用栈来实现迷宫
迷宫
下面先简单的介绍一下迷宫,我们给出的迷宫实际上是一个二维数组,在二维数组中1表示可以走通,0表示走不通,如下图所示给一个简单的迷宫:
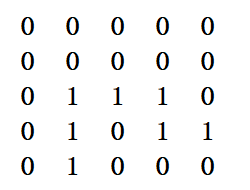
实现代码:
maze.h文件
// 用递归的方式求解简单迷宫问题
#define MAX_ROW 5
#define MAX_COL 5
#include "Stack.h"
typedef struct Maze
{
int _map[MAX_ROW][MAX_COL];
}Maze;
// 初始化迷宫地图数据
void InitMap(Maze* m, int map[MAX_ROW][MAX_COL]);
// 检测迷宫的入口是否有效
int IsValidEnter(Maze* m, Position enter);
// 检测cur位置是否为迷宫的出口
int IsMazeExit(Maze* m, Position cur, Position enter);
// 检测当前位置是否是通路
int IsPass(Maze* m, Position cur);
// 走迷宫
void PassMaze(Maze* m, Position enter);
// 真正走迷宫的操作
int _PassMaze(Maze* m, Position entry, Position cur);
// 打印迷宫地图数据
void PrintMap(Maze* m);
// 打印走过的路径
void PrintPath(Stack* s);实现代码:maze.c
//用递归的方式走迷宫
// 初始化迷宫地图数据
void InitMap(Maze* m, int map[MAX_ROW][MAX_COL])
{
assert(m);
int i = 0;
for (; i < MAX_ROW; ++i)
{
int j = 0;
for (; j < MAX_COL; ++j)
m->_map[i][j] = map[i][j];
}
}
// 检测迷宫的入口是否有效
int IsValidEnter(Maze* m, Position enter)
{
assert(m);
if (enter._x == 0 || enter._x == MAX_ROW - 1 || enter._y == 0 || enter._x == MAX_COL)
return 1 == m->_map[enter._x][enter._y];
return 0;
}
// 检测cur位置是否为迷宫的出口
int IsMazeExit(Maze* m, Position cur, Position enter)
{
assert(m);
//等于入口时不是出口
if (cur._x == enter._x&&cur._y == enter._y)
return 0;
//在边界为出口
if (cur._x == 0 || cur._x == MAX_ROW - 1 || cur._y == 0 || cur._y == MAX_COL - 1)
return 1;
return 0;
}
// 检测当前位置是否是通路
int IsPass(Maze* m, Position cur)
{
assert(m);
return 1 == m->_map[cur._x][cur._y];
}
// 走迷宫
void PassMaze(Maze* m, Position enter)
{
if (!IsValidEnter(m, enter))
{
printf("迷宫入口有误!\n");
return;
}
_PassMaze(m, enter, enter);
}
// 真正走迷宫的操作
int _PassMaze(Maze* m, Position entry, Position cur)
{
if (IsPass(m, cur))
{
Position next;
m->_map[cur._x][cur._y] = 2;
if (IsMazeExit(m, cur, entry))
return 1;
//上
next = cur;
next._x -= 1;
if(_PassMaze(m, entry, next))
return 1;
//左
next = cur;
next._y -= 1;
if (_PassMaze(m, entry, next))
return 1;
//下
next = cur;
next._x += 1;
if (_PassMaze(m, entry, next))
return 1;
//右
next = cur;
next._y += 1;
if (_PassMaze(m, entry, next))
return 1;
m->_map[cur._x][cur._y] = 3;
}
return 0;
}
// 打印迷宫地图数据
void PrintMap(Maze* m)
{
assert(m);
int i = 0;
for (; i < MAX_ROW; ++i)
{
int j = 0;
for (; j < MAX_COL; ++j)
printf("%d ", m->_map[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}
}
// 打印走过的路径
void PrintPath(Stack* s)
{
assert(s);
Position top;
while (StackSize(s) > 1)
{
top = StackTop(s);
printf("[%d,%d]<---", top._x, top._y);
StackPop(s);
}
top = StackTop(s);
printf("[%d,%d]", top._x, top._y);
}对复杂迷宫进行求解– - 迷宫中可能有多条通路,多条路径有可能构成环如下图:

对于这样的迷宫,我们可以用栈来保存路径,当找到一条路径比当前保存的路径还要小的时候就更新
实现代码:maze.c
// 初始化迷宫地图数据
void InitMap(Maze* m, int map[MAX_ROW][MAX_COL])
{
assert(m);
int i = 0;
for (; i < MAX_ROW; ++i)
{
int j = 0;
for (; j < MAX_COL; ++j)
m->_map[i][j] = map[i][j];
}
}
// 检测迷宫的入口是否有效
int IsValidEnter(Maze* m, Position enter)
{
assert(m);
if (enter._x == 0 || enter._x == MAX_ROW - 1 || enter._y == 0 || enter._y == MAX_COL)
return 1 == m->_map[enter._x][enter._y];
return 0;
}
// 检测cur位置是否为迷宫的出口
int IsMazeExit(Maze* m, Position cur, Position enter)
{
assert(m);
//等于入口时不是出口
if (cur._x == enter._x&&cur._y == enter._y)
return 0;
//在边界为出口
if (cur._x == 0 || cur._x == MAX_ROW - 1 || cur._y == 0 || cur._y == MAX_COL - 1)
return 1;
return 0;
}
// 保存最短路径
void SaveShortPath(Stack* path, Stack* shortPath)
{
int size = StackSize(path);
int i = 0;
for (; i < size; ++i)
{
if (!CheckCapacity(shortPath))
return;
shortPath->_array[i] = path->_array[i];
shortPath->_top = i+1;
}
}
// 检测当前位置的下一步是否能够走通
int IsNextPass(Maze* m, Position cur, Position next)
{
assert(m);
if (next._x<0 || next._y<0 || next._x>MAX_ROW || next._y>MAX_COL)
return 0;
if (1 == m->_map[next._x][next._y] || m->_map[next._x][next._y] > m->_map[cur._x][cur._y])
return 1;
return 0;
}
// 走迷宫
void PassMaze(Maze* m, Position enter, Stack* ShortPath)
{
assert(m);
Stack path;
StackInit(&path);
if (!IsValidEnter(m, enter))
{
printf("迷宫入口有误!\n");
return;
}
_PassMaze(m, enter, enter, &path, ShortPath);
}
// 具体走迷宫方式
void _PassMaze(Maze* m, Position entry, Position cur, Stack* path, Stack* shortPath)
{
assert(m);
Position next;
if (StackEmpty(path))
m->_map[cur._x][cur._y] = 2;
StackPush(path, cur);
if (IsMazeExit(m, cur, entry))
{
if (StackEmpty(shortPath) || StackSize(path) < StackSize(shortPath))
SaveShortPath(path, shortPath);
StackPop(path);
return;
}
//上
next = cur;
next._x -= 1;
if (IsNextPass(m, cur, next))
{
m->_map[next._x][next._y] = m->_map[cur._x][cur._y] + 1;
_PassMaze(m, entry, next, path, shortPath);
}
//左
next = cur;
next._y -= 1;
if (IsNextPass(m, cur, next))
{
m->_map[next._x][next._y] = m->_map[cur._x][cur._y] + 1;
_PassMaze(m, entry, next, path, shortPath);
}
//右
next = cur;
next._y += 1;
if (IsNextPass(m, cur, next))
{
m->_map[next._x][next._y] = m->_map[cur._x][cur._y] + 1;
_PassMaze(m, entry, next, path, shortPath);
}
//下
next = cur;
next._x += 1;
if (IsNextPass(m, cur, next))
{
m->_map[next._x][next._y] = m->_map[cur._x][cur._y] + 1;
_PassMaze(m, entry, next, path, shortPath);
}
StackPop(path);
}
// 打印迷宫地图数据
void PrintMap(Maze* m)
{
assert(m);
int i = 0;
for (; i < MAX_ROW; ++i)
{
int j = 0;
for (; j < MAX_COL; ++j)
printf("%d ", m->_map[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}
}
// 打印路径
void PrintPath(Stack* s)
{
assert(s);
Position top;
while (StackSize(s) > 1)
{
top = StackTop(s);
printf("[%d,%d]<---", top._x, top._y);
StackPop(s);
}
top = StackTop(s);
printf("[%d,%d]", top._x, top._y);
}