Java数据结构之图解单链表
链表(Linked List)介绍:
1,链表是以节点的方式来存储是链式存储
2,每个节包含 data域:存储信息 next域:指向下一个节点。
3,链表的各个节点不一定是连续存储的。
4,链表分带头结点的链表和没有头节点的链表,根据实际情况来确定
链表在内存中的存储形式 :
由此得出:链表的各个节点不一定是连续存储的。
单链表的逻辑结构示意图:
每一个节点Node中都包含一个data域和一个指针域。
链表的操作图解:
创建链表:
1、头插法:把后建立的结点插在头部。用这种方法建立起来的链表的实际顺序与输入顺序刚好向反,输出时为倒序!
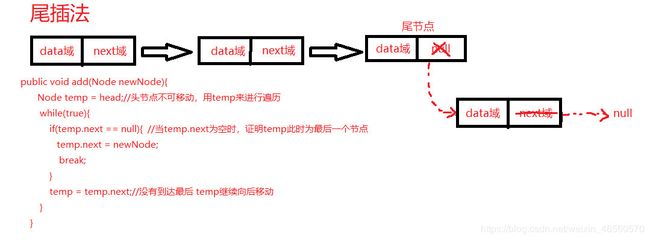
2、尾插法:将后建立的结点插在链表尾部,这种方法建立起来的链表的实际顺序与输入顺序相同
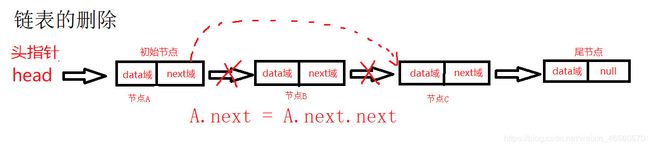
链表的删除操作:
链表的插入操作:
有关单链表的简单问题:
判断单链表中有效节点数目:
public static int numNode(Node head) { int length = 0;//计数 Node temp = head.next; if (temp == null) { //如果为空,链表为空 return 0; } while (temp != null) { //只要不为空,就继续 length++; // 计数 temp = temp.next; //temp向后移动一位 } return length; }单链表的反转操作:
//反转链表 public static void reverseList(Node head) { Node next = null; //指向当前节点的下一位 Node temp = head.next;//定一个辅助指针,帮助完成链表的遍历 Node newhead = new Node(0, "");//新建一个指针。 //遍历原本的链表,每遍历一个节点,就取出,并放入新的链表的最前端 while (temp != null) { next = temp.next; //现暂时保留当前节点的下一位,因为后面需要使用。 temp.next = newhead.next; //将temp的下一个节点指向新的链表的最前端 newhead.next = temp; //将 temp 连接到新的链表上 temp = next; // 原链表的第一位 = 原链表的第二位 } head.next = newhead.next; //将head.next 指向newhead.next实现单链表的反转 }单链表的逆序打印:
//逆序打印单链表 public static void reversePrint (Node head) { if (head.next == null) return; //创建一个栈,stack 先进后出。 Stackstack = new Stack (); Node temp = head.next; //将链表内容压入栈中 while (temp != null) { stack.push(temp); temp = temp.next; } //打印; while (!stack.empty()) { System.out.println(stack.pop());//先进后出 } }
单链表实际应用例子:
用单链表创建一个学生信息管理系统,完成对学生信息的添加,删除,修改操作。
package Linkedlist;
//过程:
// 1,首先创建一个Students类,来存每一个节点的信息
// 2,创建一个链表类,在该类中进行对链表的增加,删除,修改操作。
// 3,创建测试类
public class SingleLinkedListDemo {//单链表
public static void main (String agrs[]){
testStudent();
}
public static void testStudent(){
StudentNode stu1 = new StudentNode(6,"张三",99);
StudentNode stu2 = new StudentNode(2,"李四",99);
StudentNode stu3 = new StudentNode(3,"王五",99);
StudentNode stu4 = new StudentNode(5,"王二",99);
StudentNode stu5 = new StudentNode(4,"小红",99);
StudentNode stu6 = new StudentNode(1,"小明",99);
StudentLinkdelist studentLinkdelist = new StudentLinkdelist();//创建链表
//添加的方法一:
// studentLinkdelist.add(stu1);
// studentLinkdelist.add(stu2);
// studentLinkdelist.add(stu3);
// studentLinkdelist.add(stu4);
// studentLinkdelist.add(stu5);
// studentLinkdelist.add(stu6);
//添加方法二 :
studentLinkdelist.addsort(stu1);
studentLinkdelist.addsort(stu2);
studentLinkdelist.addsort(stu3);
studentLinkdelist.addsort(stu4);
studentLinkdelist.addsort(stu5);
studentLinkdelist.addsort(stu6);
studentLinkdelist.list();//显示一下;
//删除:
studentLinkdelist.Delete(3);
studentLinkdelist.Delete(1);
studentLinkdelist.Delete(6);
studentLinkdelist.Delete(80);
System.out.println("删除后的链表情况:");
studentLinkdelist.list();//显示一下;
//修改:
StudentNode stu7 = new StudentNode(1,"小明",99);
StudentNode stu8 = new StudentNode(5,"熊大",88);
studentLinkdelist.update(stu7);
studentLinkdelist.update(stu8);
System.out.println("修改后的链表情况:");
studentLinkdelist.list();//显示一下;
}
}
class StudentLinkdelist{
private StudentNode head = new StudentNode(0,"",0);
//初始化头节点
//添加节点:
// 方法一: 不考虑学生学号顺序,直接添加在链表的末尾
//
//头插法:
// public void add(StudentNode newNode){
// if(head.next == null){
// head.next= newNode;
// return;
// }else{
// newNode.next = head.next;
// head.next = newNode;
// return;
// }
//
// }
//尾插法:
public void add(StudentNode studentNode){
StudentNode temp = head;//头节点不可移动,用temp来进行遍历
while(true){
if(temp.next == null){ //当temp.next为空时,证明temp此时为最后一个节点
break;
}else if(temp.next.ID == studentNode.ID){
//ID相同证明 已经存在该学生。
System.out.printf("要插入学号为%d的学生已经存在。\n",studentNode.ID);
break;
}
temp = temp.next;//没有到达最后 temp继续向后移动
}
//当退出while循环,证明此时temp为最后一个节点,
// 因此将新节点添加到temp的后一位 即 temp.next = studentNode;
temp.next = studentNode;
}
//添加节点:
// 方法二: 考虑学生的学号,按学号插入链表。
public void addsort (StudentNode studentNode){
StudentNode temp = head;//头节点不可移动,用temp来进行遍历
while(true){
if(temp.next == null){//链表到达最后
studentNode.next = temp.next;
temp.next = studentNode;
break;
}
else if(temp.next.ID == studentNode.ID){
//ID相同证明 已经存在该学生。
System.out.printf("要插入学号为%d的学生已经存在。\n",studentNode.ID);
break;
}
else if(temp.next.ID > studentNode.ID){
//当前节点的下一个节点的ID 大于 要添加学生的ID
// 证明 :位置找到,在temp节点的下一位
studentNode.next = temp.next;
temp.next = studentNode;
break;
}
temp = temp.next;//temp继续向后移动
}
}
//删除节点
public void Delete (int id){
StudentNode temp = head;//头节点不可移动,用temp来进行遍历
while(true){
if(temp.next == null){ // 到达链表最后 没有找到
System.out.printf("要删除学号为%d的学生不存在。\n",id);
break;
}else if (temp.next.ID == id){//找到了该学生
temp.next = temp.next.next;
break;
}
temp = temp.next;//temp继续向后移动
}
}
//修改节点
public void update(StudentNode studentNode){
//修改节点的时候,学号不可以改变
StudentNode temp = head.next;//此时的temp从链表的第一个学生开始
// head 为头节点 初始为空
while(true){
if (temp == null ){
System.out.printf("要修改学号为%d的学生不存在。\n",studentNode.ID);
break;
}
else if(temp.ID == studentNode.ID){
//找到该学生。
temp.name = studentNode.name;
temp.mark = studentNode.mark;
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
}
//展示链表内容
public void list (){
if(head.next == null) { //判断是否为空
System.out.println("链表为空!");
return;
}
StudentNode temp = head.next;//此时的temp从链表的第一个学生开始
while(true){
if(temp == null ){
break;
}
//只要不到最后就输出。
System.out.println(temp);
temp = temp.next;
}
}
}
//定义Students 每一个Students都是一个节点;
class StudentNode{
public int ID;//学生学号。
public String name;//学生姓名。
public int mark;//学生成绩。
public StudentNode next; //指向下一个节点。
//构造器
public StudentNode(int ID,String name,int mark) {
this.ID = ID;
this.mark = mark;
this.name = name;
}
//根据自己的需求来重新写一个toString
@Override
public String toString() {
return "StudentNode{" + "ID=" + ID + ", name='" + name + ", mark=" + mark +'}';
}
}