MySQL数据库 sql语句的简单入门学习
初步学习MySQL后的一些总结
MySQL简介
MySQL在过去由于性能高、成本低、可靠性好,已经成为最流行的开源数据库,因此被广泛地应用在Internet上的中小型网站中。随着MySQL的不断成熟,它也逐渐用于更多大规模网站和应用,比如维基百科、Google和Facebook等网站。非常流行的开源软件组合LAMP中的“M”指的就是MySQL。[引自MySQL-维基百科,自由的百科全书]
安装过程请自行解决,官网下载地址:Download MySQL Community Server
启动服务
(若MySQL服务已启动,请跳过该过程)
1、图标启动
2、进系统服务启动
方法1:win + r 。 services.msc
方法2:右击计算机-->管理-->服务,找到mysql80 右击启动
连接MySQL
方法一:win + r ,输入cmd (若出现不是内部或外部命令,请设置环境变量)
在命令行内输入:mysql -u root -p ,然后敲回车
然后输入密码 ,回车即可进入
方法二:win + r cmd
输入: mysql -h localhost -P 3306 -u root -p 回车
然后输入密码,回车运行即可进入。
-h : hostname -->localhost
-P : port -->3306(该端口为下载设置时的端口,一般默认为3306)
-u : username -->root
-p : password -->自己的密码
方法三:(windows系统)可以找开始菜单,mysql文件夹
找 MySQL Command Line Client 启动,
然后输入密码。
基本的sql语句
sql 语句以分号结尾才能运行。
类比于,常见的 excel 创建写入与存储。
1、显示所有的数据库文件(打开文件夹,观看哪些excel文件一样)
语法: show databases
> show databases;
2、创建数据库 (当成创建 excel)
语法: create database 库名称
> create database test1;
3、使用某个数据库 (当成打开 一个 excel)
语法: use 数据库名称
> use test1;
4、查看数据表 (相当于看看有哪些 sheet)
语法: show tables
> show tables;
5、删除库 (删除excel)
语法: drop database 库名称
> drop database test1;
6、显示表中所有数据
语法:select * from 表名称;
对数据表进行操作
# 创建表: (相当于 我们在 excel 中新建一个sheet,然后sheet的首行规定每一列该填什么,如姓名,年龄,性别)
语法: [] 可以不写 ,也可以有
create table [if not exists] 表名称 (
字段名1 列类型 [属性] [约束] [注释],
字段名2 列类型 [属性] [约束] [注释],
......
字段名n 列类型 [属性] [约束] [注释]
);
注意点: 最后一个不用逗号,作结尾。
# 删除表:(相当于在excel 中删除一个存在的 sheet )
语法:drop table 表名称;
# 查看表结构
语法: desc 表名称;
# 查看数据表:
语法:show tables;
数据类型: 一般用在列类型上
1、数值类型:
整型: 常用的有 int bigint
浮点型:常用的有 float double
2、字符串类型 ,m 是个长度数值
char(m)
varchar(m) varchar(20) 表示20个字符
text
longtext:存个小说的长度
3、日期类型
date 2019-8-3
datetime 2019-8-3 10:05:30
timestamp 时间戳
time 10:05:30
实例
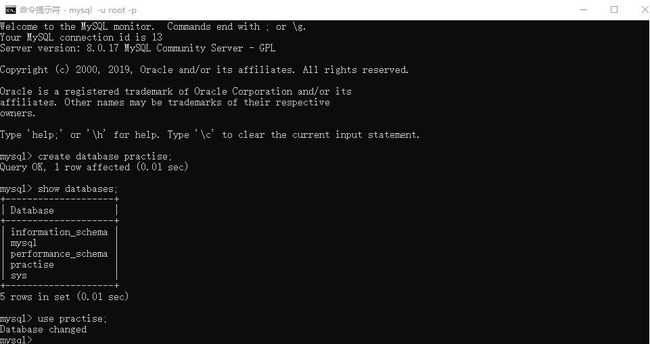
先创建一个数据库practise
> create database practise;
使用practise数据库
> use practise;
创建班级表class1,id,姓名,年龄,性别
> create table class1(
student_id int auto_increment primary key,
student_name varchar(20),
age int,
sex char(5)
)default charset=utf8;
注意:结尾设置编码,千万别忘。
属性与约束
null 空
not null 不为空
default 默认值
如: 上面的 age : age int default 18,
unique key 唯一
设置 某个列 的值都是唯一的,也就是没用重复
如 身份证号,一般是唯一的
primary key : 主键
唯一标示 (自带唯一属性,not null属性)
一个表中必须有的
一般都是数字自增
auto_increment: 自增长
必须给主键设置 ,int
它 的数值是不会回退的
foreign key : 外键
减少冗余,用来与其他表连接。
语法:
constraint 你给外键取的名字 foreign key (你想引用到外键的列名称) references 参考表的表名(列名称且这个列名称是有主键属性)
实例
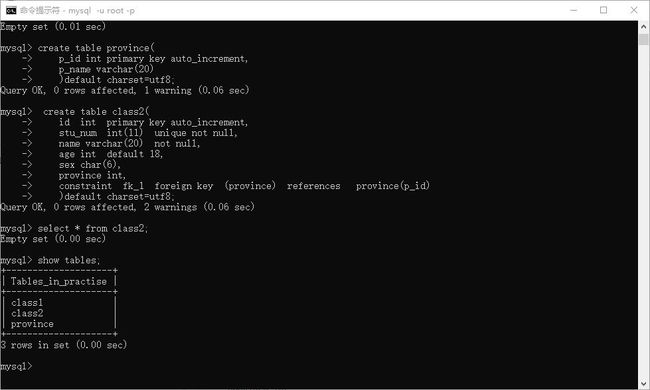
创建一个省份表
> create table province(
p_id int primary key auto_increment,
p_name varchar(20)
)default charset=utf8;
创建班级表class2,并引用province作为省份表的外键
> create table class2(
id int primary key auto_increment,
stu_num int(11) unique not null,
name varchar(20) not null,
age int default 18,
sex char(6),
province int,
constraint fk_1 foreign key (province) references province(p_id)
)default charset=utf8;
更改表结构
更改表名称
语法:alter table 旧表名 rename as 新表名
如:
> alter table class1 rename as classOne;
添加字段
语法:alter table 表名称 add 字段名 列类型[属性][约束]
如: 我们给 class2 增加电话列 phone
> alter table class2 add phone varchar(20);
删除字段
语法:alter table 表名称 drop 字段名
更改字段名称
语法:alter table 表名 change 旧字段名 新字段名列类型[属性][约束]
如: 将 name 改为 stu_name
> alter table class2 change name stu_name varchar(20) not null;
更改属性:
语法: alter table 表名称 modity 字段名 列类型 [属性][约束]
如: 将 stu_name 的 varchar(20) 改为 varchar(50)
> alter table class2 modify stu_name varchar(50) not null;
增加外键:
语法: alter table 你要增加外键的表名 add constraint 你给外键取的名字 foreign key (你想引用到外键的列名称) references 参考表的表名(列名称且这个列名称是有主键属性)
实例
1. 创建库 goods
> create database goods;
2. 使用goods库
> use goods;
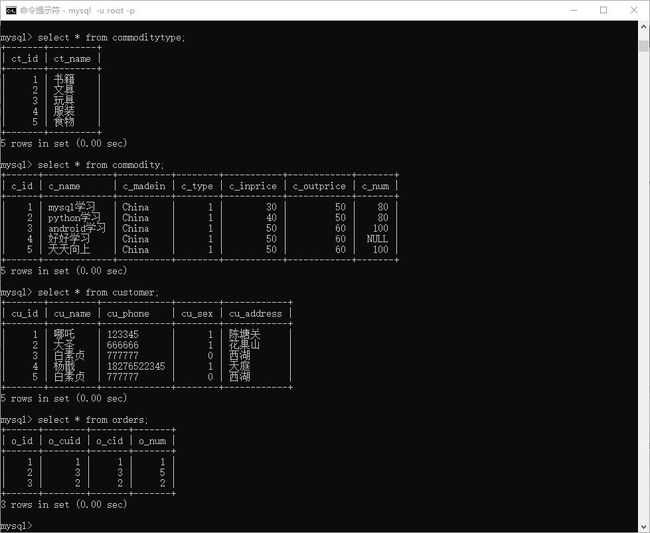
3. 创建商品种类表 commoditytype
主键 ct_id , ct_name
> create table commoditytype(
ct_id int primary key auto_increment,
ct_name varchar(50) not null
)default charset=utf8;
4. 创建商品表 commodity
c_id 主键 自增长
c_name 50个字的字符串 不为空
c_madein 50个字的字符串 不为空
c_type ,整型,外键关联到 商品表的 ct_id
c_inprice ,整型 不为空
c_outprice,整型 不为空
c_num, 整数 默认 100
> create table commodity(
c_id int primary key auto_increment,
c_name varchar(50) not null,
c_madein varchar(50) not null,
c_type int,
constraint fk_1 foreign key (c_type) references commoditytype(ct_id),
c_inprice int not null,
c_outprice int not null,
c_num int default 100
)default charset=utf8;
5. 创建 客户表 customer
cu_id 主键 自增,
cu_name 50个字 不为空,
cu_phone 20个字 ,
cu_sex int 默认 1,
cu_address 100个字符 不为空
> create table customer(
cu_id int primary key auto_increment,
cu_name varchar(50) not null,
cu_phone varchar(20),
cu_sex int default 1,
cu_address varchar(100)
)default charset=utf8;
6. 创建 订单表
> create table orders(
o_id int primary key auto_increment,
o_cuid int,
o_cid int,
o_num int
)default charset=utf8;
数据的增删改查
增
增加一条数据:
语法: insert into 表名称 [(column1,column2,...)] values (value1,value2,...);
增加多条数据:
语法: insert into 表名称 [(column1,column2,...)] values (value1,value2,...),(value1,value2,...),(value1,value2,...)...;
!注意:
1.如果列名称[(column1,column2,...)]没写 ,那么 values后面这个(值1,值2,...) 值必须依次 每一列对应
2.如果写了 列名称[(column1,column2,...)] ,后面的值是与一一对应,而且前面的列顺序可以不是从左到右
实例
> insert into commoditytype values(1,'书籍');
> insert into commoditytype (ct_name) values('文具');
> insert into commoditytype (ct_name,ct_id) values('玩具',null);
> insert into commoditytype values(null,'服装'),(null,'食物');
# 继续增加商品信息
> insert into commodity values(1,"mysql学习","China",1,30,50,80);
# 继续 增加 ,不给 第一列数值,看自增效果
> insert into commodity values(null,"python学习","China",1,40,50,80);
# 继续 增加 ,不给 最后一列数值,看默认值
> insert into commodity values(null,"android学习","China",1,50,60,default);
# 继续 增加 ,给 最后一列null,就是null,并不是显示 100
> insert into commodity values(null,"好好学习","China",1,50,60,null);
# 继续 增加 ,不给 最后一列,但是前面必须给 6个列名称,否则数量不匹配
> insert into commodity (c_id,c_name,c_madein,c_type,c_inprice,c_outprice) values(null,"天天向上","China",1,50,60);
# 用户表放几个人
> insert into customer values
(1,"哪吒",'123345',1,'陈塘关'),
(2,"大圣",'666666',1,'花果山'),
(3,"白素贞",'777777',0,'西湖'),
(4,"杨戬",'18276522345',1,'天庭');
> insert into customer values (null,"白素贞",'777777',0,'西湖');
# 订单表放几条
> insert into orders values(1,1,1,1),(2,3,3,5),(3,2,2,2);
注意: 如果忘记某列,可以 alter 增加,去navicat 内拖顺序
如果外键关联的表中没有 参考,是无法增加的。
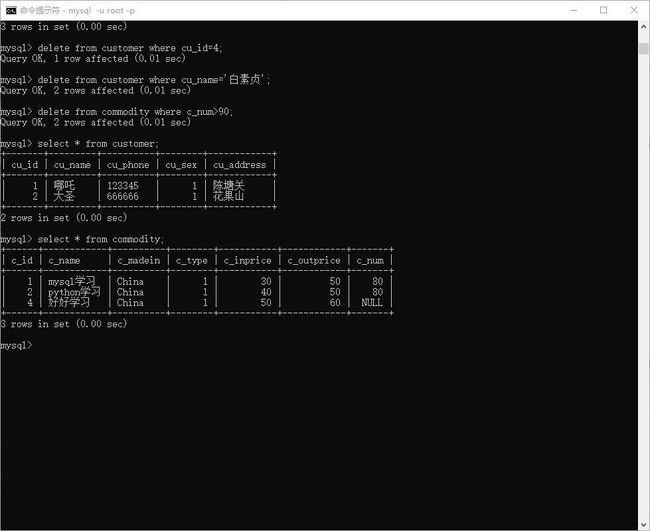
删
语法: delete from 表名称 [where 条件] ;条件一定要写,否则删完自增的效果还在。
truncate table 表名; 删除所有信息,包括自增的 主键 值 。
实例
#如 删除 杨戬 , 用 id 判断
> delete from customer where cu_id=4;
#如 删除 白素贞 , 用 cu_name 判断 . 这种删除要慎用,除非要删多个
-> delete from customer where cu_name='白素贞';
# 删除库存 大于 90 的书籍 . 区间
> delete from commodity where c_num>90;
改
语法: update 表名称 set column1=value1,column2=value2,.. [where条件];
实例
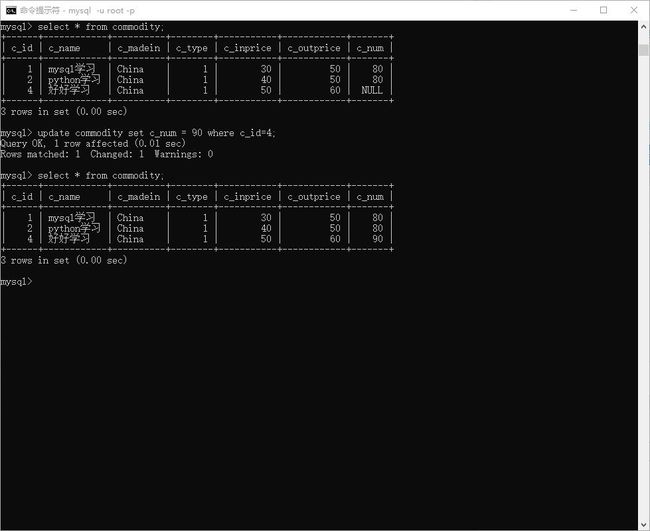
# 如我将 数据中的 null 换成90.
> update commodity set c_num = 90 where c_id=4;
查
单表查询:
查询所有数据:
select * from 表名称;
实例
查询某些字段:
> select c_id,c_name from commodity;
准备工作,将类型表commoditytype,1 改为玩具,3改为书籍
> update commoditytype set ct_name='玩具' where ct_id=1;
> update commoditytype set ct_name='书籍' where ct_id=3;
图示

将商品表情况,然后将下列语句复制过来运行增加数据
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘1’, ‘变形金刚-擎天柱’, ‘中国’, ‘1’, ‘20’, ‘50’, ‘60’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘2’, ‘变形金刚-霸天虎’, ‘中国’, ‘1’, ‘20’, ‘45’, ‘50’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘3’, ‘变形金刚-威震天’, ‘美国’, ‘1’, ‘120’, ‘245’, ‘15’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘4’, ‘魔仙玩偶1’, ‘中国’, ‘1’, ‘6’, ‘12’, ‘100’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘5’, ‘超人玩偶’, ‘中国’, ‘1’, ‘29’, ‘99’, ‘100’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘7’, ‘小霸王游戏机’, ‘中国’, ‘1’, ‘50’, ‘99’, ‘300’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘8’, ‘X-BOX游戏机’, ‘美国’, ‘1’, ‘1200’, ‘3000’, ‘12’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘9’, ‘任天堂游戏机’, ‘日本’, ‘1’, ‘300’, ‘600’, ‘30’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘10’, ‘乐高玩具-散装’, ‘中国’, ‘1’, ‘40’, ‘60’, ‘100’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘11’, ‘乐高玩具-快乐家庭’, ‘中国’, ‘1’, ‘50’, null, ‘20’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘12’, ‘乐高玩具-蝙蝠侠纪念版’, ‘新加坡’, ‘1’, ‘290’, ‘590’, ‘6’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘13’, ‘夏日有人手办’, ‘中国’, ‘1’, ‘20’, ‘50’, ‘10’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘14’, ‘EVA模型玩具’, ‘日本’, ‘1’, ‘200’, ‘450’, ‘10’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘15’, ‘平板电脑模型’, ‘中国’, ‘1’, ‘2’, ‘12’, ‘120’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘16’, ‘手机模型玩具’, ‘中国’, ‘1’, ‘7’, ‘24’, ‘60’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘17’, ‘手机模型玩具’, ‘美国’, ‘1’, ‘20’, ‘80’, ‘10’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘18’, ‘手机模型玩具’, ‘日本’, ‘1’, ‘40’, null, ‘8’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘19’, ‘hellokitty手机链’, ‘中国’, ‘1’, ‘20’, ‘60’, ‘40’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘20’, ‘水枪-小’, ‘中国’, ‘1’, ‘2’, ‘4’, ‘80’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘21’, ‘水枪-大’, ‘中国’, ‘1’, ‘10’, ‘18’, ‘80’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘22’, ‘水枪-小’, ‘中国’, ‘1’, ‘2’, ‘4’, ‘80’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘23’, ‘中华铅笔HB’, ‘中国’, ‘2’, ‘1’, ‘2’, ‘100’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘24’, ‘中华铅笔2B’, ‘中国’, ‘2’, ‘1’, ‘2’, ‘109’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘25’, ‘中华铅笔2H’, ‘中国’, ‘2’, ‘1’, ‘2’, ‘100’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘26’, ‘超人图案笔袋’, ‘中国’, ‘2’, ‘6’, ‘12’, ‘12’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘27’, ‘中华绘图橡皮’, ‘中国’, ‘2’, ‘1’, ‘2’, ‘100’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘28’, ‘西瓜图案铅笔盒’, ‘中国’, ‘2’, ‘12’, ‘20’, ‘50’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘29’, ‘hellokitty文具礼盒套装’, ‘中国’, ‘2’, ‘33’, ‘99’, ‘10’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘30’, ‘简易卷笔刀’, ‘中国’, ‘2’, ‘1’, ‘2’, ‘100’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘31’, ‘自动卷笔刀’, ‘中国’, ‘2’, ‘6’, ‘20’, ‘40’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘32’, ‘礼盒丝带-红’, ‘中国’, ‘2’, ‘2’, ‘6’, ‘80’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘33’, ‘礼盒丝带-蓝’, ‘中国’, ‘2’, ‘2’, ‘6’, ‘40’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘34’, ‘蝴蝶图案直尺’, ‘中国’, ‘2’, ‘14’, ‘26’, ‘44’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘35’, ‘折叠尺’, ‘中国’, ‘2’, ‘20’, ‘60’, ‘4’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘36’, ‘超人图案书包’, ‘中国’, ‘2’, ‘60’, ‘160’, ‘3’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘37’, ‘公主图案书包’, ‘中国’, ‘2’, ‘60’, ‘160’, ‘6’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘38’, ‘熊大图案拉杆箱-小’, ‘中国’, ‘2’, ‘160’, ‘260’, ‘1’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘39’, ‘儿童彩色铅笔’, ‘中国’, ‘2’, ‘60’, ‘80’, ‘13’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘40’, ‘快乐家族文具礼盒’, ‘中国’, ‘2’, ‘160’, ‘460’, ‘2’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘41’, ‘java入门到精通’, ‘中国’, ‘3’, ‘30’, ‘66’, ‘15’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘42’, ‘.net入门到精通’, ‘中国’, ‘3’, ‘30’, ‘59’, ‘15’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘43’, ‘php入门到精通’, ‘中国’, ‘3’, ‘30’, ‘59’, ‘25’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘44’, ‘疯狂java’, ‘中国’, ‘3’, ‘72’, ‘166’, ‘12’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘45’, ‘java思考1’, ‘美国’, ‘3’, ‘132’, ‘170’, ‘12’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘46’, ‘成语典故’, ‘中国’, ‘3’, ‘13’, ‘26’, ‘101’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘47’, ‘睡前小故事0-3’, ‘中国’, ‘3’, ‘20’, ‘40’, ‘20’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘48’, ‘睡前小故事4-7’, ‘中国’, ‘3’, ‘20’, ‘40’, ‘20’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘49’, ‘安徒生童话’, ‘中国’, ‘3’, ‘26’, ‘40’, ‘12’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘50’, ‘格林童话’, ‘中国’, ‘3’, ‘23’, ‘29’, ‘12’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘51’, ‘上下五千年’, ‘中国’, ‘3’, ‘200’, ‘400’, ‘3’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘52’, ‘电脑报15年合集’, ‘中国’, ‘3’, ‘24’, ‘52’, ‘2’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘53’, ‘哈利波特1-3’, ‘英国’, ‘3’, ‘120’, null, ‘3’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘54’, ‘新华字典’, ‘中国’, ‘3’, ‘8’, ‘17’, ‘30’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘55’, ‘英汉字典’, ‘中国’, ‘3’, ‘26’, ‘26’, ‘4’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘56’, ‘牛津英语’, ‘英国’, ‘3’, ‘217’, ‘300’, ‘16’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘57’, ‘唐诗三百首’, ‘中国’, ‘3’, ‘6’, ‘8’, ‘22’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘58’, ‘名家演讲赏析’, ‘中国’, ‘3’, ‘22’, ‘50’, ‘4’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘59’, ‘三国演义’, ‘中国’, ‘3’, ‘20’, ‘37’, ‘37’);
INSERT INTO commodity VALUES (‘60’, ‘红楼梦’, ‘中国’, ‘3’, ‘14’, ‘16’, ‘15’);
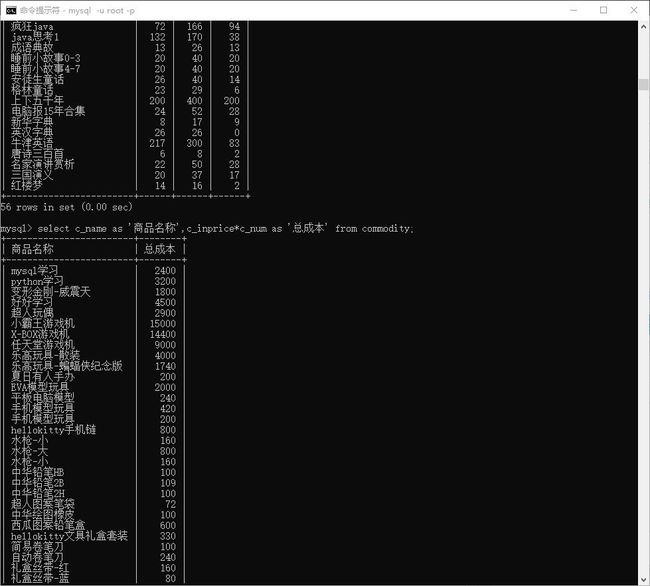
图示

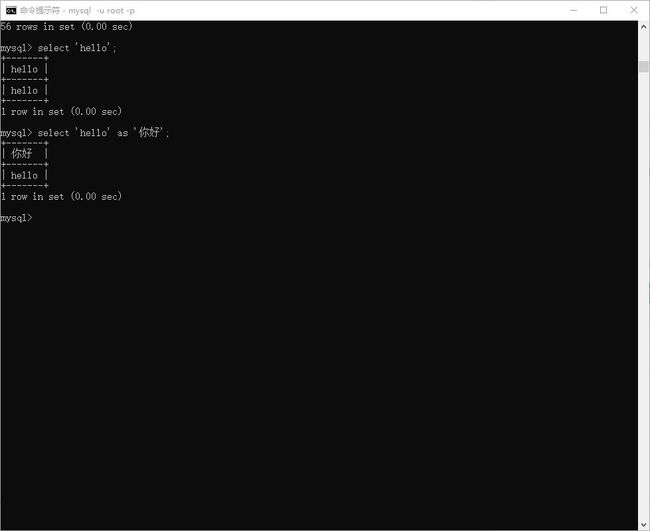
查询常量
> select 'hello';
> select 'hello' as '你好';
自定义显示名称
查询商品的名称,进价和售价
> select c_name as '商品名称',c_inprice as '进价',c_outprice as '售价' from commodity;
查询时外键作为条件
如查询所有玩具
> select * from commodity where c_type=1;
# 凭啥知道 玩具的类型是1,其实1是可以查出来的
> select * from commodity where c_type=(select ct_id from commoditytype where ct_name='玩具');
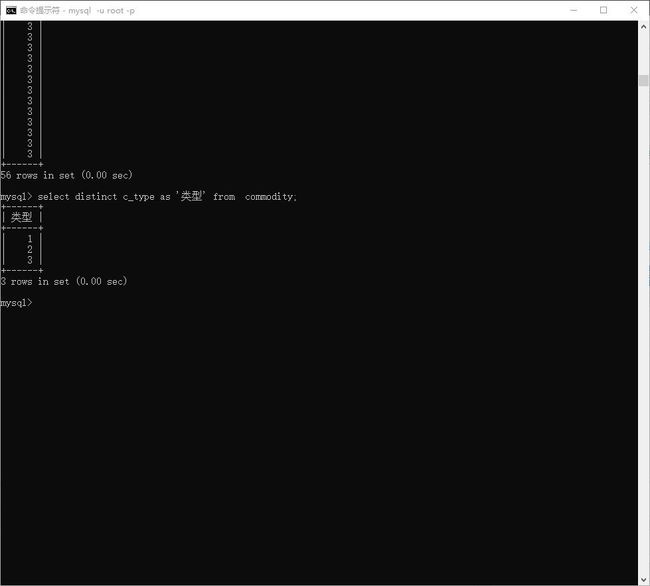
查询 所有商品的类型 筛选后的数据
distinct 用于去重
# 没有去重效果
> select c_type as '类型' from commodity;
# 有去重效果
> select distinct c_type as '类型' from commodity;
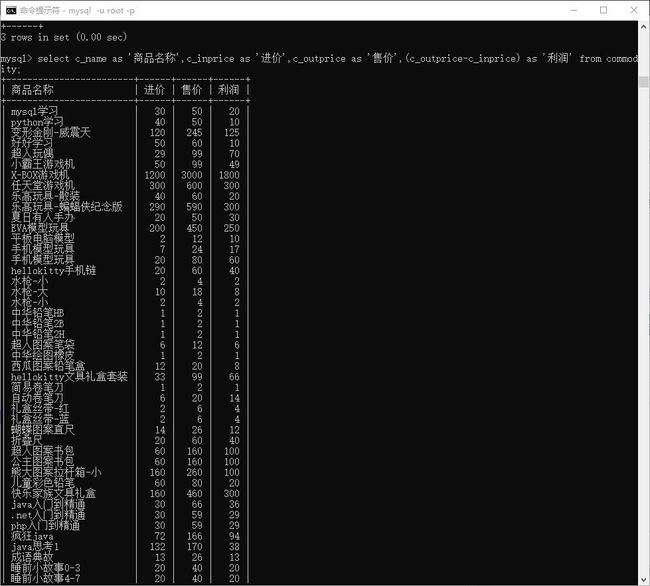
四则运算
如: 想看看每个商品 利润。显示 名称,进价,售价,利润。
> select c_name as '商品名称',c_inprice as '进价',c_outprice as '售价',(c_outprice-c_inprice) as '利润' from commodity;
如: 想看看每个商品 总成本。显示 名称 ,总成本。
> select c_name as '商品名称',c_inprice*c_num as '总成本' from commodity;
比较运算
> < = >= <= !=
____________________________________
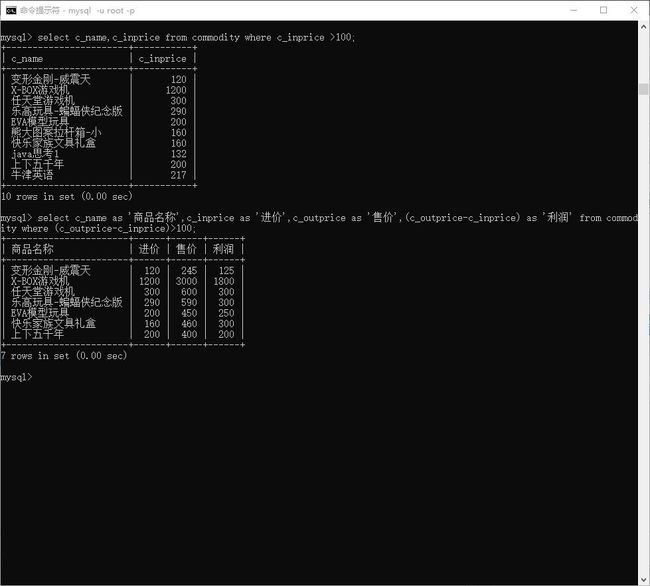
# 查询 进价大于 100 的
> select c_name,c_inprice from commodity where c_inprice >100;
# 查询利润 大于100的
> select c_name as '商品名称',c_inprice as '进价',c_outprice as '售价',(c_outprice-c_inprice) as '利润' from commodity where (c_outprice-c_inprice)>100;
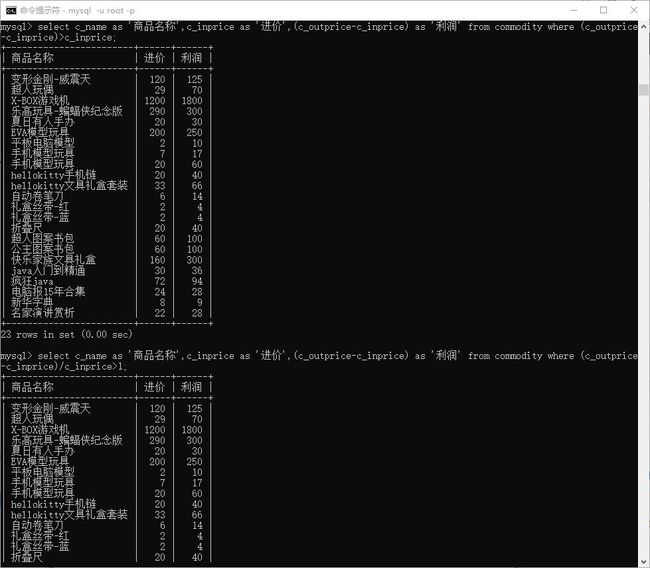
# 查询利润大于成本的
> select c_name as '商品名称',c_inprice as '进价',(c_outprice-c_inprice) as '利润' from commodity where (c_outprice-c_inprice)>c_inprice;
> select c_name as '商品名称',c_inprice as '进价',(c_outprice-c_inprice) as '利润' from commodity where (c_outprice-c_inprice)/c_inprice>1;
逻辑运算
and or not
_______________________________________________________________
# 查询产地是 中国 且 库存大于50 的
> select c_name,c_madein,c_num from commodity where c_madein='中国' and c_num>50;
# 查询产地是 中国 且 库存在 50-100 ,包括临界点 的
> select c_name,c_madein,c_num from commodity where c_madein='中国' and c_num>=50 and c_num<=100;
# 在什么之间
between 50 and 100
> select c_name,c_madein,c_num from commodity where c_madein='中国' and c_num between 50 and 100;
# 不~ 在什么之间
not between 50 and 100
> select c_name,c_madein,c_num from commodity where c_madein='中国' and c_num not between 50 and 100;
----
# 临时增加2件衣服进去
>insert into commodity values(null,"连衣裙","China",4,50,60,null);
>insert into commodity values(null,"棉袄","China",4,50,40,default);
# 临时增加两个食物的进去
>insert into commodity values(null,"海鲜","东北",5,60,80,default);
>insert into commodity values(null,"烧烤","上海",5,70,60,default);
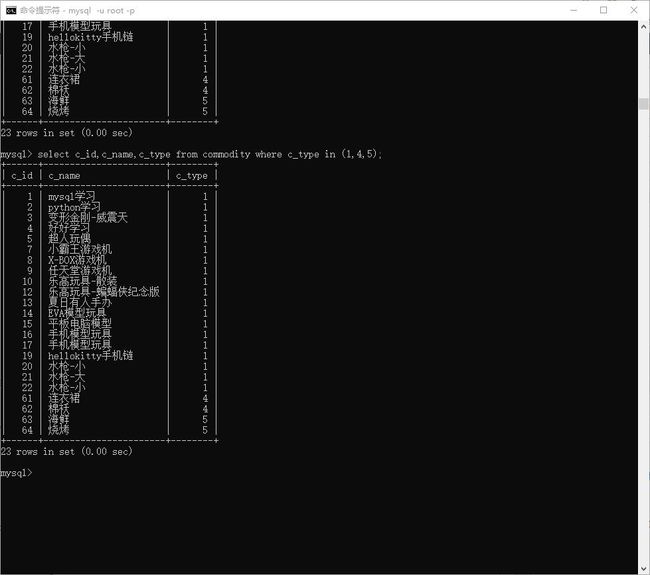
# 查询 商品类型是 服装 或 食品的
> select c_id,c_name,c_type from commodity where c_type=4 or c_type=5;
# 查询 商品类型是 服装 或 食品 或 玩具 的
> select c_id,c_name,c_type from commodity where c_type=4 or c_type=5 or c_type=1;
相当于:
> select c_id,c_name,c_type from commodity where c_type in (1,4,5);
# 产地是日本或者 美国的
> select c_id,c_name,c_madein from commodity where c_madein in ("日本","美国");
值的匹配 like (模糊查询)
一般 下划线 _ 表示一个字符
百分号 % 表示多个字符
如: _小 表示两个字符 x小
%小 表示多个字符 xxx小
%小% 表示 字符中有 小 字
实例
# 查询 产地 是 _国 的
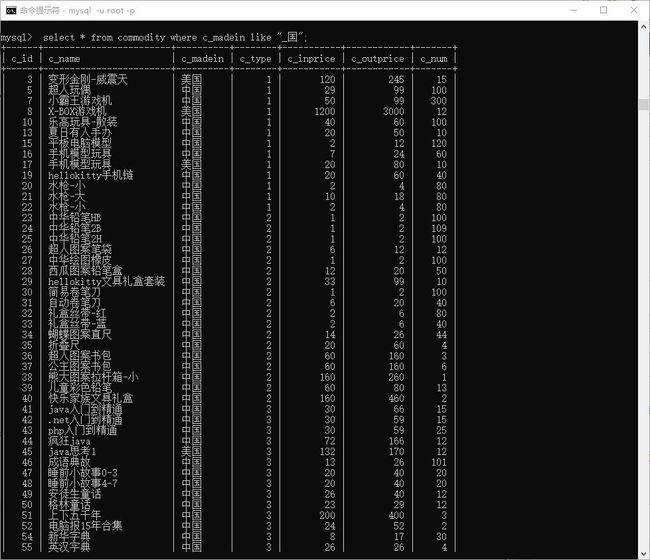
> select * from commodity where c_madein like "_国";
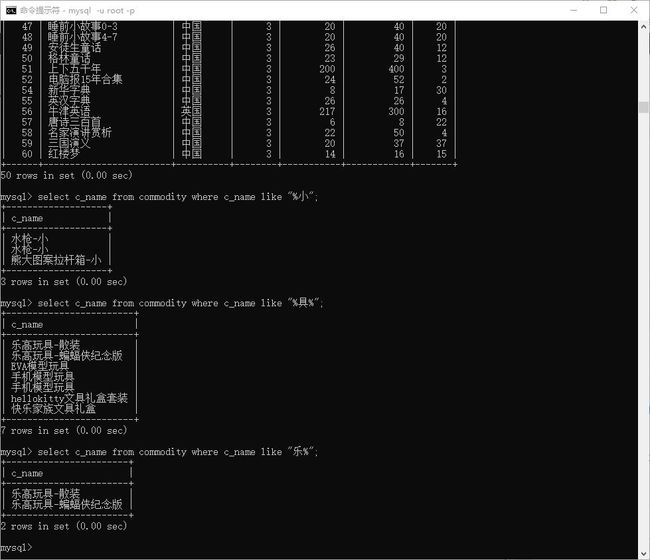
# 查询商品 结尾 是 '小' 字的
> select c_name from commodity where c_name like "%小";
# 查询商品 中 包含 '具' 字的
> select c_name from commodity where c_name like "%具%";
# 查询商品 开头 是 '乐' 字的
> select c_name from commodity where c_name like "乐%";
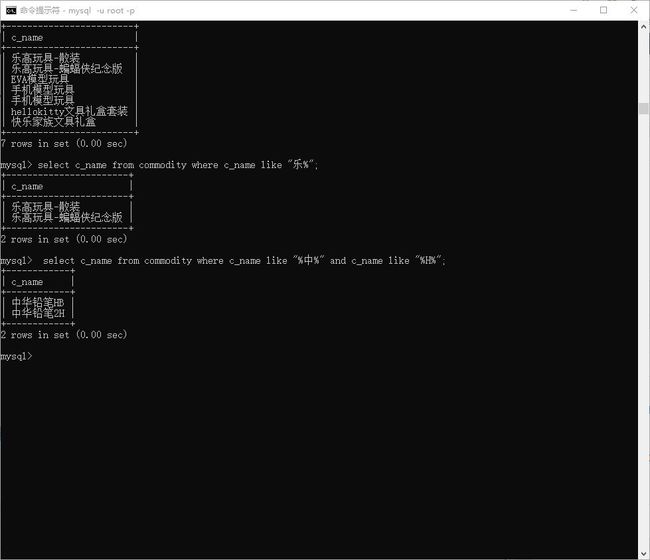
# 查询商品 中包含 '中' 和 'H' 的
> select c_name from commodity where c_name like "%中%" and c_name like "%H%";
排序
语法: order by 列名称 。 按照某一列进行排序
-- order by 列 asc (ascending) 默认升序
-- order by 列 desc(descending) 降序
_______________________________________________
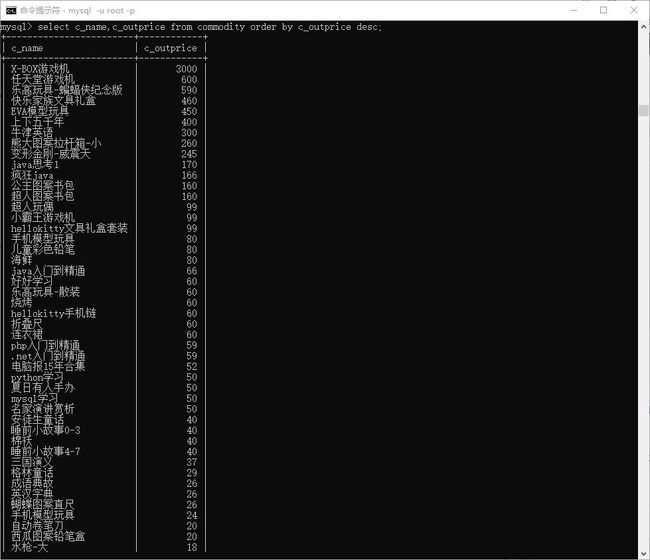
# 查询所有商品的售价,降序排序
> select c_name,c_outprice from commodity order by c_outprice desc;
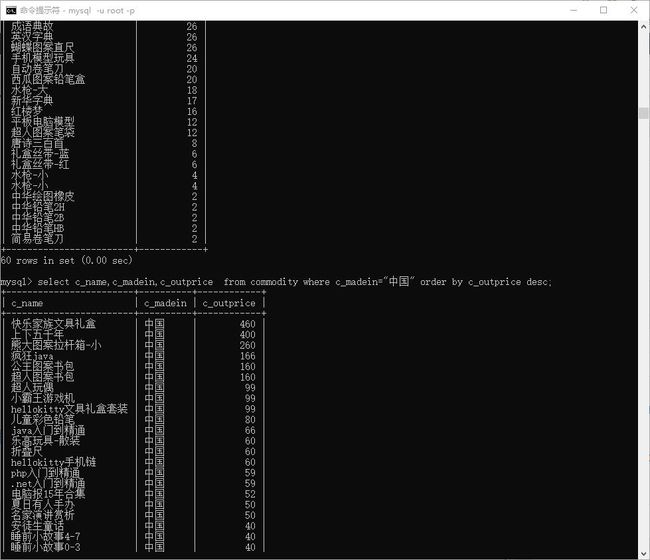
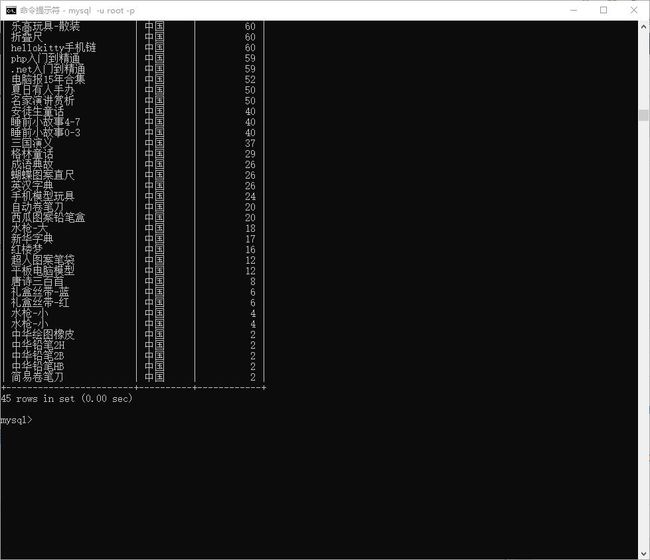
# 查询产地是中国的 所有商品的售价,降序排序
> select c_name,c_madein,c_outprice from commodity where c_madein="中国" order by c_outprice desc;
限制查询条数
语法: limit [起始值,]总条数
起始值: 默认0
limit 3 从第一条开始取3条
limit 2,4 从第三条开始,取4条
> select c_id,c_name from commodity limit 3;
函数
-- count( xxx ) 计算 xxx 的数量
# 得到 所有数据 的 数量
> select count(*) from commodity;
# 数量是可以直接拿来计算的
> select (select count(*) from commodity) * 2;
# 查询所有玩具的数量
> select count(*) from commodity where c_type=1;
> select count(c_name) as "玩具数量" from commodity where c_type=1;
-- 平均值 avg()
-- 求和 sum()
-- 最大值 max()
-- 最小值 min()
# 进价的均值
> select avg(c_inprice) as "进价均值" from commodity;
# 售价的最大值
> select max(c_outprice) as "售价最大值" from commodity;
# 售价的最小值
> select min(c_outprice) as "售价最小值" from commodity;
# 所有商品的 数量
> select sum(c_num) as "商品数量" from commodity;
>select avg(c_inprice) as "进价均值",
max(c_outprice) as "售价最大值",
min(c_outprice) as "售价最小值",
sum(c_num) as "商品数量" from commodity;
# 显示 玩具 数量
> select sum(c_num) as "玩具数量" from commodity where c_type=1;
# 这些函数都是默认 is not null 处理的
如果某个参与的值 本身 为 null,那么计算的时候是不考虑的
分组
语法: group by 列名称.
对关键字进行分组,通常 和 聚合函数 一起使用
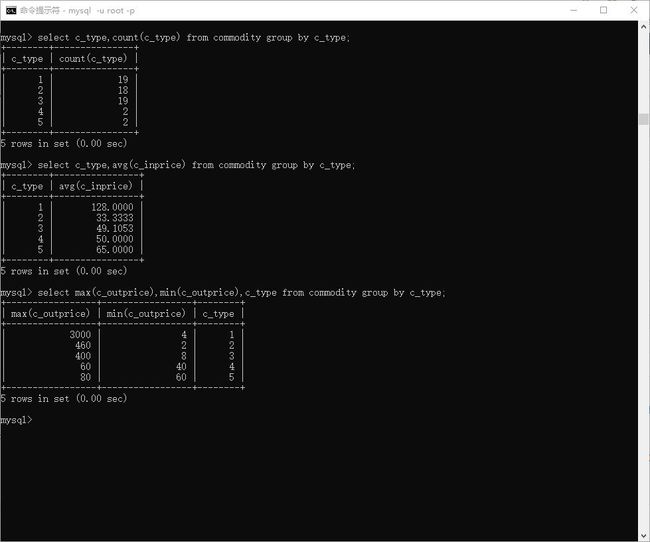
# 按照 种类 进行 分类,看每个种类的数量
> select c_type,count(c_type) from commodity group by c_type;
# 每类商品的平均 进价
> select c_type,avg(c_inprice) from commodity group by c_type;
# 每类商品中售价 最贵的最平移的
> select max(c_outprice),min(c_outprice),c_type from commodity group by c_type;
having 关键词
# where 条件筛选针对已有数据,也就是原数据
# having 条件筛选 聚合函数处理后的数据
# where 优先级高于having
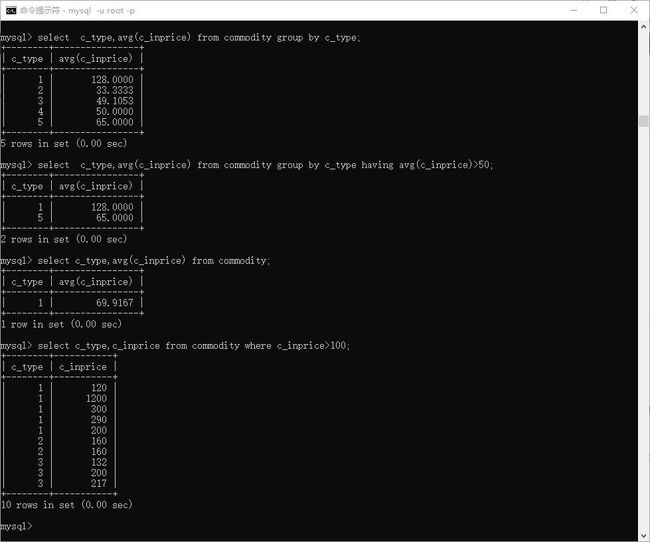
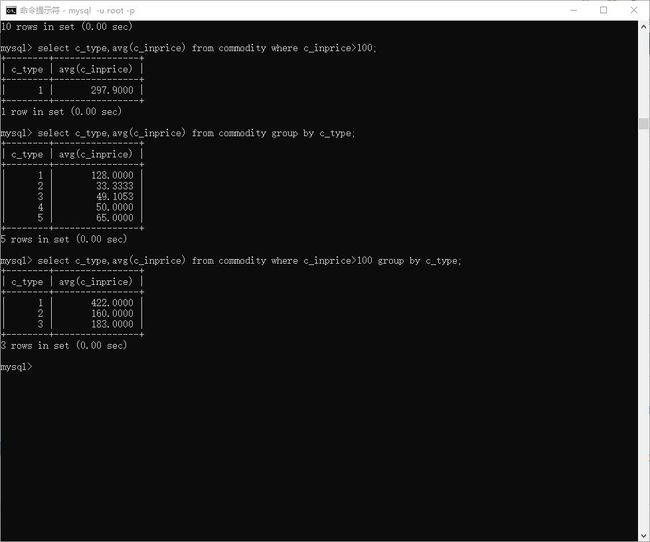
# 安照商品类型,看均价
> select c_type,avg(c_inprice) from commodity group by c_type;
# 安照商品类型,看均价 大于 50的
> select c_type,avg(c_inprice) from commodity group by c_type having avg(c_inprice)>50;
> select c_type,avg(c_inprice) from commodity;
> select c_type,c_inprice from commodity where c_inprice>100;
> select c_type,avg(c_inprice) from commodity where c_inprice>100;
> select c_type,avg(c_inprice) from commodity group by c_type;
# 选取进价 大于 100 的商品,分类后,求均值
> select c_type,avg(c_inprice) from commodity where c_inprice>100 group by c_type;
联表查询 ,多表查询
# 在前面查询中, 商品类型其实是用数字代替的
而且,我们是直接使用 1,2,3,4,5 的
# 在实际中我们不知道 具体的数字,只知道是什么商品,如玩具 ,那么如何从 commodity 中 查询出 所有玩具?
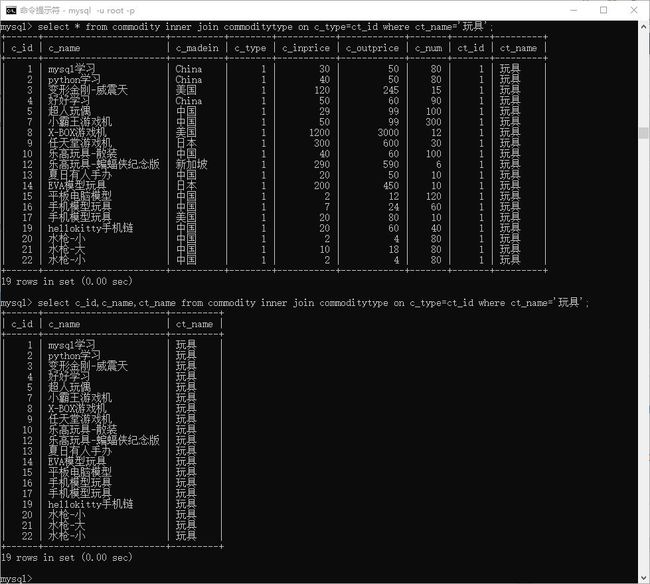
内连接查询:
语法:select xxx from 表1 inner join 表2 on 条件
# 查询出所有玩具
> select * from commodity inner join commoditytype on c_type=ct_id where ct_name='玩具';
# 还可以只显示每张表的部分内容
> select c_id,c_name,ct_name from commodity inner join commoditytype on c_type=ct_id where ct_name='玩具';
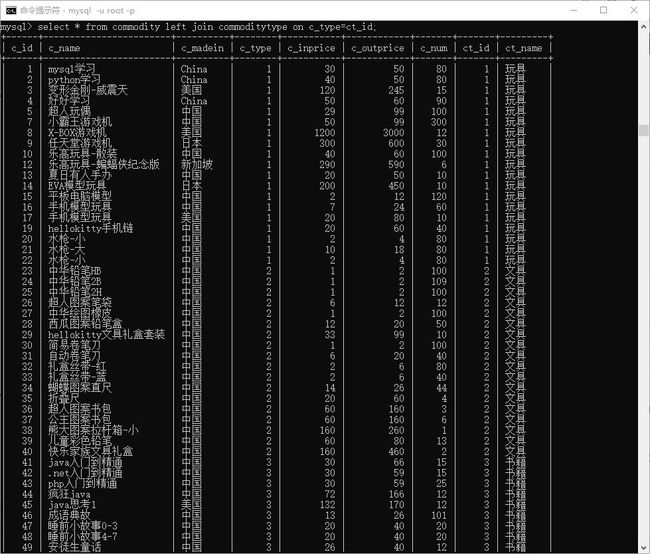
外连接查询:
语法:select xxx from 表1 left/right join 表2 on 条件
left join 左连接
right join 右连接
left 以做为主表,right以右边为主表
主表会全部显示,查不到的显示 null
# 去类型表增加几个类型
# 以 commodity 为主
> select * from commodity left join commoditytype on c_type=ct_id;
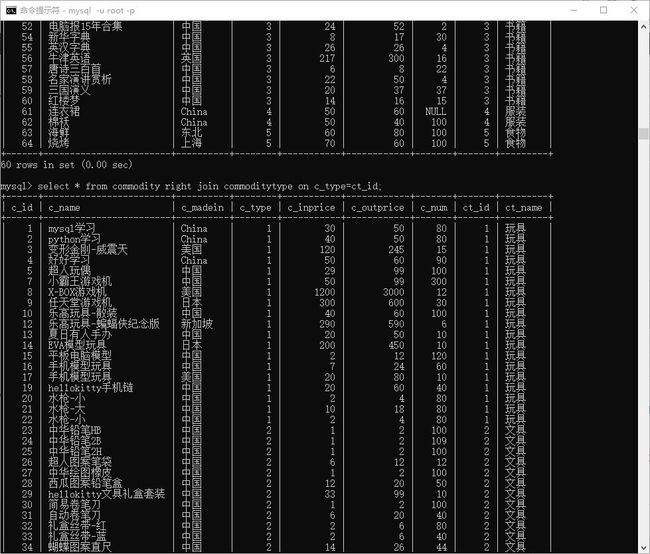
# 以 commoditytype 为主
> select * from commodity right join commoditytype on c_type=ct_id;
# 把类型放在左侧,自定义显示
> select c_id,ct_id,ct_name,c_name from commodity right join commoditytype on c_type=ct_id;
# 换下表的位置
> select * from commoditytype left join commodity on c_type=ct_id;
子查询
就是 把某个表中查出来的数据作为我们的查询条件
# 案例1:
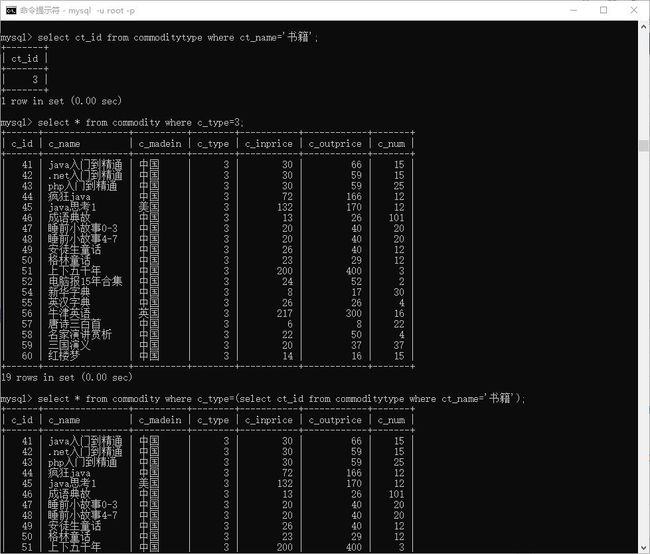
-1.1 问书籍的 ct_id 是多少?
> select ct_id from commoditytype where ct_name='书籍';
-1.2 我们知道 书籍对应着3,我们怎么从 commodity中查出所有书籍
> select * from commodity where c_type=3;
-1.3 更多的时候不知道直接的数, 把1.1 和 1.2 写一起,即子查询
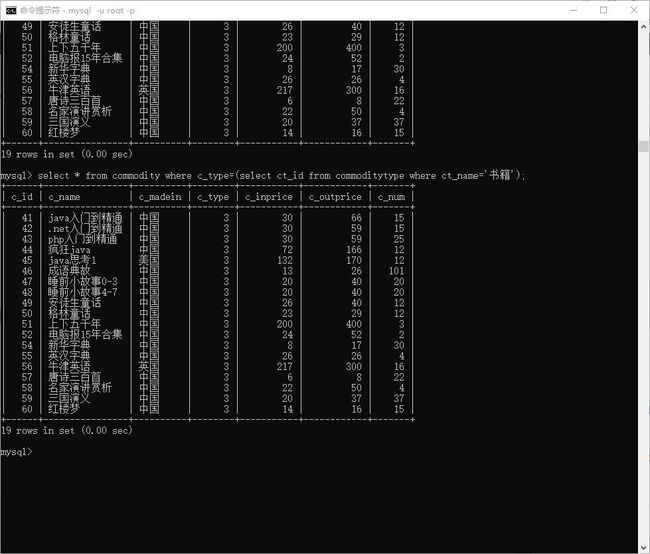
> select * from commodity where c_type=(select ct_id from commoditytype where ct_name='书籍');
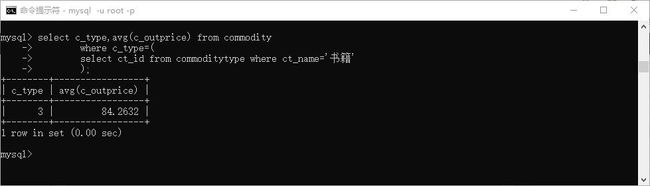
# 案例2:
- 书籍的平均售价。 最终显示类型和价格
> select c_type,avg(c_outprice) from commodity
where c_type=(
select ct_id from commoditytype where ct_name='书籍'
);
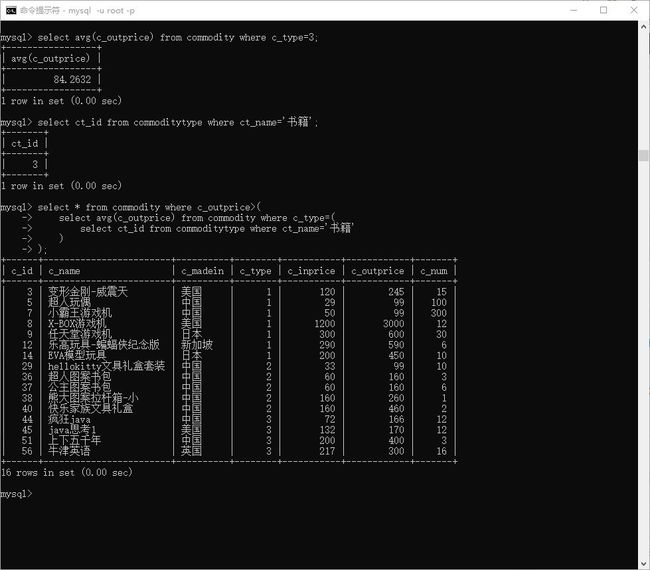
# 案例3:
- 售价大于 书籍均价的所有商品。
- 3.1 假设均价是40.
> select * from commodity where c_outprice>40;
- 3.2 求书籍售价均价
> select avg(c_outprice) from commodity where c_type=3;
-3.3 书籍的id
> select ct_id from commoditytype where ct_name='书籍';
融合进化:
> select * from commodity where c_outprice>(
select avg(c_outprice) from commodity where c_type=(
select ct_id from commoditytype where ct_name='书籍'
)
);
# 案例4:
- 售价大于 书籍均价的所有书籍。
- 4.1 取出售价 大于40的书籍.
4.1.1
> select * from commodity where c_outprice>40 and c_type=3;
4.1.2
> select * from commodity where c_type=3 having c_outprice>40;
- 4.2 求书籍售价均价
> select avg(c_outprice) from commodity where c_type=3;
- 4.3 书籍的id
> select ct_id from commoditytype where ct_name='书籍';
融合
> select * from commodity where c_outprice>(
select avg(c_outprice) from commodity where c_type=(
select ct_id from commoditytype where ct_name='书籍'
)
) and c_type=(
select ct_id from commoditytype where ct_name='书籍'
);