Shark
- 概念:
Shark是基于Spark计算框架之上且兼容Hive语法的SQL执行引擎,由于底层的计算采用了Spark,性能比MapReduce的Hive普遍快2倍以上,当数据全部load在内存的话,将快10倍以上,因此Shark可以作为交互式查询应用服务来使用。除了基于Spark的特性外,Shark是完全兼容Hive的语法,表结构以及UDF函数等,已有的HiveSql可以直接进行迁移至Shark上Shark底层依赖于Hive的解析器,查询优化器,但正是由于SHark的整体设计架构对Hive的依赖性太强,难以支持其长远发展,比如不能和Spark的其他组件进行很好的集成,无法满足Spark的一栈式解决大数据处理的需求。
SparkSQL
- SparkSQL介绍
Hive是Shark的前身,Shark是SparkSQL的前身,SparkSQL产生的根本原因是其完全脱离了Hive的限制。
SparkSQL支持查询原生的RDD。 RDD是Spark平台的核心概念,是Spark能够高效的处理大数据的各种场景的基础。
能够在Scala中写SQL语句。支持简单的SQL语法检查,能够在Scala中写Hive语句访问Hive数据,并将结果取回作为RDD使用。
- Spark on Hive和Hive on Spark
Spark on Hive: Hive只作为储存角色,Spark负责sql解析优化,执行。
Hive on Spark:Hive即作为存储又负责sql的解析优化,Spark负责执行。
- DataFrame
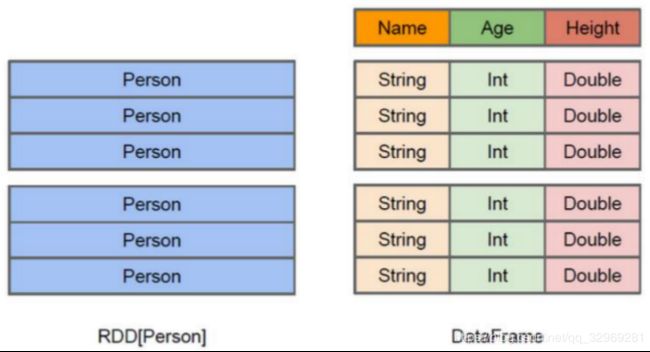
DataFrame也是一个分布式数据容器。与RDD类似,然而DataFrame更像传统数据库的二维表格,除了数据以外,还掌握数据的结构信息,即schema。同时,与Hive类似,DataFrame也支持嵌套数据类型(struct、array和map)。从API易用性的角度上 看, DataFrame API提供的是一套高层的关系操作,比函数式的RDD API要更加友好,门槛更低。
DataFrame的底层封装的是RDD,只不过RDD的泛型是Row类型。
- SparkSQL的数据源
SparkSQL的数据源可以是JSON类型的字符串,JDBC,Parquent,Hive,HDFS等。
- SparkSQL底层架构
首先拿到sql后解析一批未被解决的逻辑计划,再经过分析得到分析后的逻辑计划,再经过一批优化规则转换成一批最佳优化的逻辑计划,再经过SparkPlanner的策略转化成一批物理计划,随后经过消费模型转换成一个个的Spark任务执行。
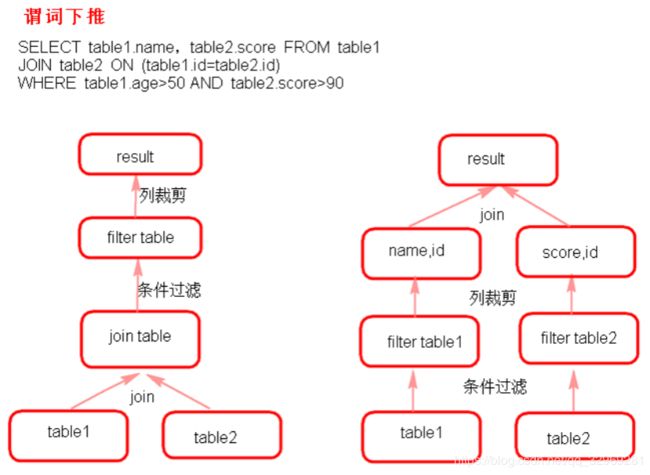
- 谓词下推(predicate Pushdown)
创建DataFrame的几种方式
- 读取json格式的文件创建DataFrame
注意:
json文件中的json数据不能嵌套json格式数据。
DataFrame是一个一个Row类型的RDD,df.rdd()/df.javaRdd()。
可以两种方式读取json格式的文件。
df.show()默认显示前20行数据。
DataFrame原生API可以操作DataFrame(不方便)。
注册成临时表时,表中的列默认按ascii顺序显示列。
java:
SparkConf conf = new SparkConf();
conf.setMaster("local").setAppName("jsonfile");
SparkContext sc = new SparkContext(conf);
SQLContext sqlContext = new SQLContext(sc);
DataFrame df = sqlContext.read().format("json").load("sparksql/json");
RDD<Row> rdd = df.rdd();
df.printSchema();
df.select(df.col("name"),df.col("age").plus(10).alias("addage")).show();
df.select(df.col("name"),df.col("age")).where(df.col("age").gt(19)).show();
df.groupBy(df.col("age")).count().show();
df.registerTempTable("jtable");
DataFrame sql = sqlContext.sql("select age,count(1) from jtable group by age");
DataFrame sql2 = sqlContext.sql("select * from jtable");
sc.stop();
scala:
val conf = new SparkConf()
conf.setMaster("local").setAppName("jsonfile")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
val sqlContext = new SQLContext(sc)
val df = sqlContext.read.json("sparksql/json")
df.show()
df.printSchema()
df.select(df.col("name")).show()
df.select(df.col("name"),df.col("age")).where(df.col("age").gt(19)).show()
df.groupBy(df.col("age")).count().show();
df.registerTempTable("jtable")
val result = sqlContext.sql("select * from jtable")
result.show()
sc.stop()
- 通过json格式的RDD创建DataFrame
java:
SparkConf conf = new SparkConf();
conf.setMaster("local").setAppName("jsonRDD");
JavaSparkContext sc = new JavaSparkContext(conf);
SQLContext sqlContext = new SQLContext(sc);
JavaRDD<String> nameRDD = sc.parallelize(Arrays.asList(
"{\"name\":\"zhangsan\",\"age\":\"18\"}",
"{\"name\":\"lisi\",\"age\":\"19\"}",
"{\"name\":\"wangwu\",\"age\":\"20\"}"
));
JavaRDD<String> scoreRDD = sc.parallelize(Arrays.asList(
"{\"name\":\"zhangsan\",\"score\":\"100\"}",
"{\"name\":\"lisi\",\"score\":\"200\"}",
"{\"name\":\"wangwu\",\"score\":\"300\"}"
));
DataFrame namedf = sqlContext.read().json(nameRDD);
DataFrame scoredf = sqlContext.read().json(scoreRDD);
namedf.registerTempTable("name");
scoredf.registerTempTable("score");
DataFrame result = sqlContext.sql("select name.name,name.age,score.score from name,score where name.name = score.name");
sc.stop();
scala:
val conf = new SparkConf()
conf.setMaster("local").setAppName("jsonrdd")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
val sqlContext = new SQLContext(sc)
val nameRDD = sc.makeRDD(Array(
"{\"name\":\"zhangsan\",\"age\":18}",
"{\"name\":\"lisi\",\"age\":19}",
"{\"name\":\"wangwu\",\"age\":20}"
))
val scoreRDD = sc.makeRDD(Array(
"{\"name\":\"zhangsan\",\"score\":100}",
"{\"name\":\"lisi\",\"score\":200}",
"{\"name\":\"wangwu\",\"score\":300}"
))
val nameDF = sqlContext.read.json(nameRDD)
val scoreDF = sqlContext.read.json(scoreRDD)
nameDF.registerTempTable("name")
scoreDF.registerTempTable("score")
val result = sqlContext.sql("select name.name,name.age,score.score from name,score where name.name = score.name")
result.show()
sc.stop()
- 非json格式的RDD创建DataFrame
1)通过反射的方式将非json格式的RDD转换成DataFrame(不建议使用)
自定义类要可序列化
自定义类的访问级别是Public
RDD转成DataFrame后会根据映射将字段按Assci码排序
将DataFrame转换成RDD时获取字段两种方式,一种是df.getInt(0)下标获取(不推荐使用),另一种是df.getAs(“列名”)获取(推荐使用)
java:
SparkConf conf = new SparkConf();
conf.setMaster("local").setAppName("RDD");
JavaSparkContext sc = new JavaSparkContext(conf);
SQLContext sqlContext = new SQLContext(sc);
JavaRDD<String> lineRDD = sc.textFile("sparksql/person.txt");
JavaRDD<Person> personRDD = lineRDD.map(new Function<String, Person>() {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@Override
public Person call(String s) throws Exception {
Person p = new Person();
p.setId(s.split(",")[0]);
p.setName(s.split(",")[1]);
p.setAge(Integer.valueOf(s.split(",")[2]));
return p;
}
});
DataFrame df = sqlContext.createDataFrame(personRDD, Person.class);
df.show();
df.registerTempTable("person");
sqlContext.sql("select name from person where id = 2").show();
JavaRDD<Row> javaRDD = df.javaRDD();
JavaRDD<Person> map = javaRDD.map(new Function<Row, Person>() {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@Override
public Person call(Row row) throws Exception {
Person p = new Person();
p.setId((String)row.getAs("id"));
p.setName((String)row.getAs("name"));
p.setAge((Integer)row.getAs("age"));
return p;
}
});
map.foreach(new VoidFunction<Person>() {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@Override
public void call(Person t) throws Exception {
System.out.println(t);
}
});
sc.stop();
scala:
val conf = new SparkConf()
conf.setMaster("local").setAppName("rddreflect")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
val sqlContext = new SQLContext(sc)
val lineRDD = sc.textFile("./sparksql/person.txt")
import sqlContext.implicits._
val personRDD = lineRDD.map { x => {
val person = Person(x.split(",")(0),x.split(",")(1),Integer.valueOf(x.split(",")(2)))
person
} }
val df = personRDD.toDF();
df.show()
val rdd = df.rdd
val result = rdd.map { x => {
Person(x.getAs("id"),x.getAs("name"),x.getAs("age"))
} }
result.foreach { println}
sc.stop()
2)动态创建Schema将非json格式的RDD转换成DataFrame
java:
SparkConf conf = new SparkConf();
conf.setMaster("local").setAppName("rddStruct");
JavaSparkContext sc = new JavaSparkContext(conf);
SQLContext sqlContext = new SQLContext(sc);
JavaRDD<String> lineRDD = sc.textFile("./sparksql/person.txt");
JavaRDD<Row> rowRDD = lineRDD.map(new Function<String, Row>() {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@Override
public Row call(String s) throws Exception {
return RowFactory.create(
String.valueOf(s.split(",")[0]),
String.valueOf(s.split(",")[1]),
Integer.valueOf(s.split(",")[2])
);
}
});
List<StructField> asList =Arrays.asList(
DataTypes.createStructField("id", DataTypes.StringType, true),
DataTypes.createStructField("name", DataTypes.StringType, true),
DataTypes.createStructField("age", DataTypes.IntegerType, true)
);
StructType schema = DataTypes.createStructType(asList);
DataFrame df = sqlContext.createDataFrame(rowRDD, schema);
sc.stop();
scala:
val conf = new SparkConf()
conf.setMaster("local").setAppName("rddStruct")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
val sqlContext = new SQLContext(sc)
val lineRDD = sc.textFile("./sparksql/person.txt")
val rowRDD = lineRDD.map { x => {
val split = x.split(",")
RowFactory.create(split(0),split(1),Integer.valueOf(split(2)))
} }
val schema = StructType(List(
StructField("id",StringType,true),
StructField("name",StringType,true),
StructField("age",IntegerType,true)
))
val df = sqlContext.createDataFrame(rowRDD, schema)
df.show()
df.printSchema()
sc.stop()
- 读取parquet文件创建DataFrame
注意:
可以将DataFrame存储成parquet文件。保存成parquet文件的方式有两种
df.write().mode(SaveMode.Overwrite)format("parquet").save("./sparksql/parquet");
df.write().mode(SaveMode.Overwrite).parquet("./sparksql/parquet");
SaveMode指定文件保存时的模式。
Overwrite:覆盖
Append:追加
ErrorIfExists:如果存在就报错
Ignore:如果存在就忽略
java:
SparkConf conf = new SparkConf();
conf.setMaster("local").setAppName("parquet");
JavaSparkContext sc = new JavaSparkContext(conf);
SQLContext sqlContext = new SQLContext(sc);
JavaRDD<String> jsonRDD = sc.textFile("sparksql/json");
DataFrame df = sqlContext.read().json(jsonRDD);
df.write().mode(SaveMode.Overwrite).format("parquet").save("./sparksql/parquet");
df.write().mode(SaveMode.Overwrite).parquet("./sparksql/parquet");
df.show();
DataFrame load = sqlContext.read().format("parquet").load("./sparksql/parquet");
load = sqlContext.read().parquet("./sparksql/parquet");
load.show();
sc.stop();
scala:
val conf = new SparkConf()
conf.setMaster("local").setAppName("parquet")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
val sqlContext = new SQLContext(sc)
val jsonRDD = sc.textFile("sparksql/json")
val df = sqlContext.read.json(jsonRDD)
df.show()
df.write.mode(SaveMode.Overwrite).format("parquet").save("./sparksql/parquet")
df.write.mode(SaveMode.Overwrite).parquet("./sparksql/parquet")
var result = sqlContext.read.parquet("./sparksql/parquet")
result = sqlContext.read.format("parquet").load("./sparksql/parquet")
result.show()
sc.stop()
- 读取JDBC中的数据创建DataFrame(MySql为例) 两种方式创建DataFrame
java:
SparkConf conf = new SparkConf();
conf.setMaster("local").setAppName("mysql");
JavaSparkContext sc = new JavaSparkContext(conf);
SQLContext sqlContext = new SQLContext(sc);
Map<String, String> options = new HashMap<String,String>();
options.put("url", "jdbc:mysql://192.168.179.4:3306/spark");
options.put("driver", "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
options.put("user", "root");
options.put("password", "123456");
options.put("dbtable", "person");
DataFrame person = sqlContext.read().format("jdbc").options(options).load();
person.show();
person.registerTempTable("person");
DataFrameReader reader = sqlContext.read().format("jdbc");
reader.option("url", "jdbc:mysql://192.168.179.4:3306/spark");
reader.option("driver", "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
reader.option("user", "root");
reader.option("password", "123456");
reader.option("dbtable", "score");
DataFrame score = reader.load();
score.show();
score.registerTempTable("score");
DataFrame result =
sqlContext.sql("select person.id,person.name,score.score from person,score where person.name = score.name");
result.show();
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("user", "root");
properties.setProperty("password", "123456");
result.write().mode(SaveMode.Overwrite).jdbc("jdbc:mysql://192.168.179.4:3306/spark", "result", properties);
sc.stop();
scala:
val conf = new SparkConf()
conf.setMaster("local").setAppName("mysql")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
val sqlContext = new SQLContext(sc)
val options = new HashMap[String,String]();
options.put("url", "jdbc:mysql://192.168.179.4:3306/spark")
options.put("driver","com.mysql.jdbc.Driver")
options.put("user","root")
options.put("password", "123456")
options.put("dbtable","person")
val person = sqlContext.read.format("jdbc").options(options).load()
person.show()
person.registerTempTable("person")
val reader = sqlContext.read.format("jdbc")
reader.option("url", "jdbc:mysql://192.168.179.4:3306/spark")
reader.option("driver","com.mysql.jdbc.Driver")
reader.option("user","root")
reader.option("password","123456")
reader.option("dbtable", "score")
val score = reader.load()
score.show()
score.registerTempTable("score")
val result = sqlContext.sql("select person.id,person.name,score.score from person,score where person.name = score.name")
result.show()
val properties = new Properties()
properties.setProperty("user", "root")
properties.setProperty("password", "123456")
result.write.mode(SaveMode.Append).jdbc("jdbc:mysql://192.168.179.4:3306/spark", "result", properties)
sc.stop()
- 读取Hive中的数据加载成DataFrame
HiveContext是SQLContext的子类,连接Hive建议使用HiveContext。
由于本地没有Hive环境,要提交到集群运行,提交命令:
./spark-submit
--master spark://node1:7077,node2:7077
--executor-cores 1
--executor-memory 2G
--total-executor-cores 1
--class com.bjsxt.sparksql.dataframe.CreateDFFromHive
/root/test/HiveTest.jar
java:
SparkConf conf = new SparkConf();
conf.setAppName("hive");
JavaSparkContext sc = new JavaSparkContext(conf);
HiveContext hiveContext = new HiveContext(sc);
hiveContext.sql("USE spark");
hiveContext.sql("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS student_infos");
hiveContext.sql("CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS student_infos (name STRING,age INT) row format delimited fields terminated by '\t' ");
hiveContext.sql("load data local inpath '/root/test/student_infos' into table student_infos");
hiveContext.sql("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS student_scores");
hiveContext.sql("CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS student_scores (name STRING, score INT) row format delimited fields terminated by '\t'");
hiveContext.sql("LOAD DATA "
+ "LOCAL INPATH '/root/test/student_scores'"
+ "INTO TABLE student_scores");
DataFrame goodStudentsDF = hiveContext.sql("SELECT si.name, si.age, ss.score "
+ "FROM student_infos si "
+ "JOIN student_scores ss "
+ "ON si.name=ss.name "
+ "WHERE ss.score>=80");
hiveContext.sql("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS good_student_infos");
goodStudentsDF.registerTempTable("goodstudent");
DataFrame result = hiveContext.sql("select * from goodstudent");
result.show();
goodStudentsDF.write().mode(SaveMode.Overwrite).saveAsTable("good_student_infos");
Row[] goodStudentRows = hiveContext.table("good_student_infos").collect();
for(Row goodStudentRow : goodStudentRows) {
System.out.println(goodStudentRow);
}
sc.stop();
scala:
val conf = new SparkConf()
conf.setAppName("HiveSource")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
val hiveContext = new HiveContext(sc)
hiveContext.sql("use spark")
hiveContext.sql("drop table if exists student_infos")
hiveContext.sql("create table if not exists student_infos (name string,age int) row format delimited fields terminated by '\t'")
hiveContext.sql("load data local inpath '/root/test/student_infos' into table student_infos")
hiveContext.sql("drop table if exists student_scores")
hiveContext.sql("create table if not exists student_scores (name string,score int) row format delimited fields terminated by '\t'")
hiveContext.sql("load data local inpath '/root/test/student_scores' into table student_scores")
val df = hiveContext.sql("select si.name,si.age,ss.score from student_infos si,student_scores ss where si.name = ss.name")
hiveContext.sql("drop table if exists good_student_infos")
df.write.mode(SaveMode.Overwrite).saveAsTable("good_student_infos")
sc.stop()

