原文转载自我的博客benym.cn
(1) 收集数据:提供文本文件。
(2) 准备数据 : 使用python解析文本文件。
(3) 分析数据 使用 Matplotlib画二维扩散图 。
(4) 训练算法:此步驟不适用于k-近邻算法。
(5) 测试算法:使用海伦提供的部分数据作为测试样本。
测试样本和非测试样本的区别在于:测试样本是已经完成分类的数据,如果预测分类与实际类别不同,则标记为一个错误。
(6) 使用算法:产生简单的命令行程序,然后可以输入一些特征数据以判断对方是否为自己喜欢的类型。
代码
from numpy import *
import operator
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def createDateSet():
group = array([[1.0, 1.1], [1.0, 1.0], [0, 0], [0, 0.1]])
labels = ['A', 'A', 'B', 'B']
return group, labels
'''
用于分类的输人向量是inX,
输入的训练样本集为dataSet,
标签向量为labels
最后的参数k表示用于选择最近邻居的数目,
其中标签向量的元素数目和矩阵dataSet的行数相同
'''
def classify0(inX, dataSet, labels, k):
dataSetSize = dataSet.shape[0]
# 距离计算
diffMat = tile(inX, (dataSetSize, 1)) - dataSet
sqDiffMat = diffMat ** 2
sqDistances = sqDiffMat.sum(axis=1)
distances = sqDistances ** 0.5
sortedDistIndicies = distances.argsort()
classCount = {}
# 选择距离最小的k个点
for i in range(k):
votellabel = labels[sortedDistIndicies[i]]
classCount[votellabel] = classCount.get(votellabel, 0) + 1
# 排序
sortedClassCount = sorted(classCount.items(), key=operator.itemgetter(1), reverse=True)
return sortedClassCount[0][0]
# 将文本记录转换到Numpy的解析程序
def file2matrix(filename):
fr = open(filename)
arrayOLines = fr.readlines()
# 得到文件行数
numberOfLines = len(arrayOLines)
# 创建返回的Numpy矩阵,将该矩阵的另一维度设置为3
returnMat = zeros((numberOfLines, 3))
classLabelVector = []
index = 0
# 解析文件数据到列表,循环处理每行数据
for line in arrayOLines:
# 截取掉所有的回车字符
line = line.strip()
# 使用tab字符\t将上一步得到的整行数据分割成一个元素列表
listFromLine = line.split('\t')
# 选取前3个元素,将他们存储到特征矩阵中
returnMat[index, :] = listFromLine[0:3]
# -1表示列表中的最后一列元素,将最后一列元素存储到向量classLabelVector中
classLabelVector.append(int(listFromLine[-1]))
index += 1
return returnMat, classLabelVector
datingDataMat, datingLabels = file2matrix('datingTestSet2.txt')
print("array:\n", datingDataMat)
print("datingLabels[0:20]\n", datingLabels[0:20])
# 绘制散点图
# 定义figure
fig = plt.figure()
#add_subplot()返回一个axes对象,里面的参数abc表示在一个figure窗口中,有a行b列个小窗口,然后本次plot在第c个窗口中。
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
# 设置颜色和散点图数据
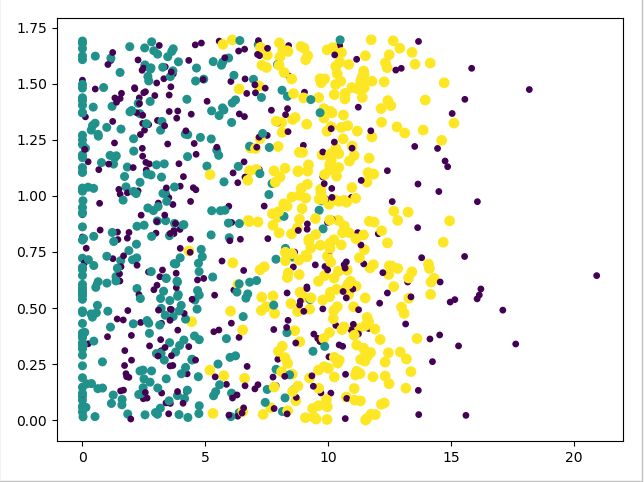
ax.scatter(datingDataMat[:, 1], datingDataMat[:, 2], 15.0 * array(datingLabels), 15.0 * array(datingLabels))
plt.show()
运行结果
array:
[[ 4.09200000e+04 8.32697600e+00 9.53952000e-01]
[ 1.44880000e+04 7.15346900e+00 1.67390400e+00]
[ 2.60520000e+04 1.44187100e+00 8.05124000e-01]
...,
[ 2.65750000e+04 1.06501020e+01 8.66627000e-01]
[ 4.81110000e+04 9.13452800e+00 7.28045000e-01]
[ 4.37570000e+04 7.88260100e+00 1.33244600e+00]]
datingLabels[0:20]
[3, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 3, 3, 1, 3, 1, 1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 3]
散点图结果:
2018年8月11日 16:49:36 新增:归一化特征值,测试代码,预测代码
因为在欧氏距离中数值差值最大的属性对计算结果的影响最大,但其实多个特征都是同等重要的属性,这样如果其中一个占的权重过大,会严重影响到计算的结果
所以在处理不同取值范围的特征值的时候,我们通常采用的方法是将数值归一化,如将取值范围处理为0到1或者-1到1之间。
公式:newValue = (oldValue - min)/(max - min)
其中min和max分别是数据集中的最小特征值和最大特征值。虽然改变数值取值范围增加了分类器的复杂度,但为了得到准确的结果,这样做是必然的
# 将数字特征值转化为0到1的区间
def autoNorm(dataSet):
# 将每列的最小值放在变量minVals中,dataSet.min(0)中的参数0使得函数可以从列中选取最小值
minVals = dataSet.min(0)
# 将每列的最大值放在变量maxVals中
maxVals = dataSet.max(0)
ranges = maxVals - minVals
normDataSet = zeros(shape(dataSet))
m = dataSet.shape[0]
# 为了归一化特征值,必须使用当前值减去最小值,然后除以取值范围
# tile()函数将变量内容复制成输入矩阵同样大小的矩阵
normDataSet = dataSet - tile(minVals, (m, 1))
# 特征值相除
normDataSet = normDataSet / tile(ranges, (m, 1))
return normDataSet, ranges, minVals
# 分类器针对约会网站的测试代码
def datingClassTest():
hoRatio = 0.10
# 首先使用file2matrix和autoNorm()函数从文件中读取数据并将其转换为归一化特征值
datingDataMat, datingLabels = file2matrix('datingTestSet2.txt')
normMat, ranges, minVals = autoNorm(datingDataMat)
# 计算测试向量的数量,决定normMat向量中哪些数据用于测试,哪些数据用于分类器的训练样本
m = normMat.shape[0]
numTestVecs = int(m * hoRatio)
errorCount = 0.0
# 将两部分数据输入到原始分类器函数classify0
for i in range(numTestVecs):
classifierResult = classify0(normMat[i, :], normMat[numTestVecs:m, :], \
datingLabels[numTestVecs:m], 3)
print("the classifier came back with:{},the real answer is:{}".format(classifierResult, datingLabels[i]))
if (classifierResult != datingLabels[i]):
errorCount += 1.0
# 计算错误率并输出结果
print("the total error rate is:{}".format(errorCount / float(numTestVecs)))
# 约会网站预测函数
def classifyPerson():
resultList = ['not at all', 'in small doses', 'in large doses']
percentTats = float(input( \
"percentage of time spent playing video games?"))
ffMiles = float(input("frequent flier miles earned per year?"))
iceCream = float(input("liters of ice cream consumed per year?"))
datingDataMat, datingLabels = file2matrix('datingTestSet2.txt')
normMat, ranges, minVals = autoNorm(datingDataMat)
inArr = array([ffMiles, percentTats, iceCream])
classifierResult = classify0((inArr - \
minVals) / ranges, normMat, datingLabels, 3)
print("You will probably like this person:", \
resultList[classifierResult - 1])
测试归一化特征值、分类器、选择喜欢的人:
# 测试归一化特征值
normMat, ranges, minVals = autoNorm(datingDataMat)
print("array:\n", normMat)
print("array:", ranges)
print("array:", minVals)
# 测试分类器
datingClassTest()
# 选择喜欢的人
classifyPerson()
运行结果
# normMat
array:
[[ 0.44832535 0.39805139 0.56233353]
[ 0.15873259 0.34195467 0.98724416]
[ 0.28542943 0.06892523 0.47449629]
...,
[ 0.29115949 0.50910294 0.51079493]
[ 0.52711097 0.43665451 0.4290048 ]
[ 0.47940793 0.3768091 0.78571804]]
# ranges
array: [ 9.12730000e+04 2.09193490e+01 1.69436100e+00]
# minVals
array: [ 0. 0. 0.001156]
# 测试分类器(数据太多了这里截取部分)
the classifier came back with:3,the real answer is:3
the classifier came back with:2,the real answer is:2
......
the classifier came back with:2,the real answer is:2
the classifier came back with:1,the real answer is:1
the classifier came back with:3,the real answer is:1
# 分类器处理约会数据集的错误率为5%(书上为2.4%....不知道怎么回事)
the total error rate is:0.05
# 输入各个属性,得到最佳约会伙伴
percentage of time spent playing video games?10
frequent flier miles earned per year?10000
liters of ice cream consumed per year?0.5
You will probably like this person: in small doses