深度学习计算机视觉实战(一) : 基于pytorch框架的MNIST手写数字识别详解(附源码)
前言
数字识别,因其识别对象蕴含信息简单(灰度图单通道即可)、应用场景广阔,成为了传统图像处理的一大Key Topic. 深度学习的兴起使得端到端学习取代了机器学习+手工设计的传统识别算法成为了热门。
本文基于pytorch框架、MNIST数据集,使用LeNet对MNIST数据集实现高精度手写数字识别。
数据集介绍参考维基百科:MNIST database.
目录
- 前言
- LeNet-5模型介绍
- 各层参数
- Pytorch代码详解
- 开发环境
- 代码详解
- 库依赖
- 超参定义
- 数据集下载打包
- 网络构建
- 训练&测试
- 运行说明
- 运行结果
- 模型实测
- 测试结果
- 完整训练源码
- 修改记录
LeNet-5模型介绍
LeNet-5出自Y. L. LeCun的论文Gradient-Based Learning Applied to Document Recognition,是一种专门设计于场景”手写体字符识别“的非常高效的卷积神经网络。LeNet-5这个网络虽然很小,但是它包含了深度学习的基本模块:卷积层,池化层,全链接层。
原文中的网络结构图见下:
 LeNet-5不含输入共7层,每个层有多个Feature Map,每个FeatureMap通过一种卷积滤波器提取输入的一种特征。
LeNet-5不含输入共7层,每个层有多个Feature Map,每个FeatureMap通过一种卷积滤波器提取输入的一种特征。
各层参数
Input
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input | 32x32x1 |
Conv1 卷积层
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input | 32x32x1 |
| Kernel Size | 5x5 |
| Kernel Number | 6 |
| Stride | 1 |
| Output | 28x28x6 |
Pool2 池化层
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input | 28x28x6 |
| Kernel Size | 2x2 |
| Stride | 2 |
| Output | 14x14x6 |
Conv3 卷积层
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input | 14x14x6 |
| Kernel Size | 5x5 |
| Kernel Number | 16 |
| Stride | 1 |
| Output | 10x10x16 |
Pool4 池化层
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input | 10x10x16 |
| Kernel Size | 2x2 |
| Stride | 2 |
| Output | 5x5x16 |
Conv5 卷积层
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input | 5x5x16 |
| Kernel Size | 5x5 |
| Kernel Number | 120 |
| Stride | 1 |
| Output | 1x1x120 |
F6 全连接层
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input | 120 |
| Output | 84 |
Output 全连接层
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Input | 84 |
| Output | 10 |
百度学术链接:Gradient-Based Learning Applied to Document Recognition.
注:本文发表于1998年,原文中的部分内容经过今年的发展有了更好的选择,如ReLU激活函数的优越性、最大池化层代替平均池化层的使用会获得更好的结果等,故实现过程中有些许改动及优化。
Pytorch代码详解
开发环境
| 工具包 | 版本 |
|---|---|
| python | 3.6.2 |
| torch | 1.0.0 |
| torchvision | 0.2.1 |
| visdom | 0.1.7 |
| matplotlib | 2.0.2 |
代码详解
库依赖
# standard library
import os
# third-party library
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.autograd import Variable
import torch.utils.data as Data # dataset
import torchvision # torch vision library
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # plot 2D data, Visualization
import visdom # python -m visdom.server
超参定义
torch.manual_seed(1) # reproducible 设定生成随机数的种子,并返回一个 torch._C.Generator 对象
# Hyper Parameters 超参数
EPOCH = 250 # train the training data n times, to save time, we just train 1 epoch
BATCH_SIZE = 8192 # Data number per batch
LR = 0.001 # learning rate
VISDOM = True # 绘图
torch.manual_seed(1) 使得每次得到的随机数(参数初始化)是固定的,无需固定随机参数可删。
数据集下载打包
torchvision.datasets中包含了MNIST数据集,我们无需另外下载。该部分自动检测数据集是否置于工作路径下,若未检测到则自动下载。
我们采用mini-batch梯度下降法进行训练,故需要生成相应的mini-batch训练集和数据集。
##############################################################################################
########################### Mnist digits dataset preparation #################################
DOWNLOAD_MNIST = False # 是否下载
if not(os.path.exists('./mnist/')) or not os.listdir('./mnist/'):
# not mnist dir or mnist is empyt dir
DOWNLOAD_MNIST = True
MNISTtrainData = torchvision.datasets.MNIST( # data size (60000, 28, 28) + label(60000)
root = './mnist/',
train = True, # this is training data
transform = torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(), # Converts a PIL.Image or numpy.ndarray to
# torch.FloatTensor of shape (C x H x W) and normalize in the range [0.0, 1.0]
download = DOWNLOAD_MNIST
)
# Data Loader for easy mini-batch return in training,
# the image batch shape will be (BATCH_SIZE, 1, 28, 28)
train_loader = Data.DataLoader(dataset=MNISTtrainData, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True)
MNISTtestData = torchvision.datasets.MNIST( # data size (10000, 28, 28) + label(10000)
root = './mnist/', train = False,
transform = torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(), # Converts a PIL.Image or numpy.ndarray to
# torch.FloatTensor of shape (C x H x W) and normalize in the range [0.0, 1.0]
download = DOWNLOAD_MNIST
)
test_loader = Data.DataLoader(dataset=MNISTtestData, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True)
网络构建
采用LeNet-5模型,详见上述。
######################## define LeNet construction & Parameters ##############################
# widith_output = (widith_input + 2 * padding - kernel_size) / stride + 1
# padding = (kernel_size - 1) / 2 if stride = 1
class LeNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(LeNet, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential( # input shape (1, 28, 28)
nn.Conv2d(
in_channels = 1, # input height 输入通道
out_channels = 6, # n_filters 输出通道
kernel_size = 5, # filter size 卷积核
stride = 1, # filter movement/step 步长
padding = 2, # if want same width and length of this image after con2d
), # output shape (6, 28, 28)
nn.ReLU(), # activation
nn.MaxPool2d( # choose max value in 2x2 area
kernel_size = 2,
stride = 2
), # output shape (6, 14, 14)
)
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential( # input shape (6, 14, 14)
nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5), # output shape (16, 10, 10)
nn.ReLU(), # activation
nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2), # output shape (16, 5, 5)
)
self.fc1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120), # fully connected layer, output 120 classes
nn.ReLU()
)
self.fc2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(120, 84), # fully connected layer, output 84 classes
nn.ReLU()
)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84, 10) # fully connected layer, output 10 classes
# define forward propagation progress
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1) # flatten the output of conv2 to (batch_size, 16 * 5 * 5)
x = self.fc1(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
output = self.fc3(x)
return output, x # return x for visualization
myLeNet = LeNet() # 网络实例化
if torch.cuda.is_available(): # cuda可用时可置于GPU中训练网络,以加快计算速度
myLeNet.cuda()
print("cuda is available, and the calculation will be moved to GPU\n")
else:
print("cuda is unavailable!")
训练&测试
采用Adam优化算法+交叉熵损失函数,并用visdom进行可视化操作。
########################### training & testing #################################
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(myLeNet.parameters(), lr = LR) # optimize all cnn parameters
loss_func = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # 交叉熵 loss the target label is not one-hotted
if VISDOM:
vis = visdom.Visdom(env=u'MNIST for leNet')
vis.line(X=torch.Tensor([1]),Y=torch.Tensor([0]),win='trainAcc', \
opts=dict(title = 'acc rate(%) for train data', ytickmin = 0, ytickmax = 100))
vis.line(X=torch.Tensor([1]),Y=torch.Tensor([0]),win='trainLoss', \
opts=dict(title = 'train loss', ytickmin = 0, ytickmax = 2.5))
vis.line(X=torch.Tensor([1]),Y=torch.Tensor([0]),win='testAcc', \
opts=dict(title = 'acc rate(%) for test data', ytickmin = 0, ytickmax = 100))
vis.line(X=torch.Tensor([1]),Y=torch.Tensor([0]),win='testLoss', \
opts=dict(title = 'test loss', ytickmin = 0, ytickmax = 2.5))
mini-batch梯度下降法,并对每个epoch记录并更新loss值和准确度。
for epoch in range(EPOCH):
for step, (x, y) in enumerate(train_loader):
# gives batch data, normalize x when iterate train_loader
if torch.cuda.is_available():
batch_x = Variable(x).cuda()
batch_y = Variable(y).cuda()
else:
batch_x = Variable(x)
batch_y = Variable(y)
output, last_layer = myLeNet(batch_x) # LeNet output
loss = loss_func(output, batch_y) # cross entropy loss
optimizer.zero_grad() # clear gradients for this training step
loss.backward() # backpropagation, compute gradients
optimizer.step() # apply gradients
_, correct_label = torch.max(output, 1) # 输出预测概率的label
# print('label', correct_label)
correct_num = (correct_label == batch_y).sum()
trainAcc = correct_num.item() / float(batch_y.size(0))
print('train: Epoch [%d/%d], Iter [%2d/%d] Loss: %.4f, Acc: %.4f' % \
(epoch + 1, EPOCH, step + 1, len(MNISTtrainData) // BATCH_SIZE + 1, \
loss.item(), trainAcc))
if VISDOM:
vis.line(X=torch.Tensor([epoch + 1]), \
Y=torch.Tensor([trainAcc * 100]), win='trainAcc', update='append')
vis.line(X=torch.Tensor([epoch + 1]),\
Y=torch.Tensor([loss]), win='trainLoss', update='append')
testAcc = 0
for _, (x, y) in enumerate(test_loader):
# gives batch data, normalize x when iterate train_loader
if torch.cuda.is_available():
batch_x = Variable(x).cuda()
batch_y = Variable(y).cuda()
else:
batch_x = Variable(x)
batch_y = Variable(y)
output, last_layer = myLeNet(batch_x) # LeNet output
loss = loss_func(output, batch_y) # cross entropy loss
_, correct_label = torch.max(output, 1) # 输出预测概率最大的值和标签
# print('label', correct_label)
correct_num = (correct_label == batch_y).sum()
testAcc += correct_num.item()
testAcc = testAcc / float(MNISTtestData.test_labels.size(0))
print('----------------test: Epoch [%d/%d] Acc: %.4f' % (epoch + 1, EPOCH, testAcc))
if VISDOM:
vis.line(X=torch.Tensor([epoch + 1]), \
Y=torch.Tensor([testAcc * 100]), win='testAcc', update='append')
vis.line(X=torch.Tensor([epoch + 1]),\
Y=torch.Tensor([loss]), win='testLoss', update='append')
torch.save(myLeNet, './ModelBackup/MNIST_lenet_model_%d_%f.pkl'%(epoch, testAcc))
最后保存模型(建议每隔几个epoch保存备用):
torch.save(myLeNet, './ModelBackup/MNIST_lenet_model_%d_%f.pkl'%(epoch, testAcc))
这样,你就有一个专门处理手写数字的简单模型了。
运行说明
- 终端启动visdom server:
python -m visdom.server
- 打开链接 http://localhost:8097/# ;
- 运行源码,visdom选定environment选定所处环境,查看曲线实时更新。
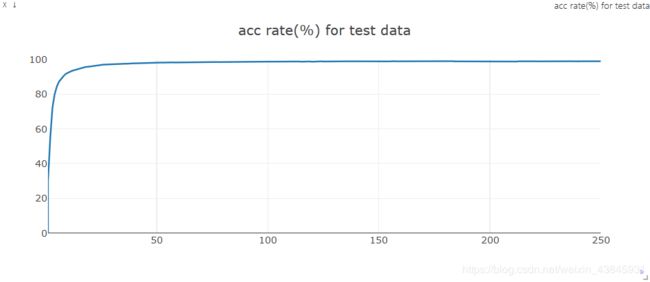
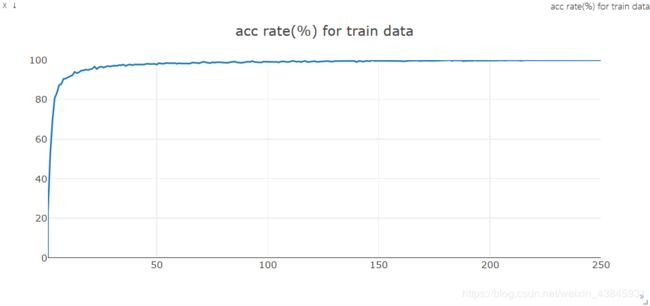
运行结果
| epoch | 训练集损失值 | 训练集准确度(%) | 测试集损失值 | 测试集准确度(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.232 | 23.38 | 2.200 | 29.94 |
| 5 | 5.142e-1 | 83.32 | 5.328e-1 | 79.95 |
| 20 | 1.488e-1 | 94.92 | 1.222e-1 | 95.97 |
| 50 | 6.347e-2 | 97.70 | 5.043e-2 | 98.13 |
| 90 | 3.147e-2 | 98.91 | 3.701e-2 | 98.69 |
| 140 | 2.868e-2 | 99.51 | 3.873e-2 | 98.86 |
| 200 | 1.300e-2 | 99.96 | 4.108e-2 | 98.85 |
| 250 | 6.061e-3 | 99.89 | 3.226e-2 | 98.91 |
在约90轮训练后,模型对训练集开始出现过拟合现象,测试集准确度随着epoch的增大变化较小,故90轮的模型较好。
训练集损失值曲线:

训练集准确度曲线:
 测试集损失值曲线:
测试集损失值曲线:

测试集准确度曲线:
模型实测
改变打开的图片文件,可以判别数字并计算概率。
整体思路
- 载入图片
- 转灰度并压缩至指定大小
- 图片归一化,使得对比度增强
- 图片输入模型
- 全连接层输出做softmax
- 得出结果
源码
import cv2
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import numpy as np
import math
from torch.autograd import Variable
from LeNet import LeNet
# 模型读取
myLeNet = torch.load('Best_LeNet_Model.pkl')
if torch.cuda.is_available():
myLeNet.cuda()
print("cuda is available, and the calculation will be moved to GPU\n")
else:
print("cuda is unavailable!")
# 文件读取->灰度->压缩
frame = cv2.imread('2.png')
originImg = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
cv2.imshow('frame', originImg)
inputImage = cv2.resize(originImg, (28, 28))
inputImage = np.ones([28,28]) * 255 - inputImage
# 灰度域拉伸
inputImage = np.floor(255 / (np.max(np.max(inputImage)) - np.min(np.min(inputImage)))
* (inputImage - np.min(np.min(inputImage))))
# 与Net输入做匹配
inputImage = np.expand_dims(inputImage, axis=0) # 维度增加!!!
inputImage = np.expand_dims(inputImage, axis=0)
# 输入必须归一化!和数据集保持一致
tensorImage = torch.FloatTensor(inputImage/255)
varImage = Variable(tensorImage).cuda()
output,_ = myLeNet(varImage) # LeNet output
_, correct_label = torch.max(output, 1) # 输出预测概率的label
# GPUtensor转numpy
npOutput = output.cpu().detach().numpy()[0]
npCorrect_label = correct_label.cpu().detach().numpy()[0]
similarity = np.exp(npOutput)/np.sum(np.exp(npOutput))
print('label:', npCorrect_label, 'similarity :', similarity[npCorrect_label]*100,'%')
测试结果
图片取自网络(随机截图)。
| 图片 | 识别结果 | 置信度(%) |
|---|---|---|
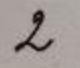 |
2 | 94.90 |
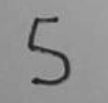 |
5 | 99.85 |
 |
7 | 97.25 |
 |
8 | 98.19 |
完整训练源码
github链接
https://github.com/HYPENG1/MNIST_train_LeNet/tree/YoooHu
# standard library
import os
# third-party library
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.autograd import Variable
import torch.utils.data as Data # dataset
import torchvision # torch vision library
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # plot 2D data, Visualization
import visdom # python -m visdom.server
torch.manual_seed(1) # reproducible 设定生成随机数的种子,并返回一个 torch._C.Generator 对象
# Hyper Parameters 超参数
EPOCH = 250 # train the training data n times, to save time, we just train 1 epoch
BATCH_SIZE = 8192 # Data number per batch
LR = 0.001 # learning rate
VISDOM = True # 绘图
##############################################################################################
########################### Mnist digits dataset preparation #################################
DOWNLOAD_MNIST = False # 是否下载
if not(os.path.exists('./mnist/')) or not os.listdir('./mnist/'):
# not mnist dir or mnist is empyt dir
DOWNLOAD_MNIST = True
MNISTtrainData = torchvision.datasets.MNIST( # data size (60000, 28, 28) + label(60000)
root = './mnist/',
train = True, # this is training data
transform = torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(), # Converts a PIL.Image or numpy.ndarray to
# torch.FloatTensor of shape (C x H x W) and normalize in the range [0.0, 1.0]
download = DOWNLOAD_MNIST
)
# Data Loader for easy mini-batch return in training,
# the image batch shape will be (BATCH_SIZE, 1, 28, 28)
train_loader = Data.DataLoader(dataset=MNISTtrainData, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True)
MNISTtestData = torchvision.datasets.MNIST( # data size (10000, 28, 28) + label(10000)
root = './mnist/', train = False,
transform = torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(), # Converts a PIL.Image or numpy.ndarray to
# torch.FloatTensor of shape (C x H x W) and normalize in the range [0.0, 1.0]
download = DOWNLOAD_MNIST
)
test_loader = Data.DataLoader(dataset=MNISTtestData, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True)
##############################################################################################
######################## define LeNet construction & Parameters ##############################
# widith_output = (widith_input + 2 * padding - kernel_size) / stride + 1
# padding = (kernel_size - 1) / 2 if stride = 1
class LeNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(LeNet, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential( # input shape (1, 28, 28)
nn.Conv2d(
in_channels = 1, # input height 输入通道
out_channels = 6, # n_filters 输出通道
kernel_size = 5, # filter size 卷积核
stride = 1, # filter movement/step 步长
padding = 2, # if want same width and length of this image after con2d
), # output shape (6, 28, 28)
nn.ReLU(), # activation
nn.MaxPool2d( # choose max value in 2x2 area
kernel_size = 2,
stride = 2
), # output shape (6, 14, 14)
)
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential( # input shape (6, 14, 14)
nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5), # output shape (16, 10, 10)
nn.ReLU(), # activation
nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2), # output shape (16, 5, 5)
)
self.fc1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120), # fully connected layer, output 120 classes
nn.ReLU()
)
self.fc2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(120, 84), # fully connected layer, output 84 classes
nn.ReLU()
)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84, 10) # fully connected layer, output 10 classes
# define forward propagation progress
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1) # flatten the output of conv2 to (batch_size, 16 * 5 * 5)
x = self.fc1(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
output = self.fc3(x)
return output, x # return x for visualization
myLeNet = LeNet() # 网络实例化
if torch.cuda.is_available():
myLeNet.cuda()
print("cuda is available, and the calculation will be moved to GPU\n")
else:
print("cuda is unavailable!")
##############################################################################################
########################### training & testing #################################
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(myLeNet.parameters(), lr = LR) # optimize all cnn parameters
loss_func = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # 交叉熵 loss the target label is not one-hotted
if VISDOM:
vis = visdom.Visdom(env=u'MNIST for leNet')
vis.line(X=torch.Tensor([1]),Y=torch.Tensor([0]),win='trainAcc', \
opts=dict(title = 'acc rate(%) for train data', ytickmin = 0, ytickmax = 100))
vis.line(X=torch.Tensor([1]),Y=torch.Tensor([0]),win='trainLoss', \
opts=dict(title = 'train loss', ytickmin = 0, ytickmax = 2.5))
vis.line(X=torch.Tensor([1]),Y=torch.Tensor([0]),win='testAcc', \
opts=dict(title = 'acc rate(%) for test data', ytickmin = 0, ytickmax = 100))
vis.line(X=torch.Tensor([1]),Y=torch.Tensor([0]),win='testLoss', \
opts=dict(title = 'test loss', ytickmin = 0, ytickmax = 2.5))
for epoch in range(EPOCH):
for step, (x, y) in enumerate(train_loader):
# gives batch data, normalize x when iterate train_loader
if torch.cuda.is_available():
batch_x = Variable(x).cuda()
batch_y = Variable(y).cuda()
else:
batch_x = Variable(x)
batch_y = Variable(y)
output, last_layer = myLeNet(batch_x) # LeNet output
loss = loss_func(output, batch_y) # cross entropy loss
optimizer.zero_grad() # clear gradients for this training step
loss.backward() # backpropagation, compute gradients
optimizer.step() # apply gradients
_, correct_label = torch.max(output, 1) # 输出预测概率的label
# print('label', correct_label)
correct_num = (correct_label == batch_y).sum()
trainAcc = correct_num.item() / float(batch_y.size(0))
print('train: Epoch [%d/%d], Iter [%2d/%d] Loss: %.4f, Acc: %.4f' % \
(epoch + 1, EPOCH, step + 1, len(MNISTtrainData) // BATCH_SIZE + 1, \
loss.item(), trainAcc))
if VISDOM:
vis.line(X=torch.Tensor([epoch + 1]), \
Y=torch.Tensor([trainAcc * 100]), win='trainAcc', update='append')
vis.line(X=torch.Tensor([epoch + 1]),\
Y=torch.Tensor([loss]), win='trainLoss', update='append')
testAcc = 0
for _, (x, y) in enumerate(test_loader):
# gives batch data, normalize x when iterate train_loader
if torch.cuda.is_available():
batch_x = Variable(x).cuda()
batch_y = Variable(y).cuda()
else:
batch_x = Variable(x)
batch_y = Variable(y)
output, last_layer = myLeNet(batch_x) # LeNet output
loss = loss_func(output, batch_y) # cross entropy loss
_, correct_label = torch.max(output, 1) # 输出预测概率最大的值和标签
# print('label', correct_label)
correct_num = (correct_label == batch_y).sum()
testAcc += correct_num.item()
testAcc = testAcc / float(MNISTtestData.test_labels.size(0))
print('----------------test: Epoch [%d/%d] Acc: %.4f' % (epoch + 1, EPOCH, testAcc))
if VISDOM:
vis.line(X=torch.Tensor([epoch + 1]), \
Y=torch.Tensor([testAcc * 100]), win='testAcc', update='append')
vis.line(X=torch.Tensor([epoch + 1]),\
Y=torch.Tensor([loss]), win='testLoss', update='append')
if epoch % 25 == 0:
torch.save(myLeNet, './ModelBackup/MNIST_lenet_model_%d_%f.pkl'%(epoch, testAcc))
修改记录
| Time | Note | Author |
|---|---|---|
| 19.4.11 | 原始版本 | Yooo_Hu |
| 19.4.12 | 添加模型实测部分 | Yooo_Hu |