrecedence(const IPAddress& ip) {
// Precedence values from RFC 3484-bis. Prefers native v4 over 6to4/Teredo.
if (ip.family() == AF_INET) {
return 30;
} else if (ip.family() == AF_INET6) {
if (IPIsLoopback(ip)) {
return 60;
} else if (IPIsULA(ip)) {
return 50;
} else if (IPIsV4Mapped(ip)) {
return 30;
} else if (IPIs6To4(ip)) {
return 20;
} else if (IPIsTeredo(ip)) {
return 10;
} else if (IPIsV4Compatibility(ip) || IPIsSiteLocal(ip) || IPIs6Bone(ip)) {
return 1;
} else {
// A 'normal' IPv6 address.
return 40;
}
}
return 0;
}
relay_preference
只在TurnPort::OnAllocateSuccess对AddAddress调用时(turnport.cc 712L)设置了值,其他的调用都为0
从代码:
int addr_pref = IPAddressPrecedence(address_.ipaddr());
int local_preference = ((network_adapter_preference << 8) | addr_pref) +
relay_preference;
return (type_preference << 24) |
(local_preference << 8) |
(256 - component_);
可以看出,优先级值的组成在比较时起的作用是:
1.先比较ice类型,如是host,srflx还是relay之类
2.比较网络类型,如以太网,wifi之类
3.比较ip地址类型,如是本地回环地址之类
搜集host跟srflx的candidate共用的方法
stunport.cc 251L
void UDPPort::PrepareAddress() {
ASSERT(requests_.empty());
if (socket_->GetState() == rtc::AsyncPacketSocket::STATE_BOUND) {
OnLocalAddressReady(socket_, socket_->GetLocalAddress());
}
}
void UDPPort::OnLocalAddressReady(rtc::AsyncPacketSocket* socket,
const rtc::SocketAddress& address) {
// When adapter enumeration is disabled and binding to the any address, the
// default local address will be issued as a candidate instead if
// |emit_local_for_anyaddress| is true. This is to allow connectivity for
// applications which absolutely requires a HOST candidate.
rtc::SocketAddress addr = address;
// If MaybeSetDefaultLocalAddress fails, we keep the "any" IP so that at
// least the port is listening.
MaybeSetDefaultLocalAddress(&addr);
AddAddress(addr, addr, rtc::SocketAddress(), UDP_PROTOCOL_NAME, "", "",
LOCAL_PORT_TYPE, ICE_TYPE_PREFERENCE_HOST, 0, false);
MaybePrepareStunCandidate();
}
void UDPPort::MaybePrepareStunCandidate() {
// Sending binding request to the STUN server if address is available to
// prepare STUN candidate.
if (!server_addresses_.empty()) {
SendStunBindingRequests();
} else {
// Port is done allocating candidates.
MaybeSetPortCompleteOrError();
}
}
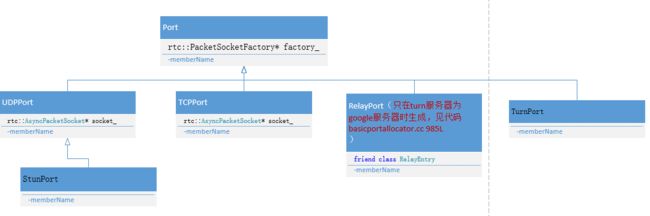
各个port的类关系如下图
3、host
AllocationSequence::createUDPPorts
也就是udpport,搜集本地地址,此时MaybePrepareStunCandidate被调用时,udpport的server_addresses_为空,不会发送bindingrequest
4、srflx
AllocationSequence::CreateStunPorts
stunport继承了udpport,搜集反射地址时,MaybePrepareStunCandidate被调用时,server_addresses_为stun服务器的地址,发送bindingrequest
5、relay
void AllocationSequence::CreateRelayPorts() {
if (IsFlagSet(PORTALLOCATOR_DISABLE_RELAY)) {
LOG(LS_VERBOSE) << "AllocationSequence: Relay ports disabled, skipping.";
return;
}
// If BasicPortAllocatorSession::OnAllocate left relay ports enabled then we
// ought to have a relay list for them here.
ASSERT(config_ && !config_->relays.empty());
if (!(config_ && !config_->relays.empty())) {
LOG(LS_WARNING)
<< "AllocationSequence: No relay server configured, skipping.";
return;
}
PortConfiguration::RelayList::const_iterator relay;
for (relay = config_->relays.begin();
relay != config_->relays.end(); ++relay) {
if (relay->type == RELAY_GTURN) {
CreateGturnPort(*relay);
} else if (relay->type == RELAY_TURN) {
CreateTurnPort(*relay);
} else {
ASSERT(false);
}
}
}
在该方法中如果turn服务器配置的是google的传统中继服务器将调用
CreateGturnPort(*relay);
生成relayport,此relayport的分析从略如果不是则调用CreateTurnPort(*relay);
生成turnport
turnport的PrepareAddress方法代码如下:
void TurnPort::PrepareAddress() {
if (credentials_.username.empty() ||
credentials_.password.empty()) {
LOG(LS_ERROR) << "Allocation can't be started without setting the"
<< " TURN server credentials for the user.";
OnAllocateError();
return;
}
if (!server_address_.address.port()) {
// We will set default TURN port, if no port is set in the address.
server_address_.address.SetPort(TURN_DEFAULT_PORT);
}
if (server_address_.address.IsUnresolvedIP()) {
ResolveTurnAddress(server_address_.address);
} else {
// If protocol family of server address doesn't match with local, return.
if (!IsCompatibleAddress(server_address_.address)) {
LOG(LS_ERROR) << "IP address family does not match: "
<< "server: " << server_address_.address.family()
<< "local: " << ip().family();
OnAllocateError();
return;
}
// Insert the current address to prevent redirection pingpong.
attempted_server_addresses_.insert(server_address_.address);
LOG_J(LS_INFO, this) << "Trying to connect to TURN server via "
<< ProtoToString(server_address_.proto) << " @ "
<< server_address_.address.ToSensitiveString();
if (!CreateTurnClientSocket()) {
LOG(LS_ERROR) << "Failed to create TURN client socket";
OnAllocateError();
return;
}
if (server_address_.proto == PROTO_UDP) {
// If its UDP, send AllocateRequest now.
// For TCP and TLS AllcateRequest will be sent by OnSocketConnect.
SendRequest(new TurnAllocateRequest(this), 0);
}
}
}
发送TurnAllocateRequest请求,也就是allocate请求
6、host tcptype
tcpport的建立
static TCPPort* Create(rtc::Thread* thread,
rtc::PacketSocketFactory* factory,
rtc::Network* network,
const rtc::IPAddress& ip,
uint16_t min_port,
uint16_t max_port,
const std::string& username,
const std::string& password,
bool allow_listen) {
TCPPort* port = new TCPPort(thread, factory, network, ip, min_port,
max_port, username, password, allow_listen);
if (!port->Init()) {
delete port;
port = NULL;
}
return port;
}
bool TCPPort::Init() {
if (allow_listen_) {
// Treat failure to create or bind a TCP socket as fatal. This
// should never happen.
socket_ = socket_factory()->CreateServerTcpSocket(
rtc::SocketAddress(ip(), 0), min_port(), max_port(),
false /* ssl */);
if (!socket_) {
LOG_J(LS_ERROR, this) << "TCP socket creation failed.";
return false;
}
socket_->SignalNewConnection.connect(this, &TCPPort::OnNewConnection);
socket_->SignalAddressReady.connect(this, &TCPPort::OnAddressReady);
}
return true;
}
在该段代码中,min_port max_port都为0,所以tcp的端口也是相同随机选择的