Spring Cache抽象-缓存注解
文章目录
- 概述
- Spring缓存的基本原理
- @Cacheable :主要针对方法配置,能够根据方法的请求参数对其结果进行缓存
- 键生成器
- 带条件的缓存
- @Cacheable 注解参数说明
- 示例-缓存管理器为SimpleCacheManager基于ConcurrentMap的配置
- @CachePut 主要针对方法配置,能够根据方法的请求参数对其结果进行缓存,和 @Cacheable 不同的是,它每次都会触发真实方法的调用
- @CachePut 注解参数说明
- 示例
- @CacheEvict 主要针对方法配置,能够根据一定的条件对缓存进行清空
- @CacheEvict注解参数说明
- 示例
- @Caching 主要针对方法配置, 是一个组注解
- @CacheConfig 类级别的全局缓存注解
- 完整示例
概述
Spring Cache提供了5种可以在方法级别或者类级别上使用的缓存注解。这些注解定义了哪些方法的返回值会被缓存或者从缓存中移除。
需要注意的是,只有public定义的方法才可以被缓存, private、protected或者使用default修饰符的方法都不能被缓存。
当在一个类上使用注解时,该类中每个公共方法的返回值都将被缓存到指定的缓存项或者从中移除。
来简单看下5种注解:
@Cacheable: triggers cache population
@CacheEvict: triggers cache eviction
@CachePut: updates the cache without interfering with the method execution
@Caching: regroups multiple cache operations to be applied on a method
@CacheConfig: shares some common cache-related settings at class-level
Spring缓存的基本原理
和 spring 的事务管理类似,spring cache 的关键原理就是 spring AOP,通过 spring AOP,其实现了在方法调用前、调用后获取方法的入参和返回值,进而实现了缓存的逻辑。
我们通过下图来理解一下
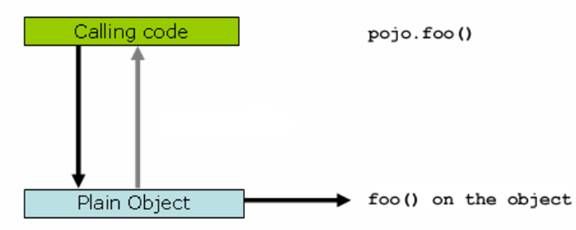
原始方法调用图:
当客户端“Calling code”调用一个普通类 Plain Object 的 foo() 方法的时候,是直接作用在 pojo 类自身对象上的,客户端拥有的是被调用者的直接的引用
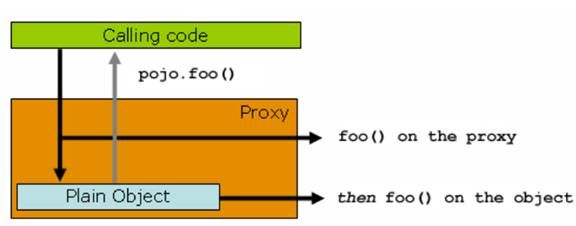
动态代理调用图:
Spring cache 利用了 Spring AOP 的动态代理技术,即当客户端尝试调用 pojo 的 foo()方法的时候,给他的不是 pojo 自身的引用,而是一个动态生成的代理类,这个时候,实际客户端拥有的是一个代理的引用,那么在调用 foo() 方法的时候,会首先调用 proxy 的 foo() 方法,这个时候 proxy 可以整体控制实际的 pojo.foo() 方法的入参和返回值,比如缓存结果,比如直接略过执行实际的 foo() 方法等,都是可以轻松做到的.
@Cacheable :主要针对方法配置,能够根据方法的请求参数对其结果进行缓存
@Cacheable是最主要注解,它指定了被注解方法的返回值是可以被缓存的。 其工作原理是Spring首先会在缓存中查找数据,如果没有则执行方法并缓存结果,然后返回数据。
缓存名称是必须要提供的,可以使用 引号、Value或者acheNames属性来定义名称。 比如
@Cacheable("artisan")
// Spring 3.X
@Cacheable(value="artisan")
// Spring 4.0新增了value的别名cacheNames,更贴切,推荐使用
@Cacheable(cacheNames="artisan")
此外,还可以以列表的形式提供多个缓存,在该列表中使用逗号分隔缓存名称,并用花括号括起来。比如
@Cacheable(cacheNames = {"cache1","cache2"})
我们看下如何在方法上使用@Cacheable
/**
*
*
* @Title: getArtisan
*
* @Description: @Cacheable(cacheNames = "littleArtisan")
* 使用名为littleArtisan的缓存
*
*
* @return
*
* @return: LittleArtisan
*/
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "littleArtisan")
public LittleArtisan getArtisan(String artisanName) {
// 方法内部实现不考虑缓存逻辑,直接实现业务
System.out.println("查找Artisan:" + artisanName);
return getFromDB(artisanName);
}
getArtisan(String artisanName) 方法以artisanName为键将Artisan缓存到littleArtisan缓存段中。
键生成器
缓存的本质就是键值对集合。 在默认情况下,缓存抽象使用方法签名以及参数作为key,并将该键与方法调用的结果作为Value,如果在Cache注解上没有指定Key,则Spring会使用KeyGenerator来生成一个key.
我们来看下org.springframework.cache.interceptor.KeyGenerator
Spring默认提供了SimpleKeyGenerator生成器。 Spring4.0废弃了3.X的DefaultKeyGenerator ,使用SimpleKeyGenerator作为默认的生成器,避免了使用DefaultKeyGenerator 造成key冲突的问题。
/**
......
* @since 3.1
* @deprecated as of Spring 4.0, in favor of {@link SimpleKeyGenerator}
* or custom {@link KeyGenerator} implementations based on hash codes
*/
@Deprecated
public class DefaultKeyGenerator implements KeyGenerator {
/**
......
* @since 4.0
* @see SimpleKey
* @see DefaultKeyGenerator
* @see org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachingConfigurer
*/
public class SimpleKeyGenerator implements KeyGenerator {
我们来看下SimpleKeyGenerator的生成Key的规则:
/**
* Generate a key based on the specified parameters.
*/
public static Object generateKey(Object... params) {
if (params.length == 0) {
return SimpleKey.EMPTY;
}
if (params.length == 1) {
Object param = params[0];
if (param != null && !param.getClass().isArray()) {
return param;
}
}
return new SimpleKey(params);
}
/**
* Create a new {@link SimpleKey} instance.
* @param elements the elements of the key
*/
public SimpleKey(Object... elements) {
Assert.notNull(elements, "Elements must not be null");
this.params = new Object[elements.length];
System.arraycopy(elements, 0, this.params, 0, elements.length);
this.hashCode = Arrays.deepHashCode(this.params);
}
通过源码 ,可以得出生成规则如下:
-
如果方法没有入参,这是用SimpleKey,EMPTY作为key
-
如果只有一个入参,这是用该入参作为Key
-
如果有多个入参,则返回包含所有入参的一个SimpleKey
此外,还可以我在声明中指定键值,@Cacheable注解提供了实现该功能的key属性,通过该属性,可以使用SpELl指定自定义键。 如下所示
@Cacheable(cacheNames="artisan" ,key="#artisan.artisanCode")
public Artisan getArtisan(Artisan,boolean checkLogout)
如果我们不想boolean checkLogout 作为key的一部分,则可以通过key属性指定使用artisanCode作为缓存键。
当然了,我们也可以实现org.springframework.cache.interceptor.KeyGenerator接口来定义个性化的key生成器。比如自定义一个MyKeyGenerator类并实现了KeyGenerator接口 ,使用如下:
@Cacheable(cacheNames="artisan" ,key="myKeyGenerator")
public Artisan getArtisan(Artisan,boolean checkLogout)
带条件的缓存
使用@Cacheable注解的condition属性可按条件进行缓存,condition属性使用了SpELl表达式动态评估方法入参是否满足缓存条件。
比如:
@Cacheable(cacheNames=”artisanCache”,condition=”#artisan.age <18`
public Artisan getArtisan(Artisan artisan){
......
}
在上述代码中, #artisan引用方法的同名入参变量,接着通过.age访问artisan入参对象的age属性。 在调用方法前,将对注解中声明的条件进行评估,满足条件才缓存。
与condition属性相反,可以使用unless属性排除某些不希望缓存的对象。 如下
@Cacheable(cacheNames=”artisanCache”,unless=”#artisan.age >= 18`
public Artisan getArtisan(Artisan artisan){
......
}
@Cacheable 注解参数说明
| 参数 | 说明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| value/cacheNames | 缓存的名称,在 spring 配置文件中定义,必须指定至少一个 | @Cacheable(cacheNames=”mycache”) 或者@Cacheable(cacheNames={”cache1”,”cache2”} |
| key | 缓存的 key,可以为空,如果指定要按照 SpEL 表达式编写,如果不指定,则缺省按照方法的所有参数进行组合 | @Cacheable(cacheNames=”artisanCache”,key=”#artisanName”) |
| condition | 缓存的条件,可以为空,使用 SpEL 编写,返回 true 或者 false,只有为 true 才进行缓存,unless属性和condition属性相反,满足条件则不进行缓存 | @Cacheable(cacheNames=”artisanCache”,condition=”#artisanName.length()>2”) |
示例-缓存管理器为SimpleCacheManager基于ConcurrentMap的配置
)
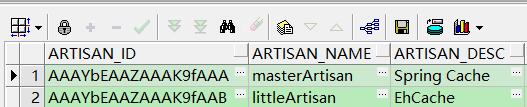
我们数据库中有个little_artisan表,表中数据如下:
我们的目标是只缓存 artisan_name=masterArtisan的数据。
步骤:
domian实体类 Artisan.java
package com.xgj.cache.springCacheAnno;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
*
*
* @ClassName: LittleArtisan
*
* @Description: Java中的缓存和序列化是息息相关的,注意实现Serializable接口
*
* @author: Mr.Yang
*
* @date: 2017年10月2日 下午1:40:53
*/
public class Artisan implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String artisanId;
private String artisanName;
private String artisanDesc;
public String getArtisanId() {
return artisanId;
}
public void setArtisanId(String artisanId) {
this.artisanId = artisanId;
}
public String getArtisanName() {
return artisanName;
}
public void setArtisanName(String artisanName) {
this.artisanName = artisanName;
}
public String getArtisanDesc() {
return artisanDesc;
}
public void setArtisanDesc(String artisanDesc) {
this.artisanDesc = artisanDesc;
}
public static long getSerialversionuid() {
return serialVersionUID;
}
}
可供查询数据库的服务层ArtisanSpringCacheService, 在其中标注缓存的对象及条件
package com.xgj.cache.springCacheAnno.cacheable;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowCallbackHandler;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.MapSqlParameterSource;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.NamedParameterJdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.xgj.cache.springCacheAnno.Artisan;
/**
*
*
* @ClassName: LittleArtisanSpringCacheService
*
* @Description: @Service标注的服务层,受Spring管理
*
* @author: Mr.Yang
*
* @date: 2017年10月2日 下午5:34:29
*/
@Service
public class ArtisanSpringCacheService {
private Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(ArtisanSpringCacheService.class);
// 模糊查询 在参数的值里设置(%),查询sql语句就只是个命名参数
private static final String selectArtisanSQL = "select artisan_id ,artisan_name ,artisan_desc "
+ " from little_artisan "
+ " where artisan_name like :artisanName ";
private NamedParameterJdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Autowired
public void setJdbcTemplate(NamedParameterJdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
}
/**
*
*
* @Title: getArtisan
*
* @Description: @Cacheable(cacheNames = "littleArtisan")
* 使用名为littleArtisan的缓存,符合#artisanName == 'masterArtisan'才缓存
*
*
* @return
*
* @return: LittleArtisan
*/
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "littleArtisan", condition = "#artisanName == 'masterArtisan'")
// @Cacheable(cacheNames = "littleArtisan", unless =
// "#artisanName == 'masterArtisan'")
public Artisan getArtisan(String artisanName) {
// 方法内部实现不考虑缓存逻辑,直接实现业务
System.out.println("根据ArtisanName查找Artisan:" + artisanName);
return getFromDB(artisanName);
}
/**
*
*
* @Title: getFromDB
*
* @Description: 这里只是为了演示下
* 使用NamedParameterJdbcTemplate模糊查询的用法。其实有可能返回的是一个List。
*
* @param artisanName
* @return
*
* @return: LittleArtisan
*/
private Artisan getFromDB(String artisanName) {
System.out.println("getFromDB");
final Artisan littleArtisan = new Artisan();
// 使用MapSqlParameterSource绑定参数 ,拼接模糊查询
MapSqlParameterSource mapSqlParameterSource = new MapSqlParameterSource()
.addValue("artisanName", "%" + artisanName + "%");
jdbcTemplate.query(selectArtisanSQL, mapSqlParameterSource,
new RowCallbackHandler() {
@Override
public void processRow(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException {
littleArtisan.setArtisanId(rs.getString("artisan_id"));
littleArtisan.setArtisanName(rs
.getString("artisan_name"));
littleArtisan.setArtisanDesc(rs
.getString("artisan_desc"));
}
});
return littleArtisan;
}
}
Spring配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:cache="http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache
http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache/spring-cache.xsd">
<!-- 扫描类包,将标注Spring注解的类自动转化Bean,同时完成Bean的注入 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.xgj.cache.springCacheAnno" />
<!-- 使用context命名空间,加载数据库的properties文件 -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:spring/jdbc.properties" />
<!-- 数据库 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource"
destroy-method="close"
p:driverClassName="${jdbc.driverClassName}"
p:url="${jdbc.url}"
p:username="${jdbc.username}"
p:password="${jdbc.password}" />
<!-- 配置namedParameterJdbcTemplate模板 -->
<bean id="namedParameterJdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.NamedParameterJdbcTemplate">
<constructor-arg ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!-- (1)添加cache命名空间和schema文件 -->
<!-- (2)开启支持缓存的配置项 -->
<cache:annotation-driven cache-manager="cacheManager" proxy-target-class="true"/>
<!-- (3) 配置cacheManger -->
<bean id="cacheManager" class="org.springframework.cache.support.SimpleCacheManager"
p:caches-ref="cacheObjects">
</bean>
<!-- (4)caches集合 -->
<util:set id="cacheObjects">
<bean class="org.springframework.cache.concurrent.ConcurrentMapCacheFactoryBean"
p:name="default"/>
<!-- @Cacheable(cacheNames = "littleArtisan")标注的cache名称 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.cache.concurrent.ConcurrentMapCacheFactoryBean"
p:name="littleArtisan"/>
</util:set>
</beans>
单元测试
package com.xgj.cache.springCacheAnno.cacheable;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import com.xgj.cache.springCacheAnno.Artisan;
public class CacheableTest {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx = null;
ArtisanSpringCacheService service = null;
@Before
public void initContext() {
// 启动Spring 容器
ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"classpath:com/xgj/cache/springCacheAnno/conf_spring.xml");
service = ctx.getBean("artisanSpringCacheService",
ArtisanSpringCacheService.class);
System.out.println("initContext successfully");
}
@Test
public void testLoadArtisanFromDBAndCache() {
Artisan littleArtisan = new Artisan();
// 第一次 从数据库中获取
littleArtisan = service.getArtisan("littleArtisan");
printArtisanInfo(littleArtisan);
// @Cacheable(cacheNames = "littleArtisan", condition =
// "#artisanName == 'masterArtisan'")
// 根据condition 来看,我们只是缓存#artisanName == 'masterArtisan'的记录
// 第一次 从数据库中获取
littleArtisan = service.getArtisan("masterArtisan");
printArtisanInfo(littleArtisan);
// 第二次 查询masterArtisan ,根据缓存条件,满足,应该从缓存中获取
littleArtisan = service.getArtisan("masterArtisan");
printArtisanInfo(littleArtisan);
// 第二次 查询littleArtisan ,根据缓存条件,不满足,应该从数据库中获取
littleArtisan = service.getArtisan("littleArtisan");
printArtisanInfo(littleArtisan);
}
private void printArtisanInfo(Artisan littleArtisan) {
System.out.println("Id:" + littleArtisan.getArtisanId());
System.out.println("Name:" + littleArtisan.getArtisanName());
System.out.println("Desc:" + littleArtisan.getArtisanDesc());
System.out.println();
}
@After
public void closeContext() {
if (ctx != null) {
ctx.close();
}
System.out.println("close context successfully");
}
}
输出结构分析
2017-10-03 01:09:30,338 INFO [main] (AbstractApplicationContext.java:583) - Refreshing org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext@5f0ab5d: startup date [Tue Oct 03 01:09:30 BOT 2017]; root of context hierarchy
2017-10-03 01:09:30,422 INFO [main] (XmlBeanDefinitionReader.java:317) - Loading XML bean definitions from class path resource [com/xgj/cache/springCacheAnno/conf_spring.xml]
initContext successfully
根据ArtisanName查找Artisan:littleArtisan
getFromDB
Id:AAAYbEAAZAAAK9fAAB
Name:littleArtisan
Desc:EhCache
根据ArtisanName查找Artisan:masterArtisan
getFromDB
Id:AAAYbEAAZAAAK9fAAA
Name:masterArtisan
Desc:Spring Cache
Id:AAAYbEAAZAAAK9fAAA
Name:masterArtisan
Desc:Spring Cache
根据ArtisanName查找Artisan:littleArtisan
getFromDB
Id:AAAYbEAAZAAAK9fAAB
Name:littleArtisan
Desc:EhCache
2017-10-03 01:09:32,826 INFO [main] (AbstractApplicationContext.java:984) - Closing org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext@5f0ab5d: startup date [Tue Oct 03 01:09:30 BOT 2017]; root of context hierarchy
close context successfully
可以看到,我们每次查询littleArtisan都是从数据库中获取,而masterArtisan只有第一次是从数据库中获取,第二次查询则是从缓存中获取数据。 反之,推理 unless ,满足条件则不进行缓存。
unless : unless ,满足条件则不进行缓存。 请注意,该条件适用于方法的返回值。#result表示方法返回值。
@Cacheable(cacheNames="products", key="#product.name", condition="#product.price<500", unless="#result.outofstock")
public Product findProduct(Product product){
..
return aproduct;
}
@CachePut 主要针对方法配置,能够根据方法的请求参数对其结果进行缓存,和 @Cacheable 不同的是,它每次都会触发真实方法的调用
@CachePut 和@Cacheable的效果几乎一样。@CachePut首先执行方法,然后将返回值放入缓存。当希望使用方法返回值来更新缓存时可以选择这种方法
如果使用了 @Cacheable 注释,则当重复使用相同参数调用方法的时候,方法本身不会被调用执行,即方法本身被略过了,结果直接从缓存中找到并返回了。
现实中并不总是如此,有些情况下我们希望方法一定会被调用,因为其除了返回一个结果,还做了其他事情,例如记录日志,调用接口等,这个时候,我们可以用 @CachePut 注释,这个注释可以确保方法被执行,同时方法的返回值也被记录到缓存中。
@CachePut 注解参数说明
和@Cacheable一样,@CachePuts也提供了key、condition、和unless属性
| 参数 | 说明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| value/cacheNames | 缓存的名称,在 spring 配置文件中定义,必须指定至少一个 | @CachePut(cacheNames=”mycache”) 或者@CachePut(cacheNames={”cache1”,”cache2”} |
| key | 缓存的 key,可以为空,如果指定要按照 SpEL 表达式编写,如果不指定,则缺省按照方法的所有参数进行组合 | @CachePut(cacheNames=”artisanCache”,key=”#artisanName”) |
| condition | 缓存的条件,可以为空,使用 SpEL 编写,返回 true 或者 false,只有为 true 才进行缓存,unless属性和condition属性相反,满足条件则不进行缓存 | @CachePut(cacheNames=”artisanCache”,condition=”#artisanName.length()>2”) |
举个场景:更新产品的操作,我们希望重新计算特定产品[可能是由于新的价格],然后将该产品存储在缓存中以供将来参考。 请注意,虽然@CacheEvict用于从缓存中删除项目[或全部],但@CachePut则是更新项目。
@CachePut(cacheNames= "products", key = "#product.name" , unless="#result==null")
public Product updateProduct(Product product) {
logger.info("");
for(Product p : products){
if(p.getName().equalsIgnoreCase(product.getName()))
p.setPrice(product.getPrice());
return p;
}
return null;
}
仅修改 将@Cacheable改为 @CachePut (这个示例不是特别合适, @CachePut比较适合更新的场景,仅演示每次都会执行的场景。) 再次测试: 可以看到使用@CachePut后,每次都从是先执方法内的逻辑。 @CacheEvict注解是@Cacheable注解的反向操作,它负责从给定的缓存中移除一个值 。 大多数缓存框架都提供了缓存数据的有效期,使用该注解可以显式的从缓存中删除失效的缓存数据。 该注解通常用于更新或者删除的操作。 单元测试 测试结果 清除后,又重新加载数据,并存入缓存。 @Caching 是一个组注解,可以为一个方法定义提供基于@Cacheable、@CacheEvict或者@CachePut注解的数组。 当我们想要指定相同类型的多个注释(例如同一方法的@CacheEvict或@CachePut)时,@Caching注释很方便。 假设我们有两个包含相同产品的缓存,使用相同的key。 现在,如果要从两个缓存中清除记录,如下即可 如果key不同呢, JDK1.8以下不允许使用重复的注解在一个方法上, 这个时候使用@Caching Spring4.0之前并没有类级别的全局缓存注解。 前面的4个注解都是基于方法的,如果在同一个类中需要缓存的方法注解属性都类似,则需要一个个的重复增加,Spring4增加了@CacheConfig类级别的注解解决这个问题。 比如 在上面的例子中,getArtisanA将使用“artisans”缓存,而getArtisanB覆盖类级别的缓存名,使用指定的“artisanB”换承诺。 另外,他们都将使用在class级别指定的keyGenerator。 Spring Cache抽象-使用Java类注解的方式整合EhCache
示例
@CachePut(cacheNames = "littleArtisan", condition = "#artisanName == 'masterArtisan'")
public Artisan getArtisan(String artisanName) {
// 方法内部实现不考虑缓存逻辑,直接实现业务
System.out.println("根据ArtisanName查找Artisan:" + artisanName);
return getFromDB(artisanName);
}
2017-10-03 01:40:26,019 INFO [main] (AbstractApplicationContext.java:583) - Refreshing org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext@7b8269b6: startup date [Tue Oct 03 01:40:26 BOT 2017]; root of context hierarchy
2017-10-03 01:40:26,139 INFO [main] (XmlBeanDefinitionReader.java:317) - Loading XML bean definitions from class path resource [com/xgj/cache/springCacheAnno/conf_spring.xml]
initContext successfully
根据ArtisanName查找Artisan:littleArtisan
getFromDB
Id:AAAYbEAAZAAAK9fAAB
Name:littleArtisan
Desc:EhCache
根据ArtisanName查找Artisan:masterArtisan
getFromDB
Id:AAAYbEAAZAAAK9fAAA
Name:masterArtisan
Desc:Spring Cache
根据ArtisanName查找Artisan:masterArtisan
getFromDB
Id:AAAYbEAAZAAAK9fAAA
Name:masterArtisan
Desc:Spring Cache
根据ArtisanName查找Artisan:littleArtisan
getFromDB
Id:AAAYbEAAZAAAK9fAAB
Name:littleArtisan
Desc:EhCache
2017-10-03 01:40:28,588 INFO [main] (AbstractApplicationContext.java:984) - Closing org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext@7b8269b6: startup date [Tue Oct 03 01:40:26 BOT 2017]; root of context hierarchy
close context successfully
@CacheEvict 主要针对方法配置,能够根据一定的条件对缓存进行清空
@CacheEvict注解参数说明
参数
说明
示例
value/cacheNames
缓存的名称,在 spring 配置文件中定义,必须指定至少一个
@CacheEvict(cacheNames=”mycache”) 或者@CacheEvict(cacheNames={”cache1”,”cache2”}
key
缓存的 key,可以为空,如果指定要按照 SpEL 表达式编写,如果不指定,则缺省按照方法的所有参数进行组合
@CachEvict(cacheNames=”artisanCache”,key=”#artisanName”)
condition
缓存的条件,可以为空,使用 SpEL 编写,返回 true 或者 false,只有为 true 才进行缓存,unless属性和condition属性相反,满足条件则不进行缓存
@CachEvict(cacheNames=”artisanCache”,condition=”#artisanName.length()>2”)
allEntries
是否清空所有缓存内容,缺省为 false,如果指定为 true,则方法调用后将立即清空所有缓存
@CachEvict(cacheNames=”artisan”,allEntries=true)”)
beforeInvocation
是否在方法执行前就清空,缺省为 false,如果指定为 true,则在方法还没有执行的时候就清空缓存,缺省情况下,如果方法执行抛出异常,则不会清空缓存
@CachEvict(cacheNames=”artisan”,beforeInvocation=true)”)
示例
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "products", key = "#product.name")
public void refreshProduct(Product product) {
//This method will remove only this specific product from 'products' cache.
}
@CacheEvict(cacheNames= "products", allEntries = true)
public void refreshAllProducts() {
//This method will remove all 'products' from cache, say as a result of flush-all API.
}
package com.xgj.cache.springCacheAnno.cacheEvict;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheEvict;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowCallbackHandler;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.MapSqlParameterSource;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.NamedParameterJdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.xgj.cache.springCacheAnno.Artisan;
/**
*
*
* @ClassName: ArtisanSpringCacheService
*
* @Description: @Service标注的服务层,受Spring管理
*
* @author: Mr.Yang
*
* @date: 2017年10月2日 下午5:34:29
*/
@Service
public class ArtisanSpringCacheEvictService {
// 模糊查询 在参数的值里设置(%),查询sql语句就只是个命名参数
private static final String selectArtisanSQL = "select artisan_id ,artisan_name ,artisan_desc "
+ " from little_artisan "
+ " where artisan_name like :artisanName ";
private NamedParameterJdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Autowired
public void setJdbcTemplate(NamedParameterJdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
}
/**
*
*
* @Title: getArtisan
*
* @Description: @Cacheable(cacheNames = "littleArtisan")
* 使用名为littleArtisan的缓存,符合#artisanName == 'masterArtisan'才缓存
*
*
* @return
*
* @return: LittleArtisan
*/
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "littleArtisan", condition = "#artisanName == 'masterArtisan'")
public Artisan getArtisan(String artisanName) {
// 方法内部实现不考虑缓存逻辑,直接实现业务
System.out.println("根据ArtisanName查找Artisan:" + artisanName);
return getFromDB(artisanName);
}
/**
*
*
* @Title: remove
*
* @Description: 清除缓存
*
* @param artisnName
*
* @return: void
*/
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "littleArtisan")
public void remove(String artisnName) {
System.out.println("littleArtisan cache removed ");
}
/**
*
*
* @Title: getFromDB
*
* @Description: 这里只是为了演示下
* 使用NamedParameterJdbcTemplate模糊查询的用法。其实有可能返回的是一个List。
*
* @param artisanName
* @return
*
* @return: Artisan
*/
private Artisan getFromDB(String artisanName) {
System.out.println("getFromDB");
final Artisan artisan = new Artisan();
// 使用MapSqlParameterSource绑定参数 ,拼接模糊查询
MapSqlParameterSource mapSqlParameterSource = new MapSqlParameterSource()
.addValue("artisanName", "%" + artisanName + "%");
jdbcTemplate.query(selectArtisanSQL, mapSqlParameterSource,
new RowCallbackHandler() {
@Override
public void processRow(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException {
artisan.setArtisanId(rs.getString("artisan_id"));
artisan.setArtisanName(rs.getString("artisan_name"));
artisan.setArtisanDesc(rs.getString("artisan_desc"));
}
});
return artisan;
}
}
package com.xgj.cache.springCacheAnno.cacheEvict;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import com.xgj.cache.springCacheAnno.Artisan;
public class CacheEvictTest {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx = null;
ArtisanSpringCacheEvictService service = null;
@Before
public void initContext() {
// 启动Spring 容器
ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"classpath:com/xgj/cache/springCacheAnno/conf_spring.xml");
service = ctx.getBean("artisanSpringCacheEvictService",
ArtisanSpringCacheEvictService.class);
System.out.println("initContext successfully");
}
@Test
public void testLoadArtisanFromDBAndCache() {
Artisan littleArtisan = new Artisan();
// @Cacheable(cacheNames = "littleArtisan", condition =
// "#artisanName == 'masterArtisan'")
// 根据condition 来看,我们只是缓存#artisanName == 'masterArtisan'的记录
// 第一次 从数据库中获取
littleArtisan = service.getArtisan("masterArtisan");
printArtisanInfo(littleArtisan);
// 第二次 查询masterArtisan ,根据缓存条件,满足,应该从缓存中获取
littleArtisan = service.getArtisan("masterArtisan");
printArtisanInfo(littleArtisan);
// 将littleArtisan从缓存中移除,再次查询masterArtisan
service.remove("masterArtisan");
littleArtisan = service.getArtisan("masterArtisan");
printArtisanInfo(littleArtisan);
// 再次 查询masterArtisan,根据缓存条件,满足,应该从缓存中获取
littleArtisan = service.getArtisan("masterArtisan");
printArtisanInfo(littleArtisan);
}
private void printArtisanInfo(Artisan littleArtisan) {
System.out.println("Id:" + littleArtisan.getArtisanId());
System.out.println("Name:" + littleArtisan.getArtisanName());
System.out.println("Desc:" + littleArtisan.getArtisanDesc());
System.out.println();
}
@After
public void closeContext() {
if (ctx != null) {
ctx.close();
}
System.out.println("close context successfully");
}
}
2017-10-03 02:11:54,223 INFO [main] (AbstractApplicationContext.java:583) - Refreshing org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext@7efeedca: startup date [Tue Oct 03 02:11:54 BOT 2017]; root of context hierarchy
2017-10-03 02:11:54,378 INFO [main] (XmlBeanDefinitionReader.java:317) - Loading XML bean definitions from class path resource [com/xgj/cache/springCacheAnno/conf_spring.xml]
initContext successfully
根据ArtisanName查找Artisan:masterArtisan
getFromDB
Id:AAAYbEAAZAAAK9fAAA
Name:masterArtisan
Desc:Spring Cache
Id:AAAYbEAAZAAAK9fAAA
Name:masterArtisan
Desc:Spring Cache
littleArtisan cache removed
根据ArtisanName查找Artisan:masterArtisan
getFromDB
Id:AAAYbEAAZAAAK9fAAA
Name:masterArtisan
Desc:Spring Cache
Id:AAAYbEAAZAAAK9fAAA
Name:masterArtisan
Desc:Spring Cache
2017-10-03 02:11:58,732 INFO [main] (AbstractApplicationContext.java:984) - Closing org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext@7efeedca: startup date [Tue Oct 03 02:11:54 BOT 2017]; root of context hierarchy
close context successfully
@Caching 主要针对方法配置, 是一个组注解
@CacheEvict(cachenames = {"products", "items"}, key = "#product.name")
public void refreshProduct(Product product) {
//This method will remove only this specific product from 'products' & 'items' cache.
}
@Caching(evict = {
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "products", key = "#product.name"),
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "items", key = "#product.id") })
public void refreshProduct2(Product product) {
// This method will remove only this specific product from 'products' &
// 'items' cache.
}
@CacheConfig 类级别的全局缓存注解
package com.xgj.cache.springCacheAnno.cacheConfig;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheConfig;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
@CacheConfig(cacheNames = "artisans", keyGenerator="myKeyGenerator")
public class ArtisanService {
@Cacheable
public Artisan getArtisanA(String artisanName) {
Artisan artisan = new Artisan();
return artisan;
}
@Cacheable(cacheNames="artisanB")
public Artisan getArtisanB(String artisanName) {
Artisan artisan = new Artisan();
return artisan;
}
}
完整示例