CUDA:并行计算实现求一个矩阵中的最大值的几种方法
(一)目的
熟悉基本的CUDA程序架构以及如何调用相应的API进行CUDA编程
(二)内容
掌握如何运用共享内存与并行归约方法计算1个矩阵中的最大值
要求:
- 实现1个矩阵(256*1024)最大值计算,初始值随机产生,值的范围限定在[1-2018]。
- 实现4个版本,分别计算运行时间
版本1:CPU实现
版本2:GPU用全局内存及并行归约(有分支发散)
版本3:GPU用全局内存及并行归约(无分支发散)
版本4:GPU用共享内存及并行归约(无分支发散)
提示:可用一个block处理一行数据
实验步骤一 软件设计分析:
- 数据类型:
根据实验要求,本实验的数据类型为一个256*1024的整型矩阵,其中元素的值为256*1024个1-2018的随机数。
二.存储方式:
矩阵在内存中的存储按照行列优先可以分为两种方式,一种是行优先的存储方式,一种是按照列优先的方式。
这两种存储方式在访问对应的位置的数据的时候有很大的差别。在cuda内部,矩阵默认是按照列优先的方式存储,如果要使用cuda device函数,就必须考虑存储方式的问题,有的时候可能需要我们队存储方式进行装换。但是无论是用那种存储方式,最终在内存中都是顺序存储的。
三.GPU程序的block和threads的相关设置:
本实验提供的英伟达实验平台每一个Grid可以按照一维或者二维的方式组织,每一个Block可以按照一维,二维或者三维的方式进行组织。每一个block最多只能有1536个线程。内核函数使用的线程总量也受到设备本身的限制。
对于本次实验,针对上文中提到的几个任务,block和threads的组织方式都可以描述为:
dim3 DimGrid = 256;
dim3 DimBlock = 1024;
即每一个grid包含256个block,而每一个block包含1024个线程。
实验步骤二 实验设备:
本地设备:PC机+Windows10操作系统
Putty远程连接工具
PsFTP远程文件传输工具
远程设备:NVIDIA-SMI 352.79
Driver Version:352.79
实验步骤三 CPU计算代码:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define Height 256
#define Width 1024
int main()
{
float time1;
cudaEvent_t start1, stop1;
cudaEventCreate(&start1);
cudaEventCreate(&stop1);
int max = 0;
int (*Mat)[Width] = new int[Height][Width];
for(int i = 0;i < Height;i++)
for(int j = 0;j < Width;j++)
Mat[i][j] = (rand() % 2018) + 1;
for(int i = 0;i < Height;i++)
{
for(int j = 0;j < Width;j++)
{
printf("%5d ",Mat[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
cudaEventRecord(start1, 0);
for(int i = 0;i < Height;i++)
for(int j = 0;j < Width;j++)
if(max < Mat[i][j])
max = Mat[i][j];
cudaEventRecord(stop1, 0);
cudaEventSynchronize(stop1);
printf("\n maxNum:%5d ",max);
cudaEventElapsedTime(&time1, start1, stop1);
printf("\n The time of calculating is : %f ms\n",teme1);
return 0;
}
实验步骤四 GPU计算代码:
1,针对第二个任务,使用全局内存及并行归约在有分支发散的情况下,GPU代码如下:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define Height 256
#define Width 1024
__global__ void findMaxOfMatrix(int a[Height][Width])
{
unsigned int t = threadIdx.x + blockIdx.x * blockDim.x;
for (unsigned int stride = 1; stride < Height * Width; stride *= 2)
{
__syncthreads();
if (t % (2 * stride) == 0)
if (a[t / Width][t % Width] < a[t / Width + (stride / Width)][(t % Width) + (stride % Width)])
{
int temp = a[t / Width][(t % Width)];
a[t / Width][(t % Width)] = a[t / Width + (stride / Width)][(t % Width) + (stride % Width)];
a[t / Width + (stride / Width)][(t % Width) + (stride % Width)] = temp;
}
}
}
int main()
{
float time1;
cudaEvent_t start1, stop1;
cudaEventCreate(&start1);
cudaEventCreate(&stop1);
int(*Mat_h)[Width] = new int[Height][Width];
for (int i = 0; i < Height; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < Width; j++)
Mat_h[i][j] = (rand() % 2018) + 1;
int(*Mat_d)[Width];
cudaMalloc((void **)&Mat_d, sizeof(int)* Height*Width);
cudaEventRecord(start1, 0);
cudaMemcpy(Mat_d, Mat_h, sizeof(int)* Height*Width, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
dim3 DimGrid = 256;
dim3 DimBlock = 1024;
findMaxOfMatrix <<
cudaMemcpy(Mat_h, Mat_d, sizeof(int)* Height*Width, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
cudaEventRecord(stop1, 0);
cudaEventSynchronize(stop1);
printf("\n maxNum:%5d ", Mat_h[0][0]);
cudaEventElapsedTime(&time1, start1, stop1);
printf("\n The time of calculating is : %f ms\n",time1);
free(Mat_h);
cudaFree(Mat_d);
return 0;
}
2,针对第三个任务,使用全局内存及并行归约在没有分支发散的情况下,GPU代码如下:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define Height 256
#define Width 1024
__global__ void findMaxOfMatrix(int a[Height][Width])
{
unsigned int t = threadIdx.x + blockIdx.x * blockDim.x;
for (unsigned int stride = Height * Width / 2; stride > 0; stride >>= 1)
{
__syncthreads();
if (t < stride)
if (a[t / Width][t % Width] < a[t / Width + (stride / Width)][(t % Width) + (stride % Width)])
{
int temp = a[t / Width][(t % Width)];
a[t / Width][(t % Width)] = a[t / Width + (stride / Width)][(t % Width) + (stride % Width)];
a[t / Width + (stride / Width)][(t % Width) + (stride % Width)] = temp;
}
}
}
int main()
{
float time1;
cudaEvent_t start1, stop1;
cudaEventCreate(&start1);
cudaEventCreate(&stop1);
int(*Mat_h)[Width] = new int[Height][Width];
for (int i = 0; i < Height; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < Width; j++)
Mat_h[i][j] = (rand() % 2018) + 1;
for (int i = 0; i < Height; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < Width; j++)
{
printf("%5d", Mat_h[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
int(*Mat_d)[Width];
cudaMalloc((void **)&Mat_d, sizeof(int)* Height*Width);
cudaEventRecord(start1, 0);
cudaMemcpy(Mat_d, Mat_h, sizeof(int)* Height*Width, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
dim3 DimGrid = 256;
dim3 DimBlock = 1024;
findMaxOfMatrix <<
cudaMemcpy(Mat_h, Mat_d, sizeof(int)* Height*Width, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
cudaEventRecord(stop1, 0);
cudaEventSynchronize(stop1);
printf("\n maxNum:%5d ", Mat_h[0][0]);
cudaEventElapsedTime(&time1, start1, stop1);
printf("\n The time of calculating is : %f ms\n",time1);
free(Mat_h);
cudaFree(Mat_d);
return 0;
}
3,针对第四个任务,使用共享内存及并行归约在没有分支发散的情况下,GPU代码如下:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define Height 256
#define Width 1024
const int N = Height * Width;
const int threadsPerBlock=1024;
const int blocksPerGrid = (N + threadsPerBlock -1) / threadsPerBlock;
__global__ void findMaxOfMatrix(int d_a[Height][Width], int d_partialMax[Width])
{
//申请共享内存,存在于每个block中
__shared__ int partialMax[threadsPerBlock];
//确定索引
int i = threadIdx.x + blockIdx.x * blockDim.x;
int tid = threadIdx.x;
//传global memory数据到shared memory
partialMax[tid]=d_a[i / Width][i % Width];
//传输同步
__syncthreads();
//在共享存储器中进行规约
for(int stride = blockDim.x / 2; stride > 0; stride >>= 1)
{
__syncthreads();
if(tid < stride)
if(partialMax[tid] < partialMax[tid+stride])
{
int temp = partialMax[tid];
partialMax[tid] = partialMax[tid+stride];
partialMax[tid+stride] = temp;
}
}
//将当前block的计算结果写回输出数组
if(tid==0)
d_partialMax[blockIdx.x] = partialMax[0];
}
int main()
{
float time1;
cudaEvent_t start1, stop1;
cudaEventCreate(&start1);
cudaEventCreate(&stop1);
//申请host端内存及初始化
int (*Mat_h)[Width] = new int[Height][Width];
int *partialMax_h = new int[blocksPerGrid];
for (int i=0; i < Height; ++i)
for(int j = 0;j < Width;j++)
Mat_h[i][j] = (rand() % 2018) + 1;
//分配Device空间
int (*Mat_d)[Width];
int *partialMax_d;
cudaMalloc((void**)&Mat_d, N*sizeof(int));
cudaMalloc((void**)&partialMax_d, blocksPerGrid*sizeof(int));
cudaEventRecord(start1, 0);
//把数据从Host传到Device
cudaMemcpy(Mat_d, Mat_h, N*sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
//调用内核函数
findMaxOfMatrix<<
//将结果传回到主机端
cudaMemcpy(partialMax_h, partialMax_d, sizeof(int)*blocksPerGrid, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
//将部分和求和
int max=0;
for (int i=0; i < blocksPerGrid; i++)
if(max < partialMax_h[i])
max = partialMax_h[i];
cudaEventRecord(stop1, 0);
cudaEventSynchronize(stop1);
printf("\n maxNum:%5d ", Mat_h[0][0]);
cudaEventElapsedTime(&time1, start1, stop1);
printf("\n The time of calculating is : %f ms\n",time1);
//释放显空间
cudaFree(Mat_d);
cudaFree(partialMax_d);
free(Mat_h);
free(partialMax_h);
return 0;
}
实验步骤五 观察输出结果:
- 版本1:CPU实现输出结果
2,版本2:GPU用全局内存及并行归约(有分支发散)输出结果
3,版本3:GPU用全局内存及并行归约(无分支发散)输出结果
4,版本4:GPU用共享内存及并行归约(无分支发散)输出结果
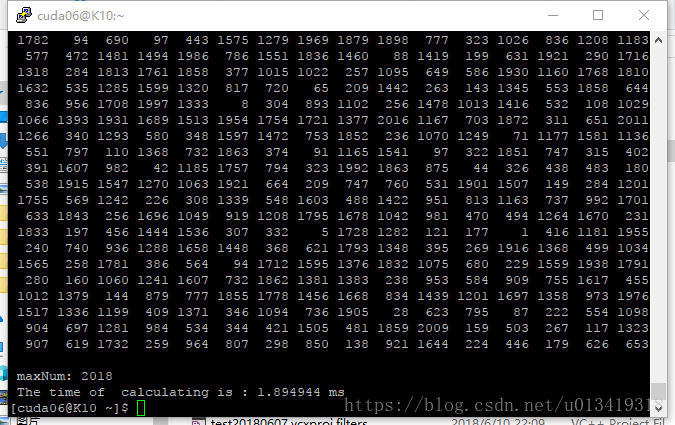
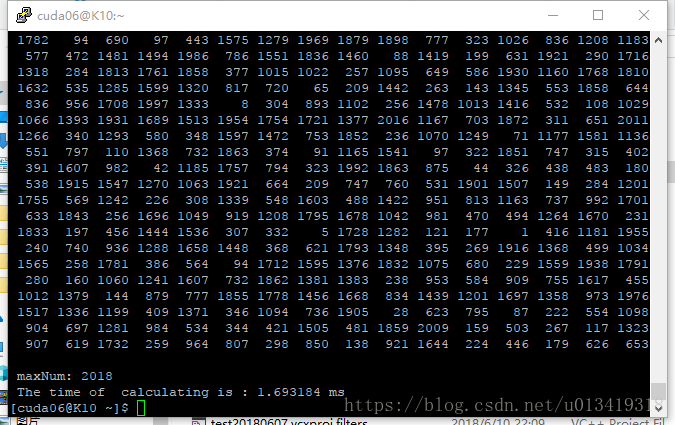
实验结论:
cpu程序计算所需时间:
版本1,CPU实现程序计算所需时间:1.647424ms
gpu程序计算所需时间:
版本2,GPU用全局内存及并行归约(有分支发散),程序计算所需时间:1.894944ms
版本3,GPU用全局内存及并行归约(无分支发散),程序计算所需时间:1.693184ms
版本4,GPU用共享内存及并行归约(无分支发散),程序计算所需时间:0.744992ms
总结:
由实验结论可以看出,同样规模数据量的计算,与CPU端的运算效率相比较,GPU端的运算并没有提高。这里的原因主要是device端与host端的数据传输的时间延迟所造成,而这里的运算量相对不大,因此体现不出GPU的优势。而版本4的运算时间不到一毫秒,明显比其他几个版本效率都要高。因为这里版本4使用了共享内存,即我的256个block中每一个block都使用了sizeof(int) * 1024大小的共享内存,在计算每一个行(1024个数据)的时候,大大减少了访问全局内存的次数。就本问题而言,在运行效率上,使用共享内存要比不试用共享内存更高效。因此,在今后的cuda程序编写中,我们要学会熟练使用共享内存,以提高程序运行效率。