I.常用的数据结构
文章目录
- 1.数组和字符串
- 1.1 字符串转换
- 1.2 例题
- 2. 链表
- 2.1 基本介绍
- 2.2常用方法
- 2.3 例题(未完成)
- 3. 栈
- 3.1 基本概念
- 3.2 应用场景
- 3.3 例题
- 例题1
- 例题2
- 例题3(未完成)
- 4. 队列(Queue)
- 特点
- 实现
- 应用场景
- 5.双端队列(Deque)
- 特点
- 实现
- 应用场景
- Java 中 对应的数据结构
- 例题
- 6. 树
- 6.1 树的形状
- 6.2 树的遍历
- 6.3 例题
- 例题1(LeetCode要订阅)
- 例题2
- 7. 优先队列
- 7.1 特点
- 7.2 应用场景
- 7.3 实现
- 7.4 例题
- 例题1
- 例题2
- 8. 图
- 8.1 基本知识点
- 8.2 相关算法
- 8.3 必会知识点
- 8.4 例题(未完成)
- 9. 前缀树(Trie)
- 9.1 应用场景
- 9.2 实例
- 例1
- 例2
- 9.3 实现
- 9.4 例题
- 10.线段树
- 10.1 引入
- 10.2 实现
- 10.3 例题(未完成)
- 11. 树状数组
- 11.1 实现
- 11.2 特点
- 11.3 例题(未完成)
1.数组和字符串
1.1 字符串转换
例子: 翻转字符串 “algorithm”.
解法: 使用两个指针指向头和尾,往中间进行寻找.
public String reverseStr(String str){
char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
int left = 0,right = chars.length-1;
while (left<=right){
swap(chars,left,right);
left++;
right--;
}
//注意使用String.valuOf 方法转为 字符串,不能使用 toString
return String.valueOf(chars);
}
private char[] swap(char[] chars,int i,int j){
char temp = chars[i];
chars[i] = chars[j];
chars[j] = temp;
return chars;
}
数组的优缺点:
- 优:构建简单
- 能在 O(1) 的时间内根据下标找到对应的元素
- 缺:构建必须一段连续的内存空间
- 查询某个元素是否存在,要遍历整个数组 O(n)
- 删除和插入某个元素,耗时,涉及到数组的拷贝 O(n)
应用场景
- 数据元素大小确定,删除/插入操作不多
1.2 例题
例题1:
LeetCode 第 242 题:给定两个字符串 s 和 t,编写一个函数来判断 t 是否是 s 的字母异位词。
字母异位词,也就是两个字符串中的相同字符的数量要对应相等.
s 等于 “anagram”,t 等于 “nagaram”,s 和 t 就互为字母异位词。
因为它们都包含有三个字符 a,一个字符 g,一个字符 m,一个字符 n,以及一个字符 r。
思路:
1)使用 哈希表. 使用数组存放每个字符出现的次数,小写字母就26个.
2)直接使用 字母的 ASCII 码作为数组下标 index
3)节约空间:使用 对应字母 - ‘a’ 得到的下标作为 大小为 26 的数组 index
public boolean isAnagram(String s, String t) {
if(s.length() != t.length()) return false;
char[] charS = s.toCharArray();
char[] charT = t.toCharArray();
int[] ss = new int[256];
int[] tt = new int[256];
//英文字母在 256 范围内
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
ss[charS[i]] ++;
tt[charT[i]] ++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < ss.length; i++) {
if(ss[i] != tt[i]) return false;
}
return true;
}
//根据都是小写字母 缩小数组大小
public boolean isAnagramI(String s, String t) {
if(s.length() != t.length()) return false;
char[] charS = s.toCharArray();
char[] charT = t.toCharArray();
int[] ss = new int[26];
int[] tt = new int[26];
for (int i = 0; i < charS.length; i++) {
int indexS = charS[i]-'a';
ss[indexS]++;
int indexT = charT[i]-'a';
tt[indexT]++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < ss.length; i++) {
if(ss[i] != tt[i]) return false;
}
return true;
}
//使用 只用一个数组的方式完成比较
public boolean isAnagramII(String s, String t) {
if(s.length() != t.length()) return false;
char[] charS = s.toCharArray();
char[] charT = t.toCharArray();
int[] tt = new int[26]; //只用一个数组 即可
for (int i = 0; i < charS.length; i++) {
int indexS = charS[i]-'a';
tt[indexS]++;
int indexT = charT[i]-'a';
tt[indexT]--; // 最后判断 tt 是否为 0
}
for(int a:tt){
if(a!=0) return false;
}
return true;
}
2. 链表
2.1 基本介绍
优缺点**
- 优:能够灵活分配内存空间
- 能够在 O(1) 的时间内完成插入/删除操作.前提是该元素的前一个元素已知
- 缺:不能像数组那样通过下标迅速读取元素,每次都要遍历获取
- 查询第 k 个元素需要 O(k) 时间
应用场景:
- 数据元素个数不确定,而且需要经常进行插入/删除操作
2.2常用方法
使用快慢指针:
- 链表的翻转
- 寻找倒数第 k 个元素
- 寻找链表中间位置的元素
- 判断链表是否有环
构建一个虚假的链表头:
2.3 例题(未完成)
例题1:
LeetCode 第 25 题:给你一个链表,每 k 个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回翻转后的链表。k 是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。如果节点总数不是 k 的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序。
思路:
不会,看不懂 烦死个人
参考:以后再看
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-nodes-in-k-group/solution/tu-jie-kge-yi-zu-fan-zhuan-lian-biao-by-user7208t/
3. 栈
3.1 基本概念
特点: 先进后出(FILO,First In Last Out)
实现: 利用一个单链表来实现栈的数据结构.因为只针对栈顶元素进行操作,所以借用单链表的头就能让所有栈的操作在 O(1) 的时间内完成.
如果打算使用数组和指针来实现相似的效果,那么一旦数组长度发生变化,时间复杂度就不再是 O(1)了
3.2 应用场景
- 解决某个问题时候,只关心最近一次的操作,并且操作完成之后,需要向前查找到更前一次的操作.
3.3 例题
栈是 leetcode 中等难度偏上题目经常使用的数据结构.
例题1
LeetCode 第 20 题:给定一个只包括 ‘(’,’)’,’{’,’}’,’[’,’]’ 的字符串,判断字符串是否有效。
有效字符串需满足:
左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
注意:空字符串可被认为是有效字符串。
思路:
- 判断是左侧括号入栈,
- 如果是右侧括号,则出栈和即将入栈的比较,
- 相等,则不入栈
- 不相等,返回false
- 注意:栈空的判断
//20 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/valid-parentheses/
// 8 ms 我写的就是个垃圾
public boolean isValid(String s) {
if (s.length() == 0) return true;
char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
String a = chars[i]+"";
if (a.equals(")") || a.equals("}") || a.equals("]")){
if(stack.isEmpty()) return false;
String pop = stack.pop()+"";
if(a.equals(")")){
if (!pop.equals("(")) return false;
}
else if(a.equals("]")){
if (!pop.equals("[")) return false;
}
else if(a.equals("}")){
if (!pop.equals("{")) return false;
}
continue;
}
stack.push(chars[i]);
}
if(stack.isEmpty()) return true;
return false;
}
//1 ms
public boolean isValidI(String s) {
if(s.isEmpty())
return true;
Stack<Character> stack=new Stack<Character>();
for(char c:s.toCharArray()){
if(c=='(')
stack.push(')');
else if(c=='{')
stack.push('}');
else if(c=='[')
stack.push(']');
else if(stack.empty()||c!=stack.pop())
return false;
}
if(stack.empty())
return true;
return false;
}
例题2
LeetCode 第 739 题:根据每日气温列表,请重新生成一个列表,对应位置的输入是你需要再等待多久温度才会升高超过该日的天数。如果之后都不会升高,请在该位置用 0 来代替。
思路:
- 解法一: 暴力破解—两个for 循环遍历
- 解法二: 利用栈
- 参考5分钟学算法的讲解
//739 https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/daily-temperatures/
public int[] dailyTemperatures(int[] T) {
int[] ret = new int[T.length];
for (int i = 0; i < T.length-1; i++) {
int count = 0;
for (int j = i+1; j < T.length; j++) {
if(T[i]<T[j]) {
count++;
ret[i] = count;
count = 0;
break;
}else
count++;
}
}
ret[T.length-1] = 0;
return ret;
}
//https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/daily-temperatures/solution/leetcode-tu-jie-739mei-ri-wen-du-by-misterbooo/
public int[] dailyTemperaturesI(int[] T) {
int[] ret = new int[T.length];
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack();
for (int i = 0; i < T.length; i++) {
if (stack.isEmpty()){
stack.push(i);
}
else {
while (!stack.isEmpty() && T[i]>T[stack.peek()] ){
Integer actualPop = stack.pop();
ret[actualPop] = i-actualPop;
}
stack.push(i);
}
}
return ret;
}
public int[] dailyTemperaturesII(int[] T) {
int[] ret = new int[T.length];
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack();
for (int i = 0; i < T.length; i++) {
while (!stack.isEmpty() && T[i]>T[stack.peek()] ){
Integer actualPop = stack.pop();
ret[actualPop] = i-actualPop;
}
stack.push(i);
}
return ret;
}
例题3(未完成)
- 求解算术表达式的结果(LeetCode 224、227、772、770)
- 求解直方图里最大的矩形区域(LeetCode 84)
4. 队列(Queue)
特点
- 先进先出(FIFO)
- 只允许在队头查看和删除数据
- 只允许在队尾查看和添加数据
实现
- 借助双链表实现队列
- 双链表的头指针允许在队列头查看和删除数据
- 双链表的尾指针允许在队尾查看和添加数据
应用场景
- 按照一定的顺序处理数据
- 且该数据的数据量在不断的变化
- 在 BFS 中,是运用队列最多的地方
5.双端队列(Deque)
特点
- 允许在队列的头和尾两端都能在 O(1) 的时间内进行数据 查看 添加 删除
实现
- 利用双链表实现
应用场景
- 用来实现一个长度动态变化的窗口 / 连续区间
Java 中 对应的数据结构
public interface Queue<E> extends Collection<E>
public interface Deque<E> extends Queue<E>
public class LinkedList<E>
extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable,
java.io.Serializable
例题
LeetCode 第 239 题:给定一个数组 nums,有一个大小为 k 的滑动窗口从数组的最左侧移动到数组的最右侧。你只可以看到在滑动窗口 k 内的数字,滑动窗口每次只向右移动一位。返回滑动窗口最大值。
public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
if(nums.length == 0) return nums;
int[] result = new int[nums.length-k+1];
int index = 0;
Deque<Integer> deque = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
//step1:头 - 移除队头,保证窗口的大小范围有效
//使用下标 好像更容易理解
if (i >= k){
if (deque.peekFirst() == i-k){
//表示窗口长度此时为 k 好像是
//使用这个判断,能确保窗口大小一直满足条件,好好理解
deque.pollFirst();
}
}
//step2:尾 - 移除当前值大于尾部的值 (可能会一直移除)
while (!deque.isEmpty() && nums[i]>nums[deque.getLast()]){
deque.pollLast();
}
//step3:尾 - 当前值加入队列
deque.addLast(i);
//step4:头 - 返回当前的队头的最大值
if (i >= k-1){
result[index++] = nums[deque.peekFirst()];
}
}
return result;
}
6. 树
6.1 树的形状
- 普通二叉树 平衡二叉树 完全二叉树 二叉搜索树
- 四叉树
- 多叉树
- 红黑树 自平衡二叉搜索树
6.2 树的遍历
-
前序遍历(根左右)
应用场景:
在树中进行搜索以及创建一棵新的树
-
中序遍历(左根右)
应用场景:
最常见的二叉搜索树,由于二叉搜索树的性质就是左孩子小于根节点,根节点小于右孩子.对二叉树进行中序遍历的时候是按顺序进行的
-
后序遍历(左右根)
应用场景:
在对某个结点进行分析的时候,需要左右子树的信息.收集信息的操作是从底部不断往上进行的.好比修剪一棵树的叶子,修剪方法是:从外面不断地往根部将叶子一片一片修剪掉.
6.3 例题
例题1(LeetCode要订阅)
上面的输出为: 4
例题2
LeetCode 第 230 题:给定一个二叉搜索树,编写一个函数 kthSmallest 来查找其中第 k 个最小的元素。
说明:你可以假设 k 总是有效的,1 ≤ k ≤ 二叉搜索树元素个数。
int count = 1;
int result = 0;
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
//中序遍历
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
//提前结束后面的递归,相当于剪枝
if (count >= k+1) {
return 0;
}
kthSmallest(root.left,k);
//print root
if(count == k){
result = root.val;
}
count++;
kthSmallest(root.right,k);
return result;
}
7. 优先队列
7.1 特点
-
能够保证每次取出的元素都是队列中优先级别最高的.
-
优先级别可以自定义.如:数据的数值越大/小,优先级越高.
-
优先队列的本质是一个二叉堆结构,利用一个数组结构来实现的完全二叉树.
换句话说:优先队列的本质是一个数组,数组里面的每个元素既有可能是其他元素的父节点,也可能是其他元素的子节点
数组第一个元素拥有最高的优先级别
7.2 应用场景
- 从一堆杂乱无章的数据中按照一定的顺序/优先级,逐步的筛选出部分/全部数据
7.3 实现
优先队列的两个基本操作:
-
向上筛选(sift up/bubble up)
当有新的数据加入到优先队列中,新的数据首先放在二叉堆的底部
然后不断进行向上筛选操作,即如果发现该**数据的优先级别比父节点的优先级别还高,**那么就和父节点元素交换.继续向上进行比较,直到无法进行交换位为止.
时间复杂度: O(logk) 即树的高度
-
向下筛选(sift down/bubble down)
当堆顶元素被取出时,要更新堆顶的元素作为下一次按照优先级顺序被取出的对象, 需要 将 堆底部的元素放置到堆顶,然后不断的对它进行向下筛选操作.
将该元素和它的两个孩子节点对比优先级,如果优先级最高的是其中一个孩子,就将该元素和那个孩子交换,反复进行,直到无法交换为止.
时间复杂度: O(logk) 即树的高度
7.4 例题
例题1
找出数组前 K 大 的数
//215
// 8 ms 使用大顶堆
public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
Queue<Integer> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2-o1;
}
});
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
priorityQueue.add(nums[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < k-1; i++) {
priorityQueue.poll();
}
return priorityQueue.poll();
}
// 19 ms 使用快排 nlogn
public int findKthLargestI(int[] nums, int k) {
//快排思想
int partition = partition(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
/**
* 长度为 6
* 求 第 2(k) 大 就是求 第 5(nums.length-k+1) 小
*
*/
int kthMax = nums.length-k+1;
while (partition != kthMax-1){
if (partition < kthMax-1){
partition = partition(nums,partition+1,nums.length-1);
}else {
partition = partition(nums,0,partition-1);
}
}
return nums[partition];
}
//返回的ret就是 分区点的下标 分区点左边都小于 array[ret],右边都大于 array[ret]
private int partition(int[] array,int p,int r){
int point = array[r];
int i=p,j=p;
for (;j<r;j++){
if (array[j] <= point){
if(i == j){
i++;
}else {
swapArray(array,i,j);
i++;
}
}
}
swapArray(array,i,j);
return i;
/*int i =p;
int j= p;
int pivot = array[r];
for(;j
}
private void swapArray(int[] array,int i,int j){
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = temp;
}
例题2
LeetCode 第 347 题:给定一个非空的整数数组,返回其中出现频率前 k 高的元素。
public int[] topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) {
Map<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
map.put(nums[i],map.getOrDefault(nums[i],0)+1);
}
List<Map.Entry<Integer,Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>(map.entrySet());
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Map.Entry<Integer, Integer>>() {
@Override
public int compare(Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> o1, Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> o2) {
return o2.getValue()-o1.getValue();
}
});
int[] result = new int[k];
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
result[i] = list.get(i).getKey();
}
return result;
}
// O(nlogn) 使用小顶堆进行优化
public int[] topKFrequentI(int[] nums, int k) {
Map<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
map.put(nums[i],map.getOrDefault(nums[i],0)+1);
}
//存入 key ,根据 key 获取的键 进行排序
Queue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
// return map.get(o2)-map.get(o1);
//使用小顶堆,后面方便优化
return map.get(o1)-map.get(o2);
}
});
for (Integer key:map.keySet()){
// O(logn) 的操作
// queue.add(key);
// O(logK) 的操作
//注意:这个地方不能 =
if (queue.size() < k){
queue.add(key);
}else {
if (map.get(key) > map.get(queue.peek())){
queue.poll();
queue.add(key);
}
}
}
//取出 k 个
int[] result = new int[k];
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
result[i] = queue.poll();
}
return result;
}
8. 图
8.1 基本知识点
8.2 相关算法
8.3 必会知识点
- 环的检测
- 二部图的检测
- 树的检测
- 拓扑排序
- 最短路径算法: 能区分特点,在合适的场合选择使用合适的算法
8.4 例题(未完成)
LeetCode 第 785 题:给定一个无向图 graph,当这个图为二部图时返回 true。
9. 前缀树(Trie)
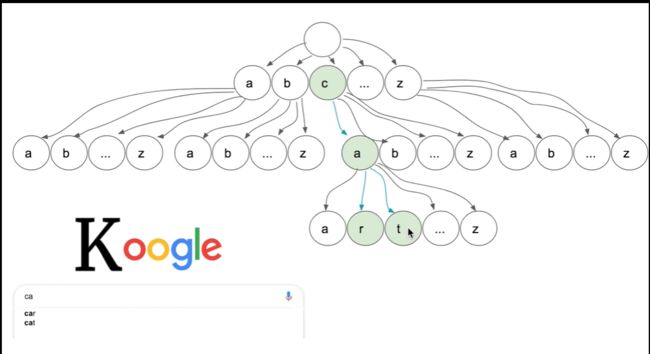
9.1 应用场景
- 前缀树被广泛应用于字典查找中,也被称为字典树
- 网站上的搜索框会罗列出以搜索文字作为开头的相关搜索信息,这里运用了前缀树进行后端的快速检索。
- 汉字拼音输入法的联想输出功能也运用了前缀树。
9.2 实例
例1
举例:给定一系列字符串,这些字符串构成了一种字典,要求你在这个字典当中找出所有以“ABC”开头的字符串。
思路
- 解法一:暴力搜索.直接遍历一遍字典,然后判断每个字符串是否是’ABC’开头.假设 N 个单词,对比的是任意的开头,长度为M, 时间复杂度为 O(M*N)
- 解法二:使用前缀树对字段存储进行优化.可以将时间复杂度将为 O(M).M表示字典中最长的那个单词的字符个数.
例2
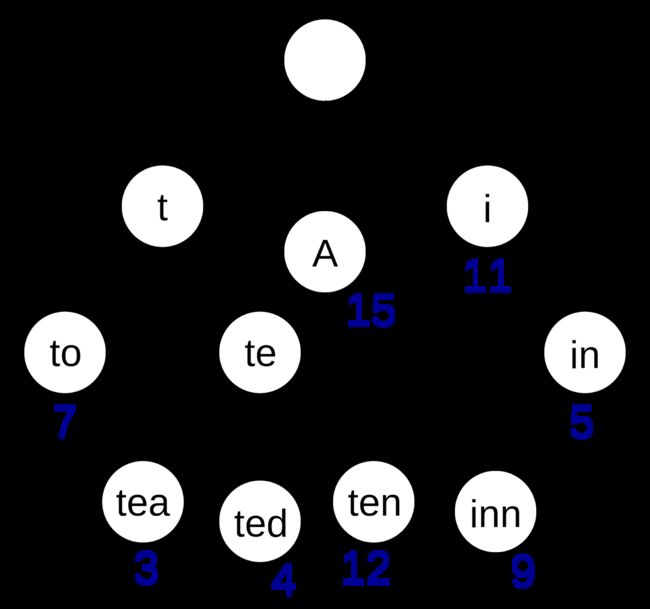
假如有一个字典,字典里面有如下词:“A”,“to”,“tea”,“ted”,“ten”,“i”,“in”,“inn”,每个单词还能有自己的一些权重值,那么用前缀树来构建这个字典将会是如下的样子:
性质
-
每个节点至少包括两个属性
children: 数组或者集合,罗列出每个分支中包含的所有字符
isEnd: 布尔值, 表示该节点是否为某字符串的结尾
-
前缀树的根节点是空的
空 是指: 只利用这个节点的 children 属性,即只关心在这个字典里,有哪些打头的字符.
-
除了根节点,其他所有节点都可能是单词的结尾,叶子节点一定是单词的结尾
9.3 实现
基于数组实现
//208
//https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/implement-trie-prefix-tree/
class Trie {
TrieNode root = null;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public Trie() {
root = new TrieNode();
}
/** Inserts a word into the trie. */
public void insert(String word) {
TrieNode cur = root;
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
char c = word.charAt(i);
if(cur.children[c -'a'] == null){
//直接插入
TrieNode child = new TrieNode();
cur.children[c - 'a'] = child;
}
//已经存在了,则插入
cur = cur.children[c - 'a'];
}
//注意将最后置为 true
cur.isWord = true;
}
/** Returns if the word is in the trie. */
public boolean search(String word) {
TrieNode cur = root;
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
char c = word.charAt(i);
if (cur.children[c - 'a'] ==null){
return false;
}
cur = cur.children[c - 'a'];
}
//要判断是单词结尾才行
return cur.isWord;
}
/** Returns if there is any word in the trie that starts with the given prefix. */
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
TrieNode cur = root;
for (int i = 0; i < prefix.length(); i++) {
char c = prefix.charAt(i);
if (cur.children[c - 'a'] == null){
return false;
}
cur = cur.children[c - 'a'];
}
return true;
}
class TrieNode{
public boolean isWord;
public TrieNode[] children;
public TrieNode(){
isWord = false;
children = new TrieNode[26];
}
}
}
基于Map实现
/**
* 使用 map 实现前缀树
*/
class TrieNode{
public boolean isWord;
public Map<Character,TrieNode> chlidren;
public TrieNode(){
isWord = false;
chlidren = new HashMap<>();
}
}
class Trie {
TrieNode root = null;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public Trie() {
root = new TrieNode();
}
/** Inserts a word into the trie. */
public void insert(String word) {
TrieNode cur = root;
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
if (!cur.chlidren.containsKey(word.charAt(i))){
TrieNode temp = new TrieNode();
//不存在则加入,要知道如何加入
cur.chlidren.put(word.charAt(i),temp);
}
cur = cur.chlidren.get(word.charAt(i));
}
cur.isWord = true;
}
/** Returns if the word is in the trie. */
public boolean search(String word) {
TrieNode cur = root;
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
if (!cur.chlidren.containsKey(word.charAt(i))){
return false;
}
cur = cur.chlidren.get(word.charAt(i));
}
return cur.isWord;
}
/** Returns if there is any word in the trie that starts with the given prefix. */
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
TrieNode cur = root;
for (int i = 0; i < prefix.length(); i++) {
if (!cur.chlidren.containsKey(prefix.charAt(i))){
return false;
}
cur = cur.chlidren.get(prefix.charAt(i));
}
return true;
}
}
9.4 例题
LeetCode 第 212 题:给定一个二维网格 board 和一个字典中的单词列表 words,找出所有同时在二维网格和字典中出现的单词。
/**
* 212
* https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/word-search-ii/
*/
public List<String> findWords(char[][] board, String[] words) {
Trie212 trie = new Trie212();
for (String word : words) {
trie.insert(word);
}
List<String> result = new LinkedList<>();
StringBuilder path = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < board[0].length; j++) {
dfs(i, j, board, trie.root, path, result);
}
}
return result;
}
private void dfs(int i, int j, char[][] board, TrieNode root, StringBuilder path, List<String> result) {
//到达终点状态-->判断是否是单词的结尾
if (root.isWord) {
result.add(path.toString());
//找到了就置为 false 防止重复搜索
root.isWord = false;
}
//越界
if (i < 0 || i >= board.length || j < 0 || j >= board[0].length) {
return;
}
char temp = board[i][j];
// 剪枝-->如果不是单词
if (temp == '#' || root.children[temp - 'a'] == null) {
return;
}
root = root.children[temp - 'a'];
//是单词的一部分
//不是结尾继续搜索
//标记已经搜索过的字符
board[i][j] = '#';
dfs(i + 1, j, board, root, path.append(temp), result);
path.deleteCharAt(path.length() - 1);
dfs(i - 1, j, board, root, path.append(temp), result);
path.deleteCharAt(path.length() - 1);
dfs(i, j + 1, board, root, path.append(temp), result);
path.deleteCharAt(path.length() - 1);
dfs(i, j - 1, board, root, path.append(temp), result);
board[i][j] = temp;
path.deleteCharAt(path.length() - 1);
//System.out.println(path);
}
/**
* 这个好像好理解一点
* 注意:
* 在递归时 +1之类的操作,使用 +1,不用 ++
* https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/word-search-ii/
*/
public List<String> findWordsI(char[][] board, String[] words) {
Trie212 trie = new Trie212();
for (String word : words) {
trie.insert(word);
}
List<String> result = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < board[0].length; j++) {
dfsI(i, j, board, trie.root, "", result);
}
}
return result;
}
private void dfsI(int i, int j, char[][] board, TrieNode root, String path, List<String> result) {
//到达终点状态-->判断是否是单词的结尾
if (root.isWord) {
result.add(path);
//找到了就置为 false 防止重复搜索
root.isWord = false;
}
//越界
if (i < 0 || i >= board.length || j < 0 || j >= board[0].length) {
return;
}
char temp = board[i][j];
// 剪枝-->如果不是单词
if (temp == '#' || root.children[temp - 'a'] == null) {
return;
}
root = root.children[temp - 'a'];
//是单词的一部分
//不是结尾继续搜索
//标记已经搜索过的字符
board[i][j] = '#';
dfsI(i + 1, j, board, root, path+temp, result);
dfsI(i - 1, j, board, root, path+temp, result);
dfsI(i, j + 1, board, root, path+temp, result);
dfsI(i, j - 1, board, root, path+temp, result);
board[i][j] = temp;
}
10.线段树
10.1 引入
10.2 实现
10.3 例题(未完成)
LeetCode 第 315 题:给定一个整数数组 nums,按要求返回一个新数组 counts,使得数组 counts 有该性质——counts[i] 的值是 nums[i] 右侧小于 nums[i] 的元素的数量。
11. 树状数组
11.1 实现
11.2 特点
- 使用数组来表示多叉树的结构
- 树状数组的第一个元素是空节点
- 如果节点 tree[y] 是 tree[x] 的父节点,那么满足条件: y= x-( x&(-x) )
11.3 例题(未完成)
LeetCode 第 308 题,求一个动态变化的二维矩阵里,任意子矩阵里的数的总和。