ElasticFusion 中的 Randomized Ferns 重定位/回环检测 论文和代码解析
Randomized Ferns 在 ElasticFusion 中地位和作用
ElasticFusion 通过 Randomized Ferns 重定位和回环检测,Randomized ferns 是实时的重定位和回环检测算法。
Randomized Ferns 对关键帧图像编码,采用特殊的编码存储方式,加快图像比较的效率。
算法流程图
编码流程
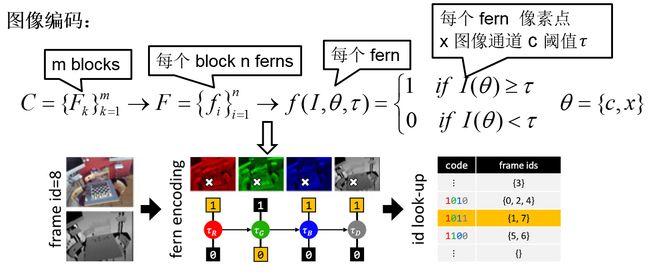
如上图,每幅图像的编码由 m 个 block 的编码组成,
每个 block 由 n 个 Ferns 组成,
每个 Fern 通过比较 c 通道像素点 x 处的像素值,和选择的阈值 θ 间的大小关系,确定编码 Fern 的编码。
如上图所示,每个 block 有一个像素位置处,4 通道编码的 Ferns 组成,白色的叉号表示的是选择的像素点的位置,4 个图像表示 RGB-D 的 4 个通道,每个 block 包含 4 个 Ferns,对应 n 的值为 4。
其中,每个 Fern 像素点的位置 x ,像素通道 c ,阈值 τ 都是在程序初始化的时候,随机选取的。
编码存储结构
算法对于关键帧的编码按照列表的形式存储,如上图右侧所示,表中的每列表示 block 编码的一种可能情况,如果 block 采用 n 个 Ferns 确定对 block 的编码,那么表有 2n 列。
对于待编码的关键帧图像,计算每个 block 的编码,根据 block 的编码,将图像的编号存储到列表中。
图像搜索
对于一幅新获取的图像 I ,首先计算每个 block 的编码 bIk ,根据 block 的编码,在上图所示的列表中,索引到在 block k 处具备相同编码的图像 J ,图像 I 和图像 J 的相似度 qIJ 加 1。
对于图像 I 所有的 block 做上述运算,可以计算得到对于存储的所有的关键帧图像的相似度。
通过相似度判别当前帧是否加入做关键帧(对于所有存储的关键帧相似度小于一定阈值),或者存在回环(和某一帧图像相似度大于一定阈值),还可以通过和相似度大的图像配准,进行重定位。
代码解析
// 随机初始化 Ferns 的位置,像素通道和阈值大小
void Ferns::generateFerns()
{
for(int i = 0; i < num; i++)
{
Fern f;
//随机初始化 Fern 的位置
f.pos(0) = widthDist(random);
f.pos(1) = heightDist(random);
// 随机初始化每个通道的阈值
f.rgbd(0) = rgbDist(random);
f.rgbd(1) = rgbDist(random);
f.rgbd(2) = rgbDist(random);
f.rgbd(3) = dDist(random);
conservatory.push_back(f);
}
}
//新输入的帧和以前帧进行比较,如果相似度小于一定阈值,则将当前帧插入作为回环检测的关键帧
bool Ferns::addFrame(GPUTexture * imageTexture, GPUTexture * vertexTexture, GPUTexture * normalTexture, const Eigen::Matrix4f & pose, int srcTime, const float threshold)
{
Imgunsigned char, 3, 1>> img(height, width);
Img verts(height, width);
Img norms(height, width);
resize.image(imageTexture, img);
resize.vertex(vertexTexture, verts);
resize.vertex(normalTexture, norms);
Frame * frame = new Frame(num,
frames.size(),
pose,
srcTime,
width * height,
(unsigned char *)img.data,
(Eigen::Vector4f *)verts.data,
(Eigen::Vector4f *)norms.data);
int * coOccurrences = new int[frames.size()];
memset(coOccurrences, 0, sizeof(int) * frames.size());
for(int i = 0; i < num; i++)
{
unsigned char code = badCode;
if(verts.at(conservatory.at(i).pos(1), conservatory.at(i).pos(0))(2) > 0)
{
const Eigen::Matrix<unsigned char, 3, 1> & pix = img.atunsigned char, 3, 1>>(conservatory.at(i).pos(1), conservatory.at(i).pos(0));
//随机选取像素点处的编码
code = (pix(0) > conservatory.at(i).rgbd(0)) << 3 |
(pix(1) > conservatory.at(i).rgbd(1)) << 2 |
(pix(2) > conservatory.at(i).rgbd(2)) << 1 |
(int(verts.at(conservatory.at(i).pos(1), conservatory.at(i).pos(0))(2) * 1000.0f) > conservatory.at(i).rgbd(3));
frame->goodCodes++;
// 计算和以前存储帧之间的相似度
for(size_t j = 0; j < conservatory.at(i).ids[code].size(); j++)
{
coOccurrences[conservatory.at(i).ids[code].at(j)]++;
}
}
frame->codes[i] = code;
}
float minimum = std::numeric_limits<float>::max();
if(frame->goodCodes > 0)
{
for(size_t i = 0; i < frames.size(); i++)
{
float maxCo = std::min(frame->goodCodes, frames.at(i)->goodCodes);
float dissim = (float)(maxCo - coOccurrences[i]) / (float)maxCo;
if(dissim < minimum)
{
minimum = dissim;
}
}
}
delete [] coOccurrences;
if((minimum > threshold || frames.size() == 0) && frame->goodCodes > 0)
{
for(int i = 0; i < num; i++)
{
if(frame->codes[i] != badCode)
{
//conservatory 存储关系:第一层 fern 的编号,第二层 code 的编号,第三层图像帧的编号
conservatory.at(i).ids[frame->codes[i]].push_back(frame->id);
}
}
frames.push_back(frame);
return true;
}
else
{
delete frame;
return false;
}
}
// 对于输入的图像进行全局的回环检测,通过判断和以前存储的帧编码相似度,判断当前帧是否作为关键帧
Eigen::Matrix4f Ferns::findFrame(std::vectorunsigned char, 3, 1>> imgSmall(height, width);
Img vertSmall(height, width);
Img normSmall(height, width);
//对输入图像降采样 8X8 倍
resize.image(imageTexture, imgSmall);
resize.vertex(vertexTexture, vertSmall);
resize.vertex(normalTexture, normSmall);
Frame * frame = new Frame(num, 0, Eigen::Matrix4f::Identity(), 0, width * height);
int * coOccurrences = new int[frames.size()];
memset(coOccurrences, 0, sizeof(int) * frames.size());
for(int i = 0; i < num; i++)
{
unsigned char code = badCode;
if(vertSmall.at(conservatory.at(i).pos(1), conservatory.at(i).pos(0))(2) > 0)
{
const Eigen::Matrix<unsigned char, 3, 1> & pix = imgSmall.atunsigned char, 3, 1>>(conservatory.at(i).pos(1), conservatory.at(i).pos(0));
//指定像素点处做编码
code = (pix(0) > conservatory.at(i).rgbd(0)) << 3 |
(pix(1) > conservatory.at(i).rgbd(1)) << 2 |
(pix(2) > conservatory.at(i).rgbd(2)) << 1 |
(int(vertSmall.at(conservatory.at(i).pos(1), conservatory.at(i).pos(0))(2) * 1000.0f) > conservatory.at(i).rgbd(3));
frame->goodCodes++;
// conservatory.at(i) 表示第 i 个 fern 总共随机采样了 num 个
// conservatory.at(i).ids[code] 表示第 i 个 fern 编码值为 code 的 vector
// conservatory.at(i).ids[code].at(j) 值表示第 at(j) 帧图像
for(size_t j = 0; j < conservatory.at(i).ids[code].size(); j++)
{
// coOccurrences[conservatory.at(i).ids[code].at(j)] 表示和第 conservatory.at(i).ids[code].at(j) 帧图像的相似度
coOccurrences[conservatory.at(i).ids[code].at(j)]++;
}
}
frame->codes[i] = code;
}
float minimum = std::numeric_limits<float>::max();
int minId = -1;
//在所有帧中找相似度最小的帧
for(size_t i = 0; i < frames.size(); i++)
{
float maxCo = std::min(frame->goodCodes, frames.at(i)->goodCodes);
float dissim = (float)(maxCo - coOccurrences[i]) / (float)maxCo;
if(dissim < minimum && time - frames.at(i)->srcTime > 300)
{
minimum = dissim;
minId = i;
}
}
//根据图像的编码计算两帧之间的相似度
float Ferns::blockHDAware(const Frame * f1, const Frame * f2)
{
int count = 0;
float val = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < num; i++)
{
if(f1->codes[i] != badCode && f2->codes[i] != badCode)
{
count++;
if(f1->codes[i] == f2->codes[i])
{
val += 1.0f;
}
}
}
return val / (float)count;
}