- Java-后端程序员个人知识总结
金肴羽
java开发语言
文章目录概要1.编程语言2.数据结构与算法3.数据库知识4.框架和库5.服务器管理6.网络知识7.版本控制8.测试9.安全知识10.系统设计11.编码规范与最佳实践12.持续学习和适应能力概要后端程序员,主要负责应用程序的逻辑、数据库交互、服务器配置以及应用的性能优化等。成为一名优秀的后台程序员,需要掌握以下技能:1.编程语言掌握至少一种后台编程语言JavaPythonHtmlJavaScript
- 海量数据查找最大K个值:数据结构与算法的选择
星辰@Sea
数据结构Java数据结构
在处理大数据集时,经常需要找到数据集中最大的K个元素,这样的需求在很多领域都有广泛应用,例如推荐系统中寻找评分最高的K个商品、数据分析中找出最重要的K个特征、搜索引擎中找到排名前K的结果等等。面对海量数据,传统的排序方法可能不再适用,因为它们通常具有较高的时间复杂度。因此,选择合适的数据结构和算法对于提高效率至关重要。本文将详细介绍如何在海量数据集中查找最大的K个值,探讨不同的数据结构与算法选择,
- 22级数据结构与算法实验2——链表
“世有神明”
链表算法数据结构
7-1两个有序链表序列的合并分数20全屏浏览题目切换布局作者DS课程组单位浙江大学已知两个非降序链表序列S1与S2,设计函数构造出S1与S2合并后的新的非降序链表S3。输入格式:输入分两行,分别在每行给出由若干个正整数构成的非降序序列,用−1表示序列的结尾(−1不属于这个序列)。数字用空格间隔。输出格式:在一行中输出合并后新的非降序链表,数字间用空格分开,结尾不能有多余空格;若新链表为空,输出NU
- 《数据结构与算法》知识点(四)
游戏原画设计
第七章查找顺序查找、折半查找、索引查找、分块查找是静态查找,动态查找有二叉排序树查找,最优二叉树查找,键树查找,哈希表查找静态查找表顺序表的顺序查找:应用范围:顺序表或线性链表表示的表,表内元素之间无序。查找过程:从表的一端开始逐个进行记录的关键字和给定值的比较。顺序有序表的二分查找。平均查找时间(n+1)/nlog2(n+1)分块查找:将表分成几块,块内无序,块间有序,即前一块中的最大值小于后一
- 数据结构与算法——7-6 列出连通集 (25分)
吃完有点累
数据结构与算法队列算法数据结构DFSBFS
7-6列出连通集(25分)给定一个有N个顶点和E条边的无向图,请用DFS和BFS分别列出其所有的连通集。假设顶点从0到N−1编号。进行搜索时,假设我们总是从编号最小的顶点出发,按编号递增的顺序访问邻接点。输入格式:输入第1行给出2个整数N(0#includetypedefintVertexType;typedefintEdgeType;#defineMAXVEX100#defineINFINITY
- 数据结构与算法 - 贪心算法
临界点oc
数据结构与算法贪心算法算法
一、贪心例子贪心算法或贪婪算法的核心思想是:1.将寻找最优解的问题分为若干个步骤2.每一步骤都采用贪心原则,选取当前最优解3.因为没有考虑所有可能,局部最优的堆叠不一定让最终解最优贪心算法是一种在每一步选择中都采取在当前状态下最好或最优(即最有利)的选择,从而希望导致结果是最好或最优的算法。这种算法通常用于求解优化问题,如最小生成树、背包问题等。贪心算法的应用:1.背包问题:给定一组物品和一个背包
- Java数据结构与算法:动态规划之斐波那契数列
省赚客APP开发者@聚娃科技
java动态规划代理模式
Java数据结构与算法:动态规划之斐波那契数列大家好,我是免费搭建查券返利机器人赚佣金就用微赚淘客系统3.0的小编。在这寒冷的季节里,让我们一同探讨Java中的动态规划,重点关注解决问题的经典代表之一——斐波那契数列。动态规划简介动态规划是一种解决问题的数学方法,通常用于优化递归算法。它通过将问题分解为子问题并保存它们的解,避免重复计算,从而提高算法效率。在动态规划的应用中,最常见的问题之一就是求
- 【数据结构与算法 | 每日一题 | 力扣篇】
Vez'nan的幸福生活
leetcode算法数据结构
1.力扣977:有序数组的平方1.1题目:给你一个按非递减顺序排序的整数数组nums,返回每个数字的平方组成的新数组,要求也按非递减顺序排序。示例1:输入:nums=[-4,-1,0,3,10]输出:[0,1,9,16,100]解释:平方后,数组变为[16,1,0,9,100]排序后,数组变为[0,1,9,16,100]示例2:输入:nums=[-7,-3,2,3,11]输出:[4,9,9,49,
- 数据结构与算法 python实现单链表实现对列
我只要一发
python数据结构与算法Python实现单链表实现对列
对列:先来的先走,后来的后走FIFO实现FIFO的实现数据结构:arroylistlinkedlistdoubllinkedlist最基本的操作,push入列pop出列单链表实现appendpopleftclassFullError(Exception):passclassEmptyError(Exception):passclassQueue(object):def__init__(self,m
- 周四 2020-01-09 08:00 - 24:30 多云 02h10m
么得感情的日更机器
南昌。二〇二〇年一月九日基本科研[1]:1.论文阅读论文--二小时十分2.论文实现实验--小时3.数学SINS推导回顾--O分4.科研参考书【】1)的《》看0/0页-5.科研文档1)组织工作[1]:例会--英语能力[2]:1.听力--十分2.单词--五分3.口语--五分4.英语文档1)编程能力[2]:1.编程语言C语言--O分2.数据结构与算法C语言数据结构--O分3.编程参考书1)陈正冲的《C语
- github源码指引:共享内存、数据结构与算法:树形结构ListTree
初级代码游戏
github源码指引共享内存数据结构与算法github共享内存树链表
初级代码游戏的专栏介绍与文章目录-CSDN博客我的github:codetoys,所有代码都将会位于ctfc库中。已经放入库中我会指出在库中的位置。这些代码大部分以Linux为目标但部分代码是纯C++的,可以在任何平台上使用。专题:共享内存、数据结构与算法_初级代码游戏的博客-CSDN博客本文讲解带有子项的链表。一、介绍与上一篇介绍的单向链表相比,多了一个子项指针。可以理解为原来的链表是兄弟关系,
- 代码随想录+力扣刷题记录+华为机考准备记录
梁慢慢慢慢
leetcode算法数据结构
为了准备华为机考的刷题记录,已压线过背景:数据结构与算法零基础,此前没有刷过题,会Python。学习路线按照代码随想录的顺序刷题,刷题平台:力扣以上大致过了一遍后开始刷华为机考真题(cdsn上购买的真题,刷题平台是购买的真题中的OJ平台,也是ACM模式)总共用时1个月。完成情况:力扣80个题+华为2024年机考真题。大部分题目都只做过1次,掌握得很不牢固,机考的时候也是压线过。时间比较紧急,做到后
- “八股文”在程序员面试中的价值:助力还是阻力?
精神阿祝
尝鲜面试职场和发展
文章目录引言1.什么是“八股文”?2.“八股文”的支持者观点2.1理论基础的重要性2.2规范与标准化2.3应对突发问题3.“八股文”的反对者观点3.1实战经验的重视3.2忽视创新与灵活性3.3学习成本与心理压力4.八股文的具体内容分析4.1数据结构与算法4.1.1数据结构的重要性4.1.2算法的应用4.2系统设计4.2.1系统的架构设计4.2.2高并发处理4.3编程语言基础4.4框架与工具的使用5
- 邓俊辉数据结构与算法学习笔记-第五章
xiaodidadada
数据结构与算法
文章目录树aa1树a2应用a3有根树a4有序树a5路径a6连通图无环图a7深度层次b在计算机中表示b1树的表示b2父节点b3孩子节点b4父亲孩子表示法b5长子兄弟表示法c二叉树c1二叉树概述c2真二叉树c3描述多叉树d二叉树d1BinNode类d2BinNode接口d3BinTree类d4高度更新d5节点插入e相关算法e1-1先序遍历转化策略e1-2遍历规则e1-3递归实现e1-4迭代实现e1-5
- 【数据结构与算法 | 每日一题力扣篇】
Vez'nan的幸福生活
leetcode算法职场和发展
1.力扣3174:清楚数字1.1题目:给你一个字符串s。你的任务是重复以下操作删除所有数字字符:删除第一个数字字符以及它左边最近的非数字字符。请你返回删除所有数字字符以后剩下的字符串。示例1:输入:s="abc"输出:"abc"解释:字符串中没有数字。示例2:输入:s="cb34"输出:""解释:一开始,我们对s[2]执行操作,s变为"c4"。然后对s[1]执行操作,s变为""。提示:1deque
- 【数据结构与算法 | 基础篇】模拟LinkedList实现的链表(无哨兵)
Vez'nan的幸福生活
java数据结构算法
1.前言我们将LinkdList视作链表,底层设计了内部类Node类,我这里依然没有用到泛型,其实加上泛型依然很简单,即将Node节点的数据域的类型由Int转换为E(),我在此不做赘述.同时实现了增删查改,遍历等操作.2.链表(无哨兵)的代码实现publicclassLinkListTestimplementsIterable{//头指针staticNodehead;//内部类privatesta
- 数据结构与算法Day25----字符串匹配(一):借助哈希算法实现
墨殇染泪
一、主串和模式串: 假设在字符串A中查找字符串B,那字符串A就是主串,字符串B就是模式串。把主串的长度记作,模式串的长度记作。因为是在主串中查找模式串,所以。二、暴力匹配算法/朴素匹配算法/BF(BruteForce)算法:1、算法思想: 在主串中,检查起始位置分别是0、1、2···且长度为的个子串,看有没有跟模式串匹配的。2、图示:3、时间复杂度: 在极端情况下,每次都比对个字符,要比对次
- Java学习 - 数据结构与算法 - 有序数组去重详解
泡芙萝莉酱
Javajava学习开发语言算法数据结构
问题给定一个有序数组,要删除数组重复出现的元素,使得每个元素只出现一次,然后返回移除重复数组后的新长度;示例:假设给定一个数组nums=[1,2,4,4],删除重复出现的元素4后,原数组变成nums=[1,2,4],此时新的数组长度为3;解决思路数组原地操作数组原地操作,此时无需创建新的数组,只需要在原来的数组上操作即可。相当于首先要找到数组中重复的元素,然后将重复的元素移除,此时就涉及到数组中的
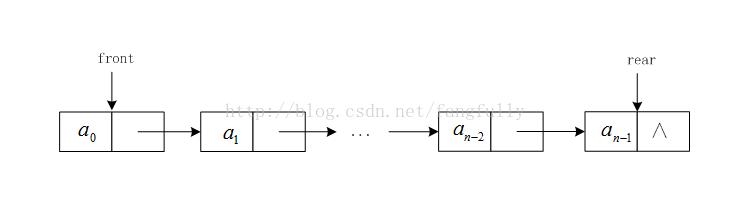
- 4. 数据结构与算法:双端队列-
sszhang
双端队列(deque,全名double-endedqueue)是一种具有队列和栈性质的线性数据结构。双端队列也拥有两端:队首(front)、队尾(rear),但与队列不同的是,插入操作在两端(队首和队尾)都可以进行,删除操作也一样。deque()创建双端队列addFront(item)向队首插入项addRear(item)向队尾插入项removeFront()返回队首的项,并从双端队列中删除该项r
- github源码指引:共享内存、数据结构与算法:字符串池StringPool
初级代码游戏
github源码指引共享内存数据结构与算法github共享内存字符串池
初级代码游戏的专栏介绍与文章目录-CSDN博客我的github:codetoys,所有代码都将会位于ctfc库中。已经放入库中我会指出在库中的位置。这些代码大部分以Linux为目标但部分代码是纯C++的,可以在任何平台上使用。专题:共享内存、数据结构与算法_初级代码游戏的博客-CSDN博客本文讲解字符串池的示例代码。字符串池是一个特殊的结构,用来减少重复的字符串存储(现实系统中会存在大量重复的字符
- 数据结构与算法之哈希表(C语言版)
jiangzhangha
算法与数据结构学习笔记算法哈希表
title:数据结构与算法之哈希表(C语言版)date:2020-07-1921:05:15categories:数据结构与算法tags:-数据结构-算法-哈希表-c数据结构与算法之哈希表(C语言版)哈希表支持一种最有效的检索方法:散列。由于计算哈希值和在数组中进行索引都只消耗固定的时间,因此哈希表最大的亮点在于其是一种运行时间在常量级别的检索方法。绝大多数的哈希函数会将一些不同的键映射到表中相同
- 数据结构与算法关系(中):如何评判一个算法的好坏
MobotStone
大家好,我是MicroStone,一个曾在三家世界500强企业担任要职的一线互联网工程师。上一节,我们了解到算法的一些特征,想必大家都掌握了算法设计要求,在学习或工作中根据业务需求设计要设计一个算法,我们要如何评估一个算法的好坏呐?下面我们来看看算法的度量方式。1、算法的效率度量方法我们知道一个算法的效率,抛开性能这些,其实值得注意的就是算法的执行时间,同一台机器上,我们使用相同数据集,利用计算机
- 聊聊自学数据结构与算法
莫天幽
数据结构算法
聊聊自学数据结构与算法大家好,我是莫幽天很高兴你能够阅读到我的文章。说道自学算法,不知道你是带着一个什么样的心情来学习,我呢是觉得基础太重要了。所以又来尝试深入的学习数据结构与算法。为什么这么说呢,我是一名Java开发的程序猿,现在jdk已经出到18了(时间北京时间:2021-07-28),但是呢开发一般还在用jdk8。一般的Java程序猿也就了解个jdk8的特性。上层变化的太快,想记忆需要长期持
- github源码指引:共享内存、数据结构与算法:平衡二叉树set带有互斥接口的
初级代码游戏
github源码指引共享内存数据结构与算法github哈希算法算法共享内存
初级代码游戏的专栏介绍与文章目录-CSDN博客我的github:codetoys,所有代码都将会位于ctfc库中。已经放入库中我会指出在库中的位置。这些代码大部分以Linux为目标但部分代码是纯C++的,可以在任何平台上使用。目录一、演示代码二、互斥层的实现2.1简单的互斥层实现2.2完整互斥接口的实现2.2.1互斥对象放在哪里2.2.2迭代器的互斥2.2.3方法的互斥三、互斥层的设计思想一、演示
- github源码指引:共享内存、数据结构与算法:平衡二叉树set的lower_bound
初级代码游戏
github源码指引共享内存数据结构与算法github哈希算法算法
初级代码游戏的专栏介绍与文章目录-CSDN博客我的github:codetoys,所有代码都将会位于ctfc库中。已经放入库中我会指出在库中的位置。这些代码大部分以Linux为目标但部分代码是纯C++的,可以在任何平台上使用。本篇专门讲解lower_bound的实现。目录一、STL的lower_bound和upper_bound是什么二、二叉树有没有lower_bound三、演示代码3.1定义数据
- java篇 常用工具类 0x03:Iterator 与 Iterable 接口
Kevin骑熊猫打老虎
javajava
文章目录Iterator接口Iterable接口手动实现Iterable接口示例Iterator接口Iterator接口在java.util包中。实现了Iterator接口的类就可以支持遍历操作。publicinterfaceIterator{//只需要关注到这两个抽象方法booleanhasNext();//还有没有下一个元素Enext();//返回下一个元素}Iterable接口Iterabl
- 编程练习题目集【目录】
绯樱殇雪
目录PTAc++javapat考试
所有负面情绪都源于你的弱小,唯有强大自己才能够百毒不侵。文章目录一、PTA1.练习(1)中国大学MOOC-陈越、何钦铭-数据结构-起步能力自测题(2)DataStructuresandAlgorithms(English)(3)数据结构与算法题目集(中文)(4)团体程序设计天梯赛-练习集(5)基础编程题目集①函数题②编程题2.考试(1)PAT(BasicLevel)Practice(中文)(2)P
- github源码指引:共享内存、数据结构与算法:作为基础的数组
初级代码游戏
github源码指引共享内存数据结构与算法github共享内存数据结构算法可扩展数组
初级代码游戏的专栏介绍与文章目录-CSDN博客我的github:codetoys,所有代码都将会位于ctfc库中。已经放入库中我会指出在库中的位置。这些代码大部分以Linux为目标但部分代码是纯C++的,可以在任何平台上使用。相关专题:共享内存、数据结构与算法_初级代码游戏的博客-CSDN博客源码位置:shmfc基础:github源码指引:源码结构、编译、运行_github编译-CSDN博客目录一
- 驾驭高效编程:一探C++ STL的奥秘
一叶之秋1412
c++开发语言
1.什么是STL2.:STL的版本2.1:原始版本2.2:P.J版本2.3:RW版本2.4:SGI版本3:STL的六大组件4:如何学习STL5:STL的缺陷1.什么是STLSTL(standdardtemplatelibrary-标准模板库):是C++标准库的重要组成部分,不仅是一个可复用的组件库,而且是一个包含数据结构与算法软件框架.2.:STL的版本2.1:原始版本AlexanderStepa
- 【数据结构与算法】从左到右快速幂和从右到左快速幂
星眺北海
数据结构与算法算法快速幂
引出问题在计算机科学中,幂运算是一种非常常见且基础的操作,尤其是在涉及到大数运算时,幂运算的效率对整个计算过程至关重要。设想以下场景:在加密算法中,如RSA算法,常常需要计算大数的幂,且这种计算必须在一定时间内完成,以确保安全性。在数值计算中,我们可能需要反复进行大规模的幂运算,如果采用最直接的计算方法,其计算量和时间将非常庞大。如果我们采用朴素的计算方法,例如计算aba^bab时,通过不断相乘a
- Java开发中,spring mvc 的线程怎么调用?
小麦麦子
springmvc
今天逛知乎,看到最近很多人都在问spring mvc 的线程http://www.maiziedu.com/course/java/ 的启动问题,觉得挺有意思的,那哥们儿问的也听仔细,下面的回答也很详尽,分享出来,希望遇对遇到类似问题的Java开发程序猿有所帮助。
问题:
在用spring mvc架构的网站上,设一线程在虚拟机启动时运行,线程里有一全局
- maven依赖范围
bitcarter
maven
1.test 测试的时候才会依赖,编译和打包不依赖,如junit不被打包
2.compile 只有编译和打包时才会依赖
3.provided 编译和测试的时候依赖,打包不依赖,如:tomcat的一些公用jar包
4.runtime 运行时依赖,编译不依赖
5.默认compile
依赖范围compile是支持传递的,test不支持传递
1.传递的意思是项目A,引用
- Jaxb org.xml.sax.saxparseexception : premature end of file
darrenzhu
xmlprematureJAXB
如果在使用JAXB把xml文件unmarshal成vo(XSD自动生成的vo)时碰到如下错误:
org.xml.sax.saxparseexception : premature end of file
很有可能时你直接读取文件为inputstream,然后将inputstream作为构建unmarshal需要的source参数。InputSource inputSource = new In
- CSS Specificity
周凡杨
html权重Specificitycss
有时候对于页面元素设置了样式,可为什么页面的显示没有匹配上呢? because specificity
CSS 的选择符是有权重的,当不同的选择符的样式设置有冲突时,浏览器会采用权重高的选择符设置的样式。
规则:
HTML标签的权重是1
Class 的权重是10
Id 的权重是100
- java与servlet
g21121
servlet
servlet 搞java web开发的人一定不会陌生,而且大家还会时常用到它。
下面是java官方网站上对servlet的介绍: java官网对于servlet的解释 写道
Java Servlet Technology Overview Servlets are the Java platform technology of choice for extending and enha
- eclipse中安装maven插件
510888780
eclipsemaven
1.首先去官网下载 Maven:
http://www.apache.org/dyn/closer.cgi/maven/binaries/apache-maven-3.2.3-bin.tar.gz
下载完成之后将其解压,
我将解压后的文件夹:apache-maven-3.2.3,
并将它放在 D:\tools目录下,
即 maven 最终的路径是:D:\tools\apache-mave
- jpa@OneToOne关联关系
布衣凌宇
jpa
Nruser里的pruserid关联到Pruser的主键id,实现对一个表的增删改,另一个表的数据随之增删改。
Nruser实体类
//*****************************************************************
@Entity
@Table(name="nruser")
@DynamicInsert @Dynam
- 我的spring学习笔记11-Spring中关于声明式事务的配置
aijuans
spring事务配置
这两天学到事务管理这一块,结合到之前的terasoluna框架,觉得书本上讲的还是简单阿。我就把我从书本上学到的再结合实际的项目以及网上看到的一些内容,对声明式事务管理做个整理吧。我看得Spring in Action第二版中只提到了用TransactionProxyFactoryBean和<tx:advice/>,定义注释驱动这三种,我承认后两种的内容很好,很强大。但是实际的项目当中
- java 动态代理简单实现
antlove
javahandlerproxydynamicservice
dynamicproxy.service.HelloService
package dynamicproxy.service;
public interface HelloService {
public void sayHello();
}
dynamicproxy.service.impl.HelloServiceImpl
package dynamicp
- JDBC连接数据库
百合不是茶
JDBC编程JAVA操作oracle数据库
如果我们要想连接oracle公司的数据库,就要首先下载oralce公司的驱动程序,将这个驱动程序的jar包导入到我们工程中;
JDBC链接数据库的代码和固定写法;
1,加载oracle数据库的驱动;
&nb
- 单例模式中的多线程分析
bijian1013
javathread多线程java多线程
谈到单例模式,我们立马会想到饿汉式和懒汉式加载,所谓饿汉式就是在创建类时就创建好了实例,懒汉式在获取实例时才去创建实例,即延迟加载。
饿汉式:
package com.bijian.study;
public class Singleton {
private Singleton() {
}
// 注意这是private 只供内部调用
private static
- javascript读取和修改原型特别需要注意原型的读写不具有对等性
bijian1013
JavaScriptprototype
对于从原型对象继承而来的成员,其读和写具有内在的不对等性。比如有一个对象A,假设它的原型对象是B,B的原型对象是null。如果我们需要读取A对象的name属性值,那么JS会优先在A中查找,如果找到了name属性那么就返回;如果A中没有name属性,那么就到原型B中查找name,如果找到了就返回;如果原型B中也没有
- 【持久化框架MyBatis3六】MyBatis3集成第三方DataSource
bit1129
dataSource
MyBatis内置了数据源的支持,如:
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC" />
<data
- 我程序中用到的urldecode和base64decode,MD5
bitcarter
cMD5base64decodeurldecode
这里是base64decode和urldecode,Md5在附件中。因为我是在后台所以需要解码:
string Base64Decode(const char* Data,int DataByte,int& OutByte)
{
//解码表
const char DecodeTable[] =
{
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
- 腾讯资深运维专家周小军:QQ与微信架构的惊天秘密
ronin47
社交领域一直是互联网创业的大热门,从PC到移动端,从OICQ、MSN到QQ。到了移动互联网时代,社交领域应用开始彻底爆发,直奔黄金期。腾讯在过去几年里,社交平台更是火到爆,QQ和微信坐拥几亿的粉丝,QQ空间和朋友圈各种刷屏,写心得,晒照片,秀视频,那么谁来为企鹅保驾护航呢?支撑QQ和微信海量数据背后的架构又有哪些惊天内幕呢?本期大讲堂的内容来自今年2月份ChinaUnix对腾讯社交网络运营服务中心
- java-69-旋转数组的最小元素。把一个数组最开始的若干个元素搬到数组的末尾,我们称之为数组的旋转。输入一个排好序的数组的一个旋转,输出旋转数组的最小元素
bylijinnan
java
public class MinOfShiftedArray {
/**
* Q69 旋转数组的最小元素
* 把一个数组最开始的若干个元素搬到数组的末尾,我们称之为数组的旋转。输入一个排好序的数组的一个旋转,输出旋转数组的最小元素。
* 例如数组{3, 4, 5, 1, 2}为{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}的一个旋转,该数组的最小值为1。
*/
publ
- 看博客,应该是有方向的
Cb123456
反省看博客
看博客,应该是有方向的:
我现在就复习以前的,在补补以前不会的,现在还不会的,同时完善完善项目,也看看别人的博客.
我刚突然想到的:
1.应该看计算机组成原理,数据结构,一些算法,还有关于android,java的。
2.对于我,也快大四了,看一些职业规划的,以及一些学习的经验,看看别人的工作总结的.
为什么要写
- [开源与商业]做开源项目的人生活上一定要朴素,尽量减少对官方和商业体系的依赖
comsci
开源项目
为什么这样说呢? 因为科学和技术的发展有时候需要一个平缓和长期的积累过程,但是行政和商业体系本身充满各种不稳定性和不确定性,如果你希望长期从事某个科研项目,但是却又必须依赖于某种行政和商业体系,那其中的过程必定充满各种风险。。。
所以,为避免这种不确定性风险,我
- 一个 sql优化 ([精华] 一个查询优化的分析调整全过程!很值得一看 )
cwqcwqmax9
sql
见 http://www.itpub.net/forum.php?mod=viewthread&tid=239011
Web翻页优化实例
提交时间: 2004-6-18 15:37:49 回复 发消息
环境:
Linux ve
- Hibernat and Ibatis
dashuaifu
Hibernateibatis
Hibernate VS iBATIS 简介 Hibernate 是当前最流行的O/R mapping框架,当前版本是3.05。它出身于sf.net,现在已经成为Jboss的一部分了 iBATIS 是另外一种优秀的O/R mapping框架,当前版本是2.0。目前属于apache的一个子项目了。 相对Hibernate“O/R”而言,iBATIS 是一种“Sql Mappi
- 备份MYSQL脚本
dcj3sjt126com
mysql
#!/bin/sh
# this shell to backup mysql
#
[email protected] (QQ:1413161683 DuChengJiu)
_dbDir=/var/lib/mysql/
_today=`date +%w`
_bakDir=/usr/backup/$_today
[ ! -d $_bakDir ] && mkdir -p
- iOS第三方开源库的吐槽和备忘
dcj3sjt126com
ios
转自
ibireme的博客 做iOS开发总会接触到一些第三方库,这里整理一下,做一些吐槽。 目前比较活跃的社区仍旧是Github,除此以外也有一些不错的库散落在Google Code、SourceForge等地方。由于Github社区太过主流,这里主要介绍一下Github里面流行的iOS库。 首先整理了一份
Github上排名靠
- html wlwmanifest.xml
eoems
htmlxml
所谓优化wp_head()就是把从wp_head中移除不需要元素,同时也可以加快速度。
步骤:
加入到function.php
remove_action('wp_head', 'wp_generator');
//wp-generator移除wordpress的版本号,本身blog的版本号没什么意义,但是如果让恶意玩家看到,可能会用官网公布的漏洞攻击blog
remov
- 浅谈Java定时器发展
hacksin
java并发timer定时器
java在jdk1.3中推出了定时器类Timer,而后在jdk1.5后由Dou Lea从新开发出了支持多线程的ScheduleThreadPoolExecutor,从后者的表现来看,可以考虑完全替代Timer了。
Timer与ScheduleThreadPoolExecutor对比:
1.
Timer始于jdk1.3,其原理是利用一个TimerTask数组当作队列
- 移动端页面侧边导航滑入效果
ini
jqueryWebhtml5cssjavascirpt
效果体验:http://hovertree.com/texiao/mobile/2.htm可以使用移动设备浏览器查看效果。效果使用到jquery-2.1.4.min.js,该版本的jQuery库是用于支持HTML5的浏览器上,不再兼容IE8以前的浏览器,现在移动端浏览器一般都支持HTML5,所以使用该jQuery没问题。HTML文件代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<h
- AspectJ+Javasist记录日志
kane_xie
aspectjjavasist
在项目中碰到这样一个需求,对一个服务类的每一个方法,在方法开始和结束的时候分别记录一条日志,内容包括方法名,参数名+参数值以及方法执行的时间。
@Override
public String get(String key) {
// long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
// System.out.println("Be
- redis学习笔记
MJC410621
redisNoSQL
1)nosql数据库主要由以下特点:非关系型的、分布式的、开源的、水平可扩展的。
1,处理超大量的数据
2,运行在便宜的PC服务器集群上,
3,击碎了性能瓶颈。
1)对数据高并发读写。
2)对海量数据的高效率存储和访问。
3)对数据的高扩展性和高可用性。
redis支持的类型:
Sring 类型
set name lijie
get name lijie
set na
- 使用redis实现分布式锁
qifeifei
在多节点的系统中,如何实现分布式锁机制,其中用redis来实现是很好的方法之一,我们先来看一下jedis包中,有个类名BinaryJedis,它有个方法如下:
public Long setnx(final byte[] key, final byte[] value) {
checkIsInMulti();
client.setnx(key, value);
ret
- BI并非万能,中层业务管理报表要另辟蹊径
张老师的菜
大数据BI商业智能信息化
BI是商业智能的缩写,是可以帮助企业做出明智的业务经营决策的工具,其数据来源于各个业务系统,如ERP、CRM、SCM、进销存、HER、OA等。
BI系统不同于传统的管理信息系统,他号称是一个整体应用的解决方案,是融入管理思想的强大系统:有着系统整体的设计思想,支持对所有
- 安装rvm后出现rvm not a function 或者ruby -v后提示没安装ruby的问题
wudixiaotie
function
1.在~/.bashrc最后加入
[[ -s "$HOME/.rvm/scripts/rvm" ]] && source "$HOME/.rvm/scripts/rvm"
2.重新启动terminal输入:
rvm use ruby-2.2.1 --default
把当前安装的ruby版本设为默