赫夫曼树实现数据压缩和解压
目录
一、为什么要进行数据压缩
二、根据字符串构建赫夫曼树
2.1 思路分析
2.2 代码实现
三、根据赫夫曼树生成赫夫曼编码
3.1 思路分析
3.2 代码实现
四、将赫夫曼编码压缩
4.1 思路分析
4.2 代码实现
4.3 赫夫曼数据压缩的完整代码
五、实现数据解压
5.1 思路分析
5.2 代码实现
六、文件的压缩
6.1 思路分析
6.2 代码实现
七、文件的解压
7.1 思路分析
7.2 代码实现
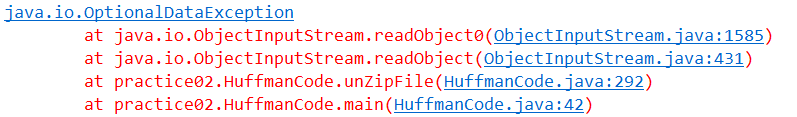
八、问题
一、为什么要进行数据压缩
- 现在有一个字符串:"i like like like java do you like a java"。
- 若按照定长编码,即每个字符都用其ASCII码来表示,则效率极低。
- 若按照变长编码,也就是统计各个字符的个数,根据个数高低按照0,1,10,11,100,101,110,111等进行编码,缺点是编码后具有二义性,比如101可能是1与10、10与1、101。
- 采用前缀编码,即字符的编码不能是其它字符编码的前缀,通过将赫夫曼树中父结点与左孩子之间的路径设为0,父结点与右孩子结点之间的路径设为1,这样得到的每个字符编码都是独立互不影响的,很神奇。
二、根据字符串构建赫夫曼树
2.1 思路分析
- 构造结点类
- 存储字符串中各字符及出现的次数
- 将各字符及其次数转换为结点中的data和weight
- 将结点加入到集合中并返回
- 根据集合构建赫夫曼树
2.2 代码实现
package practice02;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 根据字符串,构建赫夫曼树
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class HuffmanCode {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "i like like like java do you like a java";
byte[] bytes = str.getBytes();
List nodes = getList(bytes);
Node root = createHuffmanTree(nodes);
root.preOrder();
}
/**
* 该方法实现字符串到结点再到集合的转换
* @param bytes
* @return
*/
private static List getList(byte[] bytes) {
List nodes = new ArrayList();
Map map = new HashMap();
for(byte b : bytes) {
Integer count = map.get(b);
if(count == null) {
map.put(b,1);
} else {
map.put(b,count+1);
}
}
//Map.Entry表示的一对键值对对象
//entrySet()返回Set集合,集合的类型为Map.Entry类型
for(Map.Entry entry : map.entrySet()) {
nodes.add(new Node(entry.getKey(),entry.getValue()));
}
return nodes;
}
/**
* 该方法根据集合中的结点值构建赫夫曼树
* @param nodes
* @return
*/
private static Node createHuffmanTree(List nodes) {
while(nodes.size() > 1) {
Collections.sort(nodes);
Node leftnode = nodes.get(0);
Node rightnode = nodes.get(1);
Node parent = new Node(null,leftnode.weight + rightnode.weight);
parent.left = leftnode;
parent.right = rightnode;
nodes.remove(leftnode);
nodes.remove(rightnode);
nodes.add(parent);
}
return nodes.get(0);
}
}
class Node implements Comparable{
Byte data;
int weight;
Node left;
Node right;
public Node(Byte data, int weight) {
super();
this.data = data;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node [data=" + data + ", weight=" + weight + "]";
}
public void preOrder() {
System.out.println(this);
if(this.left != null) {
this.left.preOrder();
}
if(this.right != null) {
this.right.preOrder();
}
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) {
return this.weight - o.weight;
}
} 三、根据赫夫曼树生成赫夫曼编码
3.1 思路分析
纠正上面B中步骤a,应该为空类型,因为整个过程是递归进行的,有返回值就意味着会返回很多Map集合对象。
3.2 代码实现
/**
* 该方法用来产生赫夫曼编码
* @param node 赫夫曼树的根结点
* @param code 编码,0或1
* @param path 拼接并保存编码
*/
//创建Map集合
private static Map map = new HashMap();
private static void generateCodes(Node node,String code,StringBuilder path) {
//保存上次递归后的赫夫曼编码
StringBuilder path2 = new StringBuilder(path);
//追加编码
path2.append(code);
//判断当前结点
if(node != null) {
if(node.data == null) {
generateCodes(node.left,"0",path2);
generateCodes(node.right,"1",path2);
} else {
map.put(node.data, path2.toString());
}
}
} 四、将赫夫曼编码压缩
4.1 思路分析
- 找到原始的字符串,也就是"i like like like java do you like a java"这个,按照这个顺序,将Map集合中各个字符对应的赫夫曼编码拼接成一个字符串
- 定义一个字节数组,将拼接后的字符串,每8位为一组,存放到字节数组中,那么如何存放呢?
a: 首先确定这个字节数组应该有几组,也就是它的长度,这里有个公式,我没有推出来
int len = (stringBuilder.length() + 7) / 8;b:利用循环,每次截取字符串8位,将截取的字符串转换为二进制,再转换为字节类型,最后存储到字节数组中
4.2 代码实现
/**
* 该方法实现赫夫曼编码的压缩
* @param bytes 原始字符串对应的字节数组
* @param map 存放赫夫曼编码的集合
* @return 将字符串的赫夫曼编码压缩为byte[]数组并返回
*/
private static byte[] huffmanCodesByte(byte[] bytes,Map map) {
//用于拼接的临时变量
StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder();
//保存截取的字串
String temp = new String();
//开始拼接
for(byte b : bytes) {
str.append(map.get(b));
}
//求数组长度
int len = (str.length() + 7) / 8;
//临时数组
byte[] by = new byte[len];
int index = 0;
//字符串向字节数组转换
for(int i = 0; i < str.length(); i += 8) {
if(i + 8 > str.length()) {
temp = str.substring(i);
} else {
temp = str.substring(i,i+8);
}
by[index] = (byte)Integer.parseInt(temp,2);
index++;
}
return by;
} 4.3 赫夫曼数据压缩的完整代码
package practice02;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 根据字符串,构建赫夫曼树
* @author Administrator
*/
public class HuffmanCode {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "i like like like java do you like a java";
byte[] bytes = str.getBytes();
byte[] by = huffmanZip(bytes);
System.out.println("压缩后的赫夫曼编码:" + Arrays.toString(by));
}
/**
* 该方法用来封装一些操作
* @param bytes 原始字符串对应的字节数组
* @return 压缩后的字节数组
*/
private static byte[] huffmanZip(byte[] bytes) {
StringBuilder path = new StringBuilder();
List nodes = getList(bytes);
Node root = createHuffmanTree(nodes);
generateCodes(root, "", path);
return huffmanCodesByte(bytes, map);
}
/**
* 该方法实现字符串到结点再到集合的转换
* @param bytes
* @return
*/
private static List getList(byte[] bytes) {
List nodes = new ArrayList();
Map map = new HashMap();
for (byte b : bytes) {
Integer count = map.get(b);
if (count == null) {
map.put(b, 1);
} else {
map.put(b, count + 1);
}
}
// Map.Entry表示的一对键值对对象
// entrySet()返回Set集合,集合的类型为Map.Entry类型
for (Map.Entry entry : map.entrySet()) {
nodes.add(new Node(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()));
}
return nodes;
}
/**
* 该方法根据集合中的结点值构建赫夫曼树
* @param nodes
* @return
*/
private static Node createHuffmanTree(List nodes) {
while (nodes.size() > 1) {
Collections.sort(nodes);
Node leftnode = nodes.get(0);
Node rightnode = nodes.get(1);
Node parent = new Node(null, leftnode.weight + rightnode.weight);
parent.left = leftnode;
parent.right = rightnode;
nodes.remove(leftnode);
nodes.remove(rightnode);
nodes.add(parent);
}
return nodes.get(0);
}
/**
* 该方法用来产生赫夫曼编码
* @param node 赫夫曼树的根结点
* @param code 编码,0或1
* @param path 拼接并保存编码
*/
// 创建Map集合
private static Map map = new HashMap();
private static void generateCodes(Node node, String code, StringBuilder path) {
// 保存上次递归后的赫夫曼编码
StringBuilder path2 = new StringBuilder(path);
// 追加编码
path2.append(code);
// 判断当前结点
if (node != null) {
if (node.data == null) {
generateCodes(node.left, "0", path2);
generateCodes(node.right, "1", path2);
} else {
map.put(node.data, path2.toString());
}
}
}
/**
* 该方法实现赫夫曼编码的压缩
*
* @param bytes 原始字符串对应的字节数组
* @param map 存放赫夫曼编码的集合
* @return 将字符串的赫夫曼编码压缩为byte[]数组并返回
*/
private static byte[] huffmanCodesByte(byte[] bytes, Map map) {
// 用于拼接的临时变量
StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder();
// 保存截取的字串
String temp = new String();
// 开始拼接
for (byte b : bytes) {
str.append(map.get(b));
}
// 求数组长度
int len = (str.length() + 7) / 8;
// 临时数组
byte[] by = new byte[len];
int index = 0;
// 字符串向字节数组转换
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i += 8) {
if (i + 8 > str.length()) {
temp = str.substring(i);
} else {
temp = str.substring(i, i + 8);
}
by[index] = (byte) Integer.parseInt(temp, 2);
index++;
}
return by;
}
}
class Node implements Comparable {
Byte data;
int weight;
Node left;
Node right;
public Node(Byte data, int weight) {
super();
this.data = data;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node [data=" + data + ", weight=" + weight + "]";
}
public void preOrder() {
System.out.println(this);
if (this.left != null) {
this.left.preOrder();
}
if (this.right != null) {
this.right.preOrder();
}
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) {
return this.weight - o.weight;
}
}
五、实现数据解压
5.1 思路分析
5.2 代码实现
/**
* 该方法用来将byte值转换为二进制串
* @param flag 标志位,判断是否是压缩数组的最后一行
* @param b byte值
* @return
*/
private static String byteToString(boolean flag,byte b) {
int temp = b;
if(flag) {
temp |= 256;
}
String str = Integer.toBinaryString(temp);
//temp<0是为了截取byte[]最后1行为负数的情况
if(flag || temp < 0) {
return str.substring(str.length() - 8);
} else {
//最后一行为正数时,直接返回
return str;
}
}
/**
* 该方法用来解码
* @param bytes 压缩编码后的字节数组
* @param map 存储字符及其编码的集合
* @return 原始字符串对应的字节数组
*/
private static byte[] decode(byte[] bytes, Map map) {
// 拼接二进制串
StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length;i++) {
boolean flag = (i == bytes.length - 1);
str.append(byteToString(!flag, bytes[i]));
}
// 调换map集合键值对
Map map2 = new HashMap();
for (Map.Entry entry : map.entrySet()) {
map2.put(entry.getValue(), entry.getKey());
}
// 创建集合,存放byte
List list = new ArrayList();
// 串的暴力匹配
for (int i = 0; i < str.length();) {
int count = 1;
boolean flag = true;
Byte b = null;
String key = null;
while (flag) {
// i不动,count走
if (i + count > str.length()) {
key = str.substring(i);
} else {
key = str.substring(i, i + count);
}
b = map2.get(key);
if (b == null) {
// 未匹配到
count++;
} else {
flag = false;
}
}
list.add(b);
// 匹配后,i到下一个位置
i += count;
}
byte[] b = new byte[list.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) {
b[i] = list.get(i);
}
return b;
} 六、文件的压缩
6.1 思路分析
- 创建文件输入流对象读取源文件至字节数组
- 将得到的字节数组进行压缩,得到压缩后的字节数组
- 创建初始化目标地址输出流对象,并包装为对象流对象
- 利用对象流对象将压缩后的字节数组写入文件
- 为方便解压,对象流对象还要写入保存的赫夫曼编码,也就是map集合
- 关闭流对象
6.2 代码实现
/**
* 该方法实现压缩文件
* @param srcFile 源文件路径
* @param dstFile 压缩后的文件路径
*/
public static void zipFile(String srcFile, String dstFile) {
// 创建文件输入流对象
FileInputStream is = null;
// 创建文件输出流对象,存放压缩文件
OutputStream os = null;
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
try {
is = new FileInputStream(srcFile);
// 读取文件内容
byte[] b = new byte[is.available()];
is.read(b);
// 对源文件压缩
byte[] huffmanBytes = huffmanZip(b);
os = new FileOutputStream(dstFile);
// 创建与文件相关联的ObjectOutputStream
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(os);
// 将赫夫曼编码写入对象流,方便解压
oos.write(huffmanBytes);
oos.writeObject(map);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
} finally {
try {
is.close();
oos.close();
os.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
}七、文件的解压
7.1 思路分析
- 创建文件输入流对象,包装为对象输入流
- 对象输入流读取压缩文件内容至字节数组
- 进行解码,返回压缩之前的字节数组
- 将得到的字节数组写入到目标文件中
- 关闭流对象
7.2 代码实现
/**
* 该方法用来解压文件
* @param zipFile 待解压的文件
* @param dstFile 解压后的文件保存路径
*/
public static void unZipFile(String zipFile, String dstFile) {
// 创建文件输入流对象
InputStream is = null;
// 定义一个对象输入流
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
// 定义文件的输出流
OutputStream os = null;
try {
// 创建文件输入流
is = new FileInputStream(zipFile);
// 创建与is关联的对象输入流
ois = new ObjectInputStream(is);
// 读取压缩后的byte数组
byte[] huffmanBytes = (byte[]) ois.readObject();
// 读取赫夫曼编码表
Map huffmanCodes = (Map) ois.readObject();
// 解码
byte[] bytes = decode(huffmanBytes, huffmanCodes);
// 将bytes内容写入到目标文件
os = new FileOutputStream(dstFile);
os.write(bytes);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (os != null) {
os.close();
ois.close();
is.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}