FrameworkServlet初始化
FrameworkServlet是Spring web框架的基本servlet实现类,通过JavaBean的方式集成了Application context,所有新实现的servlet最好都继承于该类。该类提供了HttpServlet的所有接口实现,自带了一个web容器,它实现了WebApplicationContextAware接口,所以能根据指定的容器配置文件,来初始化自己管理的容器。
FrameworkServlet提供两个功能:
- 为每个servlet管理一个WebApplicationContext实例(即每个servlet会自己的一个web容器),每个servlet都有自己的配置空间,相互独立。(每一个
tag之间的配置属于一个namespace, 配置一个application context。) - 对每一个请求,无论是否成功处理,都会在每个请求上发布事件。(这里是不是可以做一些事情?)
FrameworkServlet初始化流程
FrameworkServlet初始化的过程其实就是WebApplication 配置文件加载(即容器初始化)的过程。
入口方法是initServletBean(),这个方法比较简单,就是打印一些初始化必要信息,然后调用initWebApplicationContext()方法来初始化配置。
实现代码如下:
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring " + getClass().getSimpleName() + " '" + getServletName() + "'");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Initializing Servlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext(); // 这个是真正初始化的方法
initFrameworkServlet(); // 初始化完成后再做一些其他初始化
}
catch (ServletException | RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String value = this.enableLoggingRequestDetails ?
"shown which may lead to unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data" :
"masked to prevent unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data";
logger.debug("enableLoggingRequestDetails='" + this.enableLoggingRequestDetails +
"': request parameters and headers will be " + value);
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
// 当容器初始化完毕后,我们会在日志文件里看到这一行日志信息
logger.info("Completed initialization in " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + " ms");
}
}
initWebApplicationContext()方法在初始化applicationContext时,会分几步来执行:
- 获取root applicationContext, 一般是web.xml文件对应的初始化配置。
- 如果当前servlet已经初始化了一个applicationContext, 那么设置parent applicationContext为第一步设置的context, 然后读取配置文件。
- 如果applicationContext为空,那么根据配置文件中设置的contextAttribute值从ServletContext中查找;
- 如果没有设置contextAttribute,那么就调用createWebApplicationContext()方法创建一个新的applicationContext,并将root applicationContext作为父容器。
实现代码如下:
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one
// has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed
// that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the
// user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) {
onRefresh(wac);
}
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
}
return wac;
}
createWebApplicationContext()方法是最核心的代码,创建XmlWebApplicationContext实例,并从xml配置文件中加载配置。
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(@Nullable ApplicationContext parent) {
Class contextClass = getContextClass();
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Fatal initialization error in servlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"': custom WebApplicationContext class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type ConfigurableWebApplicationContext");
}
// 真正初始化实现类,这个类就是通过contextClass来指定的。
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac =
(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment());
wac.setParent(parent);
// 如果有配置文件的路径,那么就设置路径
String configLocation = getContextConfigLocation();
if (configLocation != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocation);
}
// 真正加载配置的地方
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac);
return wac;
}
我们来看看核心的代码,它会设置各种属性参数,最后会调用refresh()方法,读取配置。
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac) {
// 设置contextId属性
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
// The application context id is still set to its original default value
// -> assign a more useful id based on available information
if (this.contextId != null) {
wac.setId(this.contextId);
}
else {
// Generate default id...
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(getServletContext().getContextPath()) + '/' + getServletName());
}
}
// 设置当前webApplicationContext所属于的ServletContext
wac.setServletContext(getServletContext());
// 设置ServletConfig
wac.setServletConfig(getServletConfig());
// 设置命名空间
wac.setNamespace(getNamespace());
// 设置监听器
wac.addApplicationListener(new SourceFilteringListener(wac, new ContextRefreshListener()));
// The wac environment's #initPropertySources will be called in any case when the context
// is refreshed; do it eagerly here to ensure servlet property sources are in place for
// use in any post-processing or initialization that occurs below prior to #refresh
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(getServletContext(), getServletConfig());
}
// 这是一个hook, 子类可以实现该方法
postProcessWebApplicationContext(wac);
applyInitializers(wac);
// 最终配置加载的地方
wac.refresh();
}
为什么FrameworkServlet的初始化入口是initServletBean()方法?
这就需要从FrameworkServlet的继承关系来讲解了。首先,必须明确的是,FrameworkServlet也是一个普普通通的servlet, 所以它自身也会有servlet定义的方法的实现:
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException;
public ServletConfig getServletConfig();
public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException;
public String getServletInfo();
public void destroy();
下图是类继承关系链:
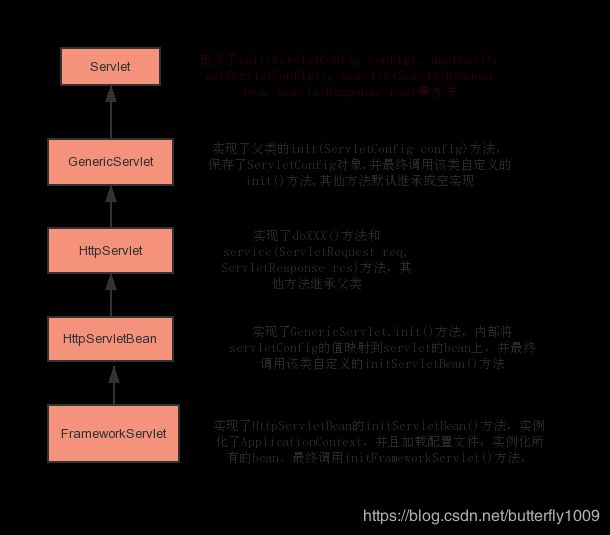
根据上图继承关系,我们可以理解初始化顺序实际上是这样的:
- web容器在实例化servlet时会调用Servlet的init(ServletConfig)方法,由于其子类GenericServlet实现了该方法,因而最终会调用GenericServlet.init(ServletConfig)方法。
- GenericServlet.init(ServletConfig)方法内部会调用其init()方法,由于该方法又是由其子类HttpServletBean实现,实际上是执行了HttpServletBean.init()方法。
- HttpServletBean.init()方法内部会调用其自定义的initServletBean()方法,但该方法实际上是由FrameworkServlet实现,实际上是执行了FrameworkServlet.initServletBean()方法。
- FrameworkServlet.initServletBean()方法内部真正初始化了applicationContext,并加载配置文件,最终调用其自定义的initFrameworkServlet()方法。
至此,当容器初始化该servlet时,通过调用init()方法,最终达到了初始化该servlet的容器的目的。
其实Servlet定义的接口很简单,子类通过不断继承,利用Java的继承和多态特性,完成了很多自定义的逻辑实现。简单的接口,完成了重要的任务。真是佩服至极!!!
如何使用FrameworkServlet类
从上面的代码分析,我们可以看到,其实只需要实现FrameworkServlet中的几个方法即可:
- initFrameworkServlet()方法
- doService()方法
- postProcessWebApplicationContext()方法
其中,子类必须实现FrameworkServlet.doService()方法,该方法用来处理所有的请求。另外两个方法可以不必实现。具体实现可以参考DispatcherSerlvet的实现。
Servlet init-param有哪些?分别是什么作用?
- contextConfigLocation
- contextClass
- contextInitializerClasses
- contextAttribute
- namespace
- publishContext
其实还有一些其他属性,采用默认值就行,在此就j不一一罗列了。
contextConfigLocation属性用来告诉FrameworkServlet容器配置的完整路径,该路径是基于WEB-INF/目录。但是如果不指定该属性,默认的路径是什么呢?
- 首先看当前servlet有没有定义namespace属性,如果有则用namespace.xml作为文件名。
- 如果没有,则用
-servlet作为namespace,比如namespace是spring-mvc-test-servlet。 - 那么完整的配置文件名就是spring-mvc-test-servlet.xml.完整路径就是/WEB-INF/spring-mvc-test-servlet.xml.
contextConfigLocation支持同时指定多个配置文件,文件之间用逗号或空格隔开。如果多个文件中定义有相同的bean, 后面的会覆盖前面的定义。如果想覆盖前面文件定义的bean, 这是一个方法。
contextClass用来制定用哪个实现类来加载这个容器资源,这些容器管理类的基类是ConfigurableWebApplicationContext, 子类必须继承实现它。通常使用比较多的是XmlWebApplicationContext,这也是spring mvc默认的实现类。
contextInitializerClasses用来指定多个ApplicationContextInitializer类,初始化这个容器,对其中的属性会做一些加工。
namespace就是当前servlet的命名空间,用来标明容器的配置文件名称和配置属性所在的空间范围。
contextAttribute用来标明当前的ApplicationContext在ServletContext中的名称,因为ServletContext中维护的对象实际上存在了Map
publishContext用来在初始化时告诉FrameworkServlet是否将applicationContext放到ServletContext里,以便后续可以在其他地方访问。
看源码我们的印象会更深一些。
/**
* Suffix for WebApplicationContext namespaces. If a servlet of this class is
* given the name "test" in a context, the namespace used by the servlet will
* resolve to "test-servlet".
*/
public static final String DEFAULT_NAMESPACE_SUFFIX = "-servlet"; // 如果没有显式地指定namespace, 那么namespace是以-sevlet做后缀。
/**
* Default context class for FrameworkServlet.
* @see org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext
*/
public static final Class DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS = XmlWebApplicationContext.class; // 缺省的容器配置类
/**
* Prefix for the ServletContext attribute for the WebApplicationContext.
* The completion is the servlet name.
*/
public static final String SERVLET_CONTEXT_PREFIX = FrameworkServlet.class.getName() + ".CONTEXT."; // WebpplicationContext在ServletContext中的属性名。
/**
* Any number of these characters are considered delimiters between
* multiple values in a single init-param String value.
*/
private static final String INIT_PARAM_DELIMITERS = ",; \t\n"; // 多个值的分隔符
/** ServletContext attribute to find the WebApplicationContext in. */
@Nullable
private String contextAttribute;
/** WebApplicationContext implementation class to create. */
private Class contextClass = DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS; // 缺省的WebApplicationContext实现类