postgreSql的监控记录表里多条不同时间的数据,只取最新的数据,并分组统计
目录
- 1. 背景
- 2. 需求:
- 3. 构建数据
- 3.1 创建表结构:
- 3.2 造数据
- 4. 需求实现
- 4.1 需求1的SQL语句
- 4.2 需求2的SQL语句
1. 背景
比如气象台的气温监控,每半小时上报一条数据,有很多个地方的气温监控,这样数据表里就会有很多地方的不同时间的气温数据
2. 需求:
- 每次查询只查最新的气温数据
- 按照不同的温度区间来分组查出,比如:高温有多少地方,正常有多少地方,低温有多少地方
3. 构建数据
3.1 创建表结构:
-- DROP TABLE public.t_temperature
CREATE TABLE public.t_temperature (
id int4 NOT NULL GENERATED ALWAYS AS IDENTITY,
place_name varchar NOT NULL,
value float8 NOT NULL,
up_time timestamp NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT t_temperature_pk PRIMARY KEY (id)
);
-- Permissions
ALTER TABLE public.t_temperature OWNER TO postgres;
GRANT ALL ON TABLE public.t_temperature TO postgres;
3.2 造数据
INSERT INTO public.t_temperature (place_name,value,up_time) VALUES
('广州',35,'2020-07-12 15:00:00.000')
,('广州',35.9,'2020-07-12 15:30:00.000')
,('深圳',30,'2020-07-12 15:30:00.000')
,('深圳',31,'2020-07-12 16:30:00.000')
,('三亚',23,'2020-07-12 16:30:00.000')
,('三亚',21,'2020-07-12 17:30:00.000')
,('北极',-1,'2020-07-12 17:30:00.000')
,('北极',-10,'2020-07-12 19:30:00.000')
;
4. 需求实现
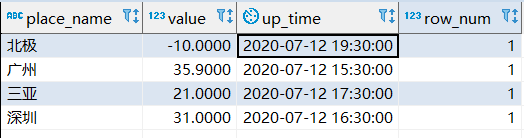
4.1 需求1的SQL语句
利用了postgreSql的一个函数:ROW_NUMBER() OVER( [ PRITITION BY col1] ORDER BY col2[ DESC ] )
select
*
from
(
select
tt.place_name,
tt.value,
tt.up_time,
row_number() over ( partition by tt.place_name
order by
tt.up_time desc) as row_num
from
t_temperature tt) aaa
where
aaa.row_num = 1
4.2 需求2的SQL语句
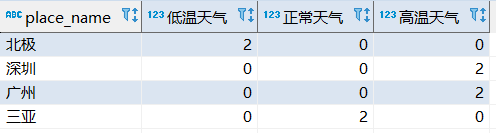
利用了一个case when then else end 用法来统计数量
select
dd.place_name,
sum(case when dd.value <= 0 then 1 else 0 end) as 低温天气,
sum(case when dd.value > 0 and dd.value < 25 then 1 else 0 end) as 正常天气,
sum(case when dd.value >= 25 then 1 else 0 end) as 高温天气
from
t_temperature dd
group by
dd.place_name
效果如下,因为没有过滤每个地方的最新数据,查出的是所有数据:
用需求1的结果来查询统计:
select
dd.place_name,
sum(case when dd.value <= 0 then 1 else 0 end) as 低温天气,
sum(case when dd.value > 0 and dd.value < 25 then 1 else 0 end) as 正常天气,
sum(case when dd.value >= 25 then 1 else 0 end) as 高温天气
from
(
select
*
from
(
select
tt.place_name,
tt.value,
tt.up_time,
row_number() over ( partition by tt.place_name
order by
tt.up_time desc) as row_num
from
t_temperature tt) aaa
where
aaa.row_num = 1) dd
group by
dd.place_name
效果如下:
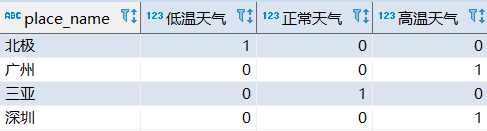
假如再嵌套一个sum统计,就能查出低温天气,正常天气,高温天气分别合计数量是多少了。
over,enjoy!