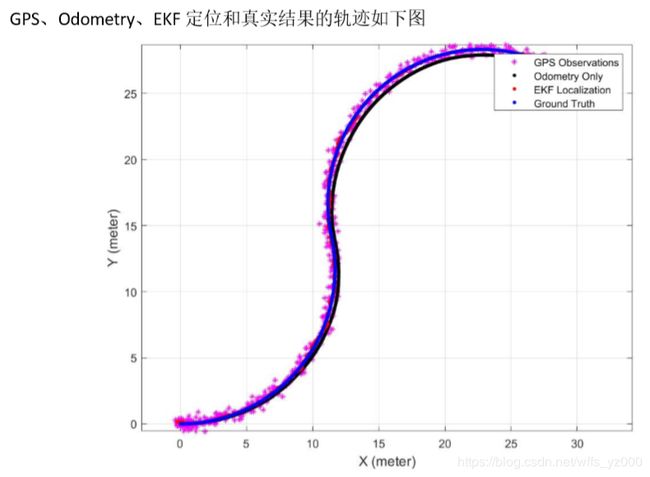
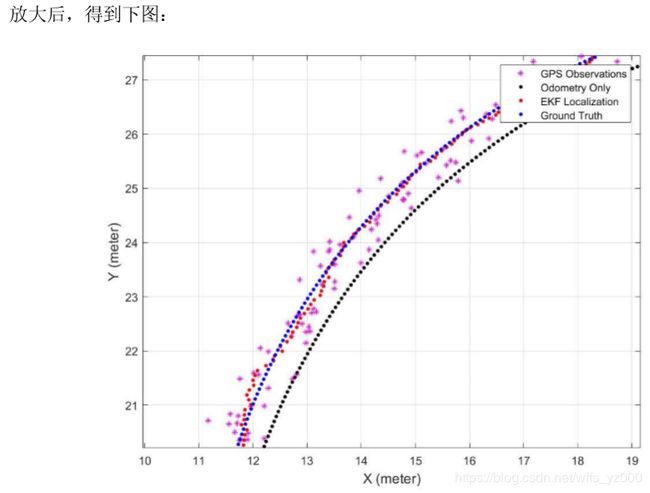
基于EKF(拓展卡尔曼滤波器)的机器人定位(MATLAB编程)
1 EKF原理
EKF是在KF的基础上,增加了对线性要求的拓展,即可以采用非线性函数表示运动方程和观测方程。
EKF的基本思想如下:

2 程序结果
3 程序代码
function [] = ekf_localization()
close all;
clear all;
disp('EKF Start!')
time = 0;
global endTime; % [sec]
endTime = 60;
global dt;
dt = 0.1; % [sec]
removeStep = 5;
nSteps = ceil((endTime - time)/dt);
estimation.time=[];
estimation.u=[];
estimation.GPS=[];
estimation.xOdom=[];
estimation.xEkf=[];
estimation.xTruth=[];
% State Vector [x y yaw]'
xEkf=[0 0 0]';
PxEkf = eye(3);
% Ground True State
xTruth=xEkf;
% Odometry Only
xOdom=xTruth;
% Observation vector [x y yaw]'
z=[0 0 0]';
% Simulation parameter
global noiseQ
noiseQ = diag([0.1 0 degreeToRadian(10)]).^2; %[Vx Vy yawrate]
global noiseR
noiseR = diag([0.5 0.5 degreeToRadian(5)]).^2;%[x y yaw]
% Covariance Matrix for motion
convQ=eye(3);
% Covariance Matrix for observation
convR=noiseR;
% Other Intial
xPred = [0 0 0]';
F = zeros(3);
H = zeros(3);
% Main loop
for i=1 : nSteps
time = time + dt;
% Input
u=robotControl(time);
% Observation
[z,xTruth,xOdom,u]=prepare(xTruth, xOdom, u);
% ------ Kalman Filter --------
% Predict
xPred = doMotion(xEkf, u);
F = jacobF(xEkf, u);
convQ = F*convQ*F'+ noiseQ;
% Update
H = jacobH(xPred);
PxEkf = convQ*H'*inv(H*convQ*H'+convR);
xEkf= doObservation(z, xPred,PxEkf);
convQ=(eye(3)-PxEkf*H)*convQ;
% -----------------------------
% Simulation estimation
estimation.time=[estimation.time; time];
estimation.xTruth=[estimation.xTruth; xTruth'];
estimation.xOdom=[estimation.xOdom; xOdom'];
estimation.xEkf=[estimation.xEkf;xEkf'];
estimation.GPS=[estimation.GPS; z'];
estimation.u=[estimation.u; u'];
% Plot in real time
% Animation (remove some flames)
if rem(i,removeStep)==0
%hold off;
plot(estimation.GPS(:,1),estimation.GPS(:,2),'*m', 'MarkerSize', 5);hold on;
plot(estimation.xOdom(:,1),estimation.xOdom(:,2),'.k', 'MarkerSize', 10);hold on;
plot(estimation.xEkf(:,1),estimation.xEkf(:,2),'.r','MarkerSize', 10);hold on;
plot(estimation.xTruth(:,1),estimation.xTruth(:,2),'.b', 'MarkerSize', 10);hold on;
axis equal;
grid on;
drawnow;
%movcount=movcount+1;
%mov(movcount) = getframe(gcf);% アニメーションのフレームをゲットする
end
end
close
finalPlot(estimation);
end
% control
function u = robotControl(time)
global endTime;
T = 10; % sec
Vx = 1.0; % m/s
Vy = 0.2; % m/s
yawrate = 5; % deg/s
% half
if time > (endTime/2)
yawrate = -5;
end
u =[ Vx*(1-exp(-time/T)) Vy*(1-exp(-time/T)) degreeToRadian(yawrate)*(1-exp(-time/T))]';
end
% all observations for
function [z, xTruth, xOdom, u] = prepare(xTruth, xOdom, u)
global noiseQ;
global noiseR;
% Ground Truth
xTruth=doMotion(xTruth, u);
% add Motion Noises
u=u+noiseQ*randn(3,1);
% Odometry Only
xOdom=doMotion(xOdom, u);
% add Observation Noises
z=xTruth+noiseR*randn(3,1);
end
%Motion Model
function x = doMotion(x, u)
global dt;
%
x_last = u;
u_tran = u;
x_last(1,:) = sqrt(u(1,:)^2+u(2,:)^2);
x_last(2,:) = 0;
x_last(3,:) = u(3,:);
u_tran(1,:) = -x_last(1,:)/x_last(3,:)*sin(x(3,:))+x_last(1,:)/x_last(3,:)*sin(x(3,:)+dt*x_last(3,:));
u_tran(2,:) = x_last(1,:)/x_last(3,:)*cos(x(3,:))-x_last(1,:)/x_last(3,:)*cos(x(3,:)+dt*x_last(3,:));
u_tran(3,:) = dt*x_last(3,:);
x = x + u_tran;
end
% Jacobian of Motion Model
function jF = jacobF(x, u)
global dt;
%
x_last = u;
x_last(1,:) = sqrt(u(1,:)^2+u(2,:)^2);
x_last(2,:) = 0;
x_last(3,:) = u(3,:);
jF = [1,0,-x_last(1,:)/x_last(3,:)*cos(x(3,:))+x_last(1,:)/x_last(3,:)*cos(x(3,:)+dt*x_last(3,:));
0,1,-x_last(1,:)/x_last(3,:)*sin(x(3,:))+x_last(1,:)/x_last(3,:)*sin(x(3,:)+dt*x_last(3,:));
0,0,1];
end
%Observation Model
function x = doObservation(z, xPred,PxEkf)
%
x = xPred+PxEkf* (z-xPred);
end
%Jacobian of Observation Model
function jH = jacobH(x)
%
jH = [1,0,0;
0,1,0;
0,0,1];
end
% finally plot the results
function []=finalPlot(estimation)
figure;
plot(estimation.GPS(:,1),estimation.GPS(:,2),'*m', 'MarkerSize', 5);hold on;
plot(estimation.xOdom(:,1), estimation.xOdom(:,2),'.k','MarkerSize', 10); hold on;
plot(estimation.xEkf(:,1), estimation.xEkf(:,2),'.r','MarkerSize', 10); hold on;
plot(estimation.xTruth(:,1), estimation.xTruth(:,2),'.b','MarkerSize', 10); hold on;
legend('GPS Observations','Odometry Only','EKF Localization', 'Ground Truth');
xlabel('X (meter)', 'fontsize', 12);
ylabel('Y (meter)', 'fontsize', 12);
grid on;
axis equal;
% calculate error
%
figure(2);
title('里程计误差和Ekf定位误差');
hold on;
nSteps = 600;
index = [];
error_Odom = [];
error_Ekf = [];
sum_Odom = 0;
sum_Ekf = 0;
for i=1:nSteps
error_Odom = [error_Odom sqrt( (estimation.xOdom(i,1)- estimation.xTruth(i,1))^2+(estimation.xOdom(i,2)-estimation.xTruth(i,2))^2)];
error_Ekf = [error_Ekf sqrt( (estimation.xEkf(i,1)- estimation.xTruth(i,1))^2+(estimation.xEkf(i,2)-estimation.xTruth(i,2))^2)];
index = [index i];
end
for i=1:nSteps
sum_Odom = sum_Odom + error_Odom(1,i);
sum_Ekf = sum_Ekf + error_Ekf(1,i);
end
error_Odom_average = sum_Odom/nSteps;
disp("纯里程计的误差为");
disp(['error_Odom_average = ',num2str(error_Odom_average)]);
error_Ekf_average = sum_Ekf/nSteps;
disp("Ekf定位的误差为");
disp(['error_Ekf_average = ',num2str(error_Ekf_average)]);
% 画图:每个状态的里程计误差和Ekf定位误差
plot(index(1,:),error_Odom(1,:))
hold on;
plot(index(1,:),error_Ekf(1,:));
hold on;
legend('error of Odom','error of Ekf');
end
function radian = degreeToRadian(degree)
radian = degree/180*pi;
end
4 估计误差
EKF模型、里程计模型(Odometry)估计的误差分别为:(与真实值比较)
结论:
可以看出,EKF模型、里程计模型(Odometry)估计的误差变化趋势不同。
EKF模型估计的误差总体趋势平稳,稳定在一定范围内;
而里程计模型(Odometry)估计的误差会随着时间不断增加,最后达到无法满足实验要求。