Flink源码剖析:Flink Async I/O的三种模式
文章目录
- 1. 维表join
- 2. richmapfunction
- 2.1 示例
- 3. asyncio
- 3.1 示例
- 3.2 Ordered模式
- 3.2.1 生产
- 3.2.2 消费
- 3.3 基于processtime的unordered模式
- 3.3.1 生产
- 3.3.2 消费
- 3.4 基于eventTime的unordered模式
- 3.4.1 生产
- 3.4.2 消费
- 4. 总结
1. 维表join
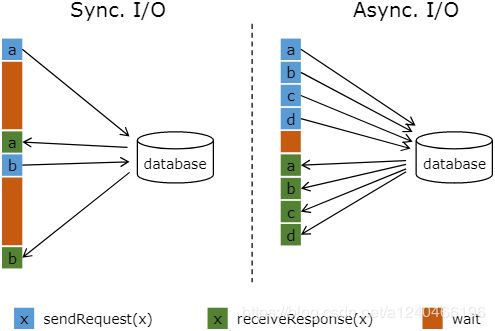
流计算系统中经常需要与外部系统进行交互,比如需要查询外部数据库以关联上用户的额外信息。通常,我们的实现方式是向数据库发送用户a的查询请求,然后等待结果返回,在这之前,我们无法发送用户b的查询请求。这是一种同步访问的模式,如下图左边所示。
图中棕色的长条表示等待时间,可以发现网络等待时间极大地阻碍了吞吐和延迟。为了解决同步访问的问题,异步模式可以并发地处理多个请求和回复。也就是说,你可以连续地向数据库发送用户a、b、c等的请求,与此同时,哪个请求先返回了就处理哪个请求,从而连续的请求之间不需要阻塞等待,如上图右边所示。这也正是 Async I/O 的实现原理。
2. richmapfunction
利用richmapfunction进行维表关联,就是典型的sync I/O的关联方式。两次请求之间阻塞进行。不适合并发量高的情形。
2.1 示例
public static final class MapWithSiteInfoFunc
extends RichMapFunction<String, String> {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MapWithSiteInfoFunc.class);
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private transient ScheduledExecutorService dbScheduler;
// 引入缓存,减小请求次数
private Map<Integer, SiteAndCityInfo> siteInfoCache;
@Override
public void open(Configuration parameters) throws Exception {
super.open(parameters);
siteInfoCache = new HashMap<>(1024);
// 利用定时线程,实现维度数据的周期性更新
dbScheduler = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(1, r -> {
Thread thread = new Thread(r, "site-info-update-thread");
thread.setUncaughtExceptionHandler((t, e) -> {
LOGGER.error("Thread " + t + " got uncaught exception: " + e);
});
return thread;
});
dbScheduler.scheduleWithFixedDelay(() -> {
try {
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner(JdbcUtil.getDataSource());
List<Map<String, Object>> info = queryRunner.query(SITE_INFO_QUERY_SQL, new MapListHandler());
for (Map<String, Object> item : info) {
siteInfoCache.put((int) item.get("site_id"), new SiteAndCityInfo(
(int) item.get("site_id"),
(String) item.getOrDefault("site_name", ""),
(long) item.get("city_id"),
(String) item.getOrDefault("city_name", "")
));
}
LOGGER.info("Fetched {} site info records, {} records in cache", info.size(), siteInfoCache.size());
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error("Exception occurred when querying: " + e);
}
}, 0, 10 * 60, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
@Override
public String map(String value) throws Exception {
JSONObject json = JSON.parseObject(value);
int siteId = json.getInteger("site_id");
String siteName = "", cityName = "";
SiteAndCityInfo info = siteInfoCache.getOrDefault(siteId, null);
if (info != null) {
siteName = info.getSiteName();
cityName = info.getCityName();
}
json.put("site_name", siteName);
json.put("city_name", cityName);
return json.toJSONString();
}
@Override
public void close() throws Exception {
// 清空缓存,关闭连接
siteInfoCache.clear();
ExecutorUtils.gracefulShutdown(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS, dbScheduler);
JdbcUtil.close();
super.close();
}
private static final String SITE_INFO_QUERY_SQL = "...";
}
3. asyncio
Flink 1.2中引入了Async IO(异步IO)来加快flink与外部系统的交互性能,提升吞吐量。其设计的核心是对原有的每条处理后的消息发送至下游operator的执行流程进行改进。其核心实现包括生产和消费两部分,生产端引入了一个AsyncWaitOperator,在其processElement/processWatermark方法中完成对消息的维表关联,随即将未处理完的Futrue对象存入队列中;消费端引入一个Emitter线程,不断从队列中消费数据并发往下游算子。
3.1 示例
简单的来说,使用 Async I/O 对应到 Flink 的 API 就是 RichAsyncFunction 这个抽象类,继承这个抽象类实现里面的open(初始化),asyncInvoke(数据异步调用),close(停止的一些操作)方法,最主要的是实现asyncInvoke 里面的方法。有如下示例,Kafka作为流表,存储用户浏览记录,Elasticsearch作为维表,存储用户年龄信息,利用async I/O对浏览记录进行加宽。
流表: 用户行为日志。某个用户在某个时刻点击或浏览了某个商品。自己造的测试数据,数据样例如下:
{"userID": "user_1", "eventTime": "2016-06-06 07:03:42", "eventType": "browse", "productID": 2}
维表: 用户基础信息。自己造的测试数据,数据存储在ES上,数据样例如下:
GET dim_user/dim_user/user
{
"_index": "dim_user",
"_type": "dim_user",
"_id": "user_1",
"_version": 1,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"age": 22
}
}
实现逻辑:
public class FlinkAsyncIO {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
String kafkaBootstrapServers = "localhost:9092";
String kafkaGroupID = "async-test";
String kafkaAutoOffsetReset= "latest";
String kafkaTopic = "asyncio";
int kafkaParallelism =2;
String esHost= "localhost";
Integer esPort= 9200;
String esUser = "";
String esPassword = "";
String esIndex = "dim_user";
String esType = "dim_user";
/**Flink DataStream 运行环境*/
Configuration config = new Configuration();
config.setInteger(RestOptions.PORT,8081);
config.setBoolean(ConfigConstants.LOCAL_START_WEBSERVER, true);
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.createLocalEnvironmentWithWebUI(config);
/**添加数据源*/
Properties kafkaProperties = new Properties();
kafkaProperties.put("bootstrap.servers",kafkaBootstrapServers);
kafkaProperties.put("group.id",kafkaGroupID);
kafkaProperties.put("auto.offset.reset",kafkaAutoOffsetReset);
FlinkKafkaConsumer010<String> kafkaConsumer = new FlinkKafkaConsumer010<>(kafkaTopic, new SimpleStringSchema(), kafkaProperties);
kafkaConsumer.setCommitOffsetsOnCheckpoints(true);
SingleOutputStreamOperator<String> source = env.addSource(kafkaConsumer).name("KafkaSource").setParallelism(kafkaParallelism);
//数据转换
SingleOutputStreamOperator<Tuple4<String, String, String, Integer>> sourceMap = source.map((MapFunction<String, Tuple4<String, String, String, Integer>>) value -> {
Tuple4<String, String, String, Integer> output = new Tuple4<>();
try {
JSONObject obj = JSON.parseObject(value);
output.f0 = obj.getString("userID");
output.f1 = obj.getString("eventTime");
output.f2 = obj.getString("eventType");
output.f3 = obj.getInteger("productID");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return output;
}).returns(new TypeHint<Tuple4<String, String, String, Integer>>(){}).name("Map: ExtractTransform");
//过滤掉异常数据
SingleOutputStreamOperator<Tuple4<String, String, String, Integer>> sourceFilter = sourceMap.filter((FilterFunction<Tuple4<String, String, String, Integer>>) value -> value.f3 != null).name("Filter: FilterExceptionData");
//Timeout: 超时时间 默认异步I/O请求超时时,会引发异常并重启或停止作业。 如果要处理超时,可以重写AsyncFunction#timeout方法。
//Capacity: 并发请求数量
/**Async IO实现流表与维表Join*/
SingleOutputStreamOperator<Tuple5<String, String, String, Integer, Integer>> result = AsyncDataStream.unorderedWait(sourceFilter, new ElasticsearchAsyncFunction(esHost,esPort,esUser,esPassword,esIndex,esType), 500, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, 10).name("Join: JoinWithDim");
/**结果输出*/
result.print().name("PrintToConsole");
env.execute();
}
}
ElasticsearchAsyncFunction:
public class ElasticsearchAsyncFunction extends RichAsyncFunction<Tuple4<String, String, String, Integer>, Tuple5<String, String, String, Integer, Integer>> {
private String host;
private Integer port;
private String user;
private String password;
private String index;
private String type;
public ElasticsearchAsyncFunction(String host, Integer port, String user, String password, String index, String type) {
this.host = host;
this.port = port;
this.user = user;
this.password = password;
this.index = index;
this.type = type;
}
private RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient;
private Cache<String, Integer> cache;
/**
* 和ES建立连接
*
* @param parameters
*/
@Override
public void open(Configuration parameters) {
//ES Client
CredentialsProvider credentialsProvider = new BasicCredentialsProvider();
credentialsProvider.setCredentials(AuthScope.ANY, new UsernamePasswordCredentials(user, password));
restHighLevelClient = new RestHighLevelClient(
RestClient
.builder(new HttpHost(host, port))
.setHttpClientConfigCallback(httpAsyncClientBuilder -> HttpAsyncClientBuilder.create()));
//初始化缓存
cache = CacheBuilder.newBuilder().maximumSize(2).expireAfterAccess(5, TimeUnit.MINUTES).build();
}
/**
* 关闭连接
*
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void close() throws Exception {
restHighLevelClient.close();
}
/**
* 异步调用
*
* @param input
* @param resultFuture
*/
@Override
public void asyncInvoke(Tuple4<String, String, String, Integer> input, ResultFuture<Tuple5<String, String, String, Integer, Integer>> resultFuture) {
// 1、先从缓存中取
Integer cachedValue = cache.getIfPresent(input.f0);
if (cachedValue != null) {
System.out.println("从缓存中获取到维度数据: key=" + input.f0 + ",value=" + cachedValue);
resultFuture.complete(Collections.singleton(new Tuple5<>(input.f0, input.f1, input.f2, input.f3, cachedValue)));
// 2、缓存中没有,则从外部存储获取
} else {
searchFromES(input, resultFuture);
}
}
/**
* 当缓存中没有数据时,从外部存储ES中获取
*
* @param input
* @param resultFuture
*/
private void searchFromES(Tuple4<String, String, String, Integer> input, ResultFuture<Tuple5<String, String, String, Integer, Integer>> resultFuture) {
// 1、构造输出对象
Tuple5<String, String, String, Integer, Integer> output = new Tuple5<>();
output.f0 = input.f0;
output.f1 = input.f1;
output.f2 = input.f2;
output.f3 = input.f3;
// 2、待查询的Key
String dimKey = input.f0;
// 3、构造Ids Query
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest();
searchRequest.indices(index);
searchRequest.types(type);
searchRequest.source(SearchSourceBuilder.searchSource().query(QueryBuilders.idsQuery().addIds(dimKey)));
RequestOptions requestOptions = RequestOptions.DEFAULT;
// 4、用异步客户端查询数据
restHighLevelClient.searchAsync(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT, new ActionListener<SearchResponse>() {
//成功响应时处理
@Override
public void onResponse(SearchResponse searchResponse) {
SearchHit[] searchHits = searchResponse.getHits().getHits();
if (searchHits.length > 0) {
JSONObject obj = JSON.parseObject(searchHits[0].getSourceAsString());
Integer dimValue = obj.getInteger("age");
output.f4 = dimValue;
cache.put(dimKey, dimValue);
System.out.println("将维度数据放入缓存: key=" + dimKey + ",value=" + dimValue);
}
resultFuture.complete(Collections.singleton(output));
}
//响应失败时处理
@Override
public void onFailure(Exception e) {
output.f4 = null;
resultFuture.complete(Collections.singleton(output));
}
});
}
//超时时处理
@Override
public void timeout(Tuple4<String, String, String, Integer> input, ResultFuture<Tuple5<String, String, String, Integer, Integer>> resultFuture) {
searchFromES(input, resultFuture);
}
}
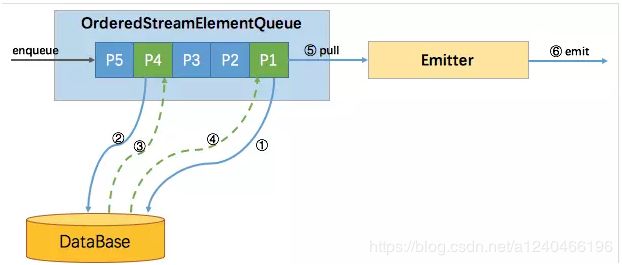
3.2 Ordered模式
Flink Async I/O又可以细分为三种,一种是有序的Ordered模式,一种是ProcessingTime 无序模式,一种是EventTime 无序。
主要区别是往下游output的顺序,有序模式会按接收的顺序继续往下游output发送,无序模式就是谁先处理完谁就先往下游发送。下图是ordered模式的原理图。
无论有序无需,都采用了Futrue/Promise设计模式,大体都遵循以下设计逻辑:
-
生产端:将每条消息封装成一个
StreamRecordQueueEntry(内部维护一个Future对象),放入StreamElementQueue中 -
生产端:消息与外部系统交互的逻辑放入AsynInvoke方法中,将交互执行结果放入
StreamRecordQueueEntry中 -
消费端:启动一个emitter线程,从
StreamElementQueue中读取已经完成的StreamRecordQueueEntry,将其结果发送至下游operator算子
下面我们分别就生产端和消费端对ordered模式进行源码分析
3.2.1 生产
AsyncWaitOperator
@Internal
public class AsyncWaitOperator<IN, OUT>
extends AbstractUdfStreamOperator<OUT, AsyncFunction<IN, OUT>>
implements OneInputStreamOperator<IN, OUT>, OperatorActions, BoundedOneInput {
@Override
public void setup(StreamTask<?, ?> containingTask, StreamConfig config, Output<StreamRecord<OUT>> output) {
super.setup(containingTask, config, output);
this.checkpointingLock = getContainingTask().getCheckpointLock();
this.inStreamElementSerializer = new StreamElementSerializer<>(
getOperatorConfig().<IN>getTypeSerializerIn1(getUserCodeClassloader()));
// create the operators executor for the complete operations of the queue entries
this.executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
// 根据项目中使用AsyncDataStream.unorderedWait还是AsyncDataStream.orderedWait方法,进行有序和无需两种模式的区分,初始化不同的队列
switch (outputMode) {
case ORDERED:
queue = new OrderedStreamElementQueue(
capacity,
executor,
this);
break;
case UNORDERED:
queue = new UnorderedStreamElementQueue(
capacity,
executor,
this);
break;
default:
throw new IllegalStateException("Unknown async mode: " + outputMode + '.');
}
}
@Override
public void open() throws Exception {
super.open();
// 启动emitter线程
this.emitter = new Emitter<>(checkpointingLock, output, queue, this);
this.emitterThread = new Thread(emitter, "AsyncIO-Emitter-Thread (" + getOperatorName() + ')');
emitterThread.setDaemon(true);
emitterThread.start();
// process stream elements from state, since the Emit thread will start as soon as all
// elements from previous state are in the StreamElementQueue, we have to make sure that the
// order to open all operators in the operator chain proceeds from the tail operator to the
// head operator.
if (recoveredStreamElements != null) {
for (StreamElement element : recoveredStreamElements.get()) {
if (element.isRecord()) {
processElement(element.<IN>asRecord());
}
else if (element.isWatermark()) {
processWatermark(element.asWatermark());
}
else if (element.isLatencyMarker()) {
processLatencyMarker(element.asLatencyMarker());
}
else {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unknown record type " + element.getClass() +
" encountered while opening the operator.");
}
}
recoveredStreamElements = null;
}
}
// 算子中的processElement方法,都会逐个处理每一条到来的数据
@Override
public void processElement(StreamRecord<IN> element) throws Exception {
// 将数据包装成StreamRecordBufferEntry对象
final StreamRecordQueueEntry<OUT> streamRecordBufferEntry = new StreamRecordQueueEntry<>(element);
addAsyncBufferEntry(streamRecordBufferEntry);
// 调用AsyncFunction接口的用户自定义实现类ElasticsearchAsyncFunction中的asyncInvoke方法,该用户实现方法中,将返回结果通过异步回调的方式,返回给StreamRecordBufferEntry对象中的Future对象
userFunction.asyncInvoke(element.getValue(), streamRecordBufferEntry);
}
private <T> void addAsyncBufferEntry(StreamElementQueueEntry<T> streamElementQueueEntry) throws InterruptedException {
assert(Thread.holdsLock(checkpointingLock));
pendingStreamElementQueueEntry = streamElementQueueEntry;
// 尝试将StreamRecordQueueEntry对象加入到队列
while (!queue.tryPut(streamElementQueueEntry)) {
// we wait for the emitter to notify us if the queue has space left again
checkpointingLock.wait();
}
pendingStreamElementQueueEntry = null;
}
}
OrderedStreamElementQueue
@Internal
public class OrderedStreamElementQueue implements StreamElementQueue {
// 往OrderedStreamElementQueue队列中插入StreamRecordBufferEntry对象
@Override
public <T> boolean tryPut(StreamElementQueueEntry<T> streamElementQueueEntry) throws InterruptedException {
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
// capacity用于控制并发请求数量,即OrderedStreamElementQueue队列中的StreamRecordBufferEntry对象的个数
if (queue.size() < capacity) {
addEntry(streamElementQueueEntry);
LOG.debug("Put element into ordered stream element queue. New filling degree " +
"({}/{}).", queue.size(), capacity);
return true;
} else {
// 如果一直插入失败,则AsyncWaitOperator#addAsyncBufferEntry方法会无限尝试插入,极致情况下,会触发Flink自身的反压机制,用户不用做任何特殊处理
LOG.debug("Failed to put element into ordered stream element queue because it " +
"was full ({}/{}).", queue.size(), capacity);
return false;
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
private <T> void addEntry(StreamElementQueueEntry<T> streamElementQueueEntry) {
assert(lock.isHeldByCurrentThread());
// 将StreamRecordBufferEntry对象插入队尾
queue.addLast(streamElementQueueEntry);
// StreamRecordBufferEntry对象中的Futrue对象一旦返回结果,则进行以下调用
streamElementQueueEntry.onComplete(
(StreamElementQueueEntry<T> value) -> {
try {
onCompleteHandler(value);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// we got interrupted. This indicates a shutdown of the executor
LOG.debug("AsyncBufferEntry could not be properly completed because the " +
"executor thread has been interrupted.", e);
} catch (Throwable t) {
operatorActions.failOperator(new Exception("Could not complete the " +
"stream element queue entry: " + value + '.', t));
}
},
executor);
}
private void onCompleteHandler(StreamElementQueueEntry<?> streamElementQueueEntry) throws InterruptedException {
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
// 队列不为空,且队首StreamRecordBufferEntry对象中的Future对象已收到返回值,则通过Condition对象唤醒emmiter线程,使其能够取出队首元素
if (!queue.isEmpty() && queue.peek().isDone()) {
LOG.debug("Signal ordered stream element queue has completed head element.");
headIsCompleted.signalAll();
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
@Override
public AsyncResult peekBlockingly() throws InterruptedException {
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
// emmiter线程在从队列中取StreamRecordBufferEntry对象时,如果队列为空 or 队首future未完成,则emmiter线程会一直阻塞
while (queue.isEmpty() || !queue.peek().isDone()) {
// Condition阻塞
headIsCompleted.await();
}
LOG.debug("Peeked head element from ordered stream element queue with filling degree " +
"({}/{}).", queue.size(), capacity);
return queue.peek();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
3.2.2 消费
Emmiter
@Internal
public class Emitter<OUT> implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
// 不断尝试读取队首元素,在OrderedStreamElementQueue#peekBlockingly中可以看到,如果队首元素中的Future对象还没有返回数据,Emitter线程会一直阻塞
while (running) {
LOG.debug("Wait for next completed async stream element result.");
AsyncResult streamElementEntry = streamElementQueue.peekBlockingly();
// 将数据发往下游算子
output(streamElementEntry);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
if (running) {
operatorActions.failOperator(e);
} else {
// Thread got interrupted which means that it should shut down
LOG.debug("Emitter thread got interrupted, shutting down.");
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
operatorActions.failOperator(new Exception("AsyncWaitOperator's emitter caught an " +
"unexpected throwable.", t));
}
}
private void output(AsyncResult asyncResult) throws InterruptedException {
if (asyncResult.isWatermark()) {
synchronized (checkpointLock) {
AsyncWatermarkResult asyncWatermarkResult = asyncResult.asWatermark();
LOG.debug("Output async watermark.");
// 如果是watermark,直接发往下游算子
output.emitWatermark(asyncWatermarkResult.getWatermark());
// 移除队首StreamRecordBufferEntry对象,注意peek和poll的区别
streamElementQueue.poll();
// notify the main thread that there is again space left in the async collector
// buffer
checkpointLock.notifyAll();
}
} else {
AsyncCollectionResult<OUT> streamRecordResult = asyncResult.asResultCollection();
if (streamRecordResult.hasTimestamp()) {
timestampedCollector.setAbsoluteTimestamp(streamRecordResult.getTimestamp());
} else {
timestampedCollector.eraseTimestamp();
}
synchronized (checkpointLock) {
LOG.debug("Output async stream element collection result.");
try {
// 取出StreamRecordBufferEntry对象中的Future对象中的join后的数据
Collection<OUT> resultCollection = streamRecordResult.get();
// 将数据发往下游算子
if (resultCollection != null) {
for (OUT result : resultCollection) {
timestampedCollector.collect(result);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
operatorActions.failOperator(
new Exception("An async function call terminated with an exception. " +
"Failing the AsyncWaitOperator.", e));
}
// 移除队首StreamRecordBufferEntry对象,注意peek和poll的区别
streamElementQueue.poll();
// notify the main thread that there is again space left in the async collector
// buffer
checkpointLock.notifyAll();
}
}
}
}
3.3 基于processtime的unordered模式
区别于ordered模式,无序模式下的StreamRecordBufferEntry对象外层又被封装了一层Set层,主要是为了应对watermark的存在,详情见下节。基于processtime的unordered模式下,虽然没有watermark,但是也跟基于eventTime的unordered模式共用了同一套逻辑,因此也多了一层Set层。
该模式下,不存在watermark类型的消息,因此所有消息的StreamRecordBufferEntry对象都是放入lastSet(此模式下,lastSet和firstSet引用相同的对象),在消息的onCompleteHandler方法中,直接将该消息的StreamRecordBufferEntry对象从lastSet中取出再放入completeQueue中,通过emitter线程发送至下游operator,因此该场景下实现的是完全无序的处理模式。
云邪在其博客 《Flink 原理与实现:Aysnc I/O》中提到的基于processtime的unordered模式的架构图,是针对Flink 1.3进行分析的,已经不再适用于Flink1.9,Flink1.9中该模式已经不需要用到uncompletedQueue,架构图如下:
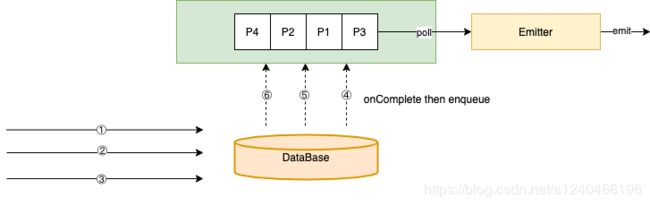
另,云邪博客中的asyncCollector等数据结构在Flink1.9中也不复存在,本文针对Flink1.9进行分析。
3.3.1 生产
UnorderedStreamElementQueue
@Internal
public class UnorderedStreamElementQueue implements StreamElementQueue {
private <T> void addEntry(StreamElementQueueEntry<T> streamElementQueueEntry) {
assert(lock.isHeldByCurrentThread());
if (streamElementQueueEntry.isWatermark()) {
lastSet = new HashSet<>(capacity);
if (firstSet.isEmpty()) {
firstSet.add(streamElementQueueEntry);
} else {
Set<StreamElementQueueEntry<?>> watermarkSet = new HashSet<>(1);
watermarkSet.add(streamElementQueueEntry);
uncompletedQueue.offer(watermarkSet);
}
uncompletedQueue.offer(lastSet);
} else {
// 基于processtime的unordered模式只会走这里,且lastSet和firstSet引用同一个对象
lastSet.add(streamElementQueueEntry);
}
streamElementQueueEntry.onComplete(
(StreamElementQueueEntry<T> value) -> {
try {
onCompleteHandler(value);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// The accept executor thread got interrupted. This is probably cause by
// the shutdown of the executor.
LOG.debug("AsyncBufferEntry could not be properly completed because the " +
"executor thread has been interrupted.", e);
} catch (Throwable t) {
operatorActions.failOperator(new Exception("Could not complete the " +
"stream element queue entry: " + value + '.', t));
}
},
executor);
numberEntries++;
}
// StreamRecordBufferEntry对象中的Future对象返回结果时进行回调
public void onCompleteHandler(StreamElementQueueEntry<?> streamElementQueueEntry) throws InterruptedException {
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
// 将StreamRecordBufferEntry对象插入completedQueue队列
// 此处将StreamRecordBufferEntry对象插入lastSet(等同于firstSet),又从其中取出,确实是比较多余的。这样做只是因为跟”基于eventTime的unordered模式”共用了一套代码
if (firstSet.remove(streamElementQueueEntry)) {
// 将StreamRecordBufferEntry对象加入completedQueue
completedQueue.offer(streamElementQueueEntry);
// 该模式下不会走下面的代码
while (firstSet.isEmpty() && firstSet != lastSet) {
firstSet = uncompletedQueue.poll();
Iterator<StreamElementQueueEntry<?>> it = firstSet.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
StreamElementQueueEntry<?> bufferEntry = it.next();
if (bufferEntry.isDone()) {
completedQueue.offer(bufferEntry);
it.remove();
}
}
}
LOG.debug("Signal unordered stream element queue has completed entries.");
hasCompletedEntries.signalAll();
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
@Override
public AsyncResult peekBlockingly() throws InterruptedException {
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
// emitter线程从completedQueue取出StreamRecordBufferEntry对象,相比ordered模式,这里不需要判断队首StreamRecordBufferEntry对象中的Future对象是否已经返回,因为只有Futrue已返回的StreamRecordBufferEntry对象才能被插入到completedQueue队列
while (completedQueue.isEmpty()) {
hasCompletedEntries.await();
}
LOG.debug("Peeked head element from unordered stream element queue with filling degree " +
"({}/{}).", numberEntries, capacity);
return completedQueue.peek();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
3.3.2 消费
Emitter线程消费逻辑同ordered模式
3.4 基于eventTime的unordered模式
该模式下虽然一段时间内的消息之间是无序的,但是由于引入了watermark,watermark1和watermark2之间的数据必须还是原来那批数据,虽然数据之间是可以是乱序的。即Set集合内部的数据,发往下游时可以乱序,但是watermark1—set—watermark2这个顺序不可以被打破。
如果watermark和数据集set直接的顺序被打乱,那么当watermark2触发窗口计算时,窗口里面的数据可能会变多或变少,影响计算的正确性。
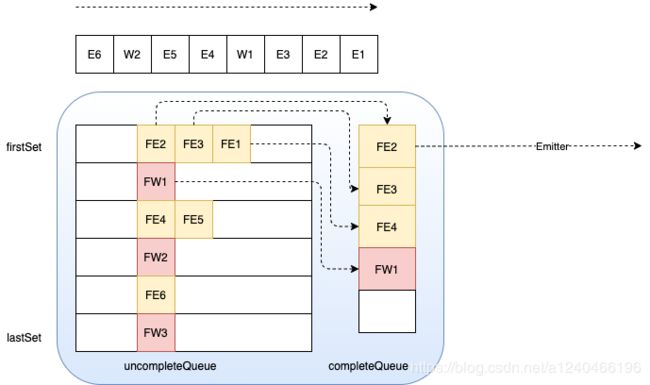
3.4.1 生产
AsyncWaitOperator
@Internal
public class AsyncWaitOperator<IN, OUT>
extends AbstractUdfStreamOperator<OUT, AsyncFunction<IN, OUT>>
implements OneInputStreamOperator<IN, OUT>, OperatorActions, BoundedOneInput {
@Override
public void processWatermark(Watermark mark) throws Exception {
WatermarkQueueEntry watermarkBufferEntry = new WatermarkQueueEntry(mark);
// 处理watermark
addAsyncBufferEntry(watermarkBufferEntry);
}
@Override
public void processElement(StreamRecord<IN> element) throws Exception {
final StreamRecordQueueEntry<OUT> streamRecordBufferEntry = new StreamRecordQueueEntry<>(element);
// 处理StreamRecordBufferEntry对象
addAsyncBufferEntry(streamRecordBufferEntry);
userFunction.asyncInvoke(element.getValue(), streamRecordBufferEntry);
}
private <T> void addAsyncBufferEntry(StreamElementQueueEntry<T> streamElementQueueEntry) throws InterruptedException {
assert(Thread.holdsLock(checkpointingLock));
pendingStreamElementQueueEntry = streamElementQueueEntry;
// 尝试将StreamRecordBufferEntry对象 or watermarkBufferEntry对象插入队列
while (!queue.tryPut(streamElementQueueEntry)) {
// we wait for the emitter to notify us if the queue has space left again
checkpointingLock.wait();
}
pendingStreamElementQueueEntry = null;
}
}
UnorderedStreamElementQueue
@Internal
public class UnorderedStreamElementQueue implements StreamElementQueue {
@Override
public <T> boolean tryPut(StreamElementQueueEntry<T> streamElementQueueEntry) throws InterruptedException {
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
if (numberEntries < capacity) {
addEntry(streamElementQueueEntry);
LOG.debug("Put element into unordered stream element queue. New filling degree " +
"({}/{}).", numberEntries, capacity);
return true;
} else {
LOG.debug("Failed to put element into unordered stream element queue because it " +
"was full ({}/{}).", numberEntries, capacity);
return false;
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
private <T> void addEntry(StreamElementQueueEntry<T> streamElementQueueEntry) {
assert(lock.isHeldByCurrentThread());
if (streamElementQueueEntry.isWatermark()) {
// 遇到watermark,将lastSet置空,方便塞入下一批StreamRecordBufferEntry对象
// 注:firstSet可以存watermarkBufferEntry对象,也可以存StreamRecordBufferEntry对象;但是
// lastSet只会存StreamRecordBufferEntry对象
lastSet = new HashSet<>(capacity);
if (firstSet.isEmpty()) {
firstSet.add(streamElementQueueEntry);
} else {
Set<StreamElementQueueEntry<?>> watermarkSet = new HashSet<>(1);
watermarkSet.add(streamElementQueueEntry);
uncompletedQueue.offer(watermarkSet);
}
uncompletedQueue.offer(lastSet);
} else {
//在没有遇到watermark之前,一直往lastSet中塞入StreamRecordBufferEntry对象
lastSet.add(streamElementQueueEntry);
}
streamElementQueueEntry.onComplete(
(StreamElementQueueEntry<T> value) -> {
try {
onCompleteHandler(value);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// The accept executor thread got interrupted. This is probably cause by
// the shutdown of the executor.
LOG.debug("AsyncBufferEntry could not be properly completed because the " +
"executor thread has been interrupted.", e);
} catch (Throwable t) {
operatorActions.failOperator(new Exception("Could not complete the " +
"stream element queue entry: " + value + '.', t));
}
},
executor);
numberEntries++;
}
// watermarkBufferEntry对象 or StreamRecordBufferEntry对象中的Futrue对象返回后的回调逻辑
public void onCompleteHandler(StreamElementQueueEntry<?> streamElementQueueEntry) throws InterruptedException {
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
// 从firstSet中取出StreamRecordBufferEntry对象,每次都是尝试从firstSet中获取StreamRecordBufferEntry对象,通过这个if逻辑来控制watermark和set之间的顺序
if (firstSet.remove(streamElementQueueEntry)) {
// 将取出的StreamRecordBufferEntry对象加入completedQueue
completedQueue.offer(streamElementQueueEntry);
while (firstSet.isEmpty() && firstSet != lastSet) {
// firstSet指针下移
firstSet = uncompletedQueue.poll();
Iterator<StreamElementQueueEntry<?>> it = firstSet.iterator();
// 遍历firstSet中的StreamRecordBufferEntry对象,如果完成,加入completedQueue队列,且移出firstSet
while (it.hasNext()) {
StreamElementQueueEntry<?> bufferEntry = it.next();
if (bufferEntry.isDone()) {
completedQueue.offer(bufferEntry);
it.remove();
}
}
}
LOG.debug("Signal unordered stream element queue has completed entries.");
hasCompletedEntries.signalAll();
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
3.4.2 消费
Emitter线程消费逻辑同ordered模式
4. 总结
-
Flink Async I/O利用队列来存储加宽前(ordered模式)或加宽后(基于processtime的unordered模式)的数据,并通过队列和Emitter轮询线程将生产数据与消费数据进行解耦。
-
ordered模式,通过将未返回结果的StreamRecordBufferEntry对象按顺序插入队列,并通过判断头结点是否返回,来控制消费顺序与生产顺序一致
-
基于processtime的unordered模式,在数据回调逻辑中,将StreamRecordBufferEntry对象插入队列,即队列中的所有StreamRecordBufferEntry对象都是已经返回异步结果并加宽后的数据。
-
基于eventTime的unordered模式,uncompleteQueue存储加宽前的数据(异步调用返回前),completeQueue存储加宽后的数据,通过firstSet这个设计,来控制watermark和数据集set之间的顺序。
参考:
http://wuchong.me/blog/2017/05/17/flink-internals-async-io/
https://www.cnblogs.com/ljygz/p/11864176.html
https://www.jianshu.com/p/f9bde854627b
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44904816/article/details/104305824?utm_medium=distribute.pc_relevant_right.none-task-blog-BlogCommendFromMachineLearnPai2-5.nonecase&depth_1-utm_source=distribute.pc_relevant_right.none-task-blog-BlogCommendFromMachineLearnPai2-5.nonecase