bindService 分析---之二
1.2 requestServiceBindingLocked
直接看ActiveServices的requestServiceBindingLocked方法,
private final boolean requestServiceBindingLocked(ServiceRecord r, IntentBindRecord i,
boolean execInFg, boolean rebind) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
•••
if ((!i.requested || rebind) && i.apps.size() > 0) {
try {
bumpServiceExecutingLocked(r, execInFg, "bind");
r.app.forceProcessStateUpTo(ActivityManager.PROCESS_STATE_SERVICE);
r.app.thread.scheduleBindService(r, i.intent.getIntent(), rebind,
r.app.repProcState);
•••
} catch (TransactionTooLargeException e) {
final boolean inDestroying = mDestroyingServices.contains(r);
serviceDoneExecutingLocked(r, inDestroying, inDestroying);
throw e;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
final boolean inDestroying = mDestroyingServices.contains(r);
serviceDoneExecutingLocked(r, inDestroying, inDestroying);
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
和上面启动服务时调用流程一样,首先从AMS进程跨进程到要绑定的服务所在进程,然后发送消息到主线程,调用对应的函数,
在这里调用handleBindService方法
private void handleBindService(BindServiceData data) {
Service s = mServices.get(data.token);
if (s != null) {
try {
data.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(s.getClassLoader());
data.intent.prepareToEnterProcess();
try {
if (!data.rebind) {
IBinder binder = s.onBind(data.intent);
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().publishService(
data.token, data.intent, binder);
} else {
s.onRebind(data.intent);
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);
}
ensureJitEnabled();
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
}
} catch (Exception e) {
•••
}
}
}
该函数首先调用服务的onBind方法得到Binder,下一步自然是通过AMS将该对象返回给发起绑定的进程。直接看AMS的publishService方法,
public void publishService(IBinder token, Intent intent, IBinder service) {
•••
synchronized(this) {
if (!(token instanceof ServiceRecord)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid service token");
}
mServices.publishServiceLocked((ServiceRecord)token, intent, service);
}
}
publishServiceLocked方法如下,
void publishServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, Intent intent, IBinder service) {
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
if (r != null) {
Intent.FilterComparison filter
= new Intent.FilterComparison(intent);
IntentBindRecord b = r.bindings.get(filter);
if (b != null && !b.received) {
b.binder = service;
b.requested = true;
b.received = true;
for (int conni=r.connections.size()-1; conni>=0; conni--) {
ArrayList clist = r.connections.valueAt(conni);
for (int i=0; i 直接调用c.conn.connected 方法,就像上一小节所论述的那样,又一次跨进程调用到发起绑定的进程中。
1.3 bringUpServiceLocked
bringUpServiceLocked方法启动服务的过程已经分析过了,这里需要说明的是在realStartServiceLocked方法启动线程过后,
会调用requestServiceBindingsLocked,最后仍然会调用requestServiceBindingLocked方法来绑定服务。
1.4小结
在onServiceConnected方法中, service参数,就是绑定的那个service的binder代理。现在已经打通了bindService()动作涉及
的三方关系:发起方、AMS、目标Service。具体的示意图如下:
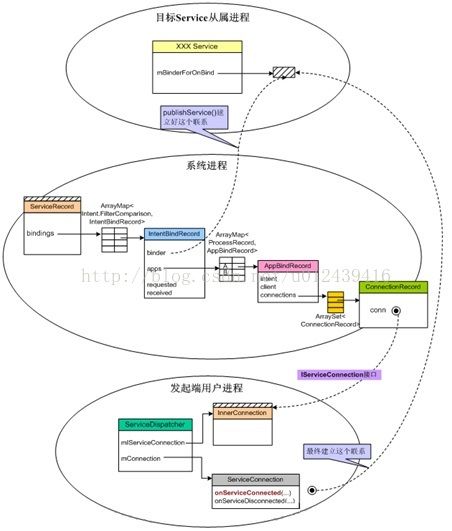
其实, bindService总体流程和startService类似,只是多了一个绑定过程。也就是多了一个被绑定服务到AMS,然后到客户端的回调过程。
并且,跨进程的交互过程和startService过程完全相同。