JS--树、二叉树(深度优先、广度优先遍历、平衡树旋转)
JS–树、二叉树(深度优先、广度优先遍历、平衡树旋转)
一、树结构和特点
1、树结构
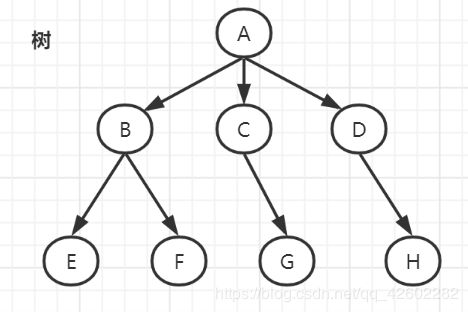
树由节点组成,从根节点出发,每个节点可以拥有子节点,没有子节点的节点叫做叶子节点。
节点的度:节点拥有子节点的个数,度为0表示叶子节点
树的高度:从根节点开始计算(1开始)到叶子节点,一共拥有的层数
树的度:树中所有节点中最大的节点度
树中特殊的计算:
- 一个二叉树第 i 层的最大结点数为:2^(i-1), i >= 1;
- 深度为k的二叉树有最大结点总数为: 2^k - 1, k >= 1;
- 对任何非空二叉树 T,若n0表示叶结点的个数、n2是度为2的 非叶结点个数,那么两者满足关系n0 = n2 + 1
特殊的树结构:
二叉树: 每一个节点最多可以有两个子节点(节点度为0-2的树)

满二叉树: 一棵二叉树的结点要么是叶子结点,要么它有两个子结点(如果一个二叉树的层数为K,且结点总数是(2^k) -1,则它就是满二叉树。)
完全二叉树: 若设二叉树的深度为k,除第 k 层外,其它各层 (1~k-1) 的结点数都达到最大个数,第k 层所有的结点都连续集中在最左边,这就是完全二叉树。
不平衡二叉树: 左右子树高度相差大于等于2
2、树的特点
对于所有的树都具有以下特点:
- 子树之间不可以相交
- 除了根节点外,每个节点有且仅有一个父节点
- 一颗N个节点的树有n-1条边
对二叉树:
- 每个节点的度最大为2,节点的度为0-2
- 树的度可能为0-2
在实际运用场景中,使用得最多的是二叉树的特殊实例——二叉搜索树,它具有二叉树的全部特点,并且:
- 树中的节点一定有序,一般是升序
二、二叉搜索树的封装
二叉树常用数组或链表来实现,实际运用当中,使用链表是最好的,这里讲解使用链表封装二叉搜索树的详细过程:
1、创建二叉树节点:在节点中应该保存当前节点的数据、左边子节点、右边子节点
class Node{
constructor(element){
this.data = element;
//左子节点
this.left = null;
//右子节点
this.right = null;
}
}
2、插入节点:首先创建二叉搜索树类BST(Binary Sort Tree的简写),在构造方法中定义一个变量root用于保存根节点;插入节点时仅需要一个参数即插入的数据,因为儿茶搜索树是有序的,因此,使用递归的方式来找到合适的位置插入节点,在插入节点时,需要创建一个辅助方法来实现递归。
//插入节点
insert(element){
let node = new Node(element);
if(this.root == null){
//当树为空时,直接将插入的节点当做根节点
this.root = node;
}else{
//从根节点开始查找,在合适位置插入
this.insertNode(this.root, node);
}
}
//辅助方法
insertNode(node, newNode){
//根据大小决定插入在当前节点的左边还是右边
if(newNode.data < node.data){
if(node.left == null){
//小于时放在左边,当左边节点为空时直接放在左边作为左边的节点
node.left = newNode;
}else{
//当左边节点部位空时递归向下寻找
this.insertNode(node.left, newNode);
}
}else{
//当节点数据大于当前节点时,放在当前节点右边作为子节点
if(node.right == null){
//当前节点的右子节点为空时,直接插入作为右边子节点
node.right = newNode;
}else{
//当前节点右子节点部位空时,递归向下寻找
this.insertNode(node.right, newNode);
}
}
}
3、先序遍历:根——左——右
在树中为提高效率,遍历树中节点时使用的是递归方式
//先序遍历 根-左-右
preOderTraversal(callback){
//callback是一个回调函数,仅用于输出当前遍历到的节点数据
//data => {console.log(data)}
//由根节点开始遍历
this.preOderTraversalNode(this.root, callback);
}
//先序遍历节点(辅助方法)
preOderTraversalNode(node, callback){
if(node != null){
callback(node.data);
//递归遍历当前节点左子树
this.preOderTraversalNode(node.left, callback);
//递归遍历当前节点右子树
this.preOderTraversalNode(node.right, callback);
}
}
4、中序遍历:左——根——右
通过中序遍历方法遍历出来的顺序是递增的
//中序遍历(升序) 左-根-右
inOderTraversal(callback){
//callback是一个回调函数,仅用于输出当前遍历到的节点数据
//data => {console.log(data)}
//从根节点开始
this.inOderTraversalNode(this.root, callback);
}
//中序遍历节点(辅助方法)
inOderTraversalNode(node, callback){
if(node != null){
//由根节点的左边开始遍历
this.inOderTraversalNode(node.left, callback);
callback(node.data);
//左边遍历完再遍历右边
this.inOderTraversalNode(node.right, callback);
}
}
5、后序遍历:左——右——根
//后序遍历 左-右-根
postOderTraversal(callback){
//callback是一个回调函数,仅用于输出当前遍历到的节点数据
//data => {console.log(data)}
//从根节点开始
this.postOderTraversalNode(this.root, callback);
}
//后序遍历节点
postOderTraversalNode(node, callback){
if(node != null){
//由当前根节点的左边开始遍历
this.postOderTraversalNode(node.left, callback);
//由当前根节点的右边开始遍历
this.postOderTraversalNode(node.right, callback);
callback(node.data);
}
}
6、获取二叉搜索树中的最大值和最小值:
最大值一定是在根节点(仅有根节点和左节点时)或者右节点找,最小值一定是在左节点或者根节点(仅一个节点时)找
//获取二叉搜索树最小值
getMin(){
//二叉树为空
if(this.root == null) return -1;
let current = this.root;
//在左子树上面找
while(current.left){
current = current.left;
}
return current.data;
}
//获取二叉搜索树最大值
getMax(){
//二叉树为空
if(this.root == null) return -1;
let current = this.root;
//在右子树上面找
while(current.right){
current = current.right;
}
return current.data;
}
7、查找某个特定的值:可以使用两种方法——循环和递归
循环方法:
//非递归方式查找某个值
searchNoBack(key){
//二叉树不为空
let current = this.root;
while(current){
if(current.data == key){
//找到就返回true
return true;
}else if(key < current.data){
//key比当前的节点数据小就在当前节点的左子树上面找
current = current.left;
}else if(key > current.data){
//key比当前节点数据大就在当前节点的右子树上面找
current = current.right;
}
}
//二叉树为空或者没有找到时
return -1;
}
递归方式:
//递归查找
searchBack(key){
return this.searchNode(this.root, key);
}
// 递归查找节点(辅助方法)
searchNode(node, key){
//二叉树为空时或者没有找到时
if(node == null) return -1;
//找到就返回true
if(node.data == key) return true;
//key比当前的节点数据小就在当前节点的左子树上面找
else if(key < node.data){
return this.searchNode(node.left, key);
}
//key比当前节点数据大就在当前节点的右子树上面找
else if(key > node.data){
return this.searchNode(node.right, key);
}
}
8、删除节点:
删除节点是二叉搜索树中最复杂的方法,删除节点将会有三种主要的情况,在每一种情况中还要细分成各种方法:
首先要找到要删除的节点以及它的父节点:
//从根节点进入
let current = this.root;
let parent = null;
//判断当前节点是父节点的左子节点
let isLeft = true;
//查找节点:
while(current.data != key){
parent = current;
if(current.data > key){
current = current.left;
isLeft = true;
}else {
current = current.right;
isLeft = false;
}
if(current == null){
return false;
}
}
(1)当要删除的节点是叶子节点时,只需要判断当前叶子节点是父节点的左子节点还是右子节点,将左子节点或者右子节点置空,JS的回收机制会自动回收没有被指向的叶子节点
//当节点是叶子节点时:
if(current.left == null && current.right == null){
//当节点是根节点时
if(current == this.root){
this.root = null;
}else if(isLeft){
// 当前节点是父节点的左子节点
parent.left = null;
}else if(!isLeft){
// 当前节点是父节点的右子节点
parent.right = null;
}
}
(2)当前节点只有一个子节点时,这个子节点可能是左子节点也可能是右子节点,而我们要删除的节点有可能是它的父节点的左子节点也有可能是它的父节点的右子节点,因此会有四种情况,在这里通过判断当前要删除的节点的子节点是左节点还是右节点来将整个情况分为两种状况,再在每一种状况中分当前要删除节点是父节点的哪个节点来分成两种情况:
//当节点有一个子节点时:
//只有左子节点
//不能写成 else if(current.left != null){,会多删除节点
else if(current.right == null){
if(current == this.root){
this.root = current.left;
}
// 当前节点是父节点的左子节点
else if(isLeft){
parent.left = current.left;
}else if(!isLeft){
// 当前节点是父节点的右子节点
parent.right = current.left;
}
//只有右子节点
//不能写成 }else if(current.right != null){,会删除多的节点
}else if(current.left == null){
if(current == this.root){
this.root = current.right;
}
// 当前节点是父节点的左子节点
if(isLeft){
parent.left = current.right;
}else if(!isLeft){
// 当前节点是父节点的右子节点
parent.right = current.right;
}
}
(3)当要删除的节点拥有两个子节点时,需要在树中找出全部比当前节点数据大的节点,然后在其中找到最小的一个节点来替代当前要删除节点的位置,并根据节点大小情况移动节点(这里先找到大的数据集合再找出集合中最小的是为了让移动动作发生得最少,对效率不会产生太大的影响)。其实,找到这个最小值只能通过当前节点的右孩子去找,在以当前节点右节点为子树的根的子树中找到最左边的左孩子即可,相当于在以当前节点右节点为子树的根的子树中调用getMin()方法:
//当要删除的节点右两个子节点时:
else{
//找到后继,后继即要找到的大于当前要删除节点值的最小值
let success = this.getSuccess(current);
if(current == this.root){
//树中只有一个节点时
this.root == success;
}else if(isLeft){
//当前要删除的节点是其父节点的左孩子
parent.left = success;
}else if(!isLeft){
//当前要删除的节点是其父节点的右孩子
parent.right = success;
}
//将当前要删除的节点的左孩子移动到替代节点下作为替代节点的左孩子
success.left = current.left;
}
return true;
}
//找到后继的辅助方法
getSuccess(node){
//用于保存找到的后继节点的父节点,初始值可以设为null
let successParent = node;
//用于保存找到的后继节点
let success = node;
//从当前节点node的右孩子开始找
let current = node.right;
while(current){
successParent = success;
success = current;
//最小的值要在左孩子上面找
current = current.left;
}
//移动节点
if(success != node.right){
successParent.left = success.right;
success.right = node.right;
}
return success;
}
8、删除节点整合
//删除节点
remove(key){
// let flag = this.searchNoBack(key);
// if(!flag) return -1;
let current = this.root;
let parent = null;
//判断当前节点是父节点的左子节点
let isLeft = true;
//查找节点:
while(current.data != key){
parent = current;
if(current.data > key){
current = current.left;
isLeft = true;
}else {
current = current.right;
isLeft = false;
}
if(current == null){
return false;
}
}
//当节点是叶子节点时:
if(current.left == null && current.right == null){
//当节点是根节点时
if(current == this.root){
this.root = null;
}else if(isLeft){
// 当前节点是父节点的左子节点
parent.left = null;
}else if(!isLeft){
// 当前节点是父节点的右子节点
parent.right = null;
}
}
//当节点有一个子节点时:
//只有左子节点
//不能写成 else if(current.left != null){,会多删除节点
else if(current.right == null){
if(current == this.root){
this.root = current.left;
}
// 当前节点是父节点的左子节点
else if(isLeft){
parent.left = current.left;
}else if(!isLeft){
// 当前节点是父节点的右子节点
parent.right = current.left;
}
//只有右子节点
//不能写成 }else if(current.right != null){,会删除多的节点
}else if(current.left == null){
if(current == this.root){
this.root = current.right;
}
// 当前节点是父节点的左子节点
if(isLeft){
parent.left = current.right;
}else if(!isLeft){
// 当前节点是父节点的右子节点
parent.right = current.right;
}
}
//当要删除的节点右两个子节点时:
else{
//找到后继
let success = this.getSuccess(current);
if(current == this.root){
this.root == success;
}else if(isLeft){
parent.left = success;
}else if(!isLeft){
parent.right = success;
}
success.left = current.left;
}
return true;
}
getSuccess(node){
//用于保存找到的后继节点的父节点,初始值可以设为null
let successParent = node;
//用于保存找到的后继节点
let success = node;
//从当前节点node的右孩子开始找
let current = node.right;
while(current){
successParent = success;
success = current;
//最小的值要在左孩子上面找
current = current.left;
}
if(success != node.right){
successParent.left = success.right;
success.right = node.right;
}
return success;
}
三、深度优先遍历和广度优先遍历
1、已知先序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历中的两个,求其他遍历顺序:
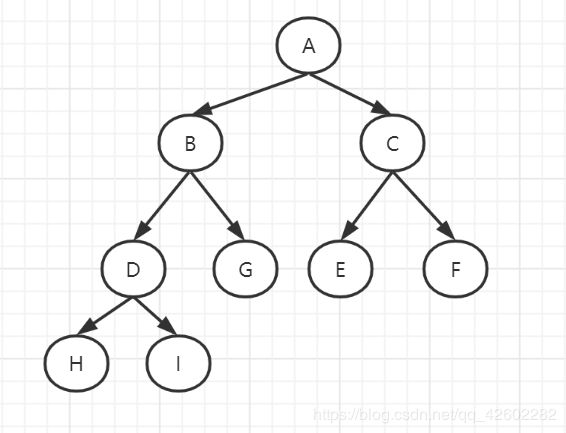
例1:已知先序遍历为:ABDHECFIG,中序遍历为:HDBEAFICG,求后序遍历
我们知道,先序遍历:根——左——右
中序遍历:左——根——右
后序遍历:左——右——根
可以根据先序遍历找到根节点A,中序遍历结果是升序排序结果,可以得到大小关系,然后根据先序遍历找到根节点的左右子节点B、C,然后根据大小关系可以画出原二叉树:
2、深度优先遍历: 从根节点开始,沿着左子树纵向遍历,知道左子树遍历完了再遍历右子树。
例如上例,深度优先遍历的顺序为:ABDHECFIG,遍历过程如下:
//深度优先遍历(栈)
function heightTraversal(root){
let s = new Stack();
s.push(root);
let k = [];
while(!s.isEmpty()){
root = s.peek();
k.push(root.data);
s.pop();
if(root.right != null) s.push(root.right);
if(root.left != null) s.push(root.left);
}
return k;
}
3、广度优先遍历: 从根节点开始,横向每层遍历。
例如上例,广度优先遍历的顺序为:ABCDEFGHI,遍历过程如下:
//广度优先遍历(队列)
function widthTraversal(root){
let q = new Queue();
q.enQueue(root);
let k = [];
while(!q.isEmpty()){
root = q.front();
k.push(root.data);
q.deQueue();
if(root.left != null) q.enQueue(root.left);
if(root.right != null) q.enQueue(root.right);
}
return k;
}
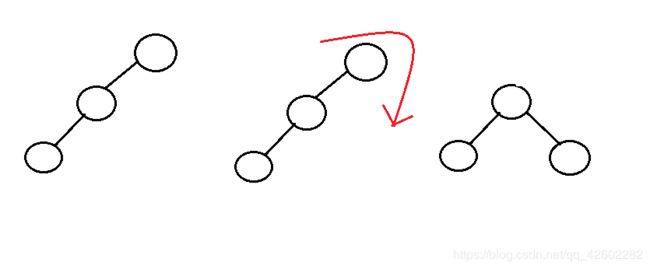
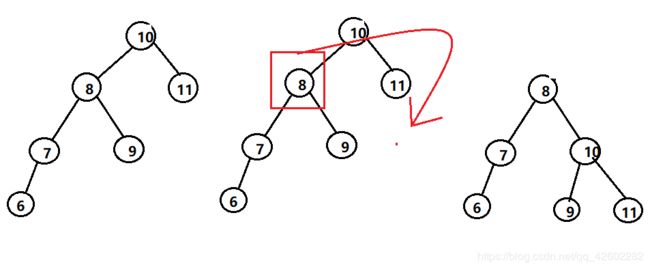
四、关于平衡二叉树的转换
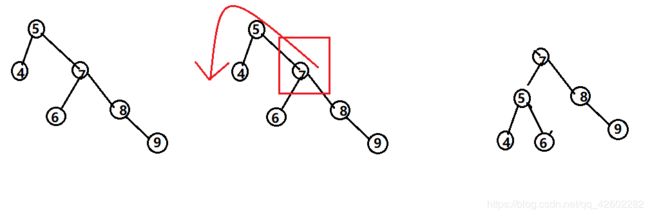
1、LL——通过右旋来将二叉树转换为平衡二叉树
2、RR——通过左旋让其转换为平衡二叉树
第一种情况:
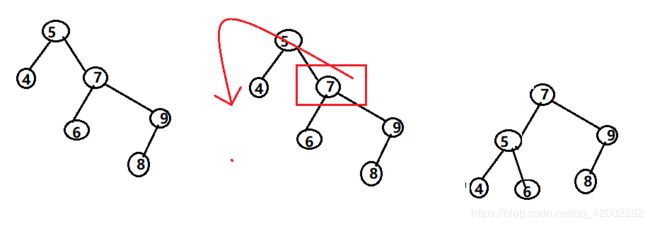
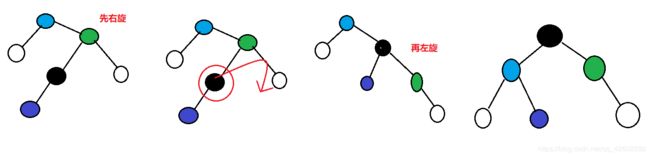
4、RL:先右旋再左旋
第三种情况: