自定义注解实现数据缓存与定时重载
公司实际项目中,有一个程序把很多配置在记录在了数据库的t_config表中,方便操作人员通过前端页面修改这些配置
前期开发人员并没有对这个表进行缓存,每个交易都实时的读取数据库中的相应配置
随着业务量不断增大,发现性能越来越低,排查后发现是上述的过于频繁的读取数据库,
由于公司暂时不接入redis等技术,因此我们就自己写了一些缓存与重载缓存的方法,将这些频繁读取的数据库信息缓存到内存中,加快了读取速度,减少了数据库操作
下面简单介绍一下这个方案,首先是表结构
CREATE TABLE `t_config` (
`ID` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`NAME` varchar(60) NOT NULL,
`DATA` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`REMARK` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`ID`)
) 对应的JavaBean
public class TConfig implements Serializable, Cloneable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1619811684138791L;
private Long id;
private String name;
private String data;
private String remark;
//………………省略get set 和构造器
//JDBCTEMPLATE的映射
public static class TConfigMapper implements RowMapper {
public TConfig mapRow(ResultSet rs, int index) throws SQLException {
TConfig tConfig = new TConfig();
Long id = rs.getLong("id");
tConfig.setId(id);
String name = rs.getString("name");
tConfig.setName(name);
String data = rs.getString("data");
tConfig.setData(data);
String remark = rs.getString("remark");
tConfig.setRemark(remark);
return tConfig;
}
}
} 项目使用到的是mysql,jre版本1.7,spring4.3.4大家族,orm用的是spring的jdbcTemplate,数据源是c3p0
接下来介绍注解,该注解很简单,只有两个字段,name代表是数据库中的name,不指定则默认为当前属性的名称
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface TConfigCache {
String name() default "";
/**
* 重载间隔时间,单位是分钟,默认5分钟,最小值是1分钟
*
* @return
*/
int intervalTime() default 5;
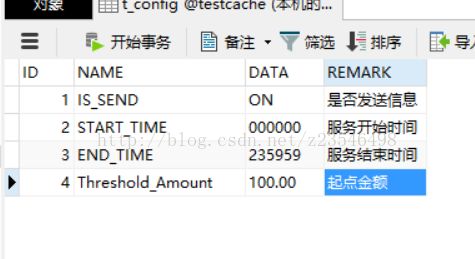
}这里先看看数据库保存的这些测试数据
接下来是ConfigsFromDB,所有的数据库配置都配在这个抽象类中,这个类只需声明变量,和指定get方法即可,无需关心变量是如何赋值与定时重载的,注意注解的值与上图的数据库数据
public abstract class ConfigsFromDB {
@TConfigCache
private String IS_SEND;
@TConfigCache
private int START_TIME; //支持基本数据类型
@TConfigCache
private Integer END_TIME;
@TConfigCache(name = "Threshold_Amount",intervalTime = 1)
private Double qiDianJinE; //起点金额
private String string; //普通属性,没有被注解
/**
* 加载完数据后回调,能做一些字段的善后工作,但不是必须的
*/
protected void afterLoad(){
if(qiDianJinE == null){
qiDianJinE = 0.0;
}
}
/**
* 加载完数据后被回调,做一些数据有效性检查,但不是必须的
* @return
*/
protected boolean checkData(){
if(START_TIME >= END_TIME){
return false;
}
return true;
}
public String getIS_SEND() {
return IS_SEND;
}
public Integer getSTART_TIME() {
return START_TIME;
}
public Integer getEND_TIME() {
return END_TIME;
}
public Double getQiDianJinE() {
return qiDianJinE;
}
public String getString() {
return string;
}
}接下来是重头戏,ConfigsFromDBImpl,继承了ConfigsFromDB,用于识别TConfigCache注解,以及为这些属性赋值,定时重载等
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository("configs")
public class ConfigsFromDBImpl extends ConfigsFromDB {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
private List fields = new ArrayList();
private final String SQL = "select * from t_config";
/**
* 基本数据类型的装箱类名转换
*/
final private static Map TYPE_MAP = new HashMap();
static {
TYPE_MAP.put("int", Integer.class.getSimpleName());
TYPE_MAP.put("double", Double.class.getSimpleName());
TYPE_MAP.put("short", Short.class.getSimpleName());
TYPE_MAP.put("long", Long.class.getSimpleName());
TYPE_MAP.put("byte", Byte.class.getSimpleName());
TYPE_MAP.put("float", Float.class.getSimpleName());
TYPE_MAP.put("boolean", Boolean.class.getSimpleName());
TYPE_MAP.put("char", Character.class.getSimpleName());
}
@PostConstruct
private void init() throws Exception {
initAnno();
if (!load()) {
// 抛出Exception,会让spring初始化失败,程序无法启动
throw new Exception("初始化ConfigsFromDB失败,程序无法启动");
}
}
private boolean load() throws Exception { //加载数据,并赋值
System.out.println("开始加载数据库配置表");
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
List configs = jdbcTemplate.query(SQL, new TConfig.TConfigMapper());//执行sql,全表查询
int length = fields.size();
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
MyField myField = fields.get(i);
Field field = myField.field;
TConfigCache anno = field.getDeclaredAnnotation(TConfigCache.class);
String name = field.getName();
if (!"".equals(anno.name())) { // 如果注解的name不是空,就取注解的
name = anno.name();
}
if (isTimeOut(myField, anno.intervalTime())) { // 判断是否超时
for (TConfig config : configs) {
if (config.getName().equals(name)) {
setValue(field, config.getData()); //给属性赋值
myField = new MyField(field, System.currentTimeMillis()); //重新设定时间
fields.set(i, myField); //放回原来的位置
configs.remove(config); //从当前数据库查询结果移走,可以减少后来者的遍历次数
System.out.println(field.getName()+"获取到的数据库值为"+config.getData());
break;
}
}
} else {
System.out.println(field.getName() + "属性未超时,无需重载");
continue;
}
}
afterLoad(); //回调数据后期加工方法
System.out.println("加载数据库配置表结束,耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime));
return checkData(); //回调数据检查方法
}
private void initAnno() { // 寻找有被TConfig注解的属性
for (Field field : this.getClass().getSuperclass().getDeclaredFields()) {
field.setAccessible(true);
if (field.isAnnotationPresent(TConfigCache.class)) { // 判断是不是TConfigCache注解过的
MyField myField = new MyField(field, 0);
fields.add(myField);
System.out.println("成功识别到" + field.getName() + "属性被注解");
}
}
}
/**
* 给属性赋值,能根据不同属性的类型,做对应的String转换
*/
private void setValue(Field field, String value) throws IllegalAccessException {
String type = field.getType().getSimpleName();
if (field.getType().isPrimitive()) { // 判断是否为int,long等基本数据类型,是的话则要获得其装箱的类型
type = TYPE_MAP.get(type);
}
switch (type) { // 注意jdk1.7以上才支持这个这种语法
case "Integer":
field.set(this, Integer.parseInt(value));
break;
case "Double":
field.set(this, Double.parseDouble(value));
break;
case "Short":
field.set(this, Short.parseShort(value));
break;
case "Long":
field.set(this, Long.parseLong(value));
break;
case "Byte":
field.set(this, Byte.parseByte(value));
break;
case "Character":
field.set(this, value);
break;
case "Boolean":
field.set(this, Boolean.parseBoolean(value)); // 对于这个转换,可以额外自定义,比如1或者ON代表true
break;
// 可以继续添加与String类型转换,如Date、BigInteger等
default:
field.set(this, value);
}
}
/**
* 判断这个属性是否超时
*
* @param myField
* @return
*/
private boolean isTimeOut(MyField myField, int intervalTime) {
long lastLoadTime = myField.lastLoadTime;
if (System.currentTimeMillis() < (lastLoadTime + (intervalTime * 60 * 1000))) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
private class MyField { // 对Field进行简单封装,使其有“上次加载时间”的属性
Field field;
long lastLoadTime = 0;
public MyField(Field field, long lastLoadTime) {
super();
this.field = field;
this.lastLoadTime = lastLoadTime;
}
public MyField(Field field) {
super();
this.field = field;
}
public MyField() {
super();
}
}
/**
* 定时加载数据
* @throws Exception
*/
@Scheduled(fixedDelay = 1 * 60 * 1000, initialDelay = 2 * 60 * 1000) // 1分钟定时调起,初始调起休眠2分钟
private void loadByTime() throws Exception {
System.out.println("@Scheduled开始重载数据");
load();
System.out.println("@Scheduled开始重载数据完成");
}
} 最后是使用的演示
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Throwable {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("./config/applicationContext.xml");
final ConfigsFromDB configs = (ConfigsFromDB) applicationContext.getBean("configs");
new Thread() { //定时打印缓存的数据
public void run() {
while (true) {
System.out.println("-----------------");
System.out.println(configs.getIS_SEND());
System.out.println(configs.getSTART_TIME());
System.out.println(configs.getEND_TIME());
System.out.println(configs.getQiDianJinE());
System.out.println("-----------------");
try {
sleep(65 * 1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
}.start();
}
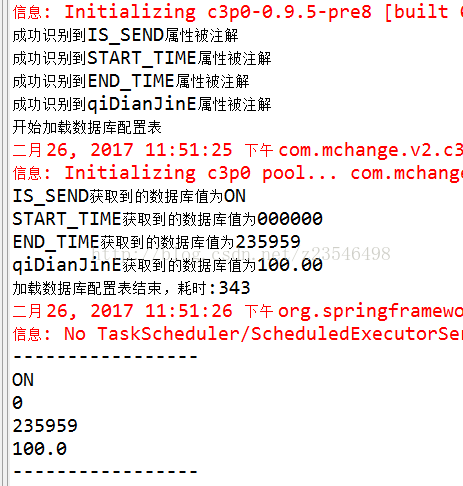
}第一次执行结果,第一次执行需要创建数据库连接等,因此速度较慢,耗时长
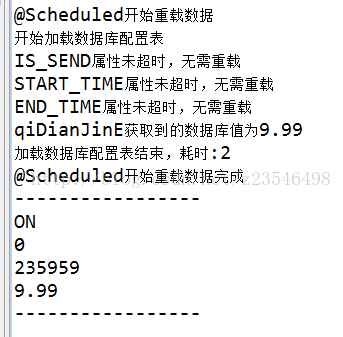
执行第一次之后,我修改了数据库的数据,使得起点金额变为9.99,在定时任务执行后,能看到打印信息如下
能看到起点金额已经修改成功了,缓存也刷新正确,此外,重新加载的耗时比起第一次是明显减少了
在程序稳定之后,有什么新的配置需要添加,就直接在ConfigsFromDB类中新增属性,指定get方法即可,ConfigsFromDBImpl基本不需要再去修改了,这样以来也能减少新增配置带来的代码编写量,毕竟偷懒才是进步的源泉嘛!