玩转数据结构(01)--数组
一、数据结构分类:
1.线性结构:数组、栈、队列、链表、哈希表...
2.树结构:二叉树、二分搜索树、AVL、红黑树、Treap、Splay、堆、Trie、线段树、K-D树、并查集、哈夫曼树...
3.图结构:邻接矩阵、邻接表
二、数组
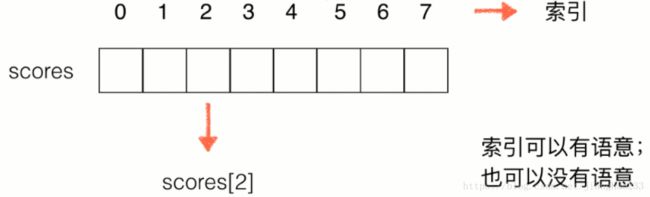
1.定义:把数据码成一排进行存放
2.图解:
3.示例代码 Main.java
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = new int[10]; //声明数组
for(int i = 0 ; i < arr.length ; i ++)
arr[i] = i;
int[] scores = new int[]{100, 99, 66};//声明数组并赋值
for(int i = 0 ; i < scores.length ; i ++)
System.out.println(scores[i]);//通过索引访问的方式来访问数组的变量
for(int score: scores) //数组具有可遍历的特性
System.out.println(score);
scores[0] = 96; ////通过索引访问的方式来修改数组的变量
for(int i = 0 ; i < scores.length ; i ++)
System.out.println(scores[i]);
}
}
输出:
4.数组基础
数组优点:快速查询;
索引可以用语义,也可以没有语义;数组最好应用于“索引有语义”的情况;
但并非所有有语义的索引都适用于数组;例: 身份证号就不适合,占用空间太大;
数组也可以处理 “索引没有语义 ”的情况;主要讨论该情况下数组的使用;
5.二次封装自己的数组
(Java 自身的数组是静态数组,不具有对内存空间增、删、改、查功能;故二次分装自己的内存,为动态数组)
例图:
自己的数组类: Array
data:数组名称
size:数组中实际装入元素的长度
capacity:数组定义的长度(容量)
代码示例:Array.java
public class Array {
private int[] data; //定义int 型数组 data
private int size; //data数组中有效元素的数量
// 构造函数,传入数组的容量capacity构造Array
public Array(int capacity){
data = new int[capacity];
size = 0;
}
// 无参数的构造函数,默认数组的容量capacity=10
public Array(){
this(10);
}
// 获取数组的容量
public int getCapacity(){
return data.length;
}
// 获取数组中的元素个数
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
// 返回数组是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
}
6.向数组中添加元素
向数组末添加元素:赋值给data[size],然后 size+1(右移即可)
向指定位置添加元素:将索引为1的值及后面的值都向后移动;先将 size-1 的元素移动到size上,直到将值放入 1 中,最后 size+1
移动100
插入到 1 的位置
示例代码:Array.java
public class Array {
private int[] data;
private int size;
// 构造函数,传入数组的容量capacity构造Array
public Array(int capacity){
data = new int[capacity];
size = 0;
}
// 无参数的构造函数,默认数组的容量capacity=10
public Array(){
this(10);
}
// 获取数组的容量
public int getCapacity(){
return data.length;
}
// 获取数组中的元素个数
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
// 返回数组是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
// 向所有元素后添加一个新元素
public void addLast(int e){
// if(size == data.length) //判断数组是否装满了
// throw new IllegalArgumentException("AddLast failed. Array is full.");
//
// data[size] = e;
// size ++;
add(size, e); //复用 add 方法
}
// 在所有元素前添加一个新元素
public void addFirst(int e){
add(0, e);
}
// 在index索引的位置插入一个新元素e
public void add(int index, int e){
if(size == data.length) //判断数组是否装满了
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Array is full.");
if(index < 0 || index > size) //索引不合格的情况
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Require index >= 0 and index <= size.");
for(int i = size - 1; i >= index ; i --)
data[i + 1] = data[i]; //数组的值右移,前面的值覆盖后面的值
data[index] = e; //e 覆盖掉原来索引的值
size ++;
}
}
7.数组中查询元素和修改元素
示例代码:Array.java
public class Array {
private int[] data;
private int size;
// 构造函数,传入数组的容量capacity构造Array
public Array(int capacity){
data = new int[capacity];
size = 0;
}
// 无参数的构造函数,默认数组的容量capacity=10
public Array(){
this(10);
}
// 获取数组的容量
public int getCapacity(){
return data.length;
}
// 获取数组中的元素个数
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
// 返回数组是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
// 向所有元素后添加一个新元素
public void addLast(int e){
add(size, e);
}
// 在所有元素前添加一个新元素
public void addFirst(int e){
add(0, e);
}
// 在index索引的位置插入一个新元素e
public void add(int index, int e){
if(size == data.length)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Array is full.");
if(index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Require index >= 0 and index <= size.");
for(int i = size - 1; i >= index ; i --)
data[i + 1] = data[i];
data[index] = e;
size ++;
}
// 获取index索引位置的元素
public int get(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Get failed. Index is illegal.");
return data[index];
}
// 修改index索引位置的元素为e
public void set(int index, int e){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Set failed. Index is illegal.");
data[index] = e;
}
@Override //覆盖父类的方法
public String toString(){
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder(); //新建字符串 res
res.append(String.format("Array: size = %d , capacity = %d\n", size, data.length)); //初始化字符串res
res.append('[');
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
res.append(data[i]); //使用索引的方式查询数据
if(i != size - 1) //不是最后一个元素就添加 ,
res.append(", ");
}
res.append(']');
return res.toString();
}
}
Main.java
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Array arr = new Array(20); //添加容量为20
for(int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i ++)
arr.addLast(i);
System.out.println(arr);
arr.add(1, 100); //在索引是 1 的位置插入 100
System.out.println(arr);
arr.addFirst(-1); //在数组首位添加 -1
System.out.println(arr);
}
}
输出:
8.数组中包含,搜索和删除元素
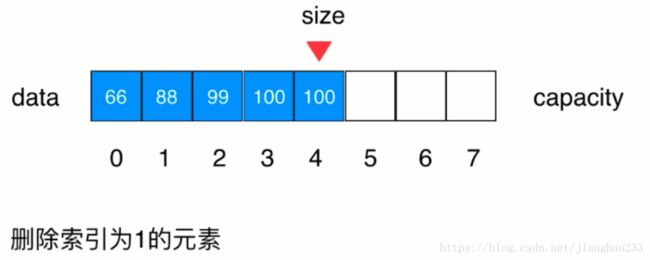
删除元素:插入元素的反过程,索引2的值 左移到 1 的值,实际是索引2赋值给索引1,覆盖掉原来的值,size 的值覆盖掉 size-1的值。size的值 -1(左移);因为要求访问数组元素 < size,故用户无法访问到 size 索引中的值(图中的100)
删除完成
示例代码:Array.java
public class Array {
private int[] data;
private int size;
// 构造函数,传入数组的容量capacity构造Array
public Array(int capacity){
data = new int[capacity];
size = 0;
}
// 无参数的构造函数,默认数组的容量capacity=10
public Array(){
this(10);
}
// 获取数组的容量
public int getCapacity(){
return data.length;
}
// 获取数组中的元素个数
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
// 返回数组是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
// 向所有元素后添加一个新元素
public void addLast(int e){
add(size, e);
}
// 在所有元素前添加一个新元素
public void addFirst(int e){
add(0, e);
}
// 在index索引的位置插入一个新元素e
public void add(int index, int e){
if(size == data.length)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Array is full.");
if(index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Require index >= 0 and index <= size.");
for(int i = size - 1; i >= index ; i --)
data[i + 1] = data[i];
data[index] = e;
size ++;
}
// 获取index索引位置的元素
public int get(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Get failed. Index is illegal.");
return data[index];
}
// 修改index索引位置的元素为e
public void set(int index, int e){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Set failed. Index is illegal.");
data[index] = e;
}
// 查找数组中是否有元素e(新增代码)
public boolean contains(int e){
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
if(data[i] == e)
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 查找数组中元素e所在的索引,如果不存在元素e,则返回-1(新增代码)
public int find(int e){
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
if(data[i] == e)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
// 从数组中删除index位置的元素, 返回删除的元素(新增代码)
public int remove(int index){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Remove failed. Index is illegal.");
int ret = data[index];
for(int i = index + 1 ; i < size ; i ++)
data[i - 1] = data[i]; //数组左移
size --;
return ret;
}
// 从数组中删除第一个元素, 返回删除的元素(新增代码)
public int removeFirst(){
return remove(0);
}
// 从数组中删除最后一个元素, 返回删除的元素(新增代码)
public int removeLast(){
return remove(size - 1);
}
// 从数组中删除元素e(新增代码)
public void removeElement(int e){
int index = find(e);
if(index != -1)
remove(index);
}
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
res.append(String.format("Array: size = %d , capacity = %d\n", size, data.length));
res.append('[');
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
res.append(data[i]);
if(i != size - 1)
res.append(", ");
}
res.append(']');
return res.toString();
}
}
Main.java
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Array arr = new Array(20);
for(int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i ++)
arr.addLast(i);
System.out.println(arr);
arr.add(1, 100);
System.out.println(arr);
arr.addFirst(-1);
System.out.println(arr);
// [-1, 0, 100, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
arr.remove(2); //删除索引为2的元素(新增代码)
System.out.println(arr);
arr.removeElement(4);//删除元素 4(新增代码)
System.out.println(arr);
arr.removeFirst();
System.out.println(arr);//删除头元素(新增代码)
}
}
输出:
8.使用泛型
泛型:使数据结构可以放置所有的“数据类型”;但只能放置类对象,不能是基本数据类型(boolean、byte、char、short、int、long、float、double),为了解决这个问题,Java 中每个基本数据类型都有对应的包装类(将本来不是类对象的变成了类对象);
基本数据类型对应的包装类[Boolean、Byte、Char、Short、Int、Long、Float、Double ] 二者之间可以互相转换
示例代码(Array.java)
public class Array { //声明为E类型的泛型数组
private E[] data; //(修改代码)
private int size;
// 构造函数,传入数组的容量capacity构造Array
public Array(int capacity){
data = (E[])new Object[capacity];//(修改代码,java 中不支持直接new出泛型数组)
//解决方式:New Object,在 Java 中任意类都是 Object 类的子类;再经过强制类型转换(E[])转换成E类型)
size = 0;
}
// 无参数的构造函数,默认数组的容量capacity=10
public Array(){
this(10);
}
// 获取数组的容量
public int getCapacity(){
return data.length;
}
// 获取数组中的元素个数
public int getSize(){
return size;
}
// 返回数组是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
// 在index索引的位置插入一个新元素e
public void add(int index, E e){ //(修改代码)
if(size == data.length)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Array is full.");
if(index < 0 || index > size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Require index >= 0 and index <= size.");
for(int i = size - 1; i >= index ; i --)
data[i + 1] = data[i];
data[index] = e;
size ++;
}
// 向所有元素后添加一个新元素
public void addLast(E e){ //(修改代码)
add(size, e);
}
// 在所有元素前添加一个新元素
public void addFirst(E e){ //(修改代码)
add(0, e);
}
// 获取index索引位置的元素
public E get(int index){ //(修改代码)
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Get failed. Index is illegal.");
return data[index];
}
// 修改index索引位置的元素为e
public void set(int index, E e){
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Set failed. Index is illegal.");
data[index] = e;
}
// 查找数组中是否有元素e
public boolean contains(E e){
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
if(data[i].equals(e)) //(修改代码,对象之间的比较用equals,值比较)
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 查找数组中元素e所在的索引,如果不存在元素e,则返回-1
public int find(E e){
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
if(data[i].equals(e)) //(修改代码,对象之间的比较用equals,值比较)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
// 从数组中删除index位置的元素, 返回删除的元素
public E remove(int index){ //(修改代码,int改为E)
if(index < 0 || index >= size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Remove failed. Index is illegal.");
E ret = data[index];
for(int i = index + 1 ; i < size ; i ++)
data[i - 1] = data[i];
size --;
data[size] = null; // loitering objects != memory leak 使数组最后引用中的值被垃圾回收
return ret;
}
// 从数组中删除第一个元素, 返回删除的元素
public E removeFirst(){ //(修改代码,int改为E)
return remove(0);
}
// 从数组中删除最后一个元素, 返回删除的元素
public E removeLast(){ //(修改代码,int改为E)
return remove(size - 1);
}
// 从数组中删除元素e
public void removeElement(E e){ //(修改代码,int改为E)
int index = find(e);
if(index != -1)
remove(index);
}
@Override
public String toString(){
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
res.append(String.format("Array: size = %d , capacity = %d\n", size, data.length));
res.append('[');
for(int i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++){
res.append(data[i]);
if(i != size - 1)
res.append(", ");
}
res.append(']');
return res.toString();
}
}
Main.java
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Array arr = new Array<>(20); //(修改代码,Array 后添加,int 类型的包装类)
for(int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i ++)
arr.addLast(i);
System.out.println(arr);
arr.add(1, 100);
System.out.println(arr);
arr.addFirst(-1);
System.out.println(arr);
// [-1, 0, 100, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
arr.remove(2);
System.out.println(arr);
arr.removeElement(4);
System.out.println(arr);
arr.removeFirst();
System.out.println(arr);
}
}
输出:与之前一样
新建 Student.java
public class Student {
private String name;
private int score;
public Student(String studentName, int studentScore){
name = studentName;
score = studentScore;
}
@Override
public String toString(){
return String.format("Student(name: %s, score: %d)", name, score);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Array arr = new Array<>();
arr.addLast(new Student("Alice", 100));
arr.addLast(new Student("Bob", 66));
arr.addLast(new Student("Charlie", 88));
System.out.println(arr);
}
}
输出: