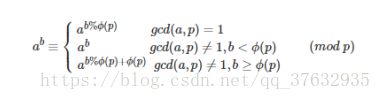2019ICPC南京站B题super_log
题目链接:https://nanti.jisuanke.com/t/41299
In Complexity theory, some functions are nearly O(1)O(1)O(1), but it is greater then O(1)O(1)O(1). For example, the complexity of a typical disjoint set is O(nα(n))O(nα(n))O(nα(n)). Here α(n)α(n)α(n) is Inverse Ackermann Function, which growth speed is very slow. So in practical application, we often assume α(n)≤4α(n) \le 4α(n)≤4.
However O(α(n))O(α(n))O(α(n)) is greater than O(1)O(1)O(1), that means if nnn is large enough, α(n)α(n)α(n) can greater than any constant value.
Now your task is let another slowly function log∗log*log∗ xxx reach a constant value bbb. Here log∗log*log∗ is iterated logarithm function, it means “the number of times the logarithm function iteratively applied on xxx before the result is less than logarithm base aaa”.
Formally, consider a iterated logarithm function loga∗log_{a}^* loga∗
Find the minimum positive integer argument xxx, let loga∗(x)≥blog_{a}^* (x) \ge bloga∗(x)≥b. The answer may be very large, so just print the result xxx after mod mmm.
Input
The first line of the input is a single integer T(T≤300)T(T\le 300)T(T≤300) indicating the number of test cases.
Each of the following lines contains 333 integers aaa , bbb and mmm.
1≤a≤10000001 \le a \le 10000001≤a≤1000000
0≤b≤10000000 \le b \le 10000000≤b≤1000000
1≤m≤10000001 \le m \le 10000001≤m≤1000000
Note that if a==1, we consider the minimum number x is 1.
Output
For each test case, output xxx mod mmm in a single line.
Hint
In the 4−th4-th4−th query, a=3a=3a=3 and b=2b=2b=2. Then log3∗(27)=1+log3∗(3)=2+log3∗(1)=3+(−1)=2≥blog_{3}^* (27) = 1+ log_{3}^* (3) = 2 + log_{3}^* (1)=3+(-1)=2 \ge blog3∗(27)=1+log3∗(3)=2+log3∗(1)=3+(−1)=2≥b, so the output is 272727 mod 16=1116 = 1116=11.
样例输入复制
5 2 0 3 3 1 2 3 1 100 3 2 16 5 3 233
样例输出复制
1 1 3 11 223
题目理解:
其实就是求a^(a^(a^(a^(a^...)))) ,其中有b个a,求其对mod取余后的结果,cf有一道题和这个类似,很经典的欧拉降幂的做法,可惜当时没做过这个专题,奈何学长强大QAQ!!!,tql,现在补的时候发现好像也不是特别难,而且数据好像就只有三组(???)。
需要知道下面的公式
具体做法参考代码实现(搬一下bzoj3884的题解,很类似,求2^(2^(2^(2^(2^...)))) mod p的结果)。
#include
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
map euler;
ll a,b,mod;
int phi(int n)
{
int now=n;
int ret=n;
if(euler.count(now)) return euler[now];
for(int i=2;i<=sqrt(n);i++)
{
if(n%i==0)
{
ret=ret/i*(i-1);
while(n%i==0)
n/=i;
}
}
if(n>1)
ret=ret/n*(n-1);
euler[now]=ret;
return ret;
}
ll MOD(ll n,int mod)
{
return n>=1);
return ret;
}
ll solve(int l,int r,int mod)
{
if(l==r||mod==1) return MOD(a,mod);
return quick_mod(a,solve(l+1,r,phi(mod)),mod);
}
int main()
{
int T;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--){
scanf("%lld%lld%lld",&a,&b,&mod);
if(a==1||b==0){
printf("%d\n",1%mod);
continue;
}
if(b==1){
printf("%d\n",a%mod);
continue;
}
ll ans=solve(1,b,mod)%mod;
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
}