Android应用内跳转Scheme协议
之前一篇文章WebView使用解析(一)之基本用法我讲过了WebView与JS交互的方式,JS调用Java代码主要是通过对象注入的方式实现的,即使用addJavascriptInterface。而JAVA调用JS代码则是通过javascript:伪协议来实现的,即javascript:methodName(params……)。
但是这种交互方式存在着不少问题:
- 1、Java 调用 js 里面的函数,效率并不是很高,估计要200ms左右,做交互性很强的事情这种速度很难让人接受。而js去调Java的方法,速度很快,50ms左右,所以尽量用js调用Java方法。
- 2、Java 调用 js 的函数,没有返回值,调用了就控制不到了。
- 3、Js 调用 Java 的方法,返回值如果是字符串,你会发现这个字符串是 native 的,转成 locale 的才能正常使用,使用 toLocaleString() 函数就可以了,不过这个函数的速度并不快、转化的字符串如果很多、将会很耗费时间。
- 4、网页中尽量不要使用jQuery,执行起来需要5-6秒,最好使用原生的js写业务脚本,以提升加载速度、改善用户体验。
- 5、Android4.2以下的系统存在着webview的js对象注入漏洞。
这里我给大家介绍另外一种Native与webview的交互方式,采用scheme的方式。
URL scheme
URI与Uri
URI位置在java.net.URI,显然是Java提供的一个类。而Uri位置在android.net.Uri,是由Android提供的一个类。所以初步可以判断,Uri是URI的“扩展”以适应Android系统的需要。
概述
android中的scheme是一种页面内跳转协议,是一种非常好的实现机制,通过定义自己的scheme协议,可以非常方便跳转app中的各个页面;通过scheme协议,服务器可以定制化告诉App跳转那个页面,可以通过通知栏消息定制化跳转页面,可以通过H5页面跳转页面等。
应用场景
客户端应用可以向操作系统注册一个URL Scheme,该scheme用于从浏览器或其他应用中启动本应用,通过scheme协议来跳转到相应的APP界面,比如商品详情,活动详情,商家详情等等界面。也可以执行某些指定动作,如完成支付等。也可以在应用内部通过H5页面来直接跳转APP某个界面。
URL Scheme应用场景分为以下4种:
- 服务器下发跳转路径,客户端根据服务器下发跳转路径跳转相应的页面
- H5页面点击描点,根据描点具体跳转路径APP端跳转具体的页面
- APP端收到服务器端下发的PUSH通知栏消息,根据消息的点击跳转路径跳转相关页面
格式
[scheme:][//host:port][path][?query][#fragment]
URL Scheme 属性分为:scheme,host,port,path,query,fragment
test://shangjia:8888/shangjiaDetail?shangjiaId=222#watsonscheme : test
host : shangjia
port : 8888
path : /shangjiaDetail
query : shangjiaId=222
fragment : watson注:
1.除了scheme、host是必须要有的,其它的几个port 、path、query、fragment,它们每一个可以选择性的要或不要,但顺序不能变。
2.其中[host:port]部分我们也可以称为authority。
3.在scheme和fragment之间的部分我们也可以称为scheme-specific-part。
[scheme:]scheme-specific-part[#fragment]
[scheme:][//authority][path][?query][#fragment]
[scheme:][//host:port][path][?query][#fragment] 代码提取
上面我们通过实例讲解了肉眼识别Uri更部分的方式,但在代码中又要怎样提取呢。下面就看看Uri中提取各部分的接口,我们换一个Uri字符串:
http://www.java.com:8080/yourpath/fileName.htm?stove=10&path=32&id=4#watsongetScheme() :获取Uri中的scheme字符串部分,在这里即http
getSchemeSpecificPart():获取Uri中的scheme-specific-part:部分,这里是://www.java.com:8080/yourpath/fileName.htm?stove=10&path=32&id=4
getFragment():获取Uri中的Fragment部分,即watson
getAuthority():获取Uri中Authority部分,即www.java.com:8080
getPath():获取Uri中path部分,即/yourpath/fileName.htm
getQuery():获取Uri中的query部分,即stove=10&path=32&id=4
getHost():获取Authority中的Host字符串,即www.java.com
getPost():获取Authority中的Port字符串,即8080
另外还有两个常用的:getPathSegments()、getQueryParameter(String key)
List< String> getPathSegments():上面我们的getPath()是把path部分整个获取下来:/yourpath/fileName.htm,getPathSegments()的作用就是依次提取出Path的各个部分的字符串,以字符串数组的形式输出。
getQueryParameter(String key):在上面我们通过getQuery()获取整个query字段:stove=10&path=32&id=4,getQueryParameter(String key)作用就是通过传进去path中某个Key的字符串,返回他对应的值。
scheme 使用
AndroidMainfest.xml 配置 scheme
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
intent-filter>
activity>
<activity
android:name=".GoodsDetailActivity"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<intent-filter>
<data android:scheme="watson" android:host="goods" android:path="/goodsDetail" android:port="8888"/>
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT"/>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW"/>
intent-filter>
activity>
<activity android:name=".LoginActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE" />
<data
android:host="login"
android:scheme="test" />
<data
android:host="start"
android:scheme="test" />
intent-filter>
activity>
application>这样我们便定义了能够接受scheme请求的activity实例,当网页或者是Android代码发送这种规则scheme的请求的时候就能够调用起对应的Activity了。
通过服务器下发跳转路径跳转相应页面
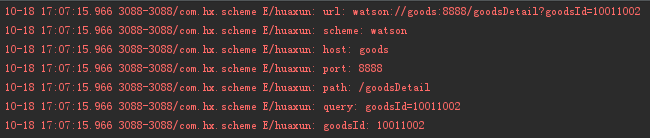
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, Uri.parse("watson://goods:8888/goodsDetail?goodsId=10011002"));
startActivity(intent);这里的”watson://goods:8888/goodsDetail?goodsId=10011002”就是服务器下发的跳转路径,当我们执行startActivity的时候就会调起GoodsDetailActivity,然后我们可以在GoodsDetailActivity种解析出scheme的内容,再做相应处理。
public class GoodsDetailActivity extends Activity{
public String TAG = "huaxun";
public void onCreate(Bundle b) {
super.onCreate(b);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_detail);
Uri uri = getIntent().getData();
if (uri != null) {
// 完整的url信息
String url = uri.toString();
Log.e(TAG, "url: " + uri);
// scheme部分
String scheme = uri.getScheme();
Log.e(TAG, "scheme: " + scheme);
// host部分
String host = uri.getHost();
Log.e(TAG, "host: " + host);
//port部分
int port = uri.getPort();
Log.e(TAG, "port: " + port);
// 访问路径
String path = uri.getPath();
Log.e(TAG, "path: " + path);
// Query部分
String query = uri.getQuery();
Log.e(TAG, "query: " + query);
//获取指定参数值
String goodsId = uri.getQueryParameter("goodsId");
Log.e(TAG, "goodsId: " + goodsId);
}
}
}通过H5页面的锚点跳转相应的页面
首先需要一个HTML文件:
<html>
<head>
<title>Js调用Androidtitle>
head>
<body>
<a href="test://start/?id=431&name=watson&age=29">跳转starta>
<a href="test://web/?id=432&name=jack&age=28">跳转weba>
<a href="test://login/?id=433&name=tom&age=27">跳转Logina>
body>
html>Java中需要加载这个本地页面,并设置WebViewClient。
web.loadUrl("file:///android_asset/web.html");
web.setWebViewClient(new WebViewClient() {
@Override
public boolean shouldOverrideUrlLoading(WebView view, String url) {
Log.v("huaxun","view = [" + view + "], url = [" + url + "]");
Uri uri = Uri.parse(url);
String id = uri.getQueryParameter("id");
String name = uri.getQueryParameter("name");
String age = uri.getQueryParameter("age");
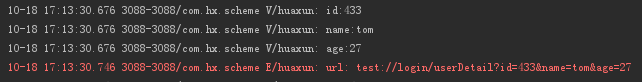
Log.v("huaxun","id:" + id);
Log.v("huaxun","name:" + name);
Log.v("huaxun","age:" + age);
if (url.startsWith("test://login")) {
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, Uri.parse("test://login/userDetail?id="+id+"&name="+name+"&age="+age));
startActivity(intent);
}
return true;
}可以发现我们为Webview设置了WebViewClient,并重写了WebViewClient的shouldOverrideUrlLoading方法,然后我们解析锚点的url,并根据解析的内容调起LoginActivity。
如果我们不想设置WebViewClient,当点击H5页面的锚点url也是可以直接跳转Activity的,是怎么实现的呢?
(1)Intent-filter中的各种匹配工作,还应该加上一个属性:
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE"/>(2)点击的url需要和Mainfest中LoginActivity配置的Scheme等数据相对应。
只要实现了以上两点就可以点击url轻松实现跳转。但是还是不建议这么做,因为在项目中可能URL Scheme协议并不止一个界面。如果你在AndroidMainfest.xml里面去给每一个可能相关的界面都配置scheme属性,那你整个界面看着也不美观,而且还都是重复的配置。所以还是建议根据URL地址来判断跳转。
根据服务器下发通知跳转相应的界面
同样的逻辑。把服务器下发的通知栏消息,里面的URL地址数据拿到,进行解析判断,然后跳转到相应的界面。
NotificationManager notifyManager = (NotificationManager) getSystemService(Context.NOTIFICATION_SERVICE);
NotificationCompat.Builder builder;
builder = new NotificationCompat.Builder(MainActivity.this);
builder.setSmallIcon(R.mipmap.ic_launcher)
.setLargeIcon(BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.mipmap.ic_launcher))
.setContentTitle("watson")
.setContentText("test schemeURL")
.setTicker("有新消息")
.setOngoing(false)
.setWhen(System.currentTimeMillis())
.setPriority(Notification.PRIORITY_DEFAULT)
.setAutoCancel(true);
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, Uri.parse("watson://goods:8888/goodsDetail?goodsId=10011002"));
PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(MainActivity.this, 0, intent, PendingIntent.FLAG_UPDATE_CURRENT);
builder.setContentIntent(pendingIntent);
Notification notification = builder.build();
notifyManager.notify(1, notification);有关Notification的知识,我就不再讲了,最重要的是PendingIntent的封装!
DEMO下载地址