Unity三维数学 ——— 向量Vector、三角函数
一、Unity 中的向量
1、向量的长度
public class sc03 : MonoBehaviour
{
// Update is called once per frame
void Update () {
Demo1();
}
void Demo1()
{
// 获取当前物体的空间坐标
Vector3 pos1 = transform.position;
//计算当前向量模长的三种方法
float m01 = Mathf.Sqrt(Mathf.Pow(pos1.x, 2) + Mathf.Pow(pos1.y, 2) + Mathf.Pow(pos1.z, 2));//Method1
float m02 = pos1.magnitude;//Method2-----Unity Provide
float m03 = Vector3.Distance(Vector3.zero, pos1);//Method3
Debug.LogFormat("{0}-----{1}-----{2}", m01, m02, m03);
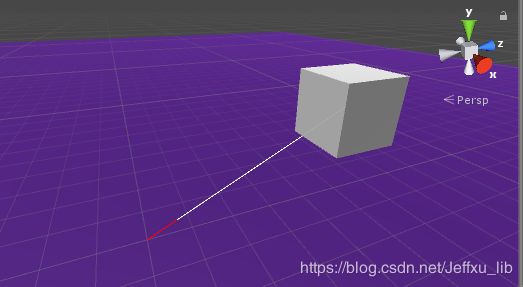
Debug.DrawLine(Vector3.zero, pos1,Color.red); //在原点到物体之间划红色的线
}
}效果如下图所示
2、向量的归一化处理(即向量的方向)
public class sc03 : MonoBehaviour
{
// Update is called once per frame
void Update () {
Demo1();
}
void Demo1()
{
// 获取当前物体的空间坐标
Vector3 pos1 = transform.position;
// 通过公式来对向量进行归一化处理
Vector3 n01 = pos1 / pos1.magnitude;
// 通过Unity的API来对向量进行归一化处理
Vector3 n02 = pos1.normalized;
Debug.DrawLine(Vector3.zero, pos1); //原点到物体间划线
Debug.DrawLine(Vector3.zero, n01,Color.red);//原点到归一化后的向量之间划线
}
}结果如下所示
3、向量的运算(求两点的方向):
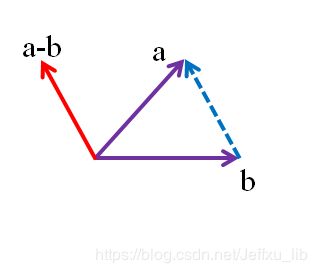
(1)、在Unity中的两个向量相减的结果,如下图的a向量减b向量,所得到的结果并不在虚线处,而是实线处。因为它是从世界坐标原点作为起点的,相当于将所减的结果由虚线平移到坐标原点处。两个向量相减的结果一定是与这两个向量共起点(即世界坐标系的原点)。在Unity中 ![]() 的结果是如下图红色箭头所指的点。
的结果是如下图红色箭头所指的点。
(2)、在Unity中用代码展示如下:
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class OperVector : MonoBehaviour
{
public Transform tf0, tf1, tf2, tf3;
void Start () {
tf0 = GameObject.Find("Sphere").GetComponent();//位于坐标原点:黑色的球
tf1 = GameObject.Find("Sphere1").GetComponent();//蓝色的球
tf2 = GameObject.Find("Sphere2").GetComponent();//紫色的球
tf3 = GameObject.Find("Sphere3").GetComponent(); //白色的球
}
// Update is called once per frame
void Update () {
Demo01();
}
///
/// 向量的方向
///
void Demo01()
{
//dir01 相当于两个向量相减之后的点
Vector3 dir01 = tf1.position - tf2.position;
//该向量的方向为:坐标原点到dir01
Debug.DrawLine(tf0.position, dir01,Color.red);
Debug.DrawLine(tf0.position, tf1.position,Color.yellow);
Debug.DrawLine(tf0.position, tf2.position,Color.yellow);
Debug.DrawLine(tf1.position, tf2.position,Color.red);
Debug.DrawLine(tf3.position, dir01,Color.blue);
}
}
结果如下
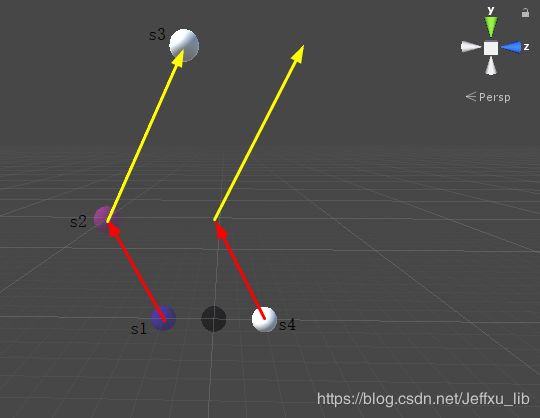
(3)、将一个向量平移到另一个地方,但方向依然保持不变。
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class Move : MonoBehaviour
{
Transform s1, s2, s3, s4;
Vector3 v1;
Vector3 v2;
Vector3 leftv1,leftv2;
void Start () {
s1 = GameObject.Find("Sphere1").GetComponent();
s2 = GameObject.Find("Sphere2").GetComponent();
s3 = GameObject.Find("Sphere3").GetComponent();
s4 = GameObject.Find("Sphere4").GetComponent();
}
private void Update()
{
// v1只表示s1到s2的向量,其长度固定,但起点位于世界坐标系的原点
v1 = s2.position - s1.position;
// v2只表示s2到s3的向量,其长度固定,起点位于世界坐标系的原点
v2 = s3.position - s2.position;
// leftv1相当于将向量v1平移到s4位置处,即方向大小保持不变,起点位于s4处。
leftv1 = s4.position + v1;
leftv2 = leftv1 + v2;
Debug.DrawLine(s1.position, s2.position, Color.red);
Debug.DrawLine(s2.position, s3.position, Color.yellow);
Debug.DrawLine(s4.position, leftv1, Color.red);
Debug.DrawLine(leftv1, leftv2, Color.yellow);
}
}
运行结果如下
二、向量的运算
1、向量的基本操作
Vector3 a, b;
//向量a[0],a[1],a[2]分别表示a.x , a.y , a.z
a[0] = a[1] = a[2] = 10;
Vector3.Angle(a, b); //返回向量a,b间的夹角,结果为度
Vector3.Cross(a, b); //向量a,b叉乘
Vector3.Dot(a, b); //向量a,b点乘
// MoveTowards 是从一个点按指定的速度匀速的移动到另一个点,可以看到移动的过程。
transform.position = Vector3.MoveTowards(this.transform.position, new Vector3(0, 0, 10),0.1f);
2、点乘与叉乘及求角度
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class OperVector : MonoBehaviour
{
private Transform tf0, tf1, tf2, tf3;
float angle01;
void Start () {
tf0 = GameObject.Find("Sphere").GetComponent();//位于坐标原点:黑色的球
tf1 = GameObject.Find("Sphere1").GetComponent();//蓝色的球
tf2 = GameObject.Find("Sphere2").GetComponent();//紫色的球
tf3 = GameObject.Find("Sphere3").GetComponent(); //白色的球
}
void Update () {
Demo02();
}
void Demo01()
{
Debug.DrawLine(tf0.position, tf1.position,Color.yellow);
Debug.DrawLine(tf0.position, tf2.position,Color.yellow);
//两向量点乘
float resultOfDot = Vector3.Dot(tf1.position, tf2.position);
/*由点乘结果求两向量的夹角时,必须先对两向量归一化处理,或者最后除以两向量模长的乘积再求反余弦
* 1、此时求的角是两向量间的最小夹角
* 2、所求的角度没有正负之分,只能看大小
* 3、对于标准化过的向量,方向完全相同,点乘结果为1,相反为-1
* 4、角度的范围是:0——180度之间
*/
float resultOfDot01 = Vector3.Dot(tf1.position.normalized, tf2.position.normalized);
angle01 = Mathf.Acos(resultOfDot01) * Mathf.Rad2Deg;
}
void Demo02()
{
Debug.DrawLine(tf0.position, tf1.position, Color.yellow);
Debug.DrawLine(tf0.position, tf2.position, Color.yellow);
//求两向量的叉乘
Vector3 resultOfCross = Vector3.Cross(tf1.position, tf2.position);
Debug.DrawLine(Vector3.zero, resultOfCross,Color.red);
//用叉乘来求两向量的夹角:叉乘求角度的范围是:0——90 度。
Vector3 resultOfCross01 = Vector3.Cross(tf1.position.normalized, tf2.position.normalized);
float angle02 = Mathf.Asin(resultOfCross01.magnitude) * Mathf.Rad2Deg;
//结合点乘和叉乘,可以计算一圈的夹角
/* 当叉乘大于0时,两向量的夹角小于180度;
* 当叉乘小于0时,两向量的夹角大于180度。
*/
if (resultOfCross.y<0)
{
float angle03 = 360 - angle01;
}
}
}
三、Unity 中三角函数的角度表示
//角度到弧度转换
float d = 60; //60度
float r1 = d * Mathf.PI / 180;
float r2 = d * Mathf.Deg2Rad;
//弧度到角度
float r = 3;
float d1 = r * 180 / Mathf.PI;
float d2 = r * Mathf.Rad2Deg;