树和二叉树——算法设计练习习题
1、设计算法求二叉树的结点个数。
void Count(BiNode *root){
if (root) {
Count(root->lchild);
number+ +; //number为数据成员
Count(root->rchild);
}
}
2、树中节点的数目
左子树中节点的数目+右子树中节点的数目+1
template
int BiTree::count(BiNode* root){
int number=0;
if (root==NULL)
number=0;
else
number=count(root->lchild)+count(root->rchild)+1;
return number;
}
3、统计叶子节点的数目
增加一个数据成员,leafcount, 初值为0
对树进行遍历。 如果一个节点是叶子,则将leafcount+1;
可以在前序、中序或后序的遍历过程中进行计算。
template
void BiTree:: countleaf(BiTreeNode * root){
if (root) {
if (root->lchild==NULL && root->rchild==NULL)
leafcount=leafcount+1;
else
{
countleaf(root->lchild);
countleaf(root->rchild);
}
}
return;
}
4、树中叶子结点的数目
左子树中叶子节点的数目+右子树中叶子节点的数目
template
int BiTree::leafcount(BiNode* root){
int number=0;
if (root==NULL)
number=0;
else if(root->lchild==NULL && root->rchild==NULL)
number=1;
else
number=leafcount(root->lchild)+leafcount(root->rchild);
return number;
}
5、计算树的高度
高度的定义:max(左子树高度,右子树高度)+1
算法分析
从根节点出发开始计算,
如果root==NULL, 高度为0;
否则,分别计算左子树的高度;右子树的高度;返回max(左子树高度,右子树高度)+1
递归的定义
template
int BiTree::cal_height(BiTreeNode * root){
int lheight=0,rheight=0;
if (root==0) return 0;
lheight=cal_height(root->lchild);
rheight=cal_height(root->rchild);
if (lheight>rheight) return lheight+1;
else return rheight+1;
}
6、输出中缀表达式。
并加上相应的括号(a+(b*(c-d)))-(e/f)
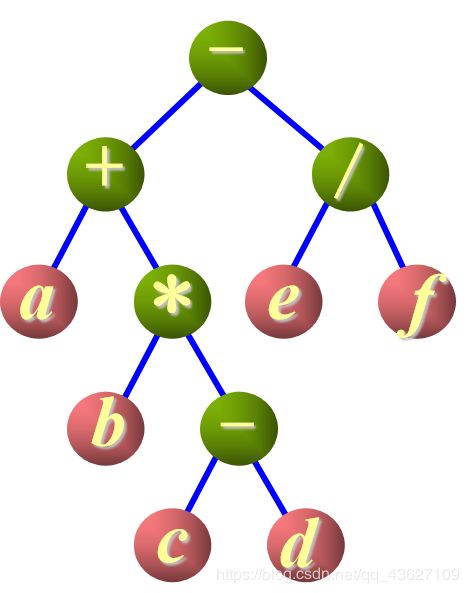
基本思想
中序遍历。
中序遍历左子树前,输出左括号
中序遍历右子树后,输出右括号
如果遍历叶子结点的左右子树,不输出括号
如果遍历根节点的左右子树,不输出括号(否则,会得到形如(a+b)的表达式)
void BiTree::In_Expression(BiNode* root){
if(root)
{
if(root!=this->root&&root->lchild!=0&&root->rchild!=0)
cout<<"(";
In_Expression(root->lchild);
cout<data;
In_Expression(root->rchild);
if(root!=this->root&&root->lchild!=0&&root->rchild!=0)
cout<<")";
}
}
7、输出二叉树逆时针旋转90后的形状
二叉树逆时针旋转90后输出
按照从右向左的顺序,中序遍历
每行输出一个结点
按照结点的层次,进行缩进。
template
void BiTree::Left_Rotate(BiNode* root,int level){
if(root){
Left_Rotate(root->rchild, level+1);
for(int i=0;idata<lchild, level+1);
}
}
8、计算二叉树的宽度
所谓宽度是指在二叉树的各层上,具有结点数最多的那一层上的结点总数 。
struct q_element{ BiNode * root; int level;};
int BiTree::Width(){
queue< struct q_element > q;
int num[100]={0,1};
q_element s,child;
BiNode *root;
root=this->root;
if(root==NULL)
return 0;
s.root=root; s.level=1; q.push(s);
while(!q.empty()) {
s=q.front();
if(s.root->lchild){
num[s.level+1]++;
child.root=s.root->lchild;
child.level=s.level+1;
q.push(child);
}
if(s.root->rchild) {
num[s.level+1]++;
child.root=s.root->rchild;
child.level=s.level+1;
q.push(child);
}
q.pop();
}
int max=0,i=1;
while(num[i]>0){
if(max8、判断一棵树是否是完全二叉树
基本思想:
基于层次遍历。
定义bool变量is_leaf,初值为false
如果is_leaf的值为true, 表示遍历的过程中遇到了叶子结点。
一旦在叶子结点之后再出现度为1、2的结点,则该树不是完全二叉树。
在层次遍历中,如果遇到一个节点
只有右儿子,没有左儿子,
false;
只有左,没有右
If (is_leaftrue) return false;
Else is_leaf=true;
两个儿子均为空
is_leaf=true
两个儿子均不空
If (is_leaftrue) return false;
将存在的儿子入队
能遍历完所有节点,即为完全二叉树
template
bool BiTree::Is_Wanquan(BiNode *root){
queue*> q;
BiNode * pointer;
bool is_leaf=false;
if(!root)
return false;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()) {
pointer=q.front(); q.pop();
if(pointer->rchild!=NULL && pointer->lchild==NULL)
return false;
else if(pointer->rchild==NULL && pointer->lchild!=NULL )
if(is_leaf)
return false;
else //如果是完全二叉树,则,该结点之后的结点应为叶子节点
is_leaf=true;
else if(pointer->rchild==NULL && pointer->lchild==NULL )
is_leaf=true;
if(pointer->lchild!=NULL)
q.push(pointer->lchild);
if(pointer->rchild!=NULL)
q.push(pointer->rchild);
}
return true;
}