知识点3-4
class和struct区别?
- C的struct与C++的class的区别
C是一种过程化的语言,struct只是作为一种复杂数据类型定义,struct中只能定义成员变量,不能定义成员函数。
- C++中的struct和class的区别
struct中成员默认是public,而class中默认是私有的
#include struct继承默认是public,而class继承默认是私有的
class Base {
public:
int x;
};
class Derived : Base { }; // is equilalent to class Derived : private Base {}
int main()
{
Derived d;
d.x = 20; // compiler error becuase inheritance is private
getchar();
return 0;
}class Base {
public:
int x;
};
struct Derived : Base { }; // is equilalent to struct Derived : public Base {}
int main()
{
Derived d;
d.x = 20; // works fine becuase inheritance is public
getchar();
return 0;
}class Base {
int x;
};
struct Derived :public Base {
void show() {
cout << x << endl;//error
}
};
int main()
{
Derived d;
d.x = 2;//error
d.show();
return 0;
}也就是说,结构体继承,原来类中私有量不能改变
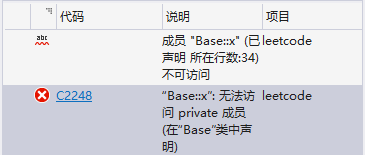
另外,类从类中继承,也是无法访问私有成员,可以访问protected成员
class Base {
private:
int x;
protected:
int y;
};
class Derived :public Base {
public:
void show() {
cout << y << endl;//ok
cout << x << endl;//error
}
};
int main()
{
Derived d;
//d.x = 2;//error
d.show();
return 0;
}逗号表达式
逗号运算符,优先级别最低,( a= 3 * 5, a * 4),先算第一个,再算第二个,最后结果为第二个式子的值。
int main(){
int a;
cout << ( a= 3 * 5, a * 4) << endl;
return 0;
}字符串结尾问题
int main(){
char a[2] = { 's','b' };
char a2[4] = { 's','b' };
char b[4] = "aa";
char *p = "aauu";
cout << a2[2] << endl;
cout << sizeof(a) << endl;
cout << sizeof(a2) << endl;
cout << sizeof(b) << endl;
cout << sizeof(p) << endl;
cout << sizeof("aa") << endl;
return 0;
}对于字符数组,如果存放形式为{‘a’,’b’},其末尾不包含’\0’
如果是数组,定义了几个,那么最终,sizeof的数值就是几
指针和引用的区别
相同点:
1. 都是地址的概念;
指针指向一块内存,它的内容是所指内存的地址;引用是某块内存的别名。
区别:
1. 指针是一个实体,而引用仅是个别名;
2. 引用使用时无需解引用(*),指针需要解引用;
3. 引用只能在定义时被初始化一次,之后不可变;指针可变;
4. 引用没有 const,指针有 const;
5. 引用不能为空,指针可以为空;
6. “sizeof 引用”得到的是所指向的变量(对象)的大小,而“sizeof 指针”得到的是指针本身(所指向的变量或对象的地址)的大小;
int main() {
char c = 'e';
char *p = &c;
cout << sizeof(c) << endl;
cout << sizeof(p) << endl;
return 0;
}
7. 指针和引用的自增(++)运算意义不一样;
8.从内存分配上看:程序为指针变量分配内存区域,而引用不需要分配内存区域。
逗号运算符
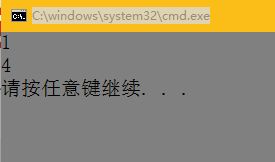
int main() {
int sum, pad, pAd;
sum = pad = 5;
//pAd = ++sum, pAd++, ++pad;
pAd = ++sum, pAd ++, ++pad;
printf("%d\n", pAd);
return 0;
}const问题
char * const p, char const * p, const char *p
再联系到本题给定声明 const char * const * pp; 多重const
其中的一篇解释较为优秀,分享出来。其中主要意思就是const的作用就是限定一个对象为只读属性
const char p 限定变量p为只读,则p=2错误。
const char *p p是一个指向char类型的指针,const 限定p指向的对象只读,但是没有限定p
char * const p,此时限定p只读,p=&a或者p++都是错误的,但是*p=3可以
const char* const p 两者皆是只读
同理,对于二级指针来看:
const char **p,限定 **p 也就是最终对象只读,而p++,*p=&.. 是合理的
const char* const *p ,限定最终对象以及p指向的指针只读
const char* const* const p,全部只读,不可更改