redis入门及其集群搭建、哨兵模式
一、Nosql概述
1、为什么要用Nosql
1.1 单机 MySQL 的美好时代
来源博客(https://www.cnblogs.com/lukelook/p/11135209.html)
在90年代,一个网站的访问量一般都不大,用单个数据库完全可以轻松应付。
在那个时候,更多的都是静态网页,动态交互类型的网站不多,数据库更是没压力。
上述架构下,我们来看看数据存储的瓶颈是什么?
DAL : Data Access Layer(数据访问层 – Hibernate,MyBatis)
数据量的总大小一个机器放不下时。
数据的索引(B+ Tree)一个机器的内存放不下时。
访问量(读写混合)一个实例不能承受。
如果满足了上述1 or 3个时,只能对数据库的整体架构进行重构。
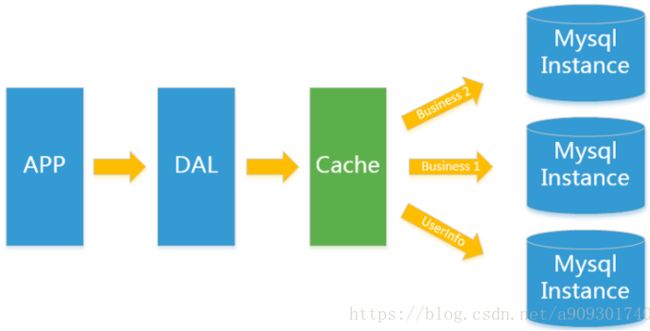
1.2 Memcached(缓存)+MySQL+垂直拆分
后来,随着访问量的上升,几乎大部分使用MySQL架构的网站在数据库上都开始出现了性能问题,web程序不再仅仅专注在功能上,同时也在追求性能。程序员们开始大量的使用缓存技术来缓解数据库的压力,优化数据库的结构和索引。开始比较流行的是通过文件缓存来缓解数据库压力,但是当访问量继续增大的时候,多台web机器通过文件缓存不能共享,大量的小文件缓存也带了了比较高的IO压力。在这个时候,缓存就自然的成为一个非常时尚的技术产品。
Memcached作为一个独立的分布式的缓存服务器,为多个web服务器提供了一个共享的高性能缓存服务,在Memcached服务器上,又发展了根据hash算法来进行多台Memcached缓存服务的扩展,然后又出现了一致性hash来解决增加或减少缓存服务器导致重新hash带来的大量缓存失效的弊端。
1.3 Mysql主从读写分离
由于数据库的写入压力增加,Memcached只能缓解数据库的读取压力。读写集中在一个数据库上让数据库不堪重负,大部分网站开始使用主从复制技术来达到读写分离,以提高读写性能和读库的可扩展性。Mysql的master-slave模式成为这个时候的网站标配了。
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-hlqWcPK1-1591769822973)(https://img2018.cnblogs.com/blog/1132619/201907/1132619-20190704215905511-2120056387.png)]
1.4 分库分表+水平拆分+mysql集群
在Memcached的高速缓存,MySQL的主从复制,读写分离的基础之上,这时MySQL主库的写压力开始出现瓶颈,而数据量的持续猛增,由于MyISAM在写数据的时候会使用表锁,在高并发写数据的情况下会出现严重的锁问题,大量的高并发MySQL应用开始使用InnoDB引擎代替MyISAM。
ps:这就是为什么 MySQL 在 5.6 版本之后使用 InnoDB 做为默认存储引擎的原因 – MyISAM 写会锁表,InnoDB 有行锁,发生冲突的几率低,并发性能高。
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-JaeCzcE2-1591769822977)(https://img2018.cnblogs.com/blog/1132619/201907/1132619-20190704220040716-730488360.png)]
同时,开始流行使用分表分库来缓解写压力和数据增长的扩展问题。这个时候,分表分库成了一个热门技术,是面试的热门问题也是业界讨论的热门技术问题。也就在这个时候,MySQL推出了还不太稳定的表分区,这也给技术实力一般的公司带来了希望。虽然MySQL推出了MySQL Cluster集群,但性能也不能很好满足互联网的要求,只是在高可靠性上提供了非常大的保证。
1.5 MySQL的扩展性瓶颈
MySQL数据库也经常存储一些大文本字段,导致数据库表非常的大,在做数据库恢复的时候就导致非常的慢,不容易快速恢复数据库。比如1000万4KB大小的文本就接近40GB的大小,如果能把这些数据从MySQL省去,MySQL将变得非常的小。关系数据库很强大,但是它并不能很好的应付所有的应用场景。MySQL的扩展性差(需要复杂的技术来实现),大数据下IO压力大,表结构更改困难,正是当前使用MySQL的开发人员面临的问题。
1.6 今天是什么样子?[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-ZlLq8Rml-1591769822981)(https://img2018.cnblogs.com/blog/1132619/201907/1132619-20190704220200946-11206502.png)]
最前面的是企业级防火墙,后面通过负载均衡主机(软负载:Nginx,硬负载:F5)在 web 服务器集群之间进行调度,再由具体的 web 服务器(Tomcat)去访问缓存,访问数据库。
1.7 为什么用NoSQL?
今天我们可以通过第三方平台(如:Google,Facebook等)可以很容易的访问和抓取数据。用户的个人信息,社交网络,地理位置,用户生成的数据和用户操作日志已经成倍的增加。我们如果要对这些用户数据进行挖掘,那SQL数据库已经不适合这些应用了, NoSQL数据库的发展也却能很好的处理这些大的数据。
2、什么是NoSQL
NoSQL = Not Only SQL (不仅仅是SQL)
关系型数据库:表格 ,行 ,列
很多的数据类型用户的个人信息,社交网络,地理位置。这些数据类型的存储不需要一个固定的格式!
不需要多月的操作就可以横向扩展的 ! Map
NoSQL,泛指非关系型数据库,主要分为四大类:
2.1 key-value存储数据库。
该类数据库使用哈希表,在哈希表中包含特定的key和与其对应的指向特定数据的指针。常用的有Redis。
2.2 列存储数据库。
该类数据库主要用来应对分布式存储的海量数据,一个键指向了多个列。常用的有HBase。
2.3 文档型数据库。
该类数据库将结构化、半结构化的文档以特定格式存储,如json格式。一个文档相当于关系型数据库中的一条记录,也是处理信息的基本单位。常用的有MongoDB。
2.4 图形数据库
该类数据库使用图形理论来存储实体之间的关系信息,最主要的组成部分是:结点集、连接节点的关系。常用的有Neo4j,朋友圈社交网络,广告推荐!如脉脉。
非关系型数据库的特点:
1.数据模型比较简单。
2.对数据库性能的要求比较高。
3.不需要高度的数据一致性。
二、Redis入门
1、Redis 是什么?
Redis(Remote Dictionary Server ),即远程字典服务 !
Redis是一个开源(BSD许可),内存数据结构存储,用作数据库,缓存和消息代理。它支持数据结构,如字符串,散列,列表,集合,带有范围查询的排序集,位图,超级日志,具有半径查询和流的地理空间索引。Redis具有内置复制,Lua脚本,LRU驱逐,事务和不同级别的磁盘持久性,并通过Redis Sentinel和Redis Cluster自动分区。您可以对这些类型运行原子操作,例如附加到字符串;递增哈希值;将元素推送到列表中;计算集合交集, 并集和差异;或者在排序集中获得排名最高的成员。
为了实现其出色的性能,Redis使用内存数据集。根据您的使用情况,您可以通过 每隔一段时间将数据集转储到磁盘或通过将每个命令附加到日志来保留它。如果您只需要功能丰富的网络内存缓存,则可以选择禁用持久性。
Redis还支持简单到设置的主从异步复制,具有非常快速的非阻塞第一次同步,自动重新连接以及在网络分割上的部分重新同步。其他功能包括:交易发布/订阅、Lua脚本、钥匙的生存时间有限、LRU逐出钥匙、自动故障转移
您可以使用大多数编程语言中的Redis。Redis是用ANSI C编写的,适用于大多数POSIX系统,如Linux,* BSD,OS X,没有外部依赖性。Linux和OS X是Redis开发和测试的两个操作系统,我们建议使用Linux进行部署。
Redis推荐都是在Linux服务器上搭建的,我们是基于Linux学习!
2、Windows安装
1、下载安装包:https://github.com/dmajkic/redis/releases
2、下载完毕得到压缩包:
3、解压到自己电脑上的环境目录下的就可以的!Redis 十分的小,只有5M
4、开启Redis,双击运行服务即可!
5、使用redis客户单来来连接redis!
3、Linux安装
1、安装编译环境 yum install gcc-c++
2、上传源码包到linux 服务器上;我已经上传到了root目录下:
/opt/software/redis-5.0.5.tar.gz
tar -xzvf redis-5.0.5.tar.gz
3、make
这里可以直接make 是因为redis已经自己写好了make file 了;也就是说不用再执行configure 了、make 后编译好的文件会保存到src目录下
cd /opt/software/redis-5.0.5
make
ll
总用量 196
-rw-rw-r-- 1 root root 75147 8月 2 17:00 00-RELEASENOTES
-rw-rw-r-- 1 root root 53 8月 2 17:00 BUGS
-rw-rw-r-- 1 root root 1805 8月 2 17:00 CONTRIBUTING
-rw-rw-r-- 1 root root 1487 8月 2 17:00 COPYING
drwxrwxr-x 7 root root 4096 9月 17 18:38 deps
-rw-rw-r-- 1 root root 11 8月 2 17:00 INSTALL
-rw-rw-r-- 1 root root 151 8月 2 17:00 Makefile
-rw-rw-r-- 1 root root 4223 8月 2 17:00 MANIFESTO
-rw-rw-r-- 1 root root 6834 8月 2 17:00 README.md
-rw-rw-r-- 1 root root 46695 8月 2 17:00 redis.conf
-rwxrwxr-x 1 root root 271 8月 2 17:00 runtest
-rwxrwxr-x 1 root root 280 8月 2 17:00 runtest-cluster
-rwxrwxr-x 1 root root 281 8月 2 17:00 runtest-sentinel
-rw-rw-r-- 1 root root 7109 8月 2 17:00 sentinel.conf
drwxrwxr-x 2 root root 4096 9月 17 18:39 src
drwxrwxr-x 10 root root 4096 8月 2 17:00 tests
drwxrwxr-x 7 root root 4096 8月 2 17:00 utils
4、make install
这一步会把src 目录下的二进制文件复制到/usr/local/bin/ 目录下;由于把文件保存到/usr/local/bin/目录下的方式不方便管理,于是我们把文件统一保存到
/usr/local/redis/bin/目录下
mkdir -p /usr/local/redis/bin/
cd src
cp redis-benchmark redis-check-aof redis-check-rdb redis-cli redis-sentinel redis-server redis-trib.rb /usr/local/redis/bin/
可以和一起 make & make install
5、修改环境变量
export PATH=/usr/local/redis/bin:$PATH
6、启动redis
redis-server
7、启动客户端
redis-cli
注意:
这样启动后有限制
1、启动服务时,会导致页面卡住,所以需要配置后天启动。
2、其他ip地址无法访问,要放开权限。
3、阿里云不安全,需要设置一个密码,这就牵扯到修改配置文件
7、将配置文件也移动至该目录
cp /opt/software/redis-5.0.5/redis.conf /usr/local/redis/bin/
8、修改配置文件
protected-mode no
bind 0.0.0.0
//后台
daemonize yes
//找到这个选项,放开注射
requirepass zn123
9、启动
cd /usr/local/redis/bin
./redis-server redis.conf
10、客户端
./redis-cli -h 127.0.0.1 -p 9379 -a 密码
4、测试性能
redis-benchmark 是一个压力测试工具!
官方自带的性能测试工具!
如何查看这些分析呢?
# 测试:100个并发连接 100000请求
redis-benchmark -h localhost -p 6379 -c 100 -n 100000
====== MSET (10 keys) ======
100000 requests completed in 1.45 seconds
100 parallel clients
3 bytes payload
keep alive: 1
66.73% <= 1 milliseconds
99.47% <= 2 milliseconds
99.99% <= 3 milliseconds
100.00% <= 3 milliseconds
68965.52 requests per second 看看美妙处理的请求
二、基础的知识
Redis 是以单线程的形式处理指令的
Redis 是C 语言写的,官方说可以支持 100000+ 的QPS。
redis默认有16个数据库,默认使用的是第0个
几个简单命令玩玩
添加 set name zs
获取 get name
切换数据库 select 4
清除当前数据库 flushdb
清除全部数据库的内容 FLUSHALL
获取所有的 keys *
设置key的过期时间,单位是秒 EXPIRE name 10 #
查看当前key的剩余时间 ttl name
查看该key是否存在 EXISTS name1
移除当前key move name 1
查看这个key类型 type age
三、五大数据类型
如果不会 help @string
1、string(字符串)
127.0.0.1:6379> help @string
APPEND key value
summary: Append a value to a key
since: 2.0.0
BITCOUNT key [start end]
summary: Count set bits in a string
since: 2.6.0
BITFIELD key [GET type offset] [SET type offset value] [INCRBY type offset increment] [OVERFLOW WRAP|SAT|FAIL]
summary: Perform arbitrary bitfield integer operations on strings
since: 3.2.0
BITOP operation destkey key [key ...]
summary: Perform bitwise operations between strings
since: 2.6.0
BITPOS key bit [start] [end]
summary: Find first bit set or clear in a string
since: 2.8.7
'重点'
DECR key
summary: Decrement the integer value of a key by one
since: 1.0.0
DECRBY key decrement
summary: Decrement the integer value of a key by the given number
since: 1.0.0
'重点'
GET key
summary: Get the value of a key
since: 1.0.0
GETBIT key offset
summary: Returns the bit value at offset in the string value stored at key
since: 2.2.0
GETRANGE key start end
summary: Get a substring of the string stored at a key
since: 2.4.0
GETSET key value
summary: Set the string value of a key and return its old value
since: 1.0.0
'重点'
INCR key
summary: Increment the integer value of a key by one
since: 1.0.0
INCRBY key increment
summary: Increment the integer value of a key by the given amount
since: 1.0.0
INCRBYFLOAT key increment
summary: Increment the float value of a key by the given amount
since: 2.6.0
‘原子性操作要么都成功,要么都失败’
MGET key [key ...]
summary: Get the values of all the given keys
since: 1.0.0
MSET key value [key value ...]
summary: Set multiple keys to multiple values
since: 1.0.1
MSETNX key value [key value ...]
summary: Set multiple keys to multiple values, only if none of the keys exist
since: 1.0.1
PSETEX key milliseconds value
summary: Set the value and expiration in milliseconds of a key
since: 2.6.0
'重点'
SET key value [expiration EX seconds|PX milliseconds] [NX|XX]
summary: Set the string value of a key
since: 1.0.0
SETBIT key offset value
summary: Sets or clears the bit at offset in the string value stored at key
since: 2.2.0
'重点'
SETEX key seconds value
summary: Set the value and expiration of a key
since: 2.0.0
'重点'
SETNX key value
summary: Set the value of a key, only if the key does not exist
since: 1.0.0
SETRANGE key offset value
summary: Overwrite part of a string at key starting at the specified offset
since: 2.2.0
STRLEN key
summary: Get the length of the value stored in a key
since: 2.2.0
127.0.0.1:6379> set user:2 aaa ex 30 nx
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> ttl user:2
(integer) 28
127.0.0.1:6379>
127.0.0.1:6379> set user zhangsan
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> setrange user 4 lisi
(integer) 8
127.0.0.1:6379> get user
"zhanlisi"
计数器(pv页面浏览量,阅读数等)
对象缓存存储,一般是将对象转化为json字符串进行存储
全局id
2、List(列表)
127.0.0.1:6379> help @list
BLPOP key [key ...] timeout
summary: Remove and get the first element in a list, or block until one is available
since: 2.0.0
BRPOP key [key ...] timeout
summary: Remove and get the last element in a list, or block until one is available
since: 2.0.0
BRPOPLPUSH source destination timeout
summary: Pop a value from a list, push it to another list and return it; or block until one is available
since: 2.2.0
LINDEX key index
summary: Get an element from a list by its index
since: 1.0.0
LINSERT key BEFORE|AFTER pivot value
summary: Insert an element before or after another element in a list
since: 2.2.0
LLEN key
summary: Get the length of a list
since: 1.0.0
LPOP key
summary: Remove and get the first element in a list
since: 1.0.0
LPUSH key value [value ...]
summary: Prepend one or multiple values to a list
since: 1.0.0
LPUSHX key value
summary: Prepend a value to a list, only if the list exists
since: 2.2.0
LRANGE key start stop
summary: Get a range of elements from a list
since: 1.0.0
LREM key count value
summary: Remove elements from a list
since: 1.0.0
LSET key index value
summary: Set the value of an element in a list by its index
since: 1.0.0
LTRIM key start stop
summary: Trim a list to the specified range
since: 1.0.0
RPOP key
summary: Remove and get the last element in a list
since: 1.0.0
RPOPLPUSH source destination
summary: Remove the last element in a list, prepend it to another list and return it
since: 1.2.0
RPUSH key value [value ...]
summary: Append one or multiple values to a list
since: 1.0.0
RPUSHX key value
summary: Append a value to a list, only if the list exists
since: 2.2.0
1、消息队列
list类型的lpop和rpush(或者反过来,lpush和rpop)能实现队列的功能,故而可以用Redis的list类型实现简单的点对点的消息队列。不过我不推荐在实战中这么使用,因为现在已经有Kafka、NSQ、RabbitMQ等成熟的消息队列了,它们的功能已经很完善了,除非是为了更深入地理解消息队列,不然我觉得没必要去重复造轮子。
2. 最新列表(例如评论)
list类型的lpush命令和lrange命令能实现最新列表的功能,每次通过lpush命令往列表里插入新的元素,然后通过lrange命令读取最新的元素列表,如朋友圈的点赞列表、评论列表。
3、Set(集合)
set中的值是不能重读的!
SADD key member [member ...]
summary: Add one or more members to a set
since: 1.0.0
SCARD key
summary: Get the number of members in a set
since: 1.0.0
SDIFF key [key ...]
summary: Subtract multiple sets
since: 1.0.0
SDIFFSTORE destination key [key ...]
summary: Subtract multiple sets and store the resulting set in a key
since: 1.0.0
SINTER key [key ...]
summary: Intersect multiple sets
since: 1.0.0
SINTERSTORE destination key [key ...]
summary: Intersect multiple sets and store the resulting set in a key
since: 1.0.0
SISMEMBER key member
summary: Determine if a given value is a member of a set
since: 1.0.0
SMEMBERS key
summary: Get all the members in a set
since: 1.0.0
SMOVE source destination member
summary: Move a member from one set to another
since: 1.0.0
SPOP key [count]
summary: Remove and return one or multiple random members from a set
since: 1.0.0
SRANDMEMBER key [count]
summary: Get one or multiple random members from a set
since: 1.0.0
SREM key member [member ...]
summary: Remove one or more members from a set
since: 1.0.0
SSCAN key cursor [MATCH pattern] [COUNT count]
summary: Incrementally iterate Set elements
since: 2.8.0
SUNION key [key ...]
summary: Add multiple sets
since: 1.0.0
127.0.0.1:6379> sscan singer2 0 match z*
1) "0"
2) 1) "zhoujie"
2) "zhoujielun"
SUNIONSTORE destination key [key ...]
summary: Add multiple sets and store the resulting set in a key
since: 1.0.0
案例:在微博中,可以将一个用户所有的关注人存在一个集合中,将其所有粉丝存在一个集合。Redis还为集合提供了求交集、并集、差集等操作,可以非常方便的实现如共同关注 功能
spop抽奖小程序
4、Hash(哈希)
Map集合,key-map! 时候这个值是一个map集合! 本质和String类型没有太大区别,还是一个简单的key-vlaue!
hash特别适合用于存储对象(应为对象可能会包含很多属性),特别是对象中有字段经常被修改。
删除
HDEL
key field [field ...]
summary: Delete one or more hash fields
since: 2.0.0
-------------------------------------
判断一个字段是否存在
HEXISTS
key field
summary: Determine if a hash field exists
since: 2.0.0
-------------------------------------
获得一个字段
HGET
key field
summary: Get the value of a hash field
since: 2.0.0
HGETALL key
summary: Get all the fields and values in a hash
since: 2.0.0
HINCRBY key field increment
summary: Increment the integer value of a hash field by the given number
since: 2.0.0
HINCRBYFLOAT key field increment
summary: Increment the float value of a hash field by the given amount
since: 2.6.0
HKEYS key
summary: Get all the fields in a hash
since: 2.0.0
HLEN key
summary: Get the number of fields in a hash
since: 2.0.0
HMGET key field [field ...]
summary: Get the values of all the given hash fields
since: 2.0.0
HMSET key field value [field value ...]
summary: Set multiple hash fields to multiple values
since: 2.0.0
HSCAN key cursor [MATCH pattern] [COUNT count]
summary: Incrementally iterate hash fields and associated values
since: 2.8.0
HSET key field value
summary: Set the string value of a hash field
since: 2.0.0
HSETNX key field value
summary: Set the value of a hash field, only if the field does not exist
since: 2.0.0
HSTRLEN key field
summary: Get the length of the value of a hash field
since: 3.2.0
HVALS key
summary: Get all the values in a hash
since: 2.0.0
5、zset(有序集合)
help @sorted_set
BZPOPMAX key [key ...] timeout
summary: Remove and return the member with the highest score from one or more sorted sets, or block until one is available
since: 5.0.0
从一个或多个已排序集合或块中移除并返回得分最高的成员,直到有一个可用为止
参数 timeout 可以理解为客户端被阻塞的最大秒数值,0 表示永久阻塞。
BZPOPMIN key [key ...] timeout
summary: Remove and return the member with the lowest score from one or more sorted sets, or block until one is available
since: 5.0.0
从一个或多个已排序集或块中移除并返回分数最低的成员,直到有一个可用为止
-------------------------------------
添加
ZADD
key [NX|XX] [CH] [INCR] score member [score member ...]
summary: Add one or more members to a sorted set, or update its score if it already exists
since: 1.2.0
ZCARD key
summary: Get the number of members in a sorted set
since: 1.2.0
ZCOUNT key min max
summary: Count the members in a sorted set with scores within the given values
since: 2.0.0
-------------------------------------
增加分数
ZINCRBY
key increment member
summary: Increment the score of a member in a sorted set
since: 1.2.0
-------------------------------------
获取交集并存储
ZINTERSTORE
destination numkeys key [key ...] [WEIGHTS weight] [AGGREGATE SUM|MIN|MAX]
summary: Intersect multiple sorted sets and store the resulting sorted set in a new key
since: 2.0.0
交叉多个排序集,并将结果排序集存储在一个新的键中
-------------------------------------
按照字典序拿到响应的value
zlexcount movie:top10 [a [z
ZLEXCOUNT
key min max
summary: Count the number of members in a sorted set between a given lexicographical range
since: 2.8.9
计算给定字典法范围之间已排序集合中的成员数 [a [b
-------------------------------------
弹出最大返回并删除
ZPOPMAX
key [count]
summary: Remove and return members with the highest scores in a sorted set
since: 5.0.0
-------------------------------------
最小
ZPOPMIN
key [count]
summary: Remove and return members with the lowest scores in a sorted set
since: 5.0.0
-------------------------------------
根据下标从第几个到第几个
ZRANGE
key start stop [WITHSCORES]
summary: Return a range of members in a sorted set, by index
since: 1.2.0
ZRANGEBYLEX
key min max [LIMIT offset count]
summary: Return a range of members in a sorted set, by lexicographical range
since: 2.8.9
-------------------------------------
拿到一个范围内的数据
ZRANGEBYSCORE
key min max [WITHSCORES] [LIMIT offset count]
summary: Return a range of members in a sorted set, by score
since: 1.0.5
-------------------------------------
排序
ZRANK
key member
summary: Determine the index of a member in a sorted set
since: 2.0.0
确定排序集合中成员的索引
-------------------------------------
删除
ZREM
key member [member ...]
summary: Remove one or more members from a sorted set
since: 1.2.0
ZREMRANGEBYLEX key min max
summary: Remove all members in a sorted set between the given lexicographical range
since: 2.8.9
lexicographical:字典序
-------------------------------------
根据序号删除
ZREMRANGEBYRANK
key start stop
summary: Remove all members in a sorted set within the given indexes
since: 2.0.0
-------------------------------------
删除规定范围内的内容
ZREMRANGEBYSCORE
key min max
summary: Remove all members in a sorted set within the given scores
since: 1.2.0
-------------------------------------
返回一个范围
ZREVRANGE
key start stop [WITHSCORES]
summary: Return a range of members in a sorted set, by index, with scores ordered from high to low
since: 1.2.0
ZREVRANGEBYLEX key max min [LIMIT offset count]
summary: Return a range of members in a sorted set, by lexicographical range, ordered from higher to lower strings.
since: 2.8.9
ZREVRANGEBYSCORE key max min [WITHSCORES] [LIMIT offset count]
summary: Return a range of members in a sorted set, by score, with scores ordered from high to low
since: 2.2.0
ZREVRANK key member
summary: Determine the index of a member in a sorted set, with scores ordered from high to low
since: 2.0.0
ZSCAN key cursor [MATCH pattern] [COUNT count]
summary: Incrementally iterate sorted sets elements and associated scores
since: 2.8.0
ZSCORE key member
summary: Get the score associated with the given member in a sorted set
since: 1.2.0
获取排序集中与给定成员相关的分数
ZUNIONSTORE destination numkeys key [key ...] [WEIGHTS weight] [AGGREGATE SUM|MIN|MAX]
summary: Add multiple sorted sets and store the resulting sorted set in a new key
since: 2.0.0
添加多个排序集,并将结果排序集存储到一个新键中
案例思路:set 排序 存储班级成绩表,工资表排序!
普通消息,1, 重要消息 2,带权重进行判断!
排行榜应用实现,取Top N 测试!
redis中list set zset的区别
| 数据结构 | 是否可重复 | 是否有序 | 应用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 列表 | 是 | 是 | 时间轴、队列 |
| 集合 | 否 | 否 | 标签、社交 |
| 有序集合 | 否 | 是 | 排行榜系统、社交 |
四、其他数据类型
1、bitmap 位图
公司记录某个人一个月的打卡情况
一年365天怎么记录一个人在某个网站的登录,活跃情况
两个状态的都能用这种方法进行性能压榨
help @string
都是操作二进制位来进行记录,就只有0 和 1 两个状态!
365 天 = 365 bit 1字节 = 8bit 46 个字节左右!
测试登录次数
127.0.0.1:6379> setbit login 0 1
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> setbit login 3 1
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> bitcount login
(integer) 2
周一:1 周二:0 周三:0 周四:1 ......
查看某一天是否有打卡!
统计操作,统计 打卡的天数!
2、Geospatial 地理位置
127.0.0.1:6379> help @geo
GEOADD key longitude latitude member [longitude latitude member ...]
summary: Add one or more geospatial items in the geospatial index represented using a sorted set
since: 3.2.0
GEODIST key member1 member2 [unit]
summary: Returns the distance between two members of a geospatial index
since: 3.2.0
GEOHASH key member [member ...]
summary: Returns members of a geospatial index as standard geohash strings
since: 3.2.0
GEOPOS key member [member ...]
summary: Returns longitude and latitude of members of a geospatial index
since: 3.2.0
GEORADIUS key longitude latitude radius m|km|ft|mi [WITHCOORD] [WITHDIST] [WITHHASH] [COUNT count] [ASC|DESC] [STORE key] [STOREDIST key]
summary: Query a sorted set representing a geospatial index to fetch members matching a given maximum distance from a point
since: 3.2.0
GEORADIUSBYMEMBER key member radius m|km|ft|mi [WITHCOORD] [WITHDIST] [WITHHASH] [COUNT count] [ASC|DESC] [STORE key] [STOREDIST key]
summary: Query a sorted set representing a geospatial index to fetch members matching a given maximum distance from a member
since: 3.2.0
朋友的定位,附近的人,打车距离计算?
在Redis3.2 版本推出了Geospatial ! 这个功能可以推算地理位置的信息,两地之间的距离。
可以查询一些测试数据:http://www.jsons.cn/lngcodeinfo/0706D99C19A781A3/
给定几个城市的经纬度:
太原:112.549248,37.857014
北京:116.405285,39.904989
成都:104.065735,30.659462
武汉:114.298572,30.584355
西安: 108.948024,34.263161
洛阳:112.434468,34.663041
getadd
# getadd 添加地理位置
# 规则:两级无法直接添加,我们一般会下载城市数据,直接通过java程序一次性导入!
# 有效的经度从-180度到180度。
# 有效的纬度从-85.05112878度到85.05112878度。
# 当坐标位置超出上述指定范围时,该命令将会返回一个错误。
# 127.0.0.1:6379> geoadd china:city 39.90 116.40 beijing
(error) ERR invalid longitude,latitude pair 39.900000,116.400000
# 参数 key 值()
#插入城市的经纬度
127.0.0.1:6379> geoadd china:city 112.549284 37.857014 taiyuan
127.0.0.1:6379> geoadd china:city 116.405285 39.904989 beijing
127.0.0.1:6379> geoadd china:city 104.065735 30.659462 chengdu
127.0.0.1:6379> geoadd china:city 114.298572 30.584355 wuhan
127.0.0.1:6379> geoadd china:city 108.948024 34.263161 xian
127.0.0.1:6379> geoadd china:city 112.434468 34.663041 luoyang
# 获取指定的城市的经度和纬度!
127.0.0.1:6379> geopos china:city beijing
1) 1) "116.40528291463851929"
2) "39.9049884229125027"
127.0.0.1:6379> geopos china:city beijing luoyang
1) 1) "116.40528291463851929"
2) "39.9049884229125027"
2) 1) "112.43446558713912964"
2) "34.6630405862934694"
#两人之间的距离!
#单位:
#m 表示单位为米。
#km 表示单位为千米。
#mi 表示单位为英里。
#ft 表示单位为英尺。
#georadius 以给定的经纬度为中心, 找出某一半径内的元素
#我附近的人? (获得所有附近的人的地址,定位!)通过半径来查询!
#获得指定数量的人,200
#所有数据应该都录入:china:city ,才会让结果更加请求!
#查询太原到北京的距离
127.0.0.1:6379> geodist china:city beijing taiyuan
"404109.2735"
127.0.0.1:6379> geodist china:city beijing taiyuan km
"404.1093"
#找某个地点(微信定位)方圆1000km内的城市,附近的朋友
127.0.0.1:6379> georadius china:city 110 32 500 km
1) "xian"
2) "luoyang"
3) "wuhan"
# 找出位于指定元素周围的其他元素!
127.0.0.1:6379> GEORADIUSBYMEMBER china:city beijing 1000 km
1) "taiyuan"
2) "beijing"
3) "xian"
4) "luoyang"
# 查看地图中全部的元素
127.0.0.1:6379> ZRANGE china:city 0 -1
1) "chengdu"
2) "xian"
3) "luoyang"
4) "wuhan"
5) "taiyuan"
6) "beijing"
# 移除指定元素!
127.0.0.1:6379> zrem china:city beijing
(integer) 1
3、 Hyperloglog(基数)-- 拓展不学
关于这个算法的一个博客:https://www.jianshu.com/p/55defda6dcd2
场景如网页的 UV (一个人访问一个网站多次,但是还是算作一个人!)
通过使用一种特殊的算法,而达到使用一个固定空间达到统计基数的作用。
这种算法有误差,是一种概率学问题。0.81% 错误率! 但对于统计UV这类的任务,是可以忽略不计的!
测试使用
如果允许有误差,那么一定可以使用 Hyperloglog !
如果不允许误差,就使用 set 或者自己的数据类型即可!
127.0.0.1:6379> help @hyperloglog
PFADD key element [element ...]
summary: Adds the specified elements to the specified HyperLogLog.
since: 2.8.9
PFCOUNT key [key ...]
summary: Return the approximated cardinality of the set(s) observed by the HyperLogLog at key(s).
since: 2.8.9
PFMERGE destkey sourcekey [sourcekey ...]
summary: Merge N different HyperLogLogs into a single one.
since: 2.8.9
127.0.0.1:6379> pfadd pf a b c d e f g
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> pfadd pf2 c d e f g
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> pfcount pf pf2
(integer) 7
127.0.0.1:6379> pfmerge a pf pf2
OK
五、持久化(面试重点)
不是所有的redis都要持久化
某些情况我们只需要当做缓存使用就可以不持久化,比如当热点数据的缓存,session的共享等。
只做缓存,如果你只希望你的数据在服务器运行的时候存在,你也可以不使用任何持久化
两种思路一种思路存数据,一种思路存命令日志。
1、RDB(Redis DataBase)
在指定的时间间隔内将内存中的数据集快照写入磁盘,也就是行话讲的Snapshot快照,它恢复时是将快
照文件直接读到内存里。
Redis会单独创建(fork)一个子进程来进行持久化,会先将数据写入到一个临时文件中,待持久化过程
都结束了,再用这个临时文件替换上次持久化好的文件。整个过程中,主进程是不进行任何IO操作的。
rdb保存的文件是dump.rdb 都是在我们的配置文件中快照中进行配置的!
a、触发机制
1、save的规则满足的情况下,会自动触发rdb规则
2、执行save, flushall 命令,也会触发我们的rdb规则!
3、退出redis,也会产生 rdb 文件!
备份就自动生成一个 dump.rdb
b、恢复rdb文件
1、只需要将rdb文件放在我们redis启动目录就可以,redis启动的时候会自动检查dump.rdb 恢复其中
的数据!
2、查看需要存在的位置
优点:
1、适合大规模的数据恢复!
2、对数据的完整性要不高!
缺点:
如果redis意外宕机了,这个最后一次修改数据就没有的了!只能保留到最后一个的save的地方。
2、AOF(Append Only File)
其实就是记录日志
将我们的所有命令都记录下来,
恢复的时候就把这个文件中的命令全部在执行一遍!
127.0.0.1:6379> config get dir
1) "dir"
2) "/usr/local/bin"
# 如果在这个目录下存在 dump.rdb 文件,启动就会自动恢复其中的数据
以日志的形式来记录每个写操作,将Redis执行过的所有指令记录下来(读操作不记录),只许追加文件,但不可以改写文件,redis启动之初会读取该文件重新构建数据,换言之,redis重启的话就根据日志文件的内容将写指令从前到后执行一次以完成数据的恢复工作。
aof保存的是 appendonly.aof 文件
默认是不开启的,我们需要手动进行配置!
appendonly yes
重启,redis 就可以生效了!
如果这个 aof 文件有错位,这时候 redis 是启动不起来的吗,我们需要修复这个aof文件
redis 给我们提供了一个工具 redis-check-aof --fix
如果文件正常,重启就可以直接恢复了!
aof 默认就是文件的无限追加,文件会越来越大!
如果 aof 文件大于 64m,太大了!redis会将文件进行重写!重写是绝对安全的!
优点:
1、每一次修改都同步,文件的完整会更加好! 可以设置
2、每秒同步一次,可能会丢失一秒的数据! 默认
3、从不同步,效率最高的!
缺点:
1、相对于数据文件来说,aof远远大于 rdb,修复的速度也比 rdb慢!
2、Aof 运行效率也要比 rdb 慢,所以我们redis默认的配置就是rdb持久化!
性能建议
因为RDB文件只用作后备用途,建议只在Slave上持久化RDB文件,而且只要15分钟备份一次就够
了。
如果Enable AOF ,好处是在最恶劣情况下也只会丢失不超过两秒数据,启动脚本较简单只load自
己的AOF文件就可以了,代价一是带来了持续的IO,二是AOF rewrite 的最后将 rewrite 过程中产
生的新数据写到新文件造成的阻塞几乎是不可避免的。
只要硬盘许可,应该尽量减少AOF rewrite的频率,AOF重写的基础大小默认值64M太小了,可以设到5G以上,,默认超过原大小100%大小重写可以改到适当的数值。
如果不Enable AOF ,仅靠 Master-Slave Repllcation 实现高可用性也可以,能省掉一大笔IO,也
减少了rewrite时带来的系统波动。代价是如果Master/Slave 同时挂了,会丢失十几分钟的数据,
启动脚本也要比较两个 Master/Slave 中的 RDB文件,载入较新的那个,微博就是这种架构。
六、事务
Redis 事务其实是一组命令的集合!
一个事务中的所有命令都会被序列化,在事务执行过程的中,会按照顺序执行!
Redis事务没有没有隔离级别的概念,和单线程也有关系!
所有的命令在事务中,并没有直接被执行!只有发起执行命令的时候才会执行!Exec
Redis单条命令式保存原子性的,但是事务不保证原子性!
redis的事务:
#开启事务
127.0.0.1:6379> multi
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> set a a
QUEUED
127.0.0.1:6379> set b b
QUEUED
127.0.0.1:6379> get a
QUEUED
127.0.0.1:6379> get b
QUEUED
#执行
127.0.0.1:6379> exec
1) OK
2) OK
3) "a"
4) "b"
127.0.0.1:6379>
六、集群搭建
1、主从复制概述
是指将一台Redis服务器的数据,复制到其他的Redis服务器。前者称为主节点(master/leader),后者称为从节点(slave/follower);数据的复制是单向的,只能由主节点到从节点。
Master以写为主,Slave 以读为主。
默认情况下,每台Redis服务器都是主节点;
且一个主节点可以有多个从节点(或没有从节点),但一个从节点只能有一个主节点。()
主从复制的作用主要包括:
1、数据冗余:主从复制实现了数据的热备份,是持久化之外的一种数据冗余方式。
2、故障恢复:当主节点出现问题时,可以由从节点提供服务,实现快速的故障恢复;实际上是一种服务
的冗余。
3、负载均衡:在主从复制的基础上,配合读写分离,可以由主节点提供写服务,由从节点提供读服务
(即写Redis数据时应用连接主节点,读Redis数据时应用连接从节点),分担服务器负载;尤其是在写
少读多的场景下,通过多个从节点分担读负载,可以大大提高Redis服务器的并发量。
4、高可用(集群)基石:除了上述作用以外,主从复制还是哨兵和集群能够实施的基础,因此说主从复
制是Redis高可用的基础。
一般来说,要将Redis运用于工程项目中,只使用一台Redis是万万不能的(宕机),原因如下:
1、从结构上,单个Redis服务器会发生单点故障,并且一台服务器需要处理所有的请求负载,压力较
大;
2、从容量上,单个Redis服务器内存容量有限,就算一台Redis服务器内存容量为256G,也不能将所有
内存用作Redis存储内存,一般来说,单台Redis最大使用内存不应该超过20G。
电商网站上的商品,一般都是一次上传,无数次浏览的,说专业点也就是"多读少写"。
对于这种场景,我们可以使如下这种架构:
主从复制,读写分离! 80% 的情况下都是在进行读操作!减缓服务器的压力!架构中经常使用!
2、一主二从设计
三台linux准备好,也可以一台机子搭建伪分布式,使用不同端口,怎么修改端口自己查
主redis 101.200.48.99
从redis 39.97.162.205
从redis 39.106.113.48
在3台linux都装好redis,参考: Redis单机安装
方式1:修改配置文件
启动时,服务器读取配置文件,并自动成为指定服务器的从服务器,从而构成主从复制的关系
在从机器上修改从redis的配置,其他(默认配置)配置略过
slaveof 101.200.48.99 6379
masterauth zn123
将redis依次启动
登录主redis客户端
[root@iZ2ze6e6csc6upi9p8vZ bin]# ./redis-cli -a zn123
Warning: Using a password with '-a' or '-u' option on the command line interface may not be safe.
127.0.0.1:6379> info replication
# Replication
role:master
connected_slaves:2
slave0:ip=39.106.113.48,port=6379,state=online,offset=168,lag=1
slave1:ip=39.97.162.205,port=6379,state=online,offset=154,lag=1
master_replid:e341f44d2e365650e9e94738c79c92dcd7d27cc5
master_replid2:0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
master_repl_offset:168
second_repl_offset:-1
repl_backlog_active:1
repl_backlog_size:1048576
repl_backlog_first_byte_offset:1
repl_backlog_histlen:168
向主redis写入数据,flushall清空数据,避免干扰
127.0.0.1:6379> set name zhangnan
OK
从redis都可以读到数据库
127.0.0.1:6379> get name
"zhangnan"
向从redis写入数据失败,默认slave-read-only yes,如果为no则可以向从写数据
127.0.0.1:6379> set age 12
(error) READONLY You can't write against a read only replica.
方式2:启动命令添加
./redis-server --slaveof 101.200.48.99 6379 --masterauth zn123
在启动redis时指定当前服务成为某个主Redis服务的从Slave
手动容灾处理
当Master服务出现故障,需手动将slave中的一个提升为master, 剩下的slave挂至新的master上(冷处理:机器挂掉了,再处理)
命令:
将主redis关闭
将39.97.162.205从redis提升为主redis
slaveof no one,将一台slave服务器提升为Master (提升某slave为master)
slaveof 39.97.162.205 6379(将slave挂至新的master上)
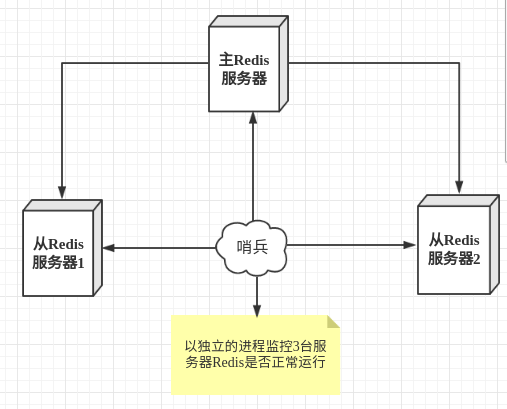
3、哨兵模式
主从切换技术的方法是:当主服务器宕机后,需要手动把一台从服务器切换为主服务器,这就需要人工干预,费事费力,还会造成一段时间内服务不可用。这不是一种推荐的方式,更多时候,我们优先考虑哨兵模式。
哨兵模式是一种特殊的模式,首先Redis提供了哨兵的命令,哨兵是一个独立的进程,作为进程,它会独立运行。其原理是哨兵通过发送命令,等待Redis服务器响应,从而监控运行的多个Redis实例。
这里的哨兵有两个作用
- 通过发送命令,让Redis服务器返回监控其运行状态,包括主服务器和从服务器。
- 当哨兵监测到master宕机,会自动将slave切换成master,然后通过发布订阅模式通知其他的从服务器,修改配置文件,让它们切换主机。
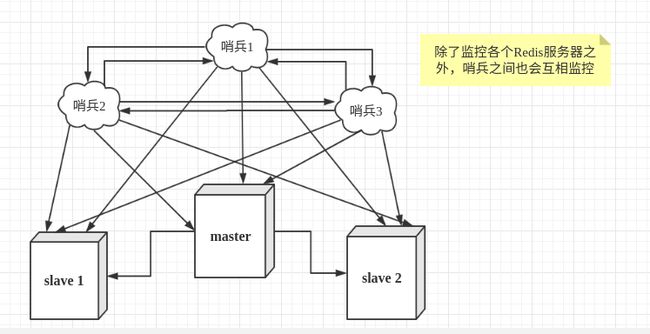
然而一个哨兵进程对Redis服务器进行监控,可能会出现问题,为此,我们可以使用多个哨兵进行监控。各个哨兵之间还会进行监控,这样就形成了多哨兵模式。
用文字描述一下故障切换(failover)的过程。假设主服务器宕机,哨兵1先检测到这个结果,系统并不会马上进行failover过程,仅仅是哨兵1主观的认为主服务器不可用,这个现象成为主观下线。当后面的哨兵也检测到主服务器不可用,并且数量达到一定值时,那么哨兵之间就会进行一次投票,投票的结果由一个哨兵发起,进行failover操作。切换成功后,就会通过发布订阅模式,让各个哨兵把自己监控的从服务器实现切换主机,这个过程称为客观下线。这样对于客户端而言,一切都是透明的。
配置哨兵模式
把哨兵配置文件拷贝一下方便使用
cp /opt/software/redis-5.0.5/sentinel.conf /usr/local/redis/bin/
配置3个哨兵和1主2从的Redis服务器来演示这个过程。
| 服务类型 | 是否是主服务器 | IP地址 | 端口 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Redis | 是 | 101.200.48.99 | 6379 |
| Redis | 否 | 39.97.162.205 | 6379 |
| Redis | 否 | 39.106.113.48 | 6379 |
| Sentinel | - | 101.200.48.99 | 26379 |
| Sentinel | - | 39.97.162.205 | 26379 |
| Sentinel | - | 39.106.113.48 | 26379 |
多哨兵监控Redis
首先配置Redis的主从服务器,修改redis.conf文件如下
# 使得Redis服务器可以跨网络访问
bind 0.0.0.0
# 设置密码
requirepass zn123
# 指定主服务器,注意:有关slaveof的配置只是配置从服务器,主服务器不需要配置
slaveof 101.200.48.99 6379
# 主服务器密码,注意:有关slaveof的配置只是配置从服务器,主服务器不需要配置
masterauth zn123
上述内容主要是配置Redis服务器,从服务器比主服务器多一个slaveof的配置和密码。
配置3个哨兵,每个哨兵的配置都是一样的。在Redis安装目录下有一个sentinel.conf文件,copy一份进行修改
# 禁止保护模式
protected-mode no
# 配置监听的主服务器,这里sentinel monitor代表监控,mymaster代表服务器的名称,可以自定义,192.168.11.128代表监控的主服务器,6379代表端口,2代表只有两个或两个以上的哨兵认为主服务器不可用的时候,才会进行failover操作。
sentinel monitor mymaster 101.200.48.99 6379 2
# sentinel author-pass定义服务的密码,mymaster是服务名称,123456是Redis服务器密码
# sentinel auth-pass
sentinel auth-pass mymaster zn123
#将配置文件拷贝到其他的机子上
scp [email protected]:/usr/local/redis/bin/sentinel.conf /usr/local/redis/bin/
上述关闭了保护模式,便于测试。
有了上述的修改,我们可以进入Redis的安装目录的src目录,通过下面的命令启动服务器和哨兵
# 启动Redis服务器进程
./redis-server redis.conf
# 启动哨兵进程
./redis-sentinel sentinel.conf
注意启动的顺序。首先是主机(101.200.48.99)的Redis服务进程,然后启动从机的服务进程,最后启动3个哨兵的服务进程。
七、缓存穿透、击穿和雪崩
1、缓存穿透
在高并发下,查询一个不存在的值时,缓存不会被命中,导致大量请求直接落到数据库上,如活动系统里面查询一个不存在的活动。
2、缓存击穿
在高并发下,对一个特定的值进行查询,但是这个时候缓存正好过期了,缓存没有命中,导致大量请求直接落到数据库上,如活动系统里面查询活动信息,但是在活动进行过程中活动缓存突然过期了。行军打仗。
3、缓存雪崩
在高并发下,大量的缓存key在同一时间失效,导致大量的请求落到数据库上,如活动系统里面同时进行着非常多的活动,但是在某个时间点所有的活动缓存全部过期。如redis直接宕机。
4、解决方案
- 直接缓存NULL值
应对缓存穿透最有效的方法是直接缓存NULL值,但是缓存NULL的时间不能太长,否则NULL数据长时间得不到更新,也不能太短,否则达不到防止缓存击穿的效果。浪费空间。
- 限流
应对缓存穿透的常用方法之一是限流,常见的限流算法有滑动窗口,令牌桶算法和漏桶算法,或者直接使用队列、加锁等,在layering-cache里面我主要使用分布式锁来做限流
- 缓存预热
- 缓存永远不过期
- 布隆过滤器-以后同学分享
八、java客户端
maven工程
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clientsgroupId>
<artifactId>jedisartifactId>
<version>3.2.0version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>fastjsonartifactId>
<version>1.2.62version>
dependency>
dependencies>
import org.junit.Test;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
/**
* @author IT楠老师
* @date 2020/5/7
**/
public class RedisTest {
@Test
public void testSet(){
Jedis jedis = new Jedis("101.200.48.99",6379);
jedis.auth("zn123");
jedis.set("name","lilei");
}
@Test
public void testGet(){
Jedis jedis = new Jedis("101.200.48.99",6379);
jedis.auth("zn123");
System.out.println(jedis.get("name"));
}
}
public class TestTX {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Jedis jedis = new Jedis("101.200.48.99", 6379);
jedis.auth("zn123");
JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject();
jsonObject.put("name","nanlaoshi");
jsonObject.put("age","29");
// 开启事务
Transaction multi = jedis.multi();
String userStr = jsonObject.toJSONString();
try {
multi.set("user1",userStr);
multi.set("user2",userStr);
int i = 1/0 ; // 代码抛出异常事务,执行失败!
multi.exec(); // 执行事务!
} catch (Exception e) {
multi.discard(); // 放弃事务
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
System.out.println(jedis.get("user1"));
System.out.println(jedis.get("user2"));
jedis.close(); // 关闭连接
}
}
}
九、redis 发布订阅入门
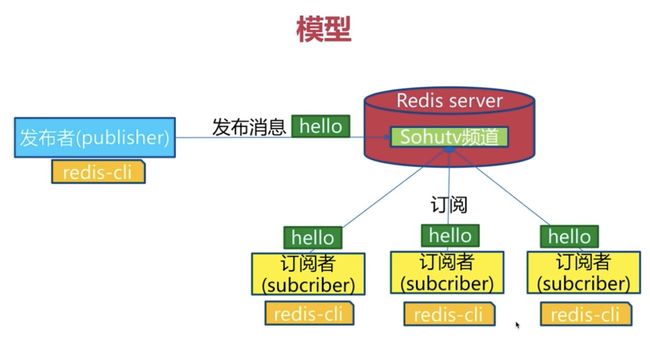
1、发布订阅模式中的角色
- 发布者(publisher)
- 订阅者(subscriber)
- 频道(channel)
如图所示:
发布者发布消息到频道,订阅了频道的订阅者可以收到消息,订阅者可以订阅不同的频道。
2、通信模型
- RedisServer中可以创建若干channel
- 一个订阅者可以订阅多个channel
- 当发布者向一个频道中发布一条消息时,所有的订阅者都将会收到消息
- Redis的发布订阅模型没有消息积压功能,即新加入的订阅者收不到发布者之前发布的消息
- 当订阅者收到消息时,消息内容如下
- 第一行:固定内容message
- 第二行:channel的名称
- 第三行:收到的新消息
4、发布订阅的 API
| 命令 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| publish channel message | 向指定的channel中发布消息 |
| subscribe channel1 [channel2…] | 订阅给定的一个或多个渠道的消息 |
| unsubcribe [channel1 [channel2…]] | 取消订阅给定的一个或多个渠道的消息 |
| pubsub numsub [channel…] | 列出给定频道的订阅者数量 |
5、发布订阅 - Jedis
//订阅
@Test
public void testSubscribe() {
Jedis jedis = new Jedis("101.200.48.99" , 6379);
jedis.auth("zn123");
jedis.subscribe(new JedisPubSub() {
@Override
public void onMessage(String channel, String message) {
System.out.println("receive channel ["+channel+"] message ["+message+"]");
}
} , "aiqiyi" , "TencentTV");
}
//发布
@Test
public void testPublish() {
Jedis jedis = new Jedis("101.200.48.99" , 6379);
jedis.auth("zn123");
jedis.publish("aiqiyi" , "天龙八部上线了!");
jedis.publish("TencentTV" , "笑傲江湖上线了!");
}