tableview 编辑整理
UITableViewCell介绍
UITableView中显示的每一个单元都是一个UITableViewCell对象,看文档的话我们会发现其初始化函数initWithStyle:reuseIdentifier:比较特别,跟我们平时看到的UIView的初始化函数不同。这个主要是为了效率考虑,因为在tableView快速滑动的滑动的过程中,频繁的alloc对象是比较费时的,于是引入了cell的重用机制,这个也是我们在dataSource中要重点注意的地方,用好重用机制会让我们的tableView滑动起来更加流畅。
我们可以通过cell的selectionStyle属性指定cell选中时的显示风格,以及通过accessoryType来指定cell右边的显示的内容,或者直接指定accessoryView来定制右边显示的view。
系统提供的UITableView也包含了四种风格的布局,分别是:
typedef enum { UITableViewCellStyleDefault, UITableViewCellStyleValue1, UITableViewCellStyleValue2, UITableViewCellStyleSubtitle } UITableViewCellStyle;
这几种文档中都有详细描述,这儿就不在累赘。然而可以想象系统提供的只是最常用的几种类型,当系统提供的风格不符合我们需要的时候,我们就需要对cell进行定制了,有以下两种定制方式可选:
1、直接向cell的contentView上面添加subView
这是比较简单的一种的,根据布局需要我们可以在不同的位置添加subView。但是此处需要注意:所有添加的subView都最好设置为不透明的,因为如果subView是半透明的话,view图层的叠加将会花费一定的时间,这会严重影响到效率。同时如果每个cell上面添加的subView个数过多的话(通常超过3,4个),效率也会受到比较大的影响。
下面我们看一个例子:
- (UITableViewCell *)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView cellForRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath { NSArray *sections = [SvTableViewDataModal sections]; SvSectionModal *sectionModal = [sections objectAtIndex:indexPath.section]; static NSString *reuseIdetify = @"SvTableViewCell"; UITableViewCell *cell = [tableView dequeueReusableCellWithIdentifier:reuseIdetify]; if (!cell) { cell = [[UITableViewCell alloc] initWithStyle:UITableViewCellStyleDefault reuseIdentifier:reuseIdetify]; cell.accessoryType = UITableViewCellAccessoryDisclosureIndicator; cell.showsReorderControl = YES; for (int i = 0; i < 6; ++i) { UILabel *label = [[UILabel alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(100 + 15 * i, 0, 30, 20)]; label.backgroundColor = [UIColor redColor]; label.text = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%d", i]; [cell.contentView addSubview:label]; [label release]; } } cell.textLabel.backgroundColor = [UIColor clearColor]; cell.textLabel.text = [sectionModal.cityNames objectAtIndex:indexPath.row]; return cell; }
在上面这个例子中,我往每个cell中添加了6个subView,而且每个subView都是半透明(UIView默认是半透明的),这个时候滑动起来明显就可以感觉到有点颤抖,不是很流畅。当把每一个subView的opaque属性设置成YES的时候,滑动会比之前流畅一些,不过还是有点儿卡。
从UITableViewCell派生一个类
通过从UITableViewCell中派生一个类,可以更深度的定制一个cell,可以指定cell在进入edit模式的时候如何相应等等。最简单的实现方式就是将所有要绘制的内容放到一个定制的subView中,并且重载该subView的drawRect方法直接把要显示的内容绘制出来(这样可以避免subView过多导致的性能瓶颈),最后再将该subView添加到cell派生类中的contentView中即可。但是这样定制的cell需要注意在数据改变的时候,通过手动调用该subView的setNeedDisplay方法来刷新界面,这个例子可以在苹果的帮助文档中的TableViewSuite工程中找到,这儿就不举例了。
观看这两种定制cell的方法,我们会发现subView都是添加在cell的contentView上面的,而不是直接加到cell上面,这样写也是有原因的。下面我们看一下cell在正常状态下和编辑状态下的构成图:
cell在正常状态下的构成图如下:
进入编辑状态下cell的构成图如下:
通过观察上面两幅图片我们可以看出来,当cell在进入编辑状态的时候,contentView会自动的缩放来给Editing control腾出位置。这也就是说如果我们把subView添加到contentView上,如果设置autoresizingMask为更具父view自动缩放的话,cell默认的机制会帮我们处理进入编辑状态的情况。而且在tableView是Grouped样式的时候,会为cell设置一个背景色,如果我们直接添加在cell上面的话,就需要自己考虑到这个背景色的显示问题,如果添加到contentView上,则可以通过view的叠加帮助我们完成该任务。综上,subView最好还是添加到cell的contentView中。
Reordering
为了使UITableVeiew进入edit模式以后,如果该cell支持reordering的话,reordering控件就会临时的把accessaryView覆盖掉。为了显示reordering控件,我们必须将cell的showsReorderControl属性设置成YES,同时实现dataSource中的tableView:moveRowAtIndexPath:toIndexPath:方法。我们还可以同时通过实现dataSource中的 tableView:canMoveRowAtIndexPath:返回NO,来禁用某一些cell的reordering功能。
下面看苹果官方的一个reordering流程图:
上图中当tableView进入到edit模式的时候,tableView会去对当前可见的cell逐个调用dataSource的tableView:canMoveRowAtIndexPath:方法(此处官方给出的流程图有点儿问题),决定当前cell是否显示reoedering控件,当开始进入拖动cell进行拖动的时候,每滑动过一个cell的时候,会去掉用delegate的tableView:targetIndexPathForMoveFromRowAtIndexPath:toProposedIndexPath:方法,去判断当前划过的cell位置是否可以被替换,如果不行则给出建议的位置。当用户放手时本次reordering操作结束,调用dataSource中的tableView:moveRowAtIndexPath:toIndexPath:方法更新tableView对应的数据。
更新数据的小例子:
// if you want show reordering control, you must implement moveRowAtndexPath, or the reordering control will not show // when use reordering end, this method is invoke - (void)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView moveRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)sourceIndexPath toIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)destinationIndexPath { // update DataModal NSArray *sections = [SvTableViewDataModal sections]; SvSectionModal *sourceSectionModal = [sections objectAtIndex:sourceIndexPath.section]; NSString *city = [[sourceSectionModal.cityNames objectAtIndex:sourceIndexPath.row] retain]; [sourceSectionModal.cityNames removeObject:city]; [SvTableViewDataModal replaceSectionAtIndex:sourceIndexPath.section withSection:sourceSectionModal]; SvSectionModal *desinationsSectionModal= [[SvTableViewDataModal sections] objectAtIndex:destinationIndexPath.section]; [desinationsSectionModal.cityNames insertObject:city atIndex:destinationIndexPath.row]; [SvTableViewDataModal replaceSectionAtIndex:destinationIndexPath.section withSection:desinationsSectionModal]; [city release]; }
上面代码中首先拿到源cell所处的section,然后从该section对应的数据中移除,然后拿到目标section的数据,然后将源cell的数据添加到目标section中,并更新回数据模型,如果我们没有正确更新数据模型的话,显示的内容将会出现异常。
Delete & Insert
cell的delete和insert操作大部分流程都是一样的,当进入编辑模式的时候具体的显示是delete![]() 还是insert
还是insert![]() 取决与该cell的editingStyle的值,editStyle的定义如下:
取决与该cell的editingStyle的值,editStyle的定义如下:
typedef enum { UITableViewCellEditingStyleNone, UITableViewCellEditingStyleDelete, UITableViewCellEditingStyleInsert } UITableViewCellEditingStyle;
当tableView进入编辑模式以后,cell上面显示的delete还是insert除了跟cell的editStyle有关,还与 tableView的delegate的tableView:editingStyleForRowAtIndexPath:方法的返回值有关(在这里唠叨一句,其实delegate提供了很多改变cell属性的机会,如非必要,还是不要去实现这些方法,因为执行这些方法也造成一定的开销)。
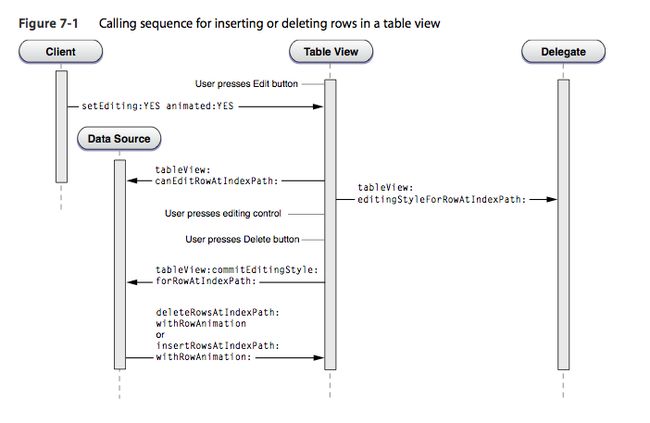
delete和insert的流程如下苹果官方文档中给出的图所示:
删除 和添加部分的代码:
#pragma mark - - (void)tableView:(UITableView *)tableView commitEditingStyle:(UITableViewCellEditingStyle)editingStyle forRowAtIndexPath:(NSIndexPath *)indexPath { NSLog(@"commit editStyle: %d", editingStyle); if (editingStyle == UITableViewCellEditingStyleDelete) { NSArray *sections = [SvTableViewDataModal sections]; SvSectionModal *sourceSectionModal = [sections objectAtIndex:indexPath.section]; [sourceSectionModal.cityNames removeObjectAtIndex:indexPath.row]; [SvTableViewDataModal replaceSectionAtIndex:indexPath.section withSection:sourceSectionModal]; [tableView deleteRowsAtIndexPaths:[NSArray arrayWithObject:indexPath] withRowAnimation:UITableViewRowAnimationRight]; } else { // do something for add it NSArray *sections = [SvTableViewDataModal sections]; SvSectionModal *sourceSectionModal = [sections objectAtIndex:indexPath.section]; [sourceSectionModal.cityNames insertObject:@"new City" atIndex:indexPath.row]; [SvTableViewDataModal replaceSectionAtIndex:indexPath.section withSection:sourceSectionModal]; [tableView insertRowsAtIndexPaths:[NSArray arrayWithObject:indexPath] withRowAnimation:UITableViewRowAnimationRight]; } }
代码中首先判断当前操作是delete操作还是insert操作,相应的更新数据,最后根据情况调用tableView的insertRowsAtIndexPaths:withRowAnimation:或者deleteRowsAtIndexPaths:withRowAnimation:方法,对tableView的视图进行更新。cell的删除和添加操作相对还是比较简单的。
Cell的Select操作
当我们在tableView中点击一个cell的时候,将会调用tableView的delegate中的tableView:didSelectRowAtIndexPath:方法。
关于tableView的cell的选中,苹果官方有以下几个建议:
1、不要使用selection来表明cell的选择状态,而应该使用accessaryView中的checkMark或者自定义accessaryView来显示选中状态。
2、当选中一个cell的时候,你应该取消前一个cell的选中。
3、如果cell选中的时候,进入下一级viewCOntroller,你应该在该级菜单从navigationStack上弹出的时候,取消该cell的选中。
这块儿再提一点,当一个cell的accessaryType为UITableViewCellAccessoryDisclosureIndicator的时候,点击该accessary区域通常会将消息继续向下传递,即跟点击cell的其他区域一样,将会掉delegate的tableView:didSelectRowAtIndexPath:方法,当时如果accessaryView为 UITableViewCellAccessoryDetailDisclosureButton的时候,点击accessaryView将会调用delegate的 tableView:accessoryButtonTappedForRowWithIndexPath:方法。
批量插入,删除,部分更新操作
UITableView提供了一个批量操作的特性,这个功能在一次进行多个row或者scetion的删除,插入,获取更新多个cell内容的时候特别好用。所有的批量操作需要包含在beginUpdates和endUpdates块中,否则会出现异常。
下面请看我demo中的一个批量操作的例子:
- (void)groupEdit:(UIBarButtonItem*)sender { [_tableView beginUpdates]; // first update the data modal [_tableView insertRowsAtIndexPaths:[NSArray arrayWithObject:[NSIndexPath indexPathForRow:0 inSection:0]] withRowAnimation:UITableViewRowAnimationTop]; [_tableView deleteSections:[NSIndexSet indexSetWithIndex:0] withRowAnimation:UITableViewRowAnimationTop]; [SvTableViewDataModal deleteSectionAtIndex:0]; SvSectionModal *section = [[SvTableViewDataModal sections] objectAtIndex:0]; [section.cityNames insertObject:@"帝都" atIndex:0]; [SvTableViewDataModal replaceSectionAtIndex:0 withSection:section]; [_tableView endUpdates]; }
上面的例子中我们可以看到先往tableView的第0个section的第0行添加一个cell,然后将第0个section删掉。按照我们程序中写的顺序,那么新添加进去的“帝都”,将不在会显示,因为包含它的整个section都已经被删除了。