笔记:CS231n(Spring 2019)Assignment 1 - kNN
Setup & Download data
首先是在相关下载作业的压缩包和数据集
Preprocessing
- 加载CIFAR10数据集
Training data shape: (50000, 32, 32, 3)
Training labels shape: (50000,)
Test data shape: (10000, 32, 32, 3)
Test labels shape: (10000,)
我们得到训练集的大小为50000张图片,每张的维度为32×32×3,同时对应50000个训练集标签(3指RGB的三个分量);
测试集的大小为10000,每张的维度为32×32×3,同时对应10000个测试集标签;
小数据集生成
我们选择原训练集中的前5000个作为新的训练集,原测试集中的前500个作为新的测试集,减小训练时间。同时,我们对每张图片进行reshape操作(np.reshape),将每张32×32×3的图片压缩成一维向量(3072,),因此训练集和测试集的大小分别为
(5000, 3072) (500, 3072)
kNN
Nearest Neighbor,顾名思义即最近邻算法。以下是对图片的L1距离计算:
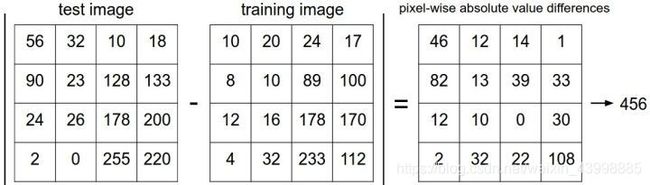
Figure:distances calculating
将待预测图片与所有训练数据进行距离计算,取其中距离最小的k张图片的标签作为自己的标签(若k大于1则与多数图片的标签相同)。这就是我们的predict函数需要实现的内容。
attention:此次作业中为L2距离计算,因此需要计算距离差的平方和,再对其开根号。
def predict(self, X, k=1, num_loops=0):
"""
Predict labels for test data using this classifier.
Inputs:
- X: A numpy array of shape (num_test, D) containing test data consisting
of num_test samples each of dimension D.
- k: The number of nearest neighbors that vote for the predicted labels.
- num_loops: Determines which implementation to use to compute distances
between training points and testing points.
Returns:
- y: A numpy array of shape (num_test,) containing predicted labels for the
test data, where y[i] is the predicted label for the test point X[i].
"""
if num_loops == 0:
dists = self.compute_distances_no_loops(X)
elif num_loops == 1:
dists = self.compute_distances_one_loop(X)
elif num_loops == 2:
dists = self.compute_distances_two_loops(X)
else:
raise ValueError('Invalid value %d for num_loops' % num_loops)
return self.predict_labels(dists, k=k)
def compute_distances_two_loops(self, X):
"""
Compute the distance between each test point in X and each training point
in self.X_train using a nested loop over both the training data and the
test data.
Inputs:
- X: A numpy array of shape (num_test, D) containing test data.
Returns:
- dists: A numpy array of shape (num_test, num_train) where dists[i, j]
is the Euclidean distance between the ith test point and the jth training
point.
"""
num_test = X.shape[0]
num_train = self.X_train.shape[0]
dists = np.zeros((num_test, num_train))
for i in range(num_test):
for j in range(num_train):
#####################################################################
# TODO: #
# Compute the l2 distance between the ith test point and the jth #
# training point, and store the result in dists[i, j]. You should #
# not use a loop over dimension, nor use np.linalg.norm(). #
#####################################################################
# *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
dists[i][j] = np.sqrt(np.sum(np.square(X[i,:] - self.X_train[j,:])))
# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
return dists
def compute_distances_one_loop(self, X):
"""
Compute the distance between each test point in X and each training point
in self.X_train using a single loop over the test data.
Input / Output: Same as compute_distances_two_loops
"""
num_test = X.shape[0]
num_train = self.X_train.shape[0]
dists = np.zeros((num_test, num_train))
for i in range(num_test):
#######################################################################
# TODO: #
# Compute the l2 distance between the ith test point and all training #
# points, and store the result in dists[i, :]. #
# Do not use np.linalg.norm(). #
#######################################################################
# *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
dists[i,:] = np.sqrt(np.sum(np.square(self.X_train - X[i,:]), axis = 1))
# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
return dists
def compute_distances_no_loops(self, X):
"""
Compute the distance between each test point in X and each training point
in self.X_train using no explicit loops.
Input / Output: Same as compute_distances_two_loops
"""
num_test = X.shape[0]
num_train = self.X_train.shape[0]
dists = np.zeros((num_test, num_train))
#########################################################################
# TODO: #
# Compute the l2 distance between all test points and all training #
# points without using any explicit loops, and store the result in #
# dists. #
# #
# You should implement this function using only basic array operations; #
# in particular you should not use functions from scipy, #
# nor use np.linalg.norm(). #
# #
# HINT: Try to formulate the l2 distance using matrix multiplication #
# and two broadcast sums. #
#########################################################################
# *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
x_test2 = np.sum(np.square(X), axis=1, keepdims=True) #(num_test,1)
x_train2 = np.sum(np.square(self.X_train), axis=1) #(1,num_train)
a = np.multiply(np.dot(X, self.X_train.T), -2)
dists = np.add(x_test2, x_train2) #广播机制
dists = np.add(dists, a)
dists = np.sqrt(dists)
# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
return dists
def predict_labels(self, dists, k=1):
"""
Given a matrix of distances between test points and training points,
predict a label for each test point.
Inputs:
- dists: A numpy array of shape (num_test, num_train) where dists[i, j]
gives the distance betwen the ith test point and the jth training point.
Returns:
- y: A numpy array of shape (num_test,) containing predicted labels for the
test data, where y[i] is the predicted label for the test point X[i].
"""
num_test = dists.shape[0]
y_pred = np.zeros(num_test)
for i in range(num_test):
# A list of length k storing the labels of the k nearest neighbors to
# the ith test point.
closest_y = []
#########################################################################
# TODO: #
# Use the distance matrix to find the k nearest neighbors of the ith #
# testing point, and use self.y_train to find the labels of these #
# neighbors. Store these labels in closest_y. #
# Hint: Look up the function numpy.argsort. #
#########################################################################
# *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
cloest_y = self.y_train[np.argsort(dists[i,:])[:k]]
# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
#########################################################################
# TODO: #
# Now that you have found the labels of the k nearest neighbors, you #
# need to find the most common label in the list closest_y of labels. #
# Store this label in y_pred[i]. Break ties by choosing the smaller #
# label. #
#########################################################################
# *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
y_pred[i] = np.argmax(np.bincount(cloest_y))
# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
return y_pred
//上述分别为双重循环做法,单循环做法和使用numpy的无循环做法
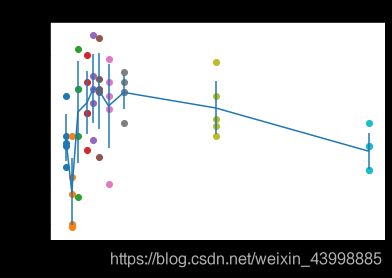
Cross-validation
num_folds = 5
k_choices = [1, 3, 5, 8, 10, 12, 15, 20, 50, 100]
X_train_folds = []
y_train_folds = []
################################################################################
# TODO: #
# Split up the training data into folds. After splitting, X_train_folds and #
# y_train_folds should each be lists of length num_folds, where #
# y_train_folds[i] is the label vector for the points in X_train_folds[i]. #
# Hint: Look up the numpy array_split function. #
################################################################################
# *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
X_train_folds = np.split(X_train, num_folds, axis=0)
y_train_folds = np.split(y_train, num_folds, axis=0)
# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
# A dictionary holding the accuracies for different values of k that we find
# when running cross-validation. After running cross-validation,
# k_to_accuracies[k] should be a list of length num_folds giving the different
# accuracy values that we found when using that value of k.
k_to_accuracies = {}
################################################################################
# TODO: #
# Perform k-fold cross validation to find the best value of k. For each #
# possible value of k, run the k-nearest-neighbor algorithm num_folds times, #
# where in each case you use all but one of the folds as training data and the #
# last fold as a validation set. Store the accuracies for all fold and all #
# values of k in the k_to_accuracies dictionary. #
################################################################################
# *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
for k in k_choices:
accuracies = []
for i in range(num_folds):
X_train_cv = np.vstack(X_train_folds[0:i] + X_train_folds[i+1:])
y_train_cv = np.hstack(y_train_folds[0:i] + y_train_folds[i+1:])
X_valid_cv = X_train_folds[i]
y_valid_cv = y_train_folds[i]
classifier.train(X_train_cv, y_train_cv)
dists = classifier.compute_distances_no_loops(X_valid_cv)
y_test_pred = classifier.predict_labels(dists, k)
num_correct = np.sum(y_test_pred == y_valid_cv)
accuracy = float(num_correct) / y_valid_cv.shape[0]
accuracies.append(accuracy)
k_to_accuracies[k] = accuracies
# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
# Print out the computed accuracies
for k in sorted(k_to_accuracies):
for accuracy in k_to_accuracies[k]:
print('k = %d, accuracy = %f' % (k, accuracy))
Ending
Assignment 1 的全部代码会在博客结束之后再全部挂出来