编译原理学习笔记之词法分析器(JAVA实现)
词法分析器: JAVA实现
- 一、程序设计:
- 1.程序运行:
- ①预处理:
- ②读取流信息,识别单词:
- ③将相关信息整理保存:
- 2.扫描器实现:
- 3.自动机原理图:
- 二、实现代码:
一、程序设计:
1.程序运行:
①预处理:
读取文本信息,将注释以及换行符和多余空格去除,生成字符流信息
②读取流信息,识别单词:
每个字符都读取,交由一个类似于自动机功能的扫描器函数处理,并生成token流
③将相关信息整理保存:
2.扫描器实现:
读入经过预处理后的文本信息,将读取的第一个字符送入类自动机中,识别出它是字母、数字或者其它一些符号后把状态标记修改为它对应类型的标记值,然后通过switch送入到相应的类自动机识别功能模块中,自动识别成单独的一个有意义的word后,查找对应的字符表,如果有则生成一个token值,如果没有则在表中新增该word,并生成一个token值
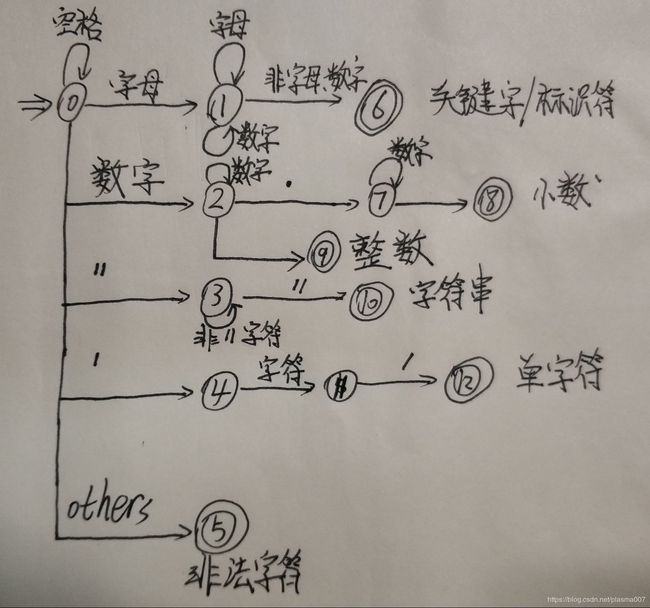
3.自动机原理图:
下面的图是一个自动机设计的原理图,程序则根据这个原理图进行相关功能的模拟实现
二、实现代码:
// NEU,SHENYANG
// @author: plasma007
import java.io.File;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.util.*;
import javax.lang.model.element.Element;
import javax.print.attribute.standard.PrinterInfo;
import org.graalvm.compiler.nodes.NodeView.Default;
public class analyzer {
String[] k = { "int", "main", "void", "if", "char", "return", "short", "long", "short", "signed", "ensigned",
"restrict", "struct", "union", "enum", "typedef", "sizeof", "auto", "static", "register", "extern", "const",
"volatitle", "break", "goto", "else", "switch", "case", "default", "continue", "do", "double", "float" };// 关键字表
String[] p = { "+", "-", "*", "/", "%",".", "++", "--", ">", "<", "=", "(", ")", "{", "}", ";", "[", "]", ":", "?", "'",
"\"", ",", "==", ">=", "<=", "!=", "&", "|", "~", "^", "<<", ">>", "!", "&&", "||", "+=", "-=", "*=", "/=",
"%=", "&=", "|=", "^=", ">>=", "<==", "*", "&" };// 运算符和界符表
List<String> i = new ArrayList<String>();// 标识符表
List<String> C = new ArrayList<String>();// 单字符表
List<String> S = new ArrayList<String>();// 多字符表
List<String> c = new ArrayList<String>();// 常数表
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String path_in = "filename"; // 读入信息文件路径
String path_out = "filename"; // 输出信息文件路径
analyzer c_txt = new analyzer(); // 创建一个c_txt的analyzer对象
String p_in = c_txt.pretreatment(path_in);// p_in为经过预处理后的文本信息(调用了预处理函数)
c_txt.scanner(p_in, path_out);// 扫描器
}
// 预处理函数, 主要处理文档中的注释
public String pretreatment(String p_in) {
String r = ""; // 用来保存去除注释后的源程序
try {
File C_txt = new File(p_in);
InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(C_txt)); // 建立一个字符流对象reader(将输入的字节流转换为字符流)
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(reader);// 创建一个缓存字符流对象read
String line = ""; // 用于保存读取每行文本信息的
while (line != null) {
// 按行读取文本信息,遇到单行注释时删除注释内容
if (line.indexOf("//") != -1) { // 如果找到"//"则舍弃包括"//"及其后全部内容
line = line.substring(0, line.indexOf("//") - 1);
}
r = r + " " + line;// 将每一行用空格隔开
line = br.readLine();// 以行读取内容,每次只读取一行
}
br.close();// 关闭此文件输入流并释放与此流有关的所有系统资源
// 删除多行注释
while (r.indexOf("/*") != -1) {// 如果文本信息中函数注释符
if (r.indexOf("*/") != -1) {
// 如果找到注释符的闭包则将注释符连同注释符之间的内容删去
r = r.substring(0, r.indexOf("/*")).concat(r.substring(r.indexOf("*/") + 2));
} else {// 如果没找到注释符的闭包,则将注释符及其后内容全部删去
r = r.substring(r.indexOf("/*"));
}
}
r = r.replaceAll(" {2,}", " ");//删去多余的空格(至少匹配 2次)
if (r.charAt(0) == ' ')
r = r.substring(1);//删去首部空格
if (r.charAt(r.length() - 1) == ' ')
r = r.substring(0, r.length() - 1);// 删去尾部空格
System.out.println(r);// 将预处理后的string输出
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return r;// 返回处理好后的字符串
}
// 扫描器实现
public void scanner(String path_in, String path_out) {
try {
String result = "";// 用来保存token流信息
int subscript = 0;// 用来计数
int t, status, pre_subscript;// 分别为: 记录单个字符的ASCII码,记忆状态,用于记录当前字符下标
String word;// 形成一个单词
String r = path_in; // 经过预处理后的文本字符流信息
while (subscript < r.length()) {// 一直将文本信息读完
t = (int) r.charAt(subscript);// 将字符转换成ASCII码的值
if (t == 32)
status = 0;// 当前字符为空格时,状态标记为0
else if ((t > 64 && t < 91) || (t > 96 && t < 123))// 65~90 A-Z,97~122 a~z
status = 1;// 如果当前字符为字符时,状态标记为1
else if (t >= 48 && t <= 57)
status = 2;// 如果当前字符为数字时,状态标记为2
else if (t == 34)
status = 3;// 如果当前字符为双引号时,状态标记为3
else if (t == 39)
status = 4;// 如果当前字符为单引号时,状态标记为4
else if ((t >= 33 && t <= 47 && t != 34 && t != 39) || (t >= 58 && t <= 64) || (t >= 91 && t <= 96)
|| (t >= 123 && t <= 126))
status = 5;// 其它字符,状态标记为5
else {
// 检测到非法字符时输出异常信息
System.out.println("status异常");
System.out.println(r.charAt(subscript));
System.out.println((int) r.charAt(subscript));
break;
}
switch (status) {// 对于每一种状态
case 0:// 空格
subscript++; // 继续识别下一个字符
break;
case 1:// 字母(单词)
// result = check_letter();
pre_subscript = subscript; // 记录读入字符时的下标
if (subscript != r.length()) {// 当前字符在文本信息内
subscript++;// 更新下标
t = (int) r.charAt(subscript);// 更新当前字符值
while (((t > 64 && t < 91) || (t > 96 && t < 123) || (t > 47 && t < 58))
&& (subscript < (r.length() - 1))) {// 65~90 A-Z,97~122 a~z,48~57 0-9
// 如果当前字符为字母或者数字时,当前字符下标+1,否则将一直读到最后一个单词
subscript++;// 更新下标
t = (int) r.charAt(subscript);// 更新当前字符值
}
}
// if (pre_subscript == subscript)
// subscript++;// 如果后面不接字母或者数字,将识别为一个标识符
word = r.substring(pre_subscript, subscript);// 将这个词从串信息删去
int if_key = 0;// 判断是不是关键字
int m;
for (m = 0; m < k.length; m++) {
if (word.equals(k[m])) {
// System.out.println(m+" "+ k[m]);
if_key = 1;// 如果能匹配到则该改状态
break;
}
}
if (if_key == 1) {// 如果是匹配成功则在token上添加一个二元组{单词,在表中的序号} 由于序号是由1开始,所以应该为下标+1
result = result.concat(" {k,").concat(String.valueOf(m + 1)).concat("}");
} else {// 匹配失败,k表中没有则判断标识符表
if (i.contains(word)) {// 如果i标识符表不为空,且表中有这个单词
result = result.concat(" {i,").concat(String.valueOf(i.indexOf(word) + 1)).concat("}");
} else {
i.add(word);// 如果标识符表中没有这个单词,则添加到标识符表
result = result.concat(" {i,").concat(String.valueOf(i.indexOf(word) + 1)).concat("}");
}
}
break;
case 2:// 数字
pre_subscript = subscript;
if (subscript != r.length()) {// 如果当前字符在文本信息内
while (t >= 48 && t <= 57 && subscript < r.length() - 1) { // 48~57 0-9
//subscript++;
//t = (int) r.charAt(subscript);
if ((int) r.charAt(subscript + 1) == 46) {//如果后面是小数点
System.out.println(t);
subscript++;
t = (int) r.charAt(subscript);
} else {// 如果数字后面是数字
while (t >= 48 && t <= 57) {
subscript++;
t = (int) r.charAt(subscript);
if( t== 46) subscript++;t = (int) r.charAt(subscript);
}
}
}
}
// 获取该改长度的字符,得到一个字
word = r.substring(pre_subscript, subscript);
// 查找c常数表,如果有则直接插入位置
if (c.contains(word)) {
result = result.concat(" {c,").concat(String.valueOf(c.indexOf(word) + 1)).concat("}");
} else {// c常数表中没有,则c表新添
c.add(word);
result = result.concat(" {c,").concat(String.valueOf(c.size())).concat("}");
}
break;
case 3:// 字符串
pre_subscript = subscript;
subscript++;
// 从双引号后一位开始识别,非双引号字符一律划为字符串内容
while ((int) r.charAt(subscript) != 34 && subscript < r.length() - 1)
subscript++;
// 字符串需要将双引号一起包括进来
word = r.substring(pre_subscript, subscript + 1);
// 如果匹配不到成对的双引号,则报错
if ((int) word.charAt(word.length() - 1) != 34)
System.out.println("双引号不成对错误");
// 查找S表,如果S表中含有这个单词
if (S.contains(word)) {
result = result.concat(" {S,").concat(String.valueOf(S.indexOf(word) + 1)).concat("}");
} else {// 如果S表中没有这个单词,则添加这个单词进表
S.add(word);
result = result.concat(" {S,").concat(String.valueOf(S.indexOf(word) + 1)).concat("}");
}
subscript++;
break;
case 4:// 字符
pre_subscript = subscript;
subscript++;
// 从单引号后面开始识别,如果是单字符
while ((int) r.charAt(subscript) != 39 && subscript < r.length() - 1)
subscript++;
// 保存单引号和单字符作为一个整体
word = r.substring(pre_subscript, subscript + 1);
// 单引号匹配不成功,则报错
if ((int) word.charAt(word.length() - 1) != 39)
System.out.println("单引号不成对错误");
// 如果C单字符表中含有这个单词
if (C.contains(word)) {
result = result.concat(" {C,").concat(String.valueOf(C.indexOf(word) + 1)).concat("}");
} else {// 如果C没有则新增
C.add(word);
result = result.concat(" {C,").concat(String.valueOf(C.indexOf(word) + 1)).concat("}");
}
subscript++;// 转向下一字符
break;
case 5:// 符号
// 如果是符号,则直接将符号取出
word = r.substring(subscript, subscript + 1);
if (subscript + 1 < r.length()) {
t = (int) r.charAt(subscript + 1);
if ((t >= 33 && t <= 47 && t != 34 && t != 39) || (t >= 58 && t <= 64) || (t >= 91 && t <= 96)
|| (t >= 123 && t <= 126)) {
char f_point1 = r.charAt(subscript);
char f_point2 = r.charAt(subscript + 1);
if ((f_point1 == '&' && f_point2 == '&') || (f_point1 == '+' && f_point2 == '+')
|| (f_point1 == '-' && f_point2 == '-') || (f_point1 == '|' && f_point2 == '|')
|| (f_point1 == '>' && f_point2 == '=') || (f_point1 == '<' && f_point2 == '=')
|| (f_point1 == '=' && f_point2 == '=') || (f_point1 == '!' && f_point2 == '=')
|| (f_point1 == '<' && f_point2 == '<') || (f_point1 == '>' && f_point2 == '>')
|| (f_point1 == '+' && f_point2 == '=') || (f_point1 == '-' && f_point2 == '=')
|| (f_point1 == '+' && f_point2 == '+') || (f_point1 == '*' && f_point2 == '=')
|| (f_point1 == '/' && f_point2 == '=') || (f_point1 == '%' && f_point2 == '=')
|| (f_point1 == '&' && f_point2 == '=') || (f_point1 == '|' && f_point2 == '=')
|| (f_point1 == '^' && f_point2 == '=')) {
word = r.substring(subscript, subscript + 2);
subscript++;
}
}
}
int mm;
int if_point = 0;
// 查找p表
for (mm = 0; mm < k.length; mm++) {
if (word.equals(p[mm])) {
// System.out.println(m+" "+ k[m]);
if_point = 1;// 如果能匹配到则该改状态
break;
}
}
if (if_point == 1) {// 如果是匹配成功
result = result.concat(" {p,").concat(String.valueOf(mm + 1)).concat("}");
} else {// 匹配失败,k表中没有则判断标识符表
System.out.println("符号非法错误:出现非法符号,不是已定义符号 " + word);
}
subscript++;
break;
default:
System.out.println("\n字符识别异常:无法识别的状态");
break;
}
}
// 将结果保存在文档中
save_result(result, i, C, S, c, p, k, path_out);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 将list<String>转换成String用于保存信息写入文档
public String get_list(List<String> t) {
String s = new String();
for (int i = 1; i < (t.size() + 1); i++) {
s = s + "\n" + i + " " + t.get(i - 1);// 添加序号,单独存放在一行,形成一个列表
}
return s;// 返回一个字符串
}
// 将信息保存在文档中
public void save_result(String result, List<String> i, List<String> C, List<String> S, List<String> c, String[] p,
String[] k, String path_out) {
try {
String show_i, show_C, show_S, show_c, show_k, show_p;
show_i = "i标识符表: " + get_list(i);
show_C = "C单字符表:" + get_list(C);
show_S = "S多字符表:" + get_list(S);
show_c = "c常数表:" + get_list(c);
show_k = "k关键字表:" + get_list(Arrays.asList(k));
show_p = "p运算符和界符表:" + get_list(Arrays.asList(p));
File writename = new File(path_out); // 如果没有则新建一个新的path_out的txt文件
writename.createNewFile(); // 创建新文件
BufferedWriter out = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(writename));
out.write(result.concat("\n\n").concat(show_i).concat("\n\n").concat(show_C).concat("\n\n").concat(show_S)
.concat("\n\n").concat(show_c).concat("\n\n").concat(show_p).concat("\n\n").concat(show_k)); // 写入
out.flush(); // 把缓存区内容压入文件
out.close(); // 最后记得关闭文件
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}