数据结构与算法C++之图的遍历(深度优先遍历)
图的遍历:深度优先遍历
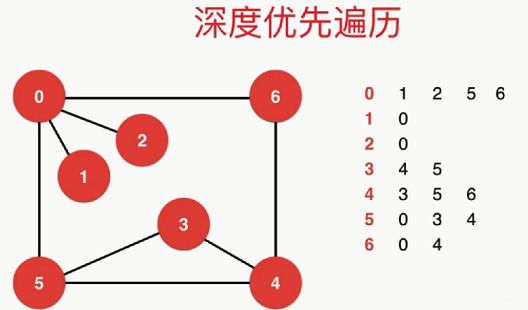
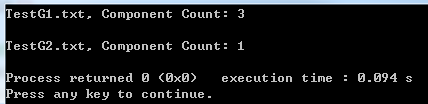
(1)首先遍历节点0,与0连接的节点有1,2,5,6,那么先遍历节点1,下面再看与节点1相连的是节点0,节点0已经遍历过了,那么继续遍历节点2,与2连接的节点是0,节点0已经遍历过了,那么开始遍历节点5,

(2)与5连接的节点有0,3,4,节点0已经遍历过了,那么开始遍历节点3,3没有被遍历过,记录下3,与节点3连接的节点是4和5,首先4没有被遍历过,记录下4,继续查看与4连接的节点3,5,6,前两个节点3和5都遍历过了,只有节点6没有被遍历过,把6记录下来,

(3)与节点6连接的有节点0和4,这两个都遍历过了,那么就退回到节点4,与节点4连接的三个节点都遍历过了,就继续退回到节点3,查看节点5,节点5已经遍历过了,而且与5连接的0,3,4已经遍历过了,退回到节点0,继续查看节点6,与6连接的节点0和4都遍历过了,遍历结束
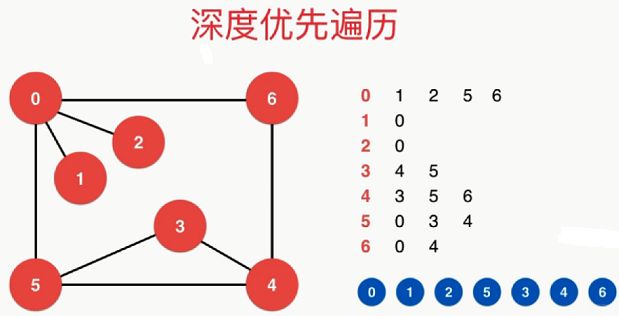
使用图遍历可以求连通分量,如下图,一共有3个连通分量
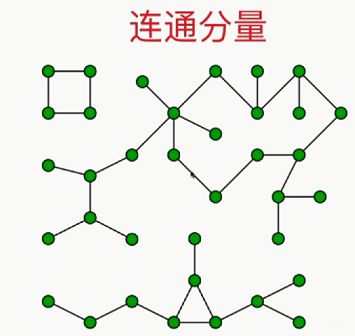
下面是程序实现
#include 深度优先遍历Component.h定义为
#include "SparseGraph.h"定义为
#include "DenseGraph.h"定义为
#include "ReadGraph.h"定义为
#include testG1.txt
第一行第一个13表示有13个节点,第二个13表示13条边
第二行到最后一行是13条边
13 13
0 5
4 3
0 1
9 12
6 4
5 4
0 2
11 12
9 10
0 6
7 8
9 11
5 3
testG2.txt
第一行第一个13表示有13个节点,第二个13表示13条边
第二行到最后一行是13条边
7 8
0 1
0 2
0 5
0 6
3 4
3 5
4 5
4 6