Spring Retry重试组件、Guava Retry重试组件
个人看法: spring-retry更好。
软硬件环境: IntelliJ IDEA、SpringBoot2.2.4.RELEASE。
Spring的Retry组件:
提示: spring-retry的使用方式可分为注解式和编码式,注解式采用代理模式依赖于AOP,而编程式则可以直接调用方法。注解式无疑更优雅,但是使用注解式的时候,要注意避免各个AOP执行顺序差异带来的问题,在这个环节的末尾,会简单介绍如何避免这个问题。本文主要介绍的是注解式用法中基础的常用的内容;至于spring-retry的编程式用法、spring-retry的注解式用法的其它内容可详见https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-retry。
准备工作:
-
第一步: 在pom.xml中引入依赖。
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.retrygroupId> <artifactId>spring-retryartifactId> dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aopartifactId> dependency>
Spring Retry的编码式使用:
提示:编码式使用spring-retry不是主要内容,这里就简单举个例子就行了。
public Object retryCoding() throws Throwable {
/*
* spring-retry1.3.x版本开始提供建造者模式支持了,可
* 详见https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-retry
*/
RetryTemplate template = new RetryTemplate();
// 设置重试策略
SimpleRetryPolicy simpleRetryPolicy = new SimpleRetryPolicy();
simpleRetryPolicy.setMaxAttempts(5);
template.setRetryPolicy(simpleRetryPolicy);
// 执行
Object result = template.execute(
new RetryCallback<Object, Throwable>() {
@Override
public Object doWithRetry(RetryContext context) throws Throwable {
// 第一次请求,不算重试, 所以第一次请求时,context.getRetryCount()值为0
throw new RuntimeException("第" + (context.getRetryCount() + 1) + "次调用失败!");
}
},
new RecoveryCallback<Object>() {
@Override
public Object recover(RetryContext context) throws Exception {
Throwable lastThrowable = context.getLastThrowable();
return "走recover逻辑了! \t异常类是" + lastThrowable.getClass().getName()
+ "\t异常信息是" + lastThrowable.getMessage();
}
});
System.out.println(result);
return result;
}
注:1.3.x开始,spring-retry提供建造者模式支持RetryTemplate的创建了。
Spring Retry的注解式使用:
- @Retryable默认项: 默认最多请求3次,默认重试时延迟1000ms再进行请求。
- 注:重试两次, 加上本身那一次一起3次。
- 注:默认在所有异常的情况下,都进行重试;若重试的这几次都没有成功,都出现了异常,那么最终抛出的是最后一次重试时出现的异常。
- 示例:
- 被调用的方法:
private int times = 0; /** * - 默认最多请求3次(注: 重试两次, 加上本身那一次一起3次) * * - 默认在所有异常的情况下,都进行重试; 若重试的这几次都没有成功,都出现了异常, * 那么最终抛出的是最后一次重试时出现的异常 */ @Retryable public String methodOne() { times++; int i = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(10); if (i < 9) { if (times == 3) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("最后一次重试时, 发生了IllegalArgumentException异常"); } throw new RuntimeException("times=" + times + ", 当前i的值为" + i); } return "在第【" + times + "】次调用时, 调通了!"; } - 测试方法:
- 程序输出:

- 被调用的方法:
- @Retryable的include与exclude: 默认最多请求3次,默认重试时延迟1000ms再进行请求。
- 在尝试次数内:
- 情况一:如果抛出的是include里面的异常(或其子类异常),那么仍然会继续重试。
- 情况二:如果抛出的是include范围外的异常(或其子类异常) 或者 抛出的是exclude里面的异常(或其子类异常), 那么不再继续重试,直接抛出异常。
注:若抛出的异常即是include里指定的异常的子类,又是exclude里指定的异常的子类,那么判断当前异常是按include走,还是按exclude走,需要根据【更短路径原则】。如下面的methodTwo方法所示, RuntimeException 是 IllegalArgumentException的超类,IllegalArgumentException 又是 NumberFormatException的超类,此时因为IllegalArgumentException离NumberFormatException“路径更短”,所以抛出的NumberFormatException按照IllegalArgumentException算,走include。
- 示例:
- 被调用的方法:
private int times = 0; /** * - 在尝试次数内, * 1. 如果抛出的是include里面的异常(或其子类异常),那么仍然会继续重试 * 2. 如果抛出的是include范围外的异常(或其子类异常) 或者 抛出的是 * exclude里面的异常(或其子类异常), 那么不再继续重试,直接抛出异常 * * 注意: 若抛出的异常即是include里指定的异常的子类,又是exclude里指定的异常的子类,那么 * 判断当前异常是按include走,还是按exclude走,需要根据【更短路径原则】。 * 如本例所示, RuntimeException 是 IllegalArgumentException的超类, * IllegalArgumentException 又是 NumberFormatException的超类, * 此时因为IllegalArgumentException离NumberFormatException“路径更短”, * 所以抛出的NumberFormatException按照IllegalArgumentException算,走include。 */ @Retryable(include = {IllegalArgumentException.class}, exclude = {RuntimeException.class}) public String methodTwo() { times++; /// if (times == 1) { /// throw new IllegalArgumentException("times=" + times + ", 发生的异常是IllegalArgumentException"); /// } /// if (times == 2) { /// throw new RuntimeException("times=" + times + ", 发生的异常是RuntimeException"); /// } if (times == 1) { throw new NumberFormatException("times=" + times + ", 发生的异常是IllegalArgumentException的子类"); } if (times == 2) { throw new ArithmeticException("times=" + times + ", 发生的异常是RuntimeException的子类"); } return "在第【" + times + "】次调用时, 调通了!"; } /** * - 在尝试次数内, * 如果抛出的是exclude里面的异常(或其子类异常),那么不再继续重试,直接抛出异常 * 如果抛出的是include里面的异常(或其子类异常),那么仍然会继续重试 */ @Retryable(include = {RuntimeException.class}, exclude = {IllegalArgumentException.class}) public String methodTwoAlpha() { times++; if (times == 1) { throw new ArithmeticException("times=" + times + ", 发生的异常是RuntimeException的子类"); } if (times == 2) { throw new NumberFormatException("times=" + times + ", 发生的异常是IllegalArgumentException的子类"); } return "在第【" + times + "】次调用时, 调通了!"; } /** * - 在尝试次数内, * 如果抛出的是include范围外的异常(或其子类异常),那么不再继续重试,直接抛出异常 * 如果抛出的是include里面的异常(或其子类异常),那么仍然会继续重试 */ @Retryable(include = {IllegalArgumentException.class}) public String methodTwoBeta() { times++; if (times == 1) { throw new NumberFormatException("times=" + times + ", 发生的异常是IllegalArgumentException的子类"); } if (times == 2) { throw new ArithmeticException("times=" + times + ", 发生的异常是RuntimeException的子类"); } return "在第【" + times + "】次调用时, 调通了!"; } - 测试方法:
- 三个测试方法对应的输出:
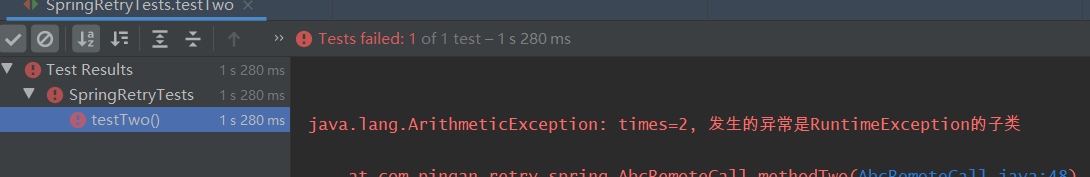

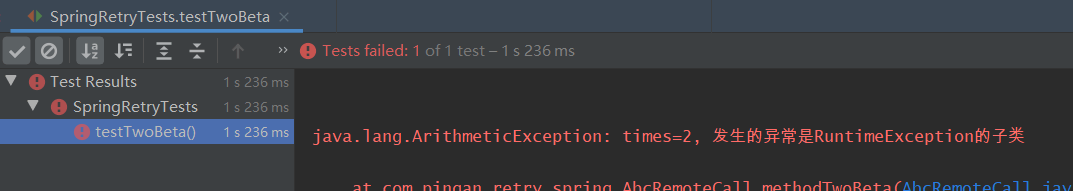
- 被调用的方法:
- 在尝试次数内:
- @Retryable的maxAttempts: maxAttempts用于指定最大尝试次数, 默认值为3。
- 连本身那一次也会被算在内(若值为5, 那么最多重试4次, 算上本身那一次5次)。
- 示例:
- 被调用的方法:
private int times = 0; /** * maxAttempts指定最大尝试次数, 默认值为3. * 注:连本身那一次也会被算在内(若值为5, 那么最多重试4次, 算上本身那一次5次) */ @Retryable(maxAttempts = 5) public String methodThere() { times++; if (times < 5) { throw new RuntimeException("times=" + times + ", 发生的异常是RuntimeException"); } return "在第【" + times + "】次调用时, 调通了!"; } - 测试方法:
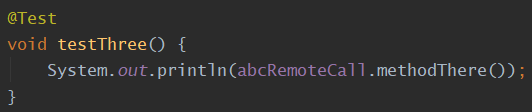
- 程序输出:
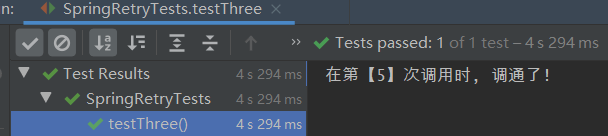
- 被调用的方法:
- @Retryable与@Recover搭配:
- 相关要点一: 我们不妨称被@Retryable标记的方法为目标方法,称被@Recover标记的方法为处理方法。那么处理方法和目标方法必须同时满足:
- 处于同一个类下。
- 两者的参数类型需要匹配 或 处理方法的参数可以多一个异常接收类(这一异常接收类必须放在第一个参数的位置)。
注:两者的参数类型匹配即可,形参名可以一样可以不一样。 - 返回值类型需要保持一致(或处理方法的返回值类型是目标方法的返回值类型的超类)。
- 相关要点二: 目标方法在进行完毕retry后,如果仍然抛出异常, 那么会去定位处理方法, 走处理方法的逻辑,定位处理方法的原则是:在同一个类下,寻找和目标方法 具有相同参数类型(P.S.可能会再参数列表首位多一个异常类参数)、相同返回值类型的标记有Recover的方法。
注:如果存在两个目标方法,他们的参数类型、返回值类型都一样,这时就需要主动指定对应的处理方法了,如:@Retryable(recover = “service1Recover”)。@Retryable注解的recover 属性,在spring-retry1.3.x版本才开始提供。
注:如果是使用的1.3.x+版本的spring-retry,推荐直接使用@Retryable(recover = "recoverMethodName")指定同类当中的处理方法的方法名。 - 示例:
- 被调用的方法:
import org.springframework.retry.annotation.Recover; import org.springframework.retry.annotation.Retryable; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /** * 目标方法:被@Retryable标记的方法 * 处理方法:被@Recover标记的方法 * * 处理方法 和 目标方法 必须满足: * 1. 处于同一个类下 * 2. 两者的参数需要保持一致 或 处理方法的参数可以多一个异常接收类(这一异常接收类必须放在第一个参数的位置) * 注:保持一致指的是参数类型保持一致,形参名可以一样可以不一样 * 3. 返回值类型需要保持一致 (或处理方法的返回值类型是目标方法的返回值类型的超类 ) * * 目标方法在进行完毕retry后,如果仍然抛出异常, 那么会去定位处理方法, 走处理方法的逻辑,定位处理方法的原则是: * - 在同一个类下,寻找和目标方法 具有 * 相同参数类型(P.S.可能会再参数列表首位多一个异常类参数)、 * 相同返回值类型 * 的标记有Recover的方法 * - 如果存在两个目标方法,他们的参数类型、返回值类型都一样, * 这时就需要主动指定对应的处理方法了, * 如:@Retryable(recover = "service1Recover") * * @author JustryDeng * @date 2020/2/25 21:40:11 */ @Component public class QwerRemoteCall { private int times = 0; /// --------------------------------------------------------- @Recover基本测试 @Retryable public String methodFour(Integer a, String b) { times++; throw new RuntimeException("times=" + times + ", 发生的异常是RuntimeException"); } @Recover private String justryDeng(Throwable th, Integer a, String b) { return "a=" + a + ", b=" + b + "\t" + "异常类是:" + th.getClass().getName() + ", 异常信息是:" + th.getMessage(); } /// 如果在@Retryable中指明了异常, 那么在@Recover中可以明确的指明是哪一种异常 /// @Retryable(RemoteAccessException.class) /// public void service() { /// // ... do something /// } /// /// @Recover /// public void recover(RemoteAccessException e) { /// // ... panic /// } /// --------------------------------------------------------- @Retryable指定对应的@Recover方法 /// 特别注意: @Retryable注解的recover属性, 在spring-retry的较高版本中才得以支持, /// 在本人使用的1.2.5.RELEASE版本中还暂不支持 /// @Retryable(recover = "service1Recover", value = RemoteAccessException.class) /// public void service1(String str1, String str2) { /// // ... do something /// } /// /// @Retryable(recover = "service2Recover", value = RemoteAccessException.class) /// public void service2(String str1, String str2) { /// // ... do something /// } /// /// @Recover /// public void service1Recover(RemoteAccessException e, String str1, String str2) { /// // ... error handling making use of original args if required /// } /// /// @Recover /// public void service2Recover(RemoteAccessException e, String str1, String str2) { /// // ... error handling making use of original args if required /// } } - 测试方法:
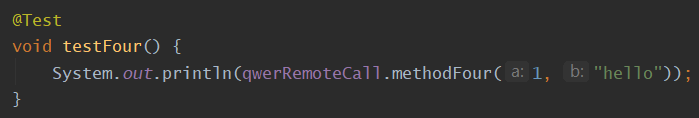
- 程序输出:

- 被调用的方法:
- 相关要点一: 我们不妨称被@Retryable标记的方法为目标方法,称被@Recover标记的方法为处理方法。那么处理方法和目标方法必须同时满足:
- @Retryable的backoff: @Retryable注解的backoff属性,可用于指定重试时的退避策略。
- 相关要点:
- @Retryable 或 @Retryable(backoff = @Backoff()), 那么默认延迟 1000ms
后重试。 - @Backoff的delay属性: 延迟多久后,再进行重试。
- 如果不想延迟, 那么需要指定@Backoff的value和delay同时为0。
- delay与multiplier搭配使用,
延迟时间 = delay * (multiplier ^ (n - 1)),其中n为第几次重试, n >= 1, 这里^为次方。
注:第二次请求,才算第一次重试。
- @Retryable 或 @Retryable(backoff = @Backoff()), 那么默认延迟 1000ms
- 示例:
- 被调用的方法:
private int times = 0; DateTimeFormatter dateTimeFormatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("HH:mm:ss"); /** * Backoff用于指定 重试时的退避策略 * - @Retryable 或 @Retryable(backoff = @Backoff()), 那么默认延迟 1000ms后重试 * 注:第一次请求时,是马上进行的,是不会延迟的 * * 效果如: * times=1, 时间是12:02:04 * times=2, 时间是12:02:05 * times=3, 时间是12:02:06 */ @Retryable(backoff = @Backoff()) public String methodFive() { times++; System.err.println("times=" + times + ", 时间是" + dateTimeFormatter.format(LocalTime.now())); throw new RuntimeException("times=" + times + ", 发生的异常是RuntimeException"); } /** * - delay: 延迟多久后,再进行重试。 * 注:第一次请求时,是马上进行的,是不会延迟的 * * 效果如: * times=1, 时间是11:46:36 * times=2, 时间是11:46:41 * times=3, 时间是11:46:46 */ @Retryable(backoff = @Backoff(delay = 5000)) public String methodFiveAlpha() { times++; System.err.println("times=" + times + ", 时间是" + dateTimeFormatter.format(LocalTime.now())); throw new RuntimeException("times=" + times + ", 发生的异常是RuntimeException"); } /** * 如果不想延迟, 那么需要指定value和delay同时为0 * 注:原因可详见javadoc 或 源码 * * 效果如: * times=1, 时间是12:05:44 * times=2, 时间是12:05:44 * times=3, 时间是12:05:44 */ @Retryable(backoff = @Backoff(value = 0, delay = 0)) public String methodFiveBeta() { times++; System.err.println("times=" + times + ", 时间是" + dateTimeFormatter.format(LocalTime.now())); throw new RuntimeException("times=" + times + ", 发生的异常是RuntimeException"); } /** * - delay: 延迟多久后,再进行重试。 * - multiplier: 乘数因子 * * 延迟时间 = delay * (multiplier ^ (n - 1)) , 其中n为第几次重试, n >= 1, 这里 ^ 为次方 * * 注:第一次请求时,是马上进行的,是不会延迟的 * 注:第二次请求时对应第一次重试 * * 效果如: * times=1, 时间是12:09:14 * times=2, 时间是12:09:17 * times=3, 时间是12:09:23 * times=4, 时间是12:09:35 * times=5, 时间是12:09:59 * 可知,延迟时间越来越大,分别是: 3 6 12 24 */ @Retryable(maxAttempts = 5, backoff = @Backoff(delay = 3000, multiplier = 2)) public String methodFiveGamma() { times++; System.err.println("times=" + times + ", 时间是" + dateTimeFormatter.format(LocalTime.now())); throw new RuntimeException("times=" + times + ", 发生的异常是RuntimeException"); } - 测试方法:

- 四个测试方法分别输出:
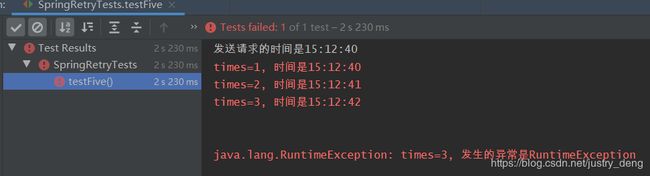
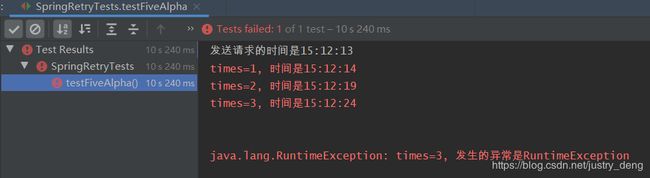
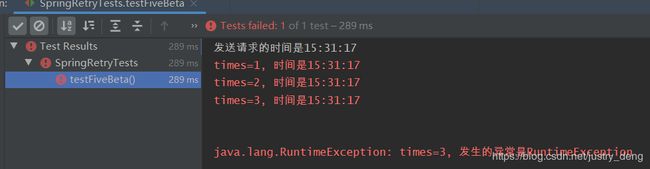

- 被调用的方法:
- 相关要点:
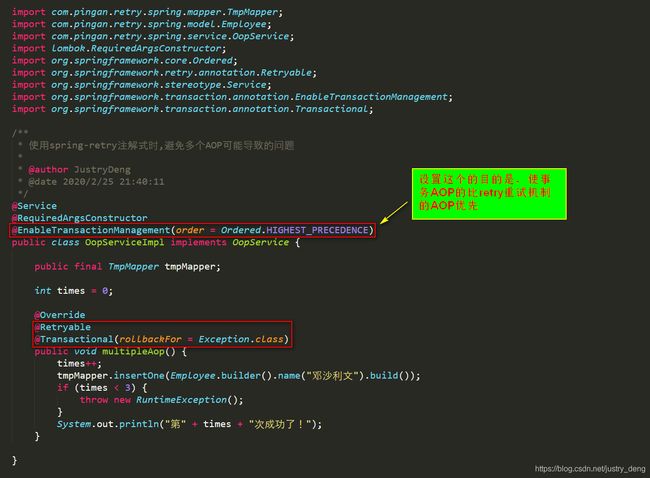
使用spring retry注解式时,避免多个AOP代理导致可能出现的问题:
-
情景说明: 就像@Transactional与@CacheEvict标注在同一个方法上、@Transactional与synchronized标注在同一个方法上一样,在并发情况下,会出现问题(会出现什么问题、怎么解决出现的问题可详见《程序员成长笔记(第二部)》相关章节)。如果@Transactional和@Retryable同时标注在了同一个方法上,那是不是也会出问题呢,从原理分析,肯定是会出现问题的,如下面的错误示例。
-
错误示例:
-
正确示例(避免方式):
将重试机制那部分代码,单独放在一个类里面,避免多个AOP作用于同一个切点。
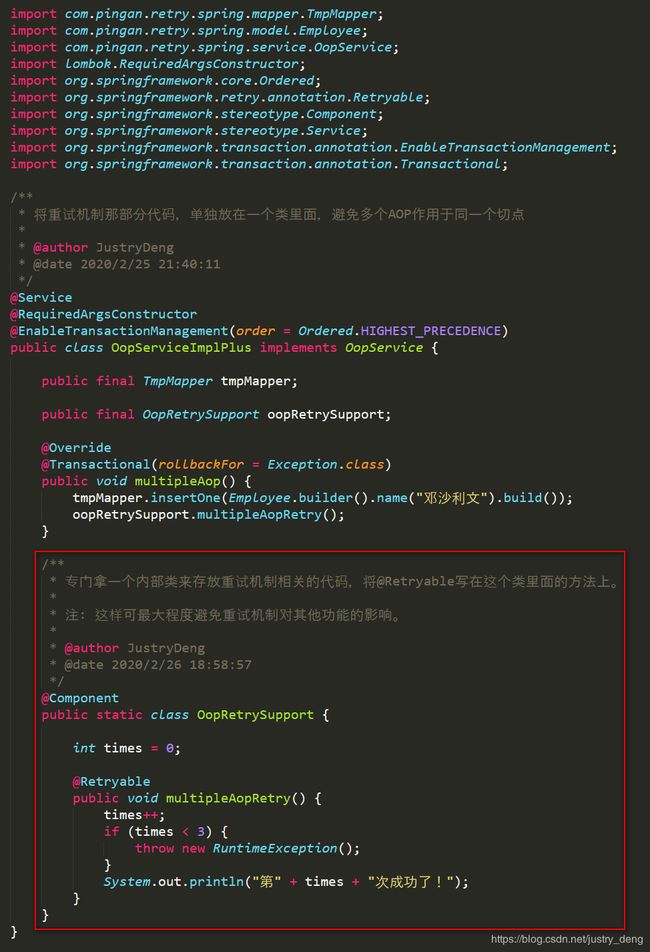 这个时候,哪怕仍然通过@EnableTransactionManagement(order = Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)把事务的AOP优先级调到了最高,也不会有什么影响了,也不会出现上面错误示例中多条数据的问题了。
这个时候,哪怕仍然通过@EnableTransactionManagement(order = Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)把事务的AOP优先级调到了最高,也不会有什么影响了,也不会出现上面错误示例中多条数据的问题了。
注:避免方式较多(如主动控制各个AOP直接的执行顺序、避免多个AOP作用于同一个切点等),推荐使用避免多个AOP作用于同一个切点。
Guava的Retry组件:
准备工作:在pom.xml中引入依赖。
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.rholdergroupId>
<artifactId>guava-retryingartifactId>
<version>2.0.0version>
dependency>
Guava Retry的使用:
比起Spring Retry的使用, Guava Retry的使用方式相对简单,这里仅给出一个简单的使用示例,更多细节可详见https://github.com/rholder/guava-retrying。
简单使用示例:
import com.github.rholder.retry.RetryException;
import com.github.rholder.retry.Retryer;
import com.github.rholder.retry.RetryerBuilder;
import com.github.rholder.retry.StopStrategies;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadLocalRandom;
import java.util.zip.DataFormatException;
/**
* Guava Retry简单使用示例
*
* @author JustryDeng
* @date 2020/2/25 21:40:11
*/
public class XyzRemoteCall {
/**
* guava retry组件 使用测试
*
* 提示:泛型 对应 要返回的数据的类型。
*/
public static void jd() {
// 创建callable, 在call()方法里面编写相关业务逻辑
Callable<Object[]> callable = new Callable<Object[]>() {
int times = 0;
@Override
public Object[] call() throws Exception {
// business logic
times++;
if (times == 1) {
throw new RuntimeException();
}
if (times == 2) {
throw new Exception();
}
// 随机一个数[origin, bound)
int randomNum = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(1, 5);
if (randomNum == 1) {
throw new DataFormatException("call()抛出了检查异常DataFormatException");
} else if (randomNum == 2) {
throw new IOException("call()抛出了检查异常IOException");
} else if (randomNum == 3) {
throw new RuntimeException("call()抛出了运行时异常RuntimeException");
}
return new Object[]{"邓沙利文", "亨得帅", "邓二洋", "JustryDeng"};
}
};
// 创建重试器
Retryer<Object[]> retryer = RetryerBuilder.[]>newBuilder()
/*
* 指定什么条件下触发重试
*
* 注:这里,只要callable中的call方法抛出的异常是Throwable或者
* 是Throwable的子类,那么这里都成立,都会进行重试。
*/
.retryIfExceptionOfType(Throwable.class)
/// .retryIfException()
/// .retryIfRuntimeException()
/// .retryIfExceptionOfType(@Nonnull Class exceptionClass)
/// .retryIfException(@Nonnull Predicate exceptionPredicate)
/// .retryIfResult(@Nonnull Predicate resultPredicate)
// 设置两次重试之间的阻塞策略(如: 设置线程sleep、设置自旋锁等等)
///.withBlockStrategy()
// 设置监听器 (这个监听器可用于监听每次请求的结果信息, 并作相应的逻辑处理。 如: 统计、预警等等)
///.withRetryListener()
// 设置延时策略, 每次重试前,都要延时一段时间,然后再发起请求。(第一次请求,是不会被延时的)
///.withWaitStrategy()
// 设置停止重试的策略(如:这里设置的是三次请求后, 不再重试)
.withStopStrategy(StopStrategies.stopAfterAttempt(3))
.build();
try {
Object[] result = retryer.call(callable);
System.err.println(Arrays.toString(result));
/*
* call()方法抛出的异常会被封装到RetryException或ExecutionException中, 进行抛出
* 所以在这里,可以通过 e.getCause()获取到call()方法实际抛出的异常
*/
} catch (RetryException|ExecutionException e) {
System.err.println("call()方法抛出的异常, 实际是" + e.getCause());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Spring Retry重试组件、Guava Retry重试组件简单梳理完毕 !
^_^ 如有不当之处,欢迎指正
^_^ 参考连接
https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-retry
https://github.com/rholder/guava-retrying
^_^ 测试代码托管连接
https://github.com/JustryDeng/CommonRepository…
^_^ 本文已经被收录进《程序员成长笔记(七)》,笔者JustryDeng