高级数据结构
#include
#define TRIE_MAX_CHAR_NUM 26
struct TrieNode{
TrieNode *child[TRIE_MAX_CHAR_NUM];
bool is_end;
TrieNode() : is_end(false){
for (int i = 0; i < TRIE_MAX_CHAR_NUM; i++){
child[i] = 0;
}
}
};
int main(){
TrieNode root;
TrieNode n1;
TrieNode n2;
TrieNode n3;
root.child['a'-'a'] = &n1;//用1-26表示26个字符
root.child['b'-'a'] = &n2;
root.child['e'-'a'] = &n3;
n2.is_end = true;
TrieNode n4;
TrieNode n5;
TrieNode n6;
n1.child['b'-'a'] = &n4;
n2.child['c'-'a'] = &n5;
n3.child['f'-'a'] = &n6;
TrieNode n7;
TrieNode n8;
TrieNode n9;
TrieNode n10;
n4.child['c'-'a'] = &n7;
n4.child['d'-'a'] = &n8;
n5.child['d'-'a'] = &n9;
n6.child['g'-'a'] = &n10;
n7.is_end = true;
n8.is_end = true;
n9.is_end = true;
n10.is_end = true;
TrieNode n11;
n7.child['d'-'a'] = &n11;
n11.is_end = true;
preorder_trie(&root, 0);
return 0;
}
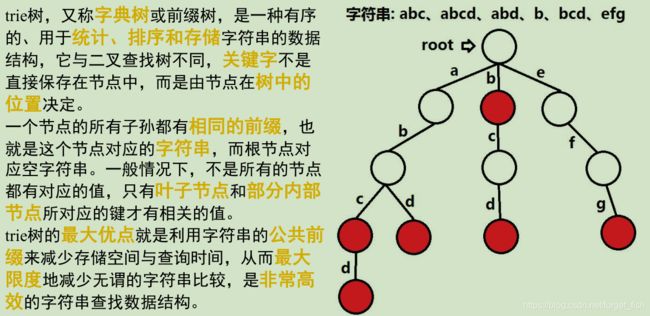
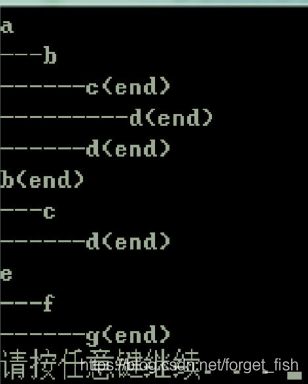
一、TRIE树的实现 LeetCode 208
题目:
实现一个 Trie (前缀树),包含 insert, search, 和 startsWith 这三个操作。
示例:
Trie trie = new Trie();
trie.insert(“apple”);
trie.search(“apple”); // 返回 true
trie.search(“app”); // 返回 false
trie.startsWith(“app”); // 返回 true
trie.insert(“app”);
trie.search(“app”); // 返回 true
说明:
你可以假设所有的输入都是由小写字母 a-z 构成的。
保证所有输入均为非空字符串。
插入思路:
单词搜索思路:

前缀搜索思路: 与单词搜索类似,不过前缀搜完就为真,不用再判断是否是一个单词的结尾
#define TRIE_MAX_CHAR_NUM 26
struct TrieNode{
TrieNode *child[TRIE_MAX_CHAR_NUM];
bool is_end;
TrieNode(): is_end(false){
for(int i=0;ichild[pos]){//如果不存在则新建该序号的节点
ptr->child[pos] = new_node();
}
ptr = ptr->child[pos];//ptr指向下一个字符的位置
word++;//word指针指向下一个字符
}
ptr->is_end = true;//一个单词结束在改单词最后一个字符所在节点的is_end标true
}
/** Returns if the word is in the trie. */
bool search(const char *word) {
TrieNode *ptr = &_root;
while(*word){
int pos = *word - 'a';
if(!ptr->child[pos])//树中不存在该字符则直接返回false
return false;
ptr = ptr->child[pos];
word++;
}
return ptr->is_end;//如果单词结束则返回最后一个字符的is_end,是最后一个字符则为真,否则为假
}
/** Returns if there is any word in the trie that starts with the given prefix. */
bool startsWith(const char *prefix) {//前缀查询和单词查询类似,只是前缀查询结束不用再查询单词是否结束,查询结束则为真
TrieNode *ptr = &_root;
while(*prefix){
int pos = *prefix - 'a';
if(!ptr->child[pos])
return false;
ptr = ptr->child[pos];
prefix++;
}
return true;
}
private:
TrieNode *new_node(){
TrieNode *node = new TrieNode();
_node_vec.push_back(node);
return node;
}
vector _node_vec;
TrieNode _root;
};
class Trie {
public:
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
Trie() {
}
/** Inserts a word into the trie. */
void insert(string word) {
_trie_tree.insert(word.c_str());
}
/** Returns if the word is in the trie. */
bool search(string word) {
return _trie_tree.search(word.c_str());
}
/** Returns if there is any word in the trie that starts with the given prefix. */
bool startsWith(string prefix) {
return _trie_tree.startsWith(prefix.c_str());
}
private:
TrieTree _trie_tree;
};
/**
* Your Trie object will be instantiated and called as such:
* Trie obj = new Trie();
* obj.insert(word);
* bool param_2 = obj.search(word);
* bool param_3 = obj.startsWith(prefix);
*/
二、添加与搜索单词 - 数据结构设计 LeetCode 211
题目:
设计一个支持以下两种操作的数据结构:
void addWord(word)
bool search(word)
search(word) 可以搜索文字或正则表达式字符串,字符串只包含字母 . 或 a-z 。 . 可以表示任何一个字母。
示例:
addWord(“bad”)
addWord(“dad”)
addWord(“mad”)
search(“pad”) -> false
search(“bad”) -> true
search(".ad") -> true
search(“b…”) -> true
说明:
你可以假设所有单词都是由小写字母 a-z 组成的。
思路:
添加单词与上一题一样,逐个遍历单词中的字符如果不存在则添加新的节点,直至单词结束;查询如图
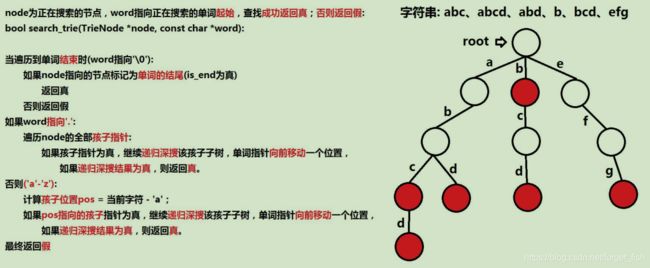
#define TRIE_MAX_CHAR_NUM 26
struct TrieNode{
TrieNode *child[TRIE_MAX_CHAR_NUM];
bool is_end;
TrieNode(): is_end(false){
for(int i=0;ichild[pos]){//如果不存在则新建该序号的节点
ptr->child[pos] = new_node();
}
ptr = ptr->child[pos];//ptr指向下一个字符的位置
word++;//word指针指向下一个字符
}
ptr->is_end = true;//一个单词结束在改单词最后一个字符所在节点的is_end标true
}
/** Returns if the word is in the trie. */
bool search_trie(TrieNode *node, const char *word){
if(*word=='\0'){
return node->is_end; //单词结束返回当前的is_end
}
if(*word=='.'){//是.则递归遍历该点之后的所有节点
for(int i=0; ichild[i]&&search_trie(node->child[i], word+1)){
return true;
}
}
}
else{
int pos = *word-'a';
if(node->child[pos] && search_trie(node->child[pos], word+1)){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
TrieNode *root(){
return &_root;
}
private:
TrieNode *new_node(){
TrieNode *node = new TrieNode();
_node_vec.push_back(node);
return node;
}
vector _node_vec;
TrieNode _root;
};
class WordDictionary {
public:
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
WordDictionary() {
}
/** Adds a word into the data structure. */
void addWord(string word) {
_trie_tree.insert(word.c_str());
}
/** Returns if the word is in the data structure. A word could contain the dot character '.' to represent any one letter. */
bool search(string word) {
return _trie_tree.search_trie(_trie_tree.root(),word.c_str());
}
private:
TrieTree _trie_tree;
};
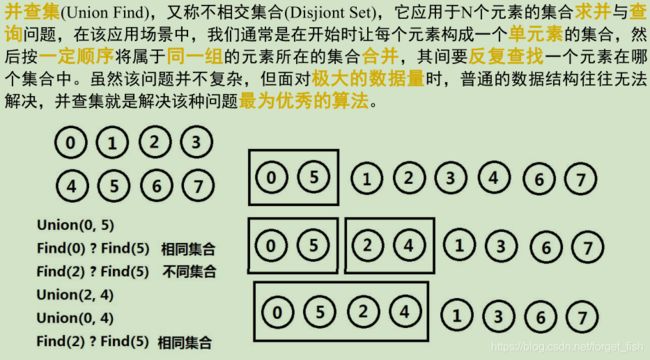
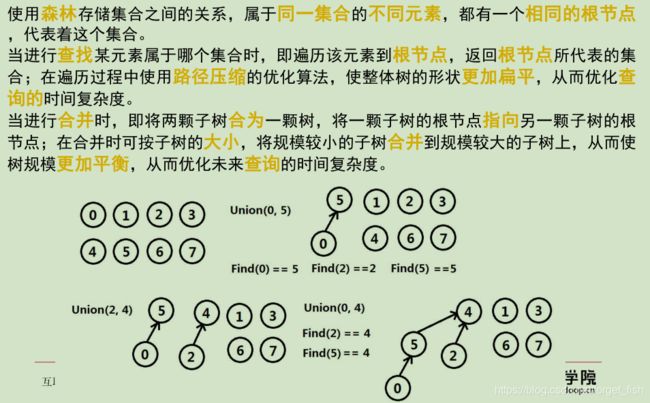
三、朋友圈 LeetCode 547
题目:
班上有 N 名学生。其中有些人是朋友,有些则不是。他们的友谊具有是传递性。如果已知 A 是 B 的朋友,B 是 C 的朋友,那么我们可以认为 A 也是 C 的朋友。所谓的朋友圈,是指所有朋友的集合。
给定一个 N * N 的矩阵 M,表示班级中学生之间的朋友关系。如果M[i][j] = 1,表示已知第 i 个和 j 个学生互为朋友关系,否则为不知道。你必须输出所有学生中的已知的朋友圈总数。
示例 1:
输入:
[[1,1,0],
[1,1,0],
[0,0,1]]
输出: 2
说明:已知学生0和学生1互为朋友,他们在一个朋友圈。
第2个学生自己在一个朋友圈。所以返回2。
示例 2:
输入:
[[1,1,0],
[1,1,1],
[0,1,1]]
输出: 1
说明:已知学生0和学生1互为朋友,学生1和学生2互为朋友,所以学生0和学生2也是朋友,所以他们三个在一个朋友圈,返回1。
方法1 深搜
class Solution {
public:
int findCircleNum(vector>& M) {
vector visited(M.size(), 0);//将所有节点记录并标记为未访问
int count=0;//朋友圈个数
for(int i=0; i> &M, vector &visited){
visited[u] = 1;//表示该节点已经访问过了
for(int i = 0; i < M[u].size(); i++){
if(visited[i]==0 && M[u][i]==1){
//如果某一未访问节点与其其他节点有连接关系,则继续搜索直到搜索完所有节点
DFS_graph(i,M,visited);
}
}
}
};
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class DisjointSet{
public:
DisjointSet(int n){
for(int i=0;i _id;
};
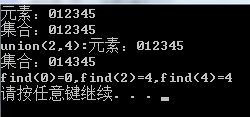
void main(){
DisjointSet dis(6);
dis.print_set();
printf("union(2,4):");
dis.union_(2,4);
dis.print_set();
printf("find(0)=%d,find(2)=%d,find(4)=%d",dis.find(0),dis.find(2),dis.find(4));
printf("\n");
system("pause");
}
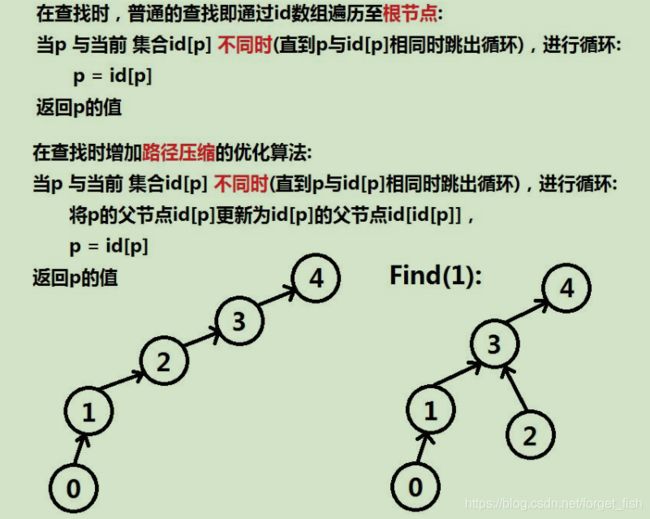
int find(int p){
while(p != _id[p]){
_id[p] = _id[_id[p]];
p = _id[p];
}
return p;
}
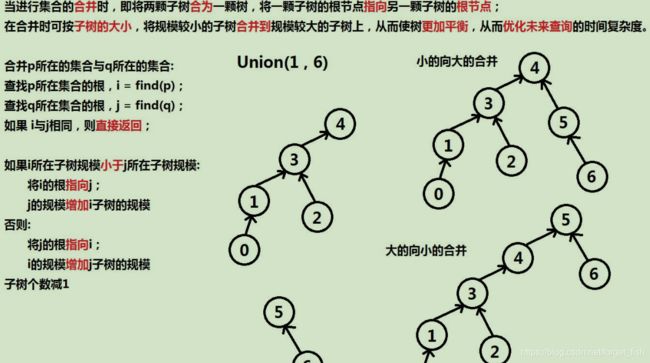
void union_(int p, int q){
int i = find(p);
int j = find(q);
if(i == j){
return;
}
if(_size[i] < _size[j]){
_id[i] = j;
_size[j] +=_size[i];
}
else{
_id[j] = i;
_size[i] += _size[j];
}
_count--;
}
并查集查找朋友圈个数:
class DisjointSet{
public:
int _count; //树的个数
DisjointSet(int n){
for(int i=0;i _id;//集合编号
vector _size;//集合大小
};
class Solution {
public:
int findCircleNum(vector>& M) {
DisjointSet disjoint_set(M.size());
for(int i=0; i 四、区域和的查询 LeetCode 307
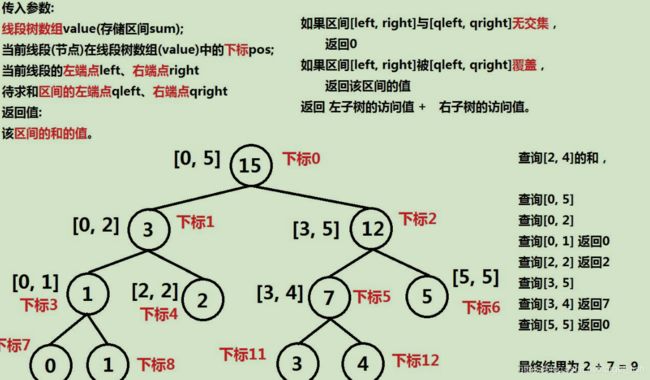
给定一个整数数组 nums,求出数组从索引 i 到 j (i ≤ j) 范围内元素的总和,包含 i, j 两点。
update(i, val) 函数可以通过将下标为 i 的数值更新为 val,从而对数列进行修改。
示例:
Given nums = [1, 3, 5]
sumRange(0, 2) -> 9
update(1, 2)
sumRange(0, 2) -> 8
说明:
数组仅可以在 update 函数下进行修改。
你可以假设 update 函数与 sumRange 函数的调用次数是均匀分布的。
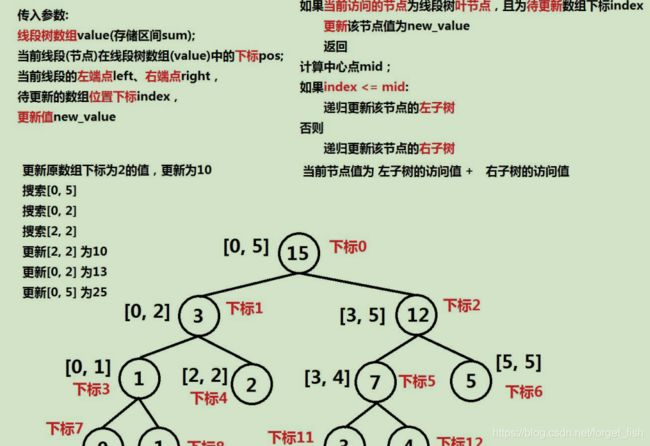
线段树:
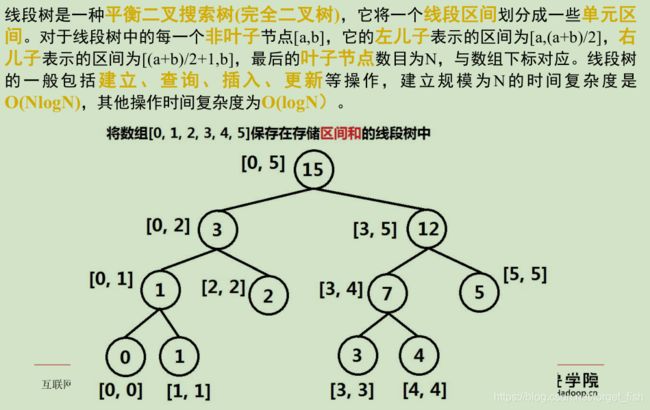
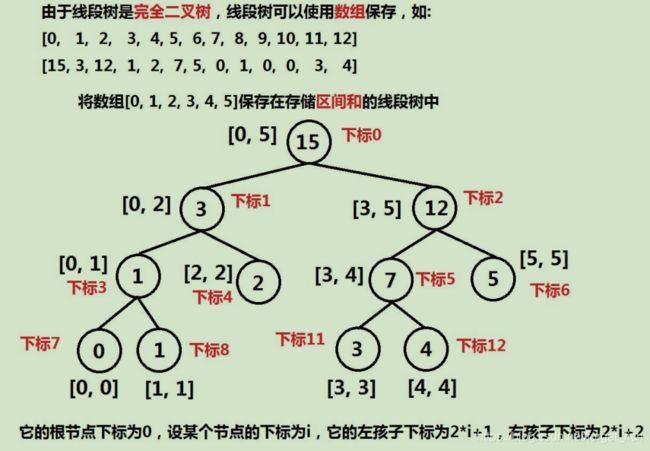
线段树的构造:
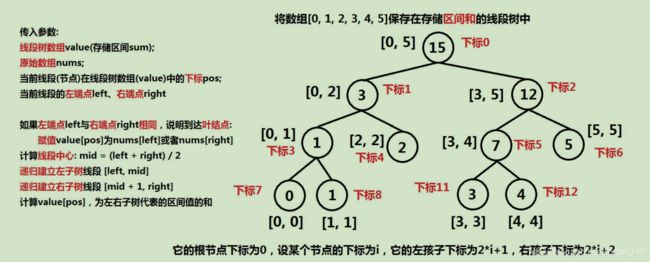
void build_segment_tree(vector &value,vector &nums,
int pos,int left,int right){
if(right==left){
value[pos] = nums[left];//到叶节点value[pos]等于叶节点的值
return;
}
int mid = (left+right)/2;
build_segment_tree(value,nums,pos*2+1,left,mid);//递归建立左子树
build_segment_tree(value,nums,pos*2+2,mid+1,right);//递归建立右子树
value[pos] = value[pos*2+1]+value[pos*2+2];
}
int sum_range_segment_tree(vector &value, int pos,
int left, int right, int qleft, int qright){
if(qleft>right||qright=right){//群建重合返回pos的值
return value[pos];
}
int mid = (left+right)/2;
return sum_range_segment_tree(value, pos*2+1,left,mid,qleft,qright) +
sum_range_segment_tree(value, pos*2+2,mid+1,right,qleft,qright);//返回左右子树之和
}
void update_segment_tree(vector &value, int pos,
int left, int right, int index, int new_value){
if(left==right&&left==index){//如果当前为叶节点且正好等于更新数值的下标,将其更新后返回
value[pos] = new_value;
return;
}
int mid = (left+right)/2;//求中点的坐标
if(index <= mid)//如果更新值的坐标比中点小则在左子树搜索更新
update_segment_tree(value,pos*2+1,left,mid,index,new_value);
else//否则在右子树搜索更新
update_segment_tree(value,pos*2+2,mid+1,right,index,new_value);
value[pos] = value[pos*2+1]+value[pos*2+2];//更新完成后当前位置的值等于左右子树相加
}
整体:
void build_segment_tree(vector &value,vector &nums,
int pos,int left,int right){
if(right==left){
value[pos] = nums[left];//到叶节点value[pos]等于叶节点的值
return;
}
int mid = (left+right)/2;
build_segment_tree(value,nums,pos*2+1,left,mid);//递归建立左子树
build_segment_tree(value,nums,pos*2+2,mid+1,right);//递归建立右子树
value[pos] = value[pos*2+1]+value[pos*2+2];
}
int sum_range_segment_tree(vector &value, int pos,
int left, int right, int qleft, int qright){
if(qleft>right||qright=right){//群建重合返回pos的值
return value[pos];
}
int mid = (left+right)/2;
return sum_range_segment_tree(value, pos*2+1,left,mid,qleft,qright) +
sum_range_segment_tree(value, pos*2+2,mid+1,right,qleft,qright);//返回左右子树之和
}
void update_segment_tree(vector &value, int pos,
int left, int right, int index, int new_value){
if(left==right&&left==index){//如果当前为叶节点且正好等于更新数值的下标,将其更新后返回
value[pos] = new_value;
return;
}
int mid = (left+right)/2;//求中点的坐标
if(index <= mid)//如果更新值的坐标比中点小则在左子树搜索更新
update_segment_tree(value,pos*2+1,left,mid,index,new_value);
else//否则在右子树搜索更新
update_segment_tree(value,pos*2+2,mid+1,right,index,new_value);
value[pos] = value[pos*2+1]+value[pos*2+2];//更新完成后当前位置的值等于左右子树相加
}
class NumArray {
public:
NumArray(vector nums) {
if(nums.size()==0){//!!数组为空
return;
}
int n=nums.size()*4;//一般线段树的大小是原来数组的4倍
for(int i=0;i _value;
int _right_end;
};
/**
* Your NumArray object will be instantiated and called as such:
* NumArray obj = new NumArray(nums);
* obj.update(i,val);
* int param_2 = obj.sumRange(i,j);
*/