全面拆解和构建5G物联网-23:LoRa终端--射频芯片SX1261 SX1262的收发数据的全寄存器设置
本文详细介绍了SX1261/2收发数据包的整个流程以及所有相关寄存器的设置。
一. 射频芯片功能模式以及与MCU之间的操作接口
1. 功能模块
![]()
2. 操作接口
![]()
在上述电路中,MCU通过SPI接口访问LoRa芯片内部的寄存器,也是通过SPI接口操作芯片内部的FIFO,用于收发数据包。
不同于那些把所有操作都直接基于“寄存器地址空间”访问的芯片,LoRa视频芯片暴露给MCU的是:基于“命令”的访问。有点类似所谓的AT命令的格式。
因此MCU是通过“命令”的方式配置、管理、控制LoRa芯片的工作方式。
同时MCU也是通过“命令”的方式,从LoRa内部data buffer中读取数据,向LoRa内部data buffer中写入数据。
SX1261/2通过GPIO busy管脚向MCU指示,当前是否正在执行某一个命令,命令的执行是否完成,以允许或禁止执行下一个命令。
MCU可以通过置位NSS复位管脚,强制SX1261/2终止正在执行的命令。
3.命令格式:
![]()
二、数据帧的发送过程
0. power on and come into standby mode.
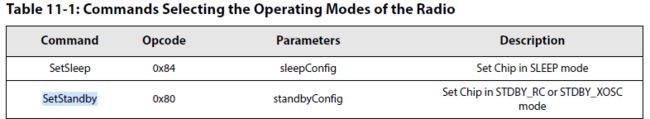
1.If not in STDBY_RC mode, then go to this mode with the command SetStandby(...):切换到standby 模式
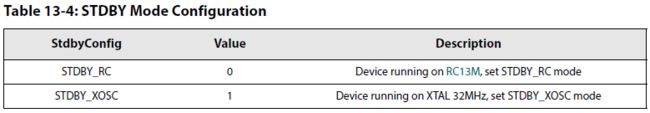
standby有两种模式,一种是RC13M工作时钟, 有VBAT电池管脚供电; 另一种是XTAL_32M工作时钟,有VDD管脚供电。
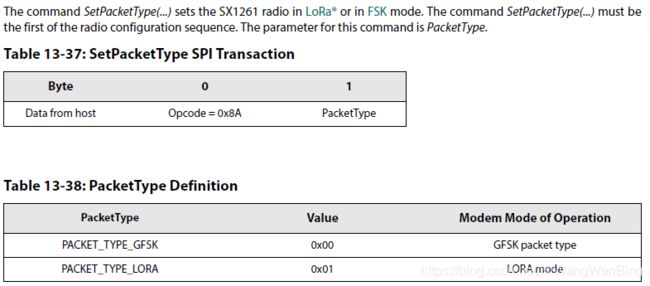
2.Define the protocol (LoRa orFSK) with the command SetPacketType(...):设置调制解调器的类型
3.Define the RF frequency with the command SetRfFrequency(...):设置过载频频率的中心频点
![]()
该公式的含义是:
FXTAL:静态震荡器的频率,在这里是32M = 32 * 10^6.
2^25是对静态震荡器32M进行分频的分频因子,相除以后得到的结果,表明每个二进制比特所代表的频率粒度,或者载波频率设置的步长。
RF_frefq:是期望的频率,比如433M或470M或其他数值。
RF_requency:期望的载波频率所对应的寄存器的值。
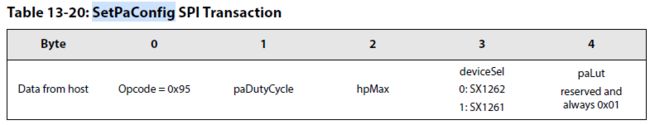
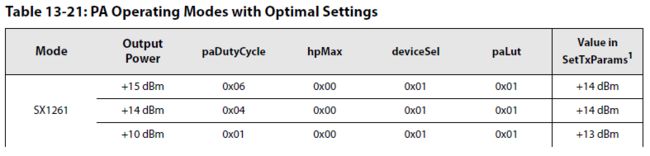
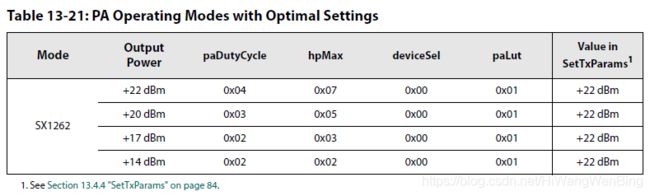
4.Define the Power Amplifier configuration with the command SetPaConfig(...):设置功率放大器功率放大倍数
设置Device最大的输出功率,很显然,SX1261和SX1262的最大功率是不一样的。
5.Define output power and ramping time with the command SetTxParams(...):设置功率放大的参数
定义的是某次发送数据包时的功率。
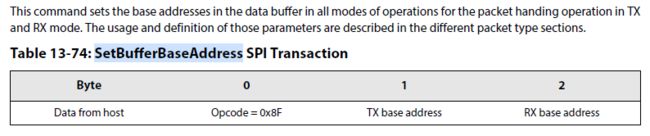
6.Define where the data payload will be stored with the command SetBufferBaseAddress(...):设置发送Bufffer的起始地址
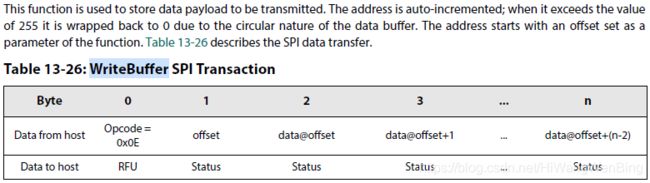
7.Send the payload to the data buffer with the command WriteBuffer(...):把需要发送payload数据写到buffer中。
把数据写到基地址+offset
注意:
写入buffer中存放的数据只包括payload净荷,不包括帧头信息:前导,同步字,长度和地址。发送时,这些信息存放在寄存器中,有自动添加到发送的物理帧中。无论是变长帧还是股东长度帧,长度域不在净荷中。
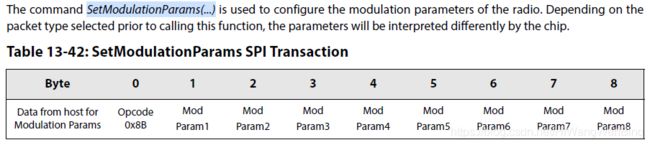
8.Define the modulation parameter according to the chosen protocol with the command SetModulationParams(...):设置调制器的参数
这里分FSK和LoRa调制解调器参数,参见如下:
(1)设置FSK调制器参数
- 设置波特率
![]()
- 设置带宽
![]()
![]()
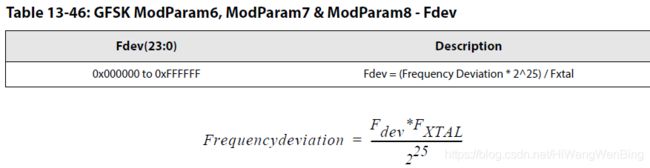
- 设置FDA
FSK上述三个参数的制约关系:
![]()
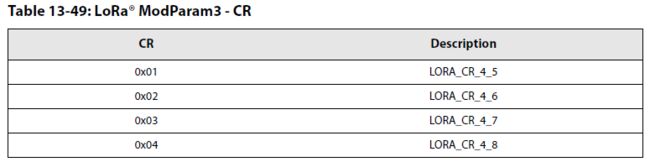
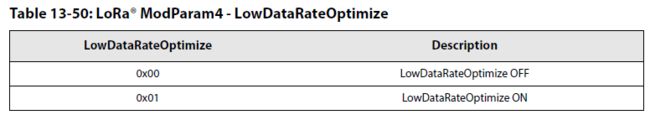
(2)设置LoRa调制解调器的参数
- 扩频因子设置
- 基带信号的带宽设置(必须大于扩频后最小带宽的要求)
- FEC纠错码长度设置
- 低速率优化功能开关设置
9. Define the frame format to be used with the command SetPacketParams(...):定义物理层帧的格式,主要是帧头信息,前导,同步字,长度和地址。数据净荷已经在第7步准备好了。
![]()
(1)设置FSK物理帧参数:
- 发送的物理层帧的前导字节的长度:(每个字节的前导的模式为0x55,即0x0101 01010)
![]()
- 接收的物理帧的前导字节的长度:
![]()
- 同步字的长度:
![]()
同步字的模式,可以通过WriteReg来设定
- 节点的地址控制开关:
![]()
节点地址是用来过滤的,因此该参数用于接受一侧的过滤,主要用于点对多点的通信模式,不能用于点对点通信。
在这种模式下,每个节点只能接收地址域与自己一致的数据包。
![]()
- 允许接受的广播地址:
- 设置数据包的长度类型:定长或变长,如果接收和发送方采用定长模式,则在数据包中就不包含长度信息,节省了数据量。
![]()
- payload的长度:发送payload长度,以及接收的最大数据的payload的长度。
![]()
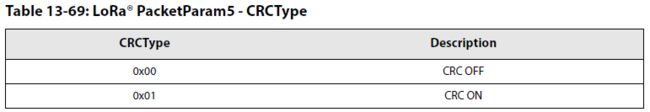
- CRC类型
![]()
- 白噪声编解码使能:
![]()
(2)LoRa物理层帧的设置
- 前导位长度设置
- payload长度特性设置:可变还是固定
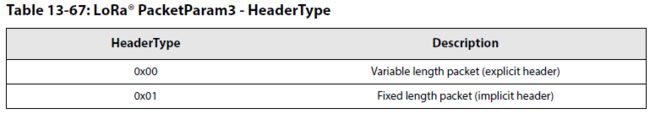
- 固定payload长度指定(在headerType=01时才有意义)
- CRC使能设置
- IQ反转设置(通常情况下,不需要更改此设置)
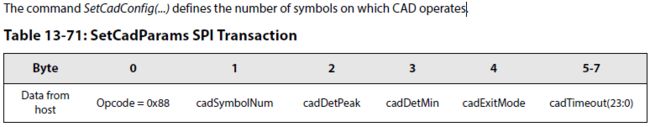
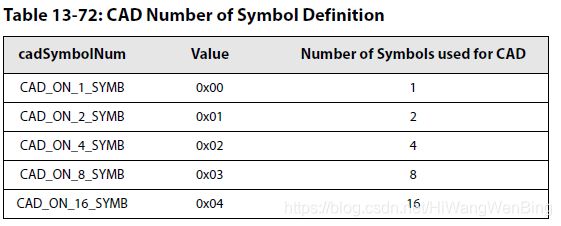
(3)CAD参数设置
10.Configure DIO and IRQ: use the command SetDioIrqParams(...) to select TxDone IRQ and map this IRQ to a DIO (DIO1, DIO2 or DIO3): 设置哪个IO哪些IO管脚用于发送中断。
Irq:定义使能哪些中断,如下是支持的中断源
DIO1-3:用于设置DIO1-3管脚是否要向外请求中断。
11.Define Sync Word value: use the command WriteReg(...) to write the value of the register via direct register access:定义双方的物理层帧的同步字。
![]()
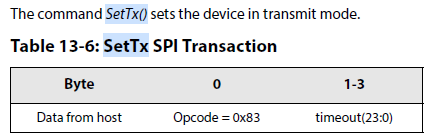
12.Set the circuit in transmitter mode to start transmission with the command SetTx(). Use the parameter to enable Timeout:启动发送
13.Wait for the IRQ TxDone or Timeout: once the packet has been sent the chip goes automatically to STDBY_RC mode:MCU等待发送的完成或超时。一旦发送数据完成,切换芯片的状态,进入standby模式。
14.Clear the IRQ TxDone flag:清除发送中断。
三、数据帧的接收过程
接收的过程与发送的过程大体相同
0. power on and come into standby mode:重启进入standby模式
1.If not in STDBY_RC mode, then set the circuit in this mode with the command SetStandby():进入standby模式
2.Define the protocol (LoRa® or FSK) with the command SetPacketType(...):设置调制解调器的类型
3.Define the RF frequency with the command SetRfFrequency(...):设置过载频频率的中心频点
4.Define where the data will be stored inside the data buffer in Rx with the command SetBufferBaseAddress(...):设置数据用于接收数据净荷的其实内存的地址。
5.Define the modulation parameter according to the chosen protocol with the command SetModulationParams(...):定义解调器的参数。
6.Define the frame format to be used with the command SetPacketParams(...):定义允许接收的合法的数据帧的格式,这也要是帧头信息:,前导,同步字,长度和地址。
这里还包括广播地址和自身的地址信息。地址信息用于指明,数据帧是否属于自己,如果地址与自动的地址不一致,需要丢掉该物理层的帧。
7.Configure DIO and irq: use the command SetDioIrqParams(...) to select the IRQ RxDone and map this IRQ to a DIO (DIO1 or DIO2 or DIO3), set IRQ Timeout as well.:定义用于接收终端的IO管脚信息。
8.Define Sync Word value: use the command WriteReg(...) to write the value of the register via direct register access:定义物理层帧的同步字。
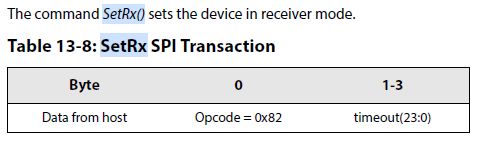
9.Set the circuit in reception mode: use the command SetRx(). Set the parameter to enable timeout or continuous mode:进入接收模式,启动数据的接收。
10.Wait for IRQ RxDone or Timeout: the chip will stay in Rx and look for a new packet if the continuous mode is selected
otherwise it will goes to STDBY_RC mode.
等待有效数据的接收,
如果不是连续接收模式,自动关闭接收,进入standby模式,
如果是 连续接收模式,允许呆在Rx模式,继续接收数据包,这种模式就需要Mux一边读数据,射频芯片一边收数据。
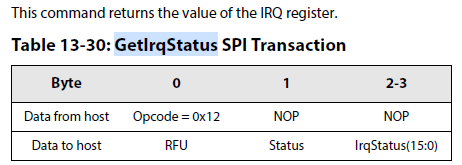
11.In case of the IRQ RxDone, check the status to ensure CRC is correct: use the command GetIrqStatus():
Note:
The IRQ RxDone means that a packet has been received but the CRC could be wrong: the user must check the CRC before
validating the packet.
如果RxDone中断,还需要检查数据包的CRC是否正确,MCU以决定,是否需要接纳该数据包 。
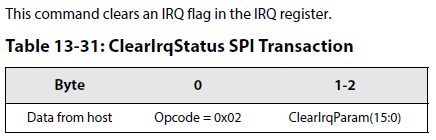
12.Clear IRQ flag RxDone or Timeout: use the command ClearIrqStatus(). In case of a valid packet (CRC OK), get the packet length and address of the first byte of the received payload by using the command GetRxBufferStatus(...):清除接收中断,获取接收到的数据包的长度。
13.In case of a valid packet (CRC OK), start reading the packet:如果CRC OK, 则从Buffer中读取数据包。