LeetCode 第 140 场周赛 【Bigram 分词】【活字印刷】【根到叶路径上的不足节点】【不同字符的最小子序列】
5083. Bigram 分词
给出第一个词 first 和第二个词 second,考虑在某些文本 text 中可能以 “first second third” 形式出现的情况,其中 second 紧随 first 出现,third 紧随 second 出现。
对于每种这样的情况,将第三个词 “third” 添加到答案中,并返回答案。
示例 1:
输入:text = "alice is a good girl she is a good student", first = "a", second = "good"
输出:["girl","student"]
示例 2:
输入:text = "we will we will rock you", first = "we", second = "will"
输出:["we","rock"]
提示:
1 <= text.length <= 1000
text 由一些用空格分隔的单词组成,每个单词都由小写英文字母组成
1 <= first.length, second.length <= 10
first 和 second 由小写英文字母组成
public static String[] findOcurrences(String text, String first, String second) {
List<String> list=new ArrayList<>();
int firstIndex=text.indexOf(first+" ");
while(firstIndex!=-1){
//如果后面紧接是second
int secondIndex=text.indexOf(second,firstIndex+first.length());
if(secondIndex==-1) {
break;
}
int length=secondIndex+second.length();
if(secondIndex!=-1&&length<(text.length()-1)) {
int space=text.indexOf(" ",length+1);
if(space==-1&&(secondIndex==firstIndex+first.length()+1)) {
list.add(text.substring(length+1));
break;
}else if(space!=-1&&(secondIndex==firstIndex+first.length()+1)){
list.add(text.substring(length+1,space));
}
}
firstIndex=text.indexOf(first+" ",firstIndex+first.length());
}
String[] res=new String [list.size()];
for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++) {
res[i]=list.get(i);
System.out.println(res[i]);
}
return res;
}
5087. 活字印刷
你有一套活字字模 tiles,其中每个字模上都刻有一个字母 tiles[i]。返回你可以印出的非空字母序列的数目。
示例 1:
输入:"AAB"
输出:8
解释:可能的序列为 "A", "B", "AA", "AB", "BA", "AAB", "ABA", "BAA"。
示例 2:
输入:"AAABBC"
输出:188
思路:递归回溯!
static boolean[] visit;
static Set<String> result;
private static String thetiles;
public static int numTilePossibilities(String tiles) {
visit = new boolean[tiles.length()];
result = new HashSet<>();
thetiles = tiles;
dfs("", tiles.length());
return result.size();
}
private static void dfs(String now, int left){
if(left == 0){
return ;
}
for(int i = 0; i < thetiles.length(); ++i){
if(!visit[i]){
visit[i] = true;
String t = now + thetiles.charAt(i);
System.out.println("t:"+t);
result.add(t);
dfs(t, left - 1);
visit[i] = false;
}
}
}
5084. 根到叶路径上的不足节点
给定一棵二叉树的根 root,请你考虑它所有 从根到叶的路径:从根到任何叶的路径。(所谓一个叶子节点,就是一个没有子节点的节点)
假如通过节点 node 的每种可能的 “根-叶” 路径上值的总和全都小于给定的 limit,则该节点被称之为「不足节点」,需要被删除。
题详情地址:https://leetcode-cn.com/contest/weekly-contest-140/problems/insufficient-nodes-in-root-to-leaf-paths/
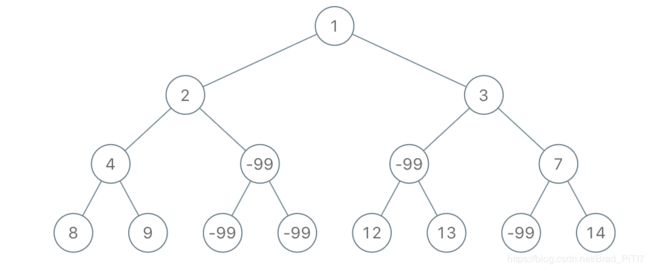
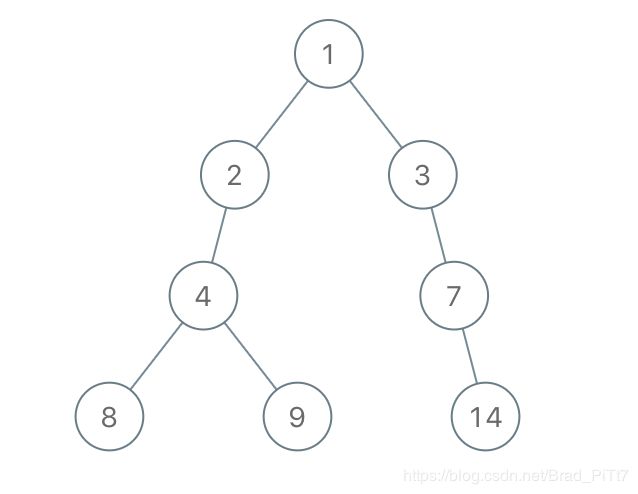
输入:root = [1,2,3,4,-99,-99,7,8,9,-99,-99,12,13,-99,14], limit = 1
输出:[1,2,3,4,null,null,7,8,9,null,14]
public TreeNode sufficientSubset(TreeNode root, int limit) {
HashSet<TreeNode> set = new HashSet<>();
getPathLength(root, limit, 0, set);
if (set.contains(root)) return null;
removeNodes(root, set);
return root;
}
private int getPathLength (TreeNode root, int limit, int current, HashSet<TreeNode> delSet) {
if (root == null) return current;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
if (current + root.val < limit) {
delSet.add(root);
}
return current + root.val;
}
int leftLength = getPathLength(root.left, limit, current + root.val, delSet);
int rightLength = getPathLength(root.right, limit, current + root.val, delSet);
if (leftLength < limit && rightLength < limit) {
delSet.add(root);
}
return leftLength > rightLength ? leftLength : rightLength;
}
private void removeNodes(TreeNode root, HashSet<TreeNode> delSet) {
if (root.left != null) {
if (delSet.contains(root.left)) {
root.left = null;
} else removeNodes(root.left, delSet);
}
if (root.right != null) {
if (delSet.contains(root.right)) {
root.right = null;
} else removeNodes(root.right, delSet);
}
}
5086. 不同字符的最小子序列
返回字符串 text 中按字典序排列最小的子序列,该子序列包含 text 中所有不同字符一次。
示例 1:
输入:"cdadabcc"
输出:"adbc"
示例 2:
输入:"abcd"
输出:"abcd"
示例 3:
输入:"ecbacba"
输出:"eacb"
示例 4:
输入:"leetcode"
输出:"letcod"
提示:
1 <= text.length <= 1000
text 由小写英文字母组成
刚开始想用先求出全排列,然后字典排序,最后依次判定是否为子序列,但是不能通过所有的测试用例,会运算超时。
public static String smallestSubsequence(String text) {
Set<Character> set = new HashSet<>();
// List listpermute=new ArrayList<>();
for (char c : text.toCharArray()) {
set.add(c);
}
char[] nums = new char[set.size()];
int count = 0;
for (char c : set) {
nums[count++] = c;
}
List<String> res = permute(nums);
Collections.sort(res);
// System.out.println(res);
for (String tmp : res) {
// System.out.println("tmp:"+tmp);
if (isSubstr(text, tmp)) {
return tmp;
}
}
return "";
}
private static boolean isSubstr(String s, String target) {
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (i < s.length() && j < target.length()) {
if (s.charAt(i) == target.charAt(j)) {
j++;
}
i++;
}
return j == target.length();
}
public static List<String> permute(char[] nums) {
List<String> res = new ArrayList<>();
List<Character> permuteList = new ArrayList<>();
boolean[] hasVisited = new boolean[nums.length];
backtracking(permuteList, res, hasVisited, nums);
return res;
}
private static void backtracking(List<Character> permuteList, List<String> res, boolean[] visited,
final char[] nums) {
if (permuteList.size() == nums.length) {
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
for(char c:permuteList) {
result.append(c);
}
res.add(result.toString()); // 重新构造一个 List
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < visited.length; i++) {
if (visited[i]) {
continue;
}
visited[i] = true;
permuteList.add(nums[i]);
backtracking(permuteList, res, visited, nums);
permuteList.remove(permuteList.size() - 1);
visited[i] = false;
}
}
不超时解法:
public String smallestSubsequence(String text) {
char[] chars = text.toCharArray();
int[] charsIndex = new int[26];
Arrays.fill(charsIndex, -1);
int count = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
if (charsIndex[(int)(chars[i] - 'a')] == -1) {
charsIndex[(int)(chars[i] - 'a')] = i;
count++;
}
}
char[] s = new char[count];
int[] start = new int[count + 1];
for(int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < 26; j++) {
if (charsIndex[j] >= 0) {
int checkCount = i;
boolean[] has = new boolean[26];
for(int t = 0; t < i; t++) {
has[s[t] - 'a'] = true;
}
boolean startEnable = false;
for(int k = i > 0 ? start[i - 1] : 0; k < chars.length; k++) {
int asc = chars[k] - 'a';
if (!startEnable && asc == j && !has[asc] ) {
startEnable = true;
has[j] = true;
checkCount ++;
start[i] = k + 1;
}
if (startEnable && !has[asc]) {
checkCount++;
has[asc] = true;
}
if (checkCount == count) {
break;
}
}
if (checkCount == count) {
s[i] = (char)('a' + j);
break;
}
}
}
}
return new String(s);
}