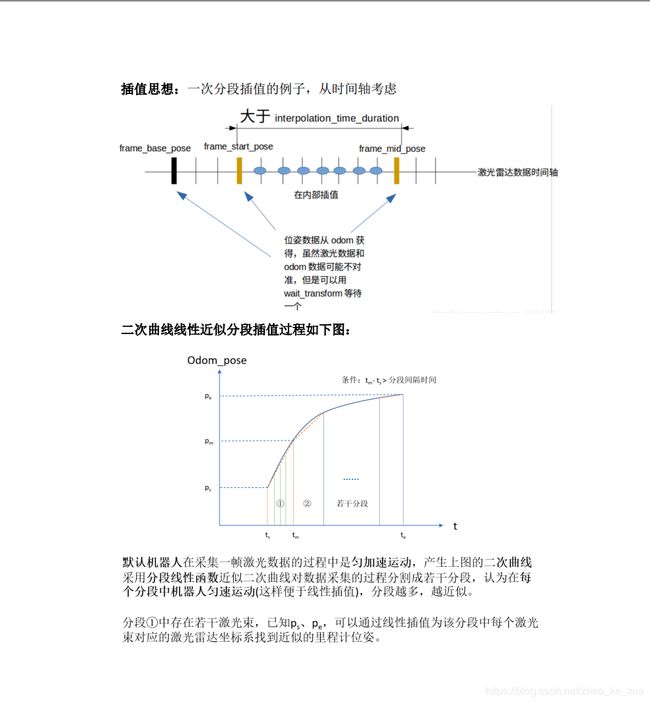
激光slam传感器处理:2D激光雷达运动畸变去除原理解释、代码实现
2D激光雷达运动畸变去除原理解释、代码实现
主要代码如下:
如果需要激光雷达去畸变完整功能包,在下面公众号发送激光雷达,即可获取。

#include