MySQL 学习笔记(四)——查询练习
查询练习
1、准备数据
准备创建 几个表:
学生表(Student):学号、姓名、性别、出生年月日、班级
课程表(Course):课程号、课程名称、教师编号
成绩表(Score) :学号、课程号、成绩
教师表(Teacher):教师编号、教师性别、教师性别、出生年月日、职称、所在部门
#创建一个selectTest新数据库
mysql> create database selectTest;
Query OK, 1 row affected, 0 warning (0.67 sec)
#创建学生表
create table student(
sno varchar(20) primary key,
sname varchar(20) not null,
ssex varchar(10) not null,
sbirthday datetime,
class varchar(20)
);
#创建老师表
create table teacher(
tno varchar(20) primary key,
tname varchar(20) not null,
tsex varchar(20) not null,
tbirthday datetime,
prof varchar(20),
depart varchar(20) not null
);
#创建课程表
create table course(
cno varchar(20) primary key,
cname varchar(20) not null,
tno varchar(20) not null,
foreign key(tno) references teacher(tno)
);
#创建成绩表
create table score(
s_no varchar(20) not null,
c_no varchar(20) not null,
degree decimal,
foreign key(s_no) references student(sno),
foreign key(c_no) references course(cno),
primary key(s_no,c_no)
);
下面添加数据:
-- 添加学生表数据
INSERT INTO student VALUES('101', '曾华', '男', '1977-09-01', '95033');
INSERT INTO student VALUES('102', '匡明', '男', '1975-10-02', '95031');
INSERT INTO student VALUES('103', '王丽', '女', '1976-01-23', '95033');
INSERT INTO student VALUES('104', '李军', '男', '1976-02-20', '95033');
INSERT INTO student VALUES('105', '王芳', '女', '1975-02-10', '95031');
INSERT INTO student VALUES('106', '陆军', '男', '1974-06-03', '95031');
INSERT INTO student VALUES('107', '王尼玛', '男', '1976-02-20', '95033');
INSERT INTO student VALUES('108', '张全蛋', '男', '1975-02-10', '95031');
INSERT INTO student VALUES('109', '赵铁柱', '男', '1974-06-03', '95031');
-- 添加教师表数据
INSERT INTO teacher VALUES('804', '李诚', '男', '1958-12-02', '副教授', '计算机系');
INSERT INTO teacher VALUES('856', '张旭', '男', '1969-03-12', '讲师', '电子工程系');
INSERT INTO teacher VALUES('825', '王萍', '女', '1972-05-05', '助教', '计算机系');
INSERT INTO teacher VALUES('831', '刘冰', '女', '1977-08-14', '助教', '电子工程系');
-- 添加课程表数据
INSERT INTO course VALUES('3-105', '计算机导论', '825');
INSERT INTO course VALUES('3-245', '操作系统', '804');
INSERT INTO course VALUES('6-166', '数字电路', '856');
INSERT INTO course VALUES('9-888', '高等数学', '831');
-- 添加添加成绩表数据
INSERT INTO score VALUES('103', '3-105', '92');
INSERT INTO score VALUES('103', '3-245', '86');
INSERT INTO score VALUES('103', '6-166', '85');
INSERT INTO score VALUES('105', '3-105', '88');
INSERT INTO score VALUES('105', '3-245', '75');
INSERT INTO score VALUES('105', '6-166', '79');
INSERT INTO score VALUES('109', '3-105', '76');
INSERT INTO score VALUES('109', '3-245', '68');
INSERT INTO score VALUES('109', '6-166', '81');
-- 查看表结构
SELECT * FROM course;
SELECT * FROM score;
SELECT * FROM student;
SELECT * FROM teacher;查看表结构:
-- 查看表结构
mysql> select * from student;
+---------+-----------+------+---------------------+--------+
| snumber | sname | ssex | sbirthday | class |
+---------+-----------+------+---------------------+--------+
| 100 | 张三 | 男 | 1999-09-01 00:00:00 | 一班 |
| 101 | 李四 | 男 | 1999-02-11 00:00:00 | 一班 |
| 102 | 王二 | 女 | 1999-09-23 00:00:00 | 一班 |
| 103 | 王尼玛 | 男 | 1988-01-11 00:00:00 | 一班 |
| 104 | 张全蛋 | 男 | 2000-09-03 00:00:00 | 一班 |
| 105 | 赵铁柱 | 男 | 1983-04-05 00:00:00 | 二班 |
| 106 | 木子 | 女 | 2000-12-16 00:00:00 | 二班 |
+---------+-----------+------+---------------------+--------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from teacher;
+---------+--------+------+---------------------+-----------+-----------------+
| tnumber | tname | tsex | tbirthday | prof | depart |
+---------+--------+------+---------------------+-----------+-----------------+
| 111 | 古一 | 女 | 0000-01-01 00:00:00 | 教授 | 化学系 |
| 112 | 王 | 男 | 2000-09-03 00:00:00 | 副教授 | 计算机系 |
| 113 | 春丽 | 女 | 1988-11-05 00:00:00 | 助教 | 英语系 |
| 114 | 刘邦 | 男 | 1978-12-03 00:00:00 | 助教 | 通信工程系 |
+---------+--------+------+---------------------+-----------+-----------------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from course;
+---------+--------------+---------+
| cnumber | cname | tnumber |
+---------+--------------+---------+
| 3-105 | 数据结构 | 112 |
| 3-245 | 模拟电路 | 113 |
| 6-166 | 人工智能 | 111 |
| 9-888 | 数字电路 | 114 |
+---------+--------------+---------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from score;
+---------+---------+--------+
| s_no | c_no | degree |
+---------+---------+--------+
| 100 | 3-245 | 85 |
| 101 | 3-245 | 95 |
| 102 | 3-105 | 83 |
| 103 | 3-105 | 89 |
| 104 | 3-245 | 66 |
| 105 | 6-166 | 60 |
| 106 | 6-166 | 92 |
+---------+---------+--------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
2、查询练习 (1-10)
1、查询student表中的所有记录
select * from student;
mysql> select * from student;
# 其中 * 表示所有字段的意思
+---------+-----------+------+---------------------+--------+
| snumber | sname | ssex | sbirthday | class |
+---------+-----------+------+---------------------+--------+
| 100 | 张三 | 男 | 1999-09-01 00:00:00 | 一班 |
| 101 | 李四 | 男 | 1999-02-11 00:00:00 | 一班 |
| 102 | 王二 | 女 | 1999-09-23 00:00:00 | 一班 |
| 103 | 王尼玛 | 男 | 1988-01-11 00:00:00 | 一班 |
| 104 | 张全蛋 | 男 | 2000-09-03 00:00:00 | 一班 |
| 105 | 赵铁柱 | 男 | 1983-04-05 00:00:00 | 二班 |
| 106 | 木子 | 女 | 2000-12-16 00:00:00 | 二班 |
+---------+-----------+------+---------------------+--------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)2、查询student表中所有记录的sname、ssex、class 列
select + 要查询的列(多个用逗号隔开) + from + 表名;
mysql> select sname,ssex,class from student;
+-----------+------+--------+
| sname | ssex | class |
+-----------+------+--------+
| 张三 | 男 | 一班 |
| 李四 | 男 | 一班 |
| 王二 | 女 | 一班 |
| 王尼玛 | 男 | 一班 |
| 张全蛋 | 男 | 一班 |
| 赵铁柱 | 男 | 二班 |
| 木子 | 女 | 二班 |
+-----------+------+--------+
7 rows in set (0.00 sec)3、查询教师的所有单位,即不重复的depart列
select distinct depart from teacher;
mysql> select distinct depart from teacher;
+-----------------+
| depart |
+-----------------+
| 化学系 |
| 计算机系 |
| 通信工程系 |
+-----------------+
3 rows in set (0.10 sec)
4、查询score表中成绩 60到90 之间的所有记录
这就要给我们查询指令加一个查询区间:( between 。。 and 。。)
mysql> select * from score where degree between 60 and 80;
也可以直接使用运算符比较:
mysql> select * from score where degree >= 60 and degree<= 90;
两条指令结果是一样的(注意between包括端点值)
mysql> select * from score where degree between 60 and 90;
+---------+---------+--------+
| snumber | cnumber | degree |
+---------+---------+--------+
| 100 | 3-245 | 85 |
| 102 | 3-105 | 83 |
| 103 | 3-105 | 89 |
| 104 | 3-245 | 66 |
| 105 | 6-166 | 60 |
+---------+---------+--------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)5、查询score表中85、95或83的记录
要用到表示或者关系的查询 in
mysql> select * from score where degree in (85,95,83);
+---------+---------+--------+
| snumber | cnumber | degree |
+---------+---------+--------+
| 100 | 3-245 | 85 |
| 101 | 3-245 | 95 |
| 102 | 3-105 | 83 |
+---------+---------+--------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
6、查询 student 表中 '95031' 班或性别为 '女' 的所有行
这就和上一个有点区别,这里筛选的是不同字段,上一个是同一个字段当中
用 or 表示或者:
mysql> select * from student where sclass='95031' or ssex='女';
+-----+--------+------+---------------------+--------+
| sno | sname | ssex | sbirthday | sclass |
+-----+--------+------+---------------------+--------+
| 102 | 匡明 | 男 | 1975-10-02 00:00:00 | 95031 |
| 103 | 王丽 | 女 | 1976-01-23 00:00:00 | 95033 |
| 105 | 王芳 | 女 | 1975-02-10 00:00:00 | 95031 |
| 106 | 陆军 | 男 | 1974-06-03 00:00:00 | 95031 |
| 108 | 张全蛋 | 男 | 1975-02-10 00:00:00 | 95031 |
| 109 | 赵铁柱 | 男 | 1974-06-03 00:00:00 | 95031 |
+-----+--------+------+---------------------+--------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)7、以 class 降序的方式查询 student 表的所有行
DESC: 降序,从高到低
ASC(默认): 升序,从低到高
SELECT * FROM student ORDER BY class DESC;
SELECT * FROM student ORDER BY class ASC;mysql> select * from student order by sclass desc;
+-----+--------+------+---------------------+--------+
| sno | sname | ssex | sbirthday | sclass |
+-----+--------+------+---------------------+--------+
| 101 | 曾华 | 男 | 1977-09-01 00:00:00 | 95033 |
| 103 | 王丽 | 女 | 1976-01-23 00:00:00 | 95033 |
| 104 | 李军 | 男 | 1976-02-20 00:00:00 | 95033 |
| 107 | 王尼玛 | 男 | 1976-02-20 00:00:00 | 95033 |
| 102 | 匡明 | 男 | 1975-10-02 00:00:00 | 95031 |
| 105 | 王芳 | 女 | 1975-02-10 00:00:00 | 95031 |
| 106 | 陆军 | 男 | 1974-06-03 00:00:00 | 95031 |
| 108 | 张全蛋 | 男 | 1975-02-10 00:00:00 | 95031 |
| 109 | 赵铁柱 | 男 | 1974-06-03 00:00:00 | 95031 |
+-----+--------+------+---------------------+--------+
9 rows in set (0.29 sec)8、 以 c_no 升序、degree 降序查询 score 表的所有行
order by 先按照第一个排,再考虑第二个排列
mysql> select * from score order by c_no asc,degree desc;
+------+-------+--------+
| s_no | c_no | degree |
+------+-------+--------+
| 103 | 3-105 | 92 |
| 105 | 3-105 | 88 |
| 109 | 3-105 | 76 |
| 103 | 3-245 | 86 |
| 105 | 3-245 | 75 |
| 109 | 3-245 | 68 |
| 103 | 6-166 | 85 |
| 109 | 6-166 | 81 |
| 105 | 6-166 | 79 |
+------+-------+--------+
9 rows in set (0.00 sec)9、查询 "95031" 班的学生人数
mysql> select count(*) from student where sclass='95031';
+----------+
| count(*) |
+----------+
| 5 |
+----------+
1 row in set (2.06 sec)10、查询 score 表中的最高分的学生学号和课程编号(子查询或排序查询)
子查询
mysql> select s_no,c_no from score where degree=(select max(degree) from score);
+------+-------+
| s_no | c_no |
+------+-------+
| 103 | 3-105 |
+------+-------+
1 row in set (2.06 sec)排序查询
select snumber,cnumber,degree from score order by degree desc limit 0,1;
这里的 limit 0,1 表示取表中从第0条取到第一条(也就是取出第一条数据)
limit 的第一个数字表示从哪里开始查,第二个数字表示查几条
mysql> select s_no,c_no,degree from score order by degree desc limit 0,1;
+---------+---------+--------+
| s_no | c_no | degree |
+---------+---------+--------+
| 101 | 3-245 | 95 |
+---------+---------+--------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
11、查询每门课的平均成绩
-- GROUP BY: 分组查询
SELECT c_no, AVG(degree) FROM score GROUP BY c_no;12、查询score表中至少有 两名学生选修 并以 3开头 的课程平均成绩(分组条件与模糊查询)
-- 首先把 c_no, AVG(degree) 通过分组查询出来
SELECT c_no, AVG(degree) FROM score GROUP BY c_no
+-------+-------------+
| c_no | AVG(degree) |
+-------+-------------+
| 3-105 | 85.3333 |
| 3-245 | 76.3333 |
| 6-166 | 81.6667 |
+-------+-------------+
-- 再查询出至少有 2 名学生选修的课程
-- HAVING: 表示持有
HAVING COUNT(c_no) >= 2
-- 并且是以 3 开头的课程
-- LIKE 表示模糊查询,"%" 是一个通配符,匹配 "3" 后面的任意字符。
AND c_no LIKE '3%';
-- 把前面的SQL语句拼接起来,
-- 后面加上一个 COUNT(*),表示将每个分组的个数也查询出来。
SELECT c_no, AVG(degree), COUNT(*) FROM score GROUP BY c_no
HAVING COUNT(c_no) >= 2 AND c_no LIKE '3%';
+-------+-------------+----------+
| c_no | AVG(degree) | COUNT(*) |
+-------+-------------+----------+
| 3-105 | 85.3333 | 3 |
| 3-245 | 76.3333 | 3 |
+-------+-------------+----------+13、查询分数大于70,小于90的sno列
select s_no,degree from score where degree between 70 and 90;要注意between是包含端点的
14、查询所有学生的sname、c_no、和degree列
当要查询的内容不在一张表中时,我们可以分开查询,但是太麻烦了。
下面使用多表查询:
select sname,c_no,degree from student,score
where student.sno = score.s_no;15、查询所有学生的s_no、cname和degree列
这些信息来自于course表和score表
select sno,cname,degree from course,score
where course.cno=score.c_no;16、查询所有学生的sname、cname和degree列(三表关联查询)
找两两之间的相同之处,写条件
这里的 sname来自student表、cname来自course表,degree来自score表,也就是我们要查询的三个字段来自三张表
select sname,cname,degree from student,course,score
where student.sno=score.s_no and course.cno=score.c_no;17、查询"95031"班学生每门课的平均分
这里用到 in表示或者条件
要将 c_no 分组一下就能得出 95031 班学生每门课的平均成绩:
select c_no,avg(degree) from score
where s_no in (select sno from student where sclass="95031")
group by c_no;18、查询选修"3-105"课程的成绩高于"109"号同学"3-105"成绩的所有同学
(子查询)
这道题读题句很困难,我们一步一步做:
a、先把109号同学的3-105课程的成绩导出来,用到了and(同时)
select degree from score where s_no="109" and c_no="3-105";b、有了这个条件,我们再加一个3-105课程就可以筛选出来了
select * from score
where c_no="3-105" and
degree>(select degree from score where s_no="109" and c_no="3-105");
19、查询成绩高于学号为"109"、课程号为"3-105"的成绩的所有记录
这题和上面那一题几乎类似,只是条件不同而已,把从3-105课程中查询大于102号同学成绩,放大到从整个表中查询比 102号同学的3-105课程成绩多的同学记录!
select * from score
where degree>(select degree from score where s_no="109" and c_no="3-105");
20、查询所有和 101 、108 号学生同年出生的 sno 、name 、birthday 列。
select sno,sname,sbirthday from student
where year(sbirthday) in (select year(sbirthday) from student where sno in (101,108));
这里不能用 = 来做条件因为这里的年份是两个值,应该用 in,有一个条件用 =,两个以上条件用 in
这里用到了内置函数year()求年份
已经知道的函数 avg()求平均值,count()求和
21、查询 '张旭' 教师任课的学生成绩表
首先找到教师编号:
select tno from teacher where tname='张旭';通过 course 表找到该教师课程号:
select cno from course where tno =
(select tno from teacher where tname='张旭');通过筛选出的课程号查询成绩表:
select * from score where c_no=
(select cno from course where tno =
(select tno from teacher where tname='张旭'));22、查询某选修课程多于5个同学的教师姓名。
这题和上题类似,也是多层嵌套的子查询
先查询人数多于5人的课程号,再查询老师的tno,再查询老师的姓名,步步嵌套
select tname from teacher where tno in (
select tno from course where cno in (
select c_no from score having count(*)>5));25、查询“计算机系”教师所教课程的成绩表
这个依然是条件嵌套,就不多重复了
select * from score where c_no in(
select cno from course where tno in(
select tno from teacher where depart='计算机系')
);26、查询 计算机系 与 电子工程系 中的不同职称的教师。
UNION 和 NOT IN 的使用
select * from teacher where depart='计算机系' and prof not in(
select prof from teacher where depart='电子工程系')
union
select * from teacher where depart='电子工程系' and prof not in(
select prof from teacher where depart='计算机系');27、查询'3-105'课程且成绩至少高于'3-245'同学的cno、sno和degree,并按degree由低到高排序
重点就是 至少 :大于其中至少一个,这就用到了 any
select c_no,s_no,degree from score where c_no='3-105' and
degree> any(select degree from score where c_no='3-245')
order by degree desc;ANY: 符合SQL语句中的任意条件。
也就是说,在 3-105 成绩中,只要有一个大于从 3-245 筛选出来的任意行就符合条件,
最后根据降序查询结果。28、查询编号为‘3-105’的课程且成绩高于课程‘3-245’课程的同学的信息?(all)
select * from score
where cno='3-105' #条件一
and degree>all(select degree from score where cno = '3-245');
只需对上一道题稍作修改。
ALL: 符合SQL语句中的所有条件。
也就是说,在 3-105 每一行成绩中,都要大于从 3-245 筛选出来全部行才算符合条件。29、查询所有教师和同学的name、sex和birthday(union、as)
select tname as name,tsex as sex,tbirthday as birthday from teacher
union
select sname,ssex,sbirthday from student;31、查询某课程成绩比该课程平均成绩低的 score 表
先查一下各门课的平均成绩
mysql> select avg(degree) from score group by cno;
+-------------+
| avg(degree) |
+-------------+
| 86.0000 |
| 82.0000 |
| 76.0000 |
+-------------+
3 rows in set (0.56 sec)
求某一门课的平均成绩:
mysql> select avg(degree) from score where cno='3-105';
+-------------+
| avg(degree) |
+-------------+
| 86.0000 |
+-------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
然后,把score复制成a、b两个表(不需要语句,直接写),具体语句如下:
select * from score a where degree<(
select avg(degree) from score b where a.c_no=b.c_no);其中的select avg(degree) from score b where a.cnumber=b.cnumber是当选中a表中的某个同学时,从b表中找到与它课程号相同的同学,然后利用这个同学的课程号求这门课平均成绩,再和a表的那个同学做比较,最后得出结果。
32、查询所有任课老师的tname和depart
这一题乍一看很简单,其实有点小条件,就是任课老师的名字。因为老师表里面可能有不任课的老师,所以要和course表进行比较,找到teccher表中教师号在课程表中存在的任课老师:
select tname,depart from teacher
where tno in (select tno from course);33、查询至少有2名男生的班号
select sclass from student
where ssex='男' group by sclass having count(*)>=2;count(*)统计男生的个数
34、查询student表中不姓’王‘的同学
select * from student where sname not like '王%'; NOT: 取反
LIKE: 模糊查询35、查询student表中每个学生的姓名和年龄
年龄=当前年份 - 出生年份,当前年份可以用year( now())来体现,再加上别名,具体语句如下:
select sname,year(now())-year(sbirthday) as '年龄' from student;36、查询student表中最大最小sbirthday的日期值
select max(sbirthday),min(sbirthday) from student;37、以班级和年龄从大到小的顺序查询student表中的记录
select * from student order by sclass desc,sbirthday;order by是先按照第一进行排列,第一个相同再按照第二个进行排列
38、查询'男'教师及其所上的课程
可以先查男教师,然后再作为条件来用(比较简单,直接写了):
select * from course
where tno in ( select tno from teacher where tsex='男');39、查询最高分同学的sno、cno和degree列
select s_no,c_no,degree from score where degree=
(select max(degree) from score);40、查询和 "李军" 同性别的所有同学 name
select sname from student where ssex=(
select ssex from student where sname='李军');41、查询和 "李军" 同性别且同班的同学 name
只需要用and再给上一题添加一个条件就OK了
select sname from student where ssex=(
select ssex from student where sname='李军')
and sclass=(
select sclass from student where sname='李军');42、查询所有选修 "计算机导论" 课程的 "男" 同学成绩表。
先从 SELECT cno FROM course WHERE cname = '计算机导论' 找到cno
再从 SELECT sno FROM student WHERE ssex = '男' 找到sno
SELECT * FROM score WHERE c_no = (
SELECT cno FROM course WHERE cname = '计算机导论'
) AND s_no IN (
SELECT sno FROM student WHERE ssex = '男'
);注意这里sno有多个要用 in ,只有一个用 =
43、使用如下命令建立一个grade表
建立一个 grade 表代表学生的成绩等级,并插入数据:
CREATE TABLE grade (
low INT(3),
upp INT(3),
grade char(1)
);
INSERT INTO grade VALUES (90, 100, 'A');
INSERT INTO grade VALUES (80, 89, 'B');
INSERT INTO grade VALUES (70, 79, 'C');
INSERT INTO grade VALUES (60, 69, 'D');
INSERT INTO grade VALUES (0, 59, 'E');
SELECT * FROM grade;
+------+------+-------+
| low | upp | grade |
+------+------+-------+
| 90 | 100 | A |
| 80 | 89 | B |
| 70 | 79 | C |
| 60 | 69 | D |
| 0 | 59 | E |
+------+------+-------+查询所有学生的 s_no 、c_no 和 grade 列。
思路是,使用区间 ( BETWEEN ) 查询,判断学生的成绩 ( degree ) 在 grade 表的 low 和 upp 之间。
SELECT s_no, c_no, grade FROM score, grade
WHERE degree BETWEEN low AND upp;
+------+-------+-------+
| s_no | c_no | grade |
+------+-------+-------+
| 101 | 3-105 | A |
| 102 | 3-105 | A |
| 103 | 3-105 | A |
| 103 | 3-245 | B |
| 103 | 6-166 | B |
| 104 | 3-105 | B |
| 105 | 3-105 | B |
| 105 | 3-245 | C |
| 105 | 6-166 | C |
| 109 | 3-105 | C |
| 109 | 3-245 | D |
| 109 | 6-166 | B |
+------+-------+-------+SQL的四种连接查询
1、内连接
inner join 或者 join
2、外连接
a、左连接:left join 或者 left outer join
b、右连接:right join 或者 right outer join
c、完全外连接:full join 或者 full outer join
就是这四种连接,下面我们举例说明:先创建一个数据库,再创建2个表
person表
id,name,cardid(来自于card表)
card表
id,name
CREATE DATABASE testJoin;
CREATE TABLE person (
id INT,
name VARCHAR(20),
cardId INT
);
CREATE TABLE card (
id INT,
name VARCHAR(20)
);
INSERT INTO card VALUES (1, '饭卡'), (2, '建行卡'), (3, '农行卡'), (4, '工商卡'), (5, '邮政卡');
SELECT * FROM card;
+------+-----------+
| id | name |
+------+-----------+
| 1 | 饭卡 |
| 2 | 建行卡 |
| 3 | 农行卡 |
| 4 | 工商卡 |
| 5 | 邮政卡 |
+------+-----------+
INSERT INTO person VALUES (1, '张三', 1), (2, '李四', 3), (3, '王五', 6);
SELECT * FROM person;
+------+--------+--------+
| id | name | cardId |
+------+--------+--------+
| 1 | 张三 | 1 |
| 2 | 李四 | 3 |
| 3 | 王五 | 6 |
+------+--------+--------+1、inner join 内连接查询
对person和card表进行连接查询,加上条件
mysql> select * from person inner join card on person.cardid=card.id;
+------+--------+--------+------+-----------+
| id | name | cardid | id | name |
+------+--------+--------+------+-----------+
| 1 | 张三 | 1 | 1 | 饭卡 |
| 2 | 李四 | 3 | 3 | 农行卡 |
+------+--------+--------+------+-----------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
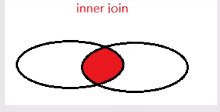
内连接查询就是两张表中的数据,通过某个字段相等,查询出相关记录数据,用 on… 表示条件,其中的inner join 可以用 join代替。
2、left join (左外连接)
mysql> select * from person left join card on person.cardid=card.id;
+------+--------+--------+------+-----------+
| id | name | cardid | id | name |
+------+--------+--------+------+-----------+
| 1 | 张三 | 1 | 1 | 饭卡 |
| 2 | 李四 | 3 | 3 | 农行卡 |
| 3 | 王五 | 6 | NULL | NULL |
+------+--------+--------+------+-----------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
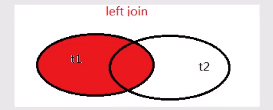
左外连接,会把左边表里面的所有数据取出来,而右边表数据如果有相等的,就显示出来,如果没有,就补 NULL
这里王五的cardid为6,在card表中没有对应,所有用NULL补上了
这里的语句,也可以用如下语句替代:left join = left outer join
3、right join(右外连接)
mysql> select * from person right join card on person.cardid=card.id;
+------+--------+--------+------+-----------+
| id | name | cardid | id | name |
+------+--------+--------+------+-----------+
| 1 | 张三 | 1 | 1 | 饭卡 |
| 2 | 李四 | 3 | 3 | 农行卡 |
| NULL | NULL | NULL | 2 | 建行卡 |
| NULL | NULL | NULL | 4 | 工商卡 |
| NULL | NULL | NULL | 5 | 邮政卡 |
+------+--------+--------+------+-----------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
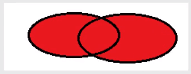
与左外连接类似,右外连接会把右边表里面的所有数据取出来,而左边表数据如果有相等的,就显示出来,如果没有,就补 NULL
上面的2、4、5都没有相等,补上NULL,6因为右边card本来就没有就不显示了
这里的语句,也可以用如下语句替代:right join = right outer join
4、full join(全外连接)
select * from person full join card on person.cardid=card.id;
ERROR 1054 (42S22): Unknown column 'person.cardid' in 'on clause'这样会报错,原因是mysql 不支持 full join
下面我们用图看一下这几种连接:
1、inner join 内连接
2、left join 左外连接
3、right join 右外连接
4、full join 全连接
全连接等于左连接和右连接合在一起的结果
mysql> select * from person left join card on person.cardid=card.id
-> union
-> select * from person right join card on person.cardid=card.id;
+------+--------+--------+------+-----------+
| id | name | cardid | id | name |
+------+--------+--------+------+-----------+
| 1 | 张三 | 1 | 1 | 饭卡 |
| 2 | 李四 | 3 | 3 | 农行卡 |
| 3 | 王五 | 6 | NULL | NULL |
| NULL | NULL | NULL | 2 | 建行卡 |
| NULL | NULL | NULL | 4 | 工商卡 |
| NULL | NULL | NULL | 5 | 邮政卡 |
+------+--------+--------+------+-----------+
6 rows in set (0.01 sec)
左边是全部,右边也是全部,对应的没有的就补上NULL