鬼吹灯文本挖掘5:sklearn实现文本聚类和文本分类
鬼吹灯文本挖掘1:jieba分词和CountVectorizer向量化
鬼吹灯文本挖掘2:wordcloud 词云展示
鬼吹灯文本挖掘3:关键词提取和使用sklearn 计算TF-IDF矩阵
鬼吹灯文本挖掘4:LDA模型提取文档主题 sklearn LatentDirichletAllocation和gensim LdaModel
鬼吹灯文本挖掘5:sklearn实现文本聚类和文本分类
1. 准备数据
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import re
import jieba
# 章节判断用变量预处理
def is_chap_head(tmpstr):
import re
pattern = re.compile('^第.{1,7}[章|回]')
return len(pattern.findall(tmpstr))
# 获取停用词库
my_stop_words_path = 'G:\\myLearning\\pythonLearning201712\\myDicts\\新建文件夹\\综合stopword.txt'
stop_words_dict = []
with open(my_stop_words_path, errors='ignore') as fr:
for line in fr.readlines():
stop_words_dict.append(line.strip())
# 自定义分词函数
def my_cut(inTxt):
inTxt = re.sub('[a-zA-Z0-9]','',inTxt)
jieba.lcut(inTxt)
words_list = jieba.lcut(inTxt)
return ' '.join([w for w in words_list if w not in stop_words_dict and len(w) > 1])
def my_cut2(inTxt):
inTxt = re.sub('[a-zA-Z0-9]','',inTxt)
jieba.lcut(inTxt)
words_list = jieba.lcut(inTxt)
return [w for w in words_list if w not in stop_words_dict and len(w) > 1]
# 1. 定义读取数据的函数
def get_txt_data(file_name, words_dict_path, chap_merge = False, cut_func = my_cut2):
# 先获取射雕各章节字符串文档
raw = pd.read_csv(file_name, names = ['txt'],sep = 'aaa',encoding = 'utf-8', engine = 'python')
raw['is_chap_head'] = raw.txt.apply(is_chap_head)
# raw['chap'] = 0 #初始化所有章节为0
# 章节判断
chap_num = 0
for i in range(len(raw)):
if raw['is_chap_head'][i] == 1:
chap_num += 1
raw.loc[i,'chap'] = chap_num
del raw['is_chap_head']
if chap_merge:
raw = raw.groupby(['chap']).sum()
jieba.load_userdict(words_dict_path)
raw['words_list'] = raw.txt.apply(cut_func)
return raw
file_path = 'G:\\自学笔记\\学习笔记:Python数据分析--玩转文本挖掘\\txt文档\\'
dict_path = 'G:\\自学笔记\\学习笔记:Python数据分析--玩转文本挖掘\\词库\\'
txt_names = ['斗破苍穹.txt','诛仙.txt','金庸-射雕英雄传txt精校版.txt',\
'鬼吹灯之精绝古城txt全本精校版.txt', '鬼吹灯之云南虫谷txt全本精校版.txt']
dict_names = ['斗破苍穹词库.txt','诛仙词库.txt','金庸小说词库.txt','鬼吹灯词库.txt']
%time dpcq_df = get_txt_data(file_path + txt_names[0], dict_path + dict_names[0], chap_merge = True ) # 文章太长,耗时较长
%time zx_df = get_txt_data(file_path + txt_names[1], dict_path + dict_names[1], chap_merge = True )
%time sdyxz_df = get_txt_data(file_path + txt_names[2], dict_path + dict_names[2], chap_merge = True )
%time gcd1_df = get_txt_data(file_path + txt_names[3], dict_path + dict_names[3], chap_merge = True )
%time gcd2_df = get_txt_data(file_path + txt_names[4], dict_path + dict_names[3], chap_merge = True )2. 文档相似度的计算
# 1. 使用gensim中的word2vec实习
from gensim.models.word2vec import Word2Vec
n_dim = 300 # 指定向量维度,大样本量是300至500较好
w2vmodel = Word2Vec(size = n_dim, min_count = 10) # 至少在10个文档中出现过
w2vmodel.build_vocab(dpcq_df.words_list) # 生成词表
w2vmodel
%time w2vmodel.train(dpcq_df.words_list,total_examples = w2vmodel.corpus_count, epochs = 10)
# 训练完毕的模型实质
print(w2vmodel.wv['薰儿'].shape)
w2vmodel.wv['薰儿']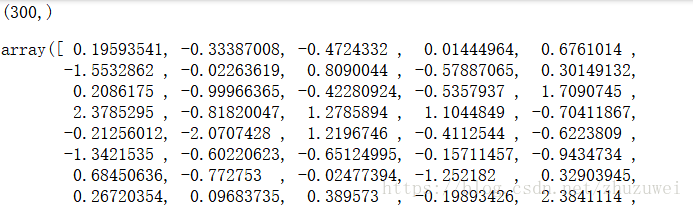
# 词向量间的相似度
w2vmodel.wv.most_similar('斗技')
[('功法', 0.7798707485198975),
('身法斗技', 0.7401365637779236),
('地阶', 0.7358179688453674),
('玄阶高级', 0.7349050045013428),
('地阶中级', 0.728278398513794),
('秘法', 0.7270081639289856),
('魂技', 0.7150101661682129),
('地阶斗技', 0.6921431422233582),
('帝印决', 0.6878658533096313),
('飞行斗技', 0.6844722032546997)]# 寻找对应关系
w2vmodel.wv.most_similar(positive=['萧炎','异火'],negative=['小医仙'],topn=10)
[('兽火', 0.4644716680049896),
('净莲妖火', 0.4551411271095276),
('骨灵冷火', 0.4455055594444275),
('火焰', 0.4415768086910248),
('陨落心炎', 0.44030460715293884),
('海心焰', 0.439494252204895),
('佛怒火莲', 0.43488609790802),
('青莲地心火', 0.4333166480064392),
('九龙雷罡火', 0.429574579000473),
('五轮', 0.4264797568321228)]# 寻找不合群的词
w2vmodel.wv.doesnt_match('萧炎 熏儿 小医仙 美杜莎 纳兰嫣然 彩鳞'.split())
'萧炎'
# 寻找不合群的词
w2vmodel.wv.doesnt_match('海心焰 青莲地心火 陨落心炎 净莲妖火 纳兰嫣然'.split())
'纳兰嫣然'# 2. 基于词袋模型的计算:sklearn实现
cleanchap = [my_cut(w) for w in gcd2_df.txt]
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
countvec = CountVectorizer(min_df=5)
resmtx = countvec.fit_transform(cleanchap)
from sklearn.metrics.pairwise import pairwise_distances
print(pairwise_distances(resmtx, metric = 'cosine').shape)
pairwise_distances(resmtx, metric = 'cosine')
(56, 56)
Out[17]:
array([[0. , 0.35040081, 0.42686292, ..., 0.65277582, 0.73983346,
0.67113954],
[0.35040081, 0. , 0.41634138, ..., 0.67092083, 0.73334226,
0.67347242],
[0.42686292, 0.41634138, 0. , ..., 0.72646148, 0.76235288,
0.73821901],
...,
[0.65277582, 0.67092083, 0.72646148, ..., 0. , 0.52471631,
0.39741077],
[0.73983346, 0.73334226, 0.76235288, ..., 0.52471631, 0. ,
0.5853083 ],
[0.67113954, 0.67347242, 0.73821901, ..., 0.39741077, 0.5853083 ,
0. ]])# 使用TF-IDF矩阵进行相似度计算
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfTransformer
transformer = TfidfTransformer()
tfidf = transformer.fit_transform(resmtx) # 基于词频矩阵X计算TF-IDF值
pairwise_distances(tfidf[:5],metric='cosine')
array([[0. , 0.54725386, 0.68972 , 0.78551127, 0.80340229],
[0.54725386, 0. , 0.63548046, 0.75853139, 0.8193562 ],
[0.68972 , 0.63548046, 0. , 0.5750506 , 0.56698607],
[0.78551127, 0.75853139, 0.5750506 , 0. , 0.3775796 ],
[0.80340229, 0.8193562 , 0.56698607, 0.3775796 , 0. ]])# 3 gensim实现: gensim计算的相似矩阵很难被sklearn直接使用
from gensim import similarities
from gensim import corpora, models
chaplist = [my_cut2(w) for w in gcd1_df.txt]
dictionary = corpora.Dictionary(chaplist)
corpus = [dictionary.doc2bow(text) for text in chaplist] # 仍为list of list
simmtx = similarities.MatrixSimilarity(corpus)
simmtx
# 4. 基于LDA计算余弦相似度
# 检索和第一回内容最相似(所属主题相同)的章节
simmtx = similarities.MatrixSimilarity(corpus) # 使用的矩阵种类需要和拟合模型时相同
simmtx
simmtx.index[:].shape
(33, 15668) # 使用gensim的LDA拟合结果进行演示
from gensim.models.ldamodel import LdaModel
tfidf_model = models.TfidfModel(corpus) # 建立TF-IDF模型
corpus_tfidf = tfidf_model[corpus] # 对所需文档计算TF-IDF结果
%time ldamodel = LdaModel(corpus_tfidf, id2word = dictionary, num_topics = 10, passes = 5)
query = gcd1_df.txt[1]
quer_bow = dictionary.doc2bow(my_cut2(query))
lda_vec = ldamodel[quer_bow] # 转换为lda模型下的向量
sims = simmtx[lda_vec] # 进行矩阵内向量和所提供向量的余弦相似度查询
sims = sorted(enumerate(sims), key = lambda item:-item[1])
sims
3. 文档聚类
# 进行聚类分析
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
clf = KMeans(n_clusters = 5)
s = clf.fit(tfidf)
print(s)
clf.cluster_centers_print(len(clf.labels_))
clf.labels_
56
Out[26]:
array([0, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 0, 2, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 3, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4])gcd2_df['clsres'] = clf.labels_
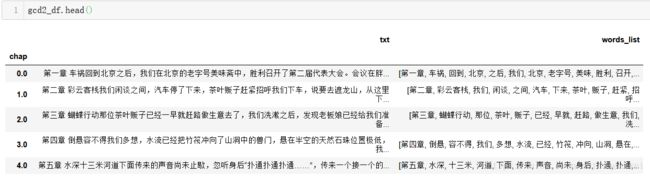
gcd2_df.head()chapgrp = gcd2_df.groupby('clsres')
chapcls = chapgrp.agg(sum) # 只有字符串列的情况下,sum函数自动转为合并字符串
cuttxt = lambda x: ' '.join(my_cut2(x))
chapclsres = chapcls.txt.apply(cuttxt)
chapclsres
clsres
0 第一章 车祸 回到 北京 之后 我们 北京 老字号 美味 胜利 召开 第二届 代表大会 会议...
1 第三十五章 凌云宫 会仙殿 天宫 宏伟 华丽 宫殿 正下方 只觉 整个 无比 渺小 宫殿 这...
2 第二章 彩云客栈 我们 闲谈 之间 汽车 下来 茶叶 贩子 赶紧 招呼 我们 下车 遮龙山 ...
3 第九章 鬼信号 自从 离开 部队 之后 经常 噩梦 整晚 整晚 失眠 北京 做起 古玩 生意...
4 第五十二章 康巴阿公 杨轻叹 一声 说道 若言琴 琴声 何不 若言声 指头 何不 于君 指上...
Name: txt, dtype: object# 列出关键词以刻画类别特征
import jieba.analyse as ana
ana.set_stop_words('G:\\自学笔记\\学习笔记:Python数据分析--玩转文本挖掘\\词库\\停用词.txt')
for item in chapclsres:
print(ana.extract_tags(item, topK = 10))
['胖子', '献王', '杨说', '东西', '献王墓', '尸洞', '墓室', '女尸', '尸体', '葫芦洞']
['胖子', '水银', '献王', '壁画', '石碑', '宫殿', '天宫', '厉鬼', '巫衣', '杨说']
['竹筏', '胖子', '遮龙山', '献王', '献王墓', '山洞', '河道', '水中', '探照灯', '痋术']
['胖子', '玉棺', '机舱', '杨说', '信号', '登山', '献王', '肉线', '树上', '树身']
['喇嘛', '大个子', '格玛', '干事', '连长', '狼群', '古坟', '魔国', '饿狼', '军医']gcd2_df2 = gcd2_df[['txt', 'words_list']]
zx_df['y'] = 'zx'
sdyxz_df['y'] = 'sdyxz'
gcd1_df['y'] = 'gcd1'
gcd2_df2['y'] = 'gcd2'
all_txt = pd.concat([zx_df, sdyxz_df, gcd1_df, gcd2_df2], axis = 0) #按行合并
all_txt.head()
joinx = lambda x: ' '.join(x)
all_words = all_txt.words_list.apply(joinx)
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer, TfidfTransformer, TfidfVectorizer
count_vectorizer = CountVectorizer(min_df = 5)
countMat = count_vectorizer.fit_transform(all_words)
countMat
<388x17224 sparse matrix of type ''
with 394507 stored elements in Compressed Sparse Row format>
tfidf_transformer = TfidfTransformer()
tfidf_vec = tfidf_transformer.fit_transform(countMat)
tfidf_vec
<388x17224 sparse matrix of type ''
with 394507 stored elements in Compressed Sparse Row format>
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
km = KMeans(n_clusters=4)
y_pred = km.fit_predict(tfidf_vec)
km.cluster_centers_
array([[0.00160436, 0. , 0.00056069, ..., 0.00271158, 0.00254711,
0. ],
[0.00280139, 0.00070697, 0.00055412, ..., 0.00033704, 0. ,
0. ],
[0.00043656, 0.00270005, 0.00024102, ..., 0. , 0. ,
0.00053978],
[0.00287647, 0.00190007, 0.00010306, ..., 0. , 0. ,
0.00159731]]) 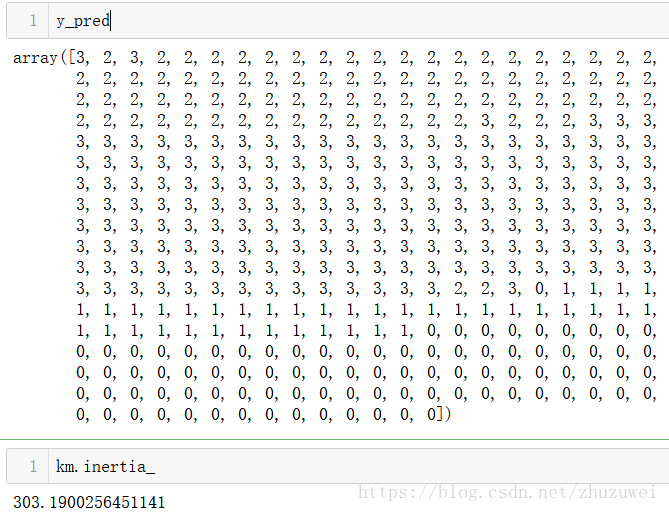
4. 文档分类
1) 直接分类
cutlist = lambda x: ' '.join(x)
x_data = all_txt.words_list.apply(cutlist)
y_data = list(all_txt.y)
# (1) 按词频分类
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer, TfidfTransformer, TfidfVectorizer
count_vectorizer = CountVectorizer(min_df = 5)
all_words_count = count_vectorizer.fit_transform(x_data)
all_words_count
<388x17224 sparse matrix of type ''
with 394507 stored elements in Compressed Sparse Row format>
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(all_words_count, y_data, test_size = 0.2)
# 尝试逻辑回归和SVM
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.svm import SVC
my_lr = LogisticRegression()
my_svm1 = SVC(kernel = 'linear')
my_svm2 = SVC(kernel='rbf')
%time my_lr.fit(x_train,y_train)
%time my_svm1.fit(x_train,y_train)
%time my_svm2.fit(x_train,y_train)
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
print(classification_report(y_test, my_lr.predict(x_test)))
print(classification_report(y_test, my_svm1.predict(x_test)))
print(classification_report(y_test, my_svm2.predict(x_test))) precision recall f1-score support
gcd1 1.00 1.00 1.00 7
gcd2 1.00 1.00 1.00 10
sdyxz 1.00 1.00 1.00 5
zx 1.00 1.00 1.00 56
avg / total 1.00 1.00 1.00 78
precision recall f1-score support
gcd1 1.00 0.86 0.92 7
gcd2 0.83 1.00 0.91 10
sdyxz 1.00 1.00 1.00 5
zx 1.00 0.98 0.99 56
avg / total 0.98 0.97 0.97 78
precision recall f1-score support
gcd1 1.00 0.29 0.44 7
gcd2 0.62 1.00 0.77 10
sdyxz 1.00 1.00 1.00 5
zx 1.00 0.98 0.99 56
avg / total 0.95 0.92 0.91 78# (2) 只考虑词是否出现
tests = np.nonzero(all_words_count) # 找出非0值的行列索引
tests
(array([ 0, 0, 0, ..., 387, 387, 387], dtype=int32),
array([6988, 2301, 8935, ..., 1103, 6942, 9357], dtype=int32))
new_all_words_count = all_words_count
new_all_words_count[tests[0],tests[1]] = 1
new_all_words_count
<388x17224 sparse matrix of type ''
with 394507 stored elements in Compressed Sparse Row format>
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(new_all_words_count, y_data, test_size = 0.2)
my_lr = LogisticRegression()
my_svm1 = SVC(kernel = 'linear')
my_svm2 = SVC(kernel='rbf')
%time my_lr.fit(x_train,y_train)
%time my_svm1.fit(x_train,y_train)
%time my_svm2.fit(x_train,y_train)
print(classification_report(y_test, my_lr.predict(x_test)))
print(classification_report(y_test, my_svm1.predict(x_test)))
print(classification_report(y_test, my_svm2.predict(x_test))) precision recall f1-score support
gcd1 1.00 0.75 0.86 4
gcd2 0.95 1.00 0.97 19
sdyxz 1.00 1.00 1.00 10
zx 1.00 1.00 1.00 45
avg / total 0.99 0.99 0.99 78
precision recall f1-score support
gcd1 1.00 0.75 0.86 4
gcd2 0.95 1.00 0.97 19
sdyxz 1.00 1.00 1.00 10
zx 1.00 1.00 1.00 45
avg / total 0.99 0.99 0.99 78
precision recall f1-score support
gcd1 0.00 0.00 0.00 4
gcd2 0.00 0.00 0.00 19
sdyxz 1.00 1.00 1.00 10
zx 0.66 1.00 0.80 45
avg / total 0.51 0.71 0.59 782)PCA降维
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
pca = PCA(n_components=0.9)
#PCA不支持sparse mat的操作,先转换为标准矩阵
all_wc_mtx = all_words_count.todense()
new_x = pca.fit_transform(all_wc_mtx)
new_x_train,new_x_test,new_y_train,new_y_test = train_test_split(new_x,y_data,test_size = 0.3)
new_x_train.shape
(271, 147)my_lr2 = LogisticRegression()
my_svm21 = SVC(kernel='linear')
my_svm22 = SVC(kernel='rbf')
%time my_lr2.fit(new_x_train, new_y_train)
%time my_svm21.fit(new_x_train, new_y_train)
%time my_svm22.fit(new_x_train, new_y_train)
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
print(classification_report(new_y_test, my_lr2.predict(new_x_test)))
print(classification_report(new_y_test, my_svm21.predict(new_x_test)))
print(classification_report(new_y_test, my_svm22.predict(new_x_test)))precision recall f1-score support
gcd1 0.69 1.00 0.82 9
gcd2 0.85 1.00 0.92 11
sdyxz 1.00 0.83 0.91 12
zx 1.00 0.95 0.98 85
avg / total 0.96 0.95 0.95 117
precision recall f1-score support
gcd1 0.82 1.00 0.90 9
gcd2 1.00 1.00 1.00 11
sdyxz 1.00 1.00 1.00 12
zx 1.00 0.98 0.99 85
avg / total 0.99 0.98 0.98 117
precision recall f1-score support
gcd1 0.00 0.00 0.00 9
gcd2 1.00 0.18 0.31 11
sdyxz 0.00 0.00 0.00 12
zx 0.74 1.00 0.85 85
avg / total 0.63 0.74 0.65 1173)使用卡方检验进行特征选择后再分类
from sklearn.feature_selection import SelectKBest,chi2
"""可尝试选不同的k"""
model1 = SelectKBest(chi2, k=100) # 选择100个最好的特征
new_x2 = model1.fit_transform(all_words_count,y_data)
new_x2
<388x100 sparse matrix of type ''
with 3482 stored elements in Compressed Sparse Row format> new_x_train2, new_x_test2, new_y_train2, new_y_test2 = train_test_split(new_x2, y_data, test_size = 0.3)
my_lr3 = LogisticRegression()
my_svm31 = SVC(kernel='linear')
my_svm32 = SVC(kernel='rbf')
%time my_lr3.fit(new_x_train2, new_y_train2)
%time my_svm31.fit(new_x_train2, new_y_train2)
%time my_svm32.fit(new_x_train2, new_y_train2)
print(classification_report(new_y_test2, my_lr3.predict(new_x_test2)))
print(classification_report(new_y_test2, my_svm31.predict(new_x_test2)))
print(classification_report(new_y_test2, my_svm32.predict(new_x_test2)))precision recall f1-score support
gcd1 1.00 0.82 0.90 11
gcd2 0.87 1.00 0.93 13
sdyxz 1.00 0.93 0.97 15
zx 0.99 1.00 0.99 78
avg / total 0.98 0.97 0.97 117
precision recall f1-score support
gcd1 1.00 0.91 0.95 11
gcd2 1.00 1.00 1.00 13
sdyxz 1.00 1.00 1.00 15
zx 0.99 1.00 0.99 78
avg / total 0.99 0.99 0.99 117
precision recall f1-score support
gcd1 1.00 0.09 0.17 11
gcd2 0.92 0.85 0.88 13
sdyxz 0.00 0.00 0.00 15
zx 0.75 1.00 0.86 78
avg / total 0.70 0.77 0.68 117