自己编写的基2时域抽取FFT、IFFT的C++实现代码,另附DFT与IDFT的原始实现
介绍
网络上的原理介绍非常丰富,具体请自行搜索网络资源。
本算法依靠FFT流图进行布置。
算法 ##
进行完所有的原理推导后,我们可以得到如下的16点FFT流图:

通过上图可以看出整个流图输入序列的顺序已经被颠倒,这实际上是输入序列中元素的序号进行了比特位的逆序排列,即其二进制比特位发生了镜像,例如001变为了100。另外一共有三个镶嵌的循环。
为了实现输入序列的比特逆序排列,要使用雷德算法进行实现。
下面进行FFT算法的核心讲解:
第一层循环:

第二层循环:

第三层循环:
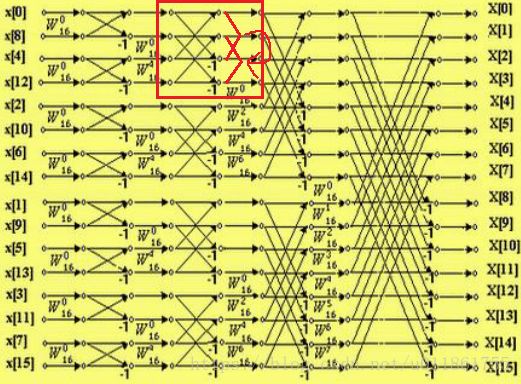
每一次循环中的蝴蝶运算操作请参阅网络资源。
FFT和IFFT的结果与DFT和IDFT的结果有一定的偏差,且由于计算机计算的精度关系,反变换结果与原始输入序列不一定完全相同。
下面给出代码:
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
double PI = 3.1415926535897933;
//定义复数结构体
typedef struct complex_number
{
double real;
double imagine;
}complex_number;
//定义旋转因子
complex_number omega_num(int k, int n, int input_length);
complex_number omega_num(int k, int n, int input_length)
{
//k是傅里叶变换结果的序号
//n是求解DFT时的序号
//input_length是输入序列的长度
complex_number omega_num;
omega_num.real = cos(-2 * PI * k * n / input_length);
omega_num.imagine = sin(-2 * PI * k * n / input_length);
return omega_num;
}
//定义复数乘法的函数
complex_number complex_multiply(complex_number a, complex_number b);
complex_number complex_multiply(complex_number a, complex_number b)
{
complex_number result;
result.real = a.real*b.real - a.imagine*b.imagine;
result.imagine = a.real*b.imagine + a.imagine*b.real;
return result;
}
void main()
{
//FFT - 快速傅里叶变换!
//初始化 - 常量、变量的定义。
const int input_length = 4;//输入数组的长度
double input[input_length] = { 1,2,3,4 };
//将输入数组进行比特倒位排列 - 雷德算法
for (int j = 0, i = 0; i < input_length - 1; i++)//这里实现了奇偶前后分开排序
{
int k;
if (i < j)//如果i
{
double temp;
temp = input[j];
input[j] = input[i];
input[i] = temp;
}
k = input_length / 2;//求j的下一个倒位序
while (j >= k)//如果k<=j,表示j的最高位为1
{
j = j - k;//把最高位变成0
k = k / 2;//k/2,比较次高位,依次类推,逐个比较,直到某个位为0
}
j = j + k;
}
////显示比特逆排序的结果
//比特逆序数结束后,原输入序列已经发生改变~~~,如果要用原始DFT公式进行FFT的验算,则需要将原始输入序列重新定义。
//核心部分:FFT迭代-------------------------------------------------------------------
int EachLayer_length;//蝶形运算数量。每执行一次外循环时,每个区域的蝶形运算器的数量的2倍
complex_number FFT_Output[input_length];
//由于最底层的输入是实数,而输出也是实数,所以单独拿出来进行循环
//最底层
for (int a = 0; a < input_length; a += 2)
{
double temp;
temp = input[a];
input[a] = input[a] + input[a + 1];//注意这一步完成以后input[a]的值将改变,必须将原始input[a]的值放在临时变量中保存。
input[a + 1] = temp - input[a + 1];
}
//显示最底层的计算结果
//for (int i = 0; i < input_length; i++)
//{
// cout << input[i] << endl;
//}
//将最底层计算出的结果全部赋值给FFT输出变量,即FFT_Output
for (int b = 0; b < input_length; b++)
{
FFT_Output[b].real = input[b];
FFT_Output[b].imagine = 0;
}
//从倒数第二层开始循环,保证所有的输入与输出都是复数
for (int s = 2; s <= log(input_length) / log(2); s++)
{
EachLayer_length = (int)pow(2, s);//每一次最外层循环时,每层的蝶形运算数量,是蝶形运算器数量的2倍。
for (int m = 0; m < input_length; m = m + EachLayer_length)
{
for (int n = 0; n < EachLayer_length / 2; n++)
{
complex_number temp;//定义临时复数变量。
//蝶形运算
temp.real = FFT_Output[m + n].real;
temp.imagine = FFT_Output[m + n].imagine;
FFT_Output[m + n].real = FFT_Output[m + n].real + complex_multiply(FFT_Output[m + n + EachLayer_length / 2], omega_num(1, n*input_length/(1 << s), input_length)).real;
FFT_Output[m + n].imagine = FFT_Output[m + n].imagine + complex_multiply(FFT_Output[m + n + EachLayer_length / 2], omega_num(1, n*input_length / (1 << s), input_length)).imagine;
FFT_Output[m + n + EachLayer_length / 2].real = temp.real - complex_multiply(FFT_Output[m + n + EachLayer_length / 2], omega_num(1, n*input_length / (1 << s), input_length)).real;
FFT_Output[m + n + EachLayer_length / 2].imagine = temp.imagine - complex_multiply(FFT_Output[m + n + EachLayer_length / 2], omega_num(1, n*input_length / (1 << s), input_length)).imagine;
}
}
}
EachLayer_length = 0;//为后面的IFFT使用而将该变量置零。
cout << "FFT变换结果为:\n";
for (int q = 0; q < input_length; q++)
{
if (FFT_Output[q].imagine < 0)
cout << FFT_Output[q].real << FFT_Output[q].imagine << "i" << endl;
else if (FFT_Output[q].imagine == 0)
cout << FFT_Output[q].real << endl;
else
cout << FFT_Output[q].real << "+" << FFT_Output[q].imagine << "i" << endl;
}
cout << endl;
//IFFT - 快速傅里叶逆变换!具体的循环原理请参照IFFT流图。
//直接将FFT的输出结果作为输入,输入到FFT算法中,输出结果的实部就是IFFT的实序列。
//定义需要使用的变量
complex_number IFFT_Input[input_length];//IFFT的输入序列
complex_number IFFT_Output[input_length];//IFFT的输出序列
//将上文中FFT的计算结果全部赋给IFFT_Input,并对IFFT_Input的虚部取共轭;
for (int a = 0; a < input_length; a++)
{
IFFT_Input[a].real = FFT_Output[a].real;
IFFT_Input[a].imagine = -FFT_Output[a].imagine;
}
//对输入的复数序列进行比特逆序排序 - 雷德算法
//首先对输入序列的实数部分进行排序
for (int j = 0, i = 0; i < input_length - 1; i++)
{
int k;
if (i < j)
{
complex_number temp;
temp = IFFT_Input[j];
IFFT_Input[j] = IFFT_Input[i];
IFFT_Input[i] = temp;
}
k = input_length / 2;
while (j >= k)
{
j = j - k;
k = k / 2;
}
j = j + k;
}
//核心部分:IFFT迭代,与FFT迭代一模一样-------------------------------------------------
//从倒数第一层开始循环
for (int s = 1; s <= log(input_length) / log(2); s++)
{
EachLayer_length = (int)pow(2, s);//每一次最外层循环时,每层的蝶形运算数量,是蝶形运算器数量的2倍。
for (int m = 0; m < input_length; m = m + EachLayer_length)
{
for (int n = 0; n < EachLayer_length / 2; n++)
{
complex_number temp;//定义临时复数变量。
//蝶形运算
temp.real = IFFT_Input[m + n].real;
temp.imagine = IFFT_Input[m + n].imagine;
IFFT_Input[m + n].real = IFFT_Input[m + n].real + complex_multiply(IFFT_Input[m + n + EachLayer_length / 2], omega_num(1, n*input_length / (1 << s), input_length)).real;
IFFT_Input[m + n].imagine = IFFT_Input[m + n].imagine + complex_multiply(IFFT_Input[m + n + EachLayer_length / 2], omega_num(1, n*input_length / (1 << s), input_length)).imagine;
IFFT_Input[m + n + EachLayer_length / 2].real = temp.real - complex_multiply(IFFT_Input[m + n + EachLayer_length / 2], omega_num(1, n*input_length / (1 << s), input_length)).real;
IFFT_Input[m + n + EachLayer_length / 2].imagine = temp.imagine - complex_multiply(IFFT_Input[m + n + EachLayer_length / 2], omega_num(1, n*input_length / (1 << s), input_length)).imagine;
}
}
}
//将计算完成的结果赋给输出序列IFFT_Output并显示结果
cout << "IFFT结果:\n";
for (int c = 0; c < input_length; c++)
{
IFFT_Output[c].real = IFFT_Input[c].real / input_length;
cout << IFFT_Output[c].real << endl;
}
cout << endl;
//应用原始DFT公式对FFT算法进行验算
const int input_length1 = 4;
double input1[input_length1] = { 1,2,3,4 };
complex_number DFT_sum, DFT_Output[input_length1];
for (int k = 0; k < input_length1; k++)
{
DFT_sum.real = DFT_sum.imagine = 0;
for (int n = 0; n < input_length1; n++)
{
DFT_sum.real += input1[n] * omega_num(k, n, input_length1).real;
DFT_sum.imagine += input1[n] * omega_num(k, n, input_length1).imagine;
}
DFT_Output[k].real = DFT_sum.real;
DFT_Output[k].imagine = DFT_sum.imagine;
}
cout << "DFT变换结果为:\n";
for (int q = 0; q < input_length1; q++)
{
if (DFT_Output[q].imagine < 0)
cout << DFT_Output[q].real << DFT_Output[q].imagine << "i" << endl;
else if (DFT_Output[q].imagine == 0)
cout << DFT_Output[q].real << endl;
else
cout << DFT_Output[q].real << "+" << DFT_Output[q].imagine << "i" << endl;
}
cout << endl;
//下面进行IDFT
double output_IDFT[input_length1], IDFT_sum;
for (int n = 0; n < input_length1; n++)
{
IDFT_sum = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < input_length1; k++)
{
//这里一定注意复数与复数相乘的法则,不仅要将实数部分相乘,由于i*i=-1,所以还要减去虚数部分相乘的结果!
IDFT_sum += DFT_Output[k].real*omega_num(k, -n, input_length1).real - DFT_Output[k].imagine*omega_num(k, -n, input_length1).imagine;
}
output_IDFT[n] = IDFT_sum / input_length1;
}
cout << "IDFT变换结果为:\n";
for (int q = 0; q < input_length1; q++)
cout << output_IDFT[q] << endl;
cout << endl;
}